MIT 6.5840 (Spring, 2024) 通关指南——Lab 1: MapReduce
MIT 6.5840 (Spring, 2024) – Lab 1: MapReduce
👨💻 Charles
🔗 实验手册: 6.5840 Lab 1: MapReduce
📃 MapReduce 论文原文: mapreduce-osdi04.pdf
✍️ 本系列前文: MIT 6.5840 (Spring, 2024) 通关指南——入门篇
文章目录
- MIT 6.5840 (Spring, 2024) -- Lab 1: MapReduce
- 代码理解
- baseline:串行实现
- todo:并行实现
- `coordinator.go`
- `worker.go`
- 代码实现
- `coordinator.go`
- 初始化
- 处理 Map 任务
- 处理 Reduce 任务
- 监控任务情况(防超时)
- `rpc.go`
- worker 获取 Map 任务
- worker 提交 Map 结果
- worker 获取 Reduce 任务
- worker 提交 Reduce 结果
- `worker.go`
- 初始化
- 处理 Map 任务
- 处理 Reduce 任务
- 实验结果
- 踩坑记录/建议
代码理解
baseline:串行实现
首先,看看 Lab 中已给出的一个串行版 MapReduce —— src/main/mrsequential.go ,这是我们后续自己实现并行版本的重要参考。在 mrsequential.go 中,有 mapf 和 reducef 两个组件,分别对应 Map 任务和 Reduce 任务:
mapf, reducef := loadPlugin(os.Args[1])
可以看到,它们是通过插件的形式导入的, loadPlugin 的实现在 mrsequential.go 中,利用了golang的 plugin 库,所以我们可以看到实验手册运行 mrsequential.go 之前先运行了:
go build -buildmode=plugin ../mrapps/wc.go
即将 wc.go 编译为 wc.so (动态加载共享库),之后运行 mrsequential.go 的时候就可以这样使用 wc.go 中的各种方法:
go run mrsequential.go wc.so pg*.txt
Anyway,其实就是说,Map 和 Reduce 的实现要到 src/mrapps/wc.go 中去找。源代码也挺简单的,实现方法为:
-
Split:以非字母符号为分隔符,将输入文件拆分为若干个单词,存到切片
words中 -
Map:顺序处理
words的单词,对于每个单词w,构建一个键值对{w, 1},将这个键值对存到一个切片kva中 -
Reduce:统计
kva中,每个单词的个数(在kva排序后,相同的单词挨在一起,把它们放到新切片values := []string{}中,Reduce其实就是返回len(values))
todo:并行实现
本实验主要需要在已提供的代码基础上,完善 mr/coordinator.go 、 mr/worker.go 、 mr/rpc.go 。为了实现单 coordinator、多 worker 的并行架构,coordinator 需要负责给各 worker 分配 Map 任务和 Reduce 任务,并监控 worker 的工作情况、在发生超时的时候将其任务重新分配给其他 worker;同时,每个 worker 需要通过 RPC 调用 coordinator 的 Map 方法和 Reduce 方法,并保存相关结果、告知 coordinator 完成情况。
coordinator.go
我们需要实现的并行版 MapReduce 的主程序在 src/main/mrcoordinator.go 中,它负责调用 MakeCoordinator 构建 coordinator (任务分发者,相当于server)——这是在 src/mr/coordinator.go 中实现的,这个文件中已经声明/提示了我们 需要补全 的若干方法(见注释)。
coordinator 启动后,会通过 server() 方法创建一个 goroutine 来监听 src/mr/worker.go 的 RPC 调用请求:
//
// start a thread that listens for RPCs from worker.go
//
func (c *Coordinator) server() {rpc.Register(c)rpc.HandleHTTP()//l, e := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")sockname := coordinatorSock()os.Remove(sockname)l, e := net.Listen("unix", sockname)if e != nil {log.Fatal("listen error:", e)}go http.Serve(l, nil)
}关于RPC的使用方法, worker.go 和 coordinator.go 中都有示例函数,所用的相关参数/方法定义在 src/mr/rpc.go 中。
建议先在现有代码上尝试 RPC 调用示例函数(
worker.go里面有个CallExample()基本可以直接用),从而熟悉代码框架。关于 RPC 以及 golang 中如何使用 RPC,建议逢山开路,遇到不懂的就问 AI 🤖
worker.go
worker.go 即 map 和 reduce 任务的执行者,需要补全 Worker 方法:
// main/mrworker.go calls this function.
func Worker(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue,reducef func(string, []string) string) {...}
关键在于处理和 coordinator 的通信(需要通过 RPC 调用,获取任务、执行任务)。
代码实现
完整代码: MIT-6.5840/src/mr at lab1 · Charles-T-T/MIT-6.5840
coordinator.go
Coordinator 结构体定义如下:
type Coordinator struct {mu sync.RWMutexnMap intnReduce inttoMapTasks chan MapTasktoReduceTasks chan ReduceTaskremainMapTask map[string]string // filename -> workerIDremainReduceTask map[string]string // reduceID -> workerIDworkerRegistry map[string]string // workerID -> workerAddrallMapDone boolallReduceDone bool
}
-
mu:读写锁,用于防止多个worker访问同一个coordinator成员出现冲突 -
workerRegistry:记录已经注册了的worker——只有已注册的worker提交的Map或Reduce结果才会被接受(防止收到超时worker的任务结果——已被重新分配了)原本设计的是workerID ➡️ workerAddr(worker 的 sock 地址)的一个哈希表,但是后续实现中发现维护 coordinator 和 worker 的双向通信似乎没必要,故这里仅当作一个集合使用。
-
nMap和nReduce:需要执行的Map和Reduce任务总数 -
其余成员变量作用易从其名称得出
初始化
// create a Coordinator.
// main/mrcoordinator.go calls this function.
// nReduce is the number of reduce tasks to use.
func MakeCoordinator(files []string, nReduce int) *Coordinator {c := Coordinator{nMap: len(files),nReduce: nReduce,toMapTasks: make(chan MapTask, len(files)),toReduceTasks: make(chan ReduceTask, nReduce),remainMapTask: make(map[string]string),remainReduceTask: make(map[string]string),workerRegistry: make(map[string]string),allMapDone: false,allReduceDone: false,}...
处理 Map 任务
初始化后,启动一个 goroutine 来处理 Map 任务:
// Manage Map tasks
go func() {// Init todo Map tasksfor i, file := range files {mapTask := MapTask{Filename: file,MapID: strconv.Itoa(i),NMap: c.nMap,NReduce: c.nReduce,}c.toMapTasks <- mapTaskDPrintf("Get todo-file: %s\n", file)c.remainMapTask[file] = "init"}// Wait all Map tasks to be donefor len(c.remainMapTask) > 0 {time.Sleep(time.Second)}close(c.toMapTasks)c.allMapDone = trueDPrintf("All map tasks done.\n")
}()
处理 Reduce 任务
启动另一个 goroutine 来处理 Reduce 任务:
// Manage Reduce tasks
go func() {// output files for reduce resultsfor i := 0; i < nReduce; i++ {c.toReduceTasks <- ReduceTask{ReduceID: strconv.Itoa(i)}c.remainReduceTask[strconv.Itoa(i)] = "init"}// Wait all Map tasks to be donefor !c.allMapDone {time.Sleep(time.Second)}// Wait all Reduce tasks to be donefor len(c.remainReduceTask) > 0 {time.Sleep(time.Second)}close(c.toReduceTasks)c.allReduceDone = trueDPrintf("All reduce tasks done.\n")
}()
监控任务情况(防超时)
每次 worker 开始一个任务后,coordinator 就会启动一个 goroutine ——如果 10s(实验手册建议的超时时间)后任务仍未完成则视为超时,需要将该任务放回 todo-channel 中,等待其他 worker 认领:
// Monitor a Map task, reassign it if time out.
func (c *Coordinator) monitorMapTask(file string, mapID string) {time.Sleep(time.Second * 10) // wait for 10sworkerID, exist := c.remainMapTask[file]if exist {c.mu.Lock()delete(c.workerRegistry, workerID)DPrintf("Map job by %s time out!\n", workerID)c.mu.Unlock()c.toMapTasks <- MapTask{Filename: file, MapID: mapID, NMap: c.nMap, NReduce: c.nReduce}}
}// Monitor a Reduce task, reassign it if time out.
func (c *Coordinator) monitorReduceTask(reduceID string) {time.Sleep(time.Second * 10) // wait for 10sworkerID, exist := c.remainReduceTask[reduceID]if exist {c.mu.Lock()delete(c.workerRegistry, workerID)DPrintf("Reduce job by %s time out!\n", workerID)c.mu.Unlock()c.toReduceTasks <- ReduceTask{ReduceID: reduceID}}
}
rpc.go
worker 需要 RPC 调用 coordinator 的各方法均写在 rpc.go 中。
worker 获取 Map 任务
每个worker启动后,会首先尝试从coordinator的 toMapTasks channel 中获取一个Map任务,如果所有Map任务已完成、channel已关闭,则返回任务的 AllMapDone 字段为 true ;如果获取任务成功,则worker在 workerRegistry 注册,同时coordinator启动监视( c.monitorMapTask ),以在任务超时后重新分配任务。
func (c *Coordinator) WorkerGetMapTask(workerID string, mapTask *MapTask) error {toMapTask, ok := <-c.toMapTasksif ok {mapTask.Filename = toMapTask.FilenamemapTask.MapID = toMapTask.MapIDmapTask.NReduce = toMapTask.NReduce} else {mapTask.AllMapDone = true // all Map tasks already done.mapTask.AllReduceDone = c.allReduceDonereturn nil}// worker registersc.mu.Lock()c.workerRegistry[workerID] = workerSock(workerID)c.remainMapTask[toMapTask.Filename] = workerIDgo c.monitorMapTask(toMapTask.Filename, toMapTask.MapID)c.mu.Unlock()return nil
}
worker 提交 Map 结果
worker 完成其 Map 任务后,需要告知 coordinator,随后 coordinator 会从 remainMapTask 中移除该任务,视为任务完成。coordinator 只接受注册了的 worker 的结果。
worker 具体处理 Map 任务的过程在
worker.go中,此处只是“通知任务完成”。
func (c *Coordinator) WorkerGiveMapRes(mapTask MapTask, reply *string) error {// Coordinator only accepts results from worker IN workerRegistryworkerID := mapTask.WorkerIDfilename := mapTask.Filename_, exist := c.workerRegistry[workerID]if !exist {DPrintf("Illegal map result: get from unknown worker: %s\n", workerID)return nil}c.mu.Lock()DPrintf("Successfully get map result from: %s\n", workerID)delete(c.remainMapTask, filename)c.mu.Unlock()return nil
}
worker 获取 Reduce 任务
实现思路和获取 Map 任务的一致:
func (c *Coordinator) WorkerGetReduceTask(workerID string, reduceTask *ReduceTask) error {toReduceTask, ok := <-c.toReduceTasksif ok {*reduceTask = toReduceTaskreduceTask.WorkerID = workerIDreduceTask.TempResFile = fmt.Sprintf("mr-tmp-%s", workerID)} else {reduceTask.AllReduceDone = true // all Reduce tasks already done.return nil}// worker registersc.mu.Lock()c.workerRegistry[workerID] = workerSock(workerID)c.remainReduceTask[toReduceTask.ReduceID] = workerIDgo c.monitorReduceTask(toReduceTask.ReduceID)c.mu.Unlock()return nil
}
worker 提交 Reduce 结果
实现思路和提交 Map 结果的一致:
func (c *Coordinator) WorkerGiveReduceRes(reduceTask ReduceTask, reply *string) error {// Coordinator only accepts results from worker in workerRegistryworkerID := reduceTask.WorkerID_, exist := c.workerRegistry[workerID]if !exist {DPrintf("Illegal reduce result: get from unknown worker: %s\n", workerID)return nil}newname := fmt.Sprintf("mr-out-%s", reduceTask.ReduceID)*reply = newnameerr := os.Rename(reduceTask.TempResFile, newname)if err != nil {DPrintf("Error when rename temp file: %v\n", err)}c.mu.Lock()DPrintf("Successfully get reduce result from: %s\n", workerID)delete(c.remainReduceTask, reduceTask.ReduceID)c.mu.Unlock()return nil
}
worker.go
worker 采用的 Map 和 Reduce 方法是通过不同插件载入的,我们不需要关心其实现,直接用就行了。
初始化
workerID := strconv.Itoa(os.Getpid())
mapDone := false // flag whether all Map tasks have been finished
reduceDone := false // flag whether all Reduce tasks have been finished
处理 Map 任务
worker 启动后,周期性尝试从 coordinator 那里获取一个 Map 任务,获取任务后处理、向 coordinator 提交结果,直到收到所有 Map 任务已完成的通知,则将 mapDone 置为 true :
// Do the map task
for !mapDone {mapTask := MapTask{WorkerID: workerID}DPrintf("<%s> ask for a map task...\n", workerID)call("Coordinator.WorkerGetMapTask", workerID, &mapTask)DPrintf("<%s> get task: %s\n", workerID, mapTask.Filename)if !mapTask.AllMapDone {file, err := os.Open(mapTask.Filename)if err != nil {DPrintf("cannot open %v\n", mapTask.Filename)return}content, err := io.ReadAll(file)if err != nil {DPrintf("cannot read %v\n", mapTask.Filename)return}file.Close()kva := mapf(mapTask.Filename, string(content))saveMapRes(kva, mapTask.MapID, mapTask.NReduce)mapTask.Result = kvavar reply stringcall("Coordinator.WorkerGiveMapRes", mapTask, &reply)} else {mapDone = truereduceDone = mapTask.AllReduceDoneDPrintf("All map tasks done.\n")}time.Sleep(500 * time.Millisecond)
}
其中,Map 任务产生的中间结果需要保存到文件中,参考实验手册的 hint:

实现如下:
func saveMapRes(kva []KeyValue, mapID string, nReduce int) {reduceChunks := make(map[string][]KeyValue) // reduceID -> kvsfor _, kv := range kva {reduceID := strconv.Itoa(ihash(kv.Key) % nReduce)reduceChunks[reduceID] = append(reduceChunks[reduceID], kv)}for reduceID, kvs := range reduceChunks {oname := fmt.Sprintf("mr-%s-%s.json", mapID, reduceID)ofile, _ := os.Create(oname)defer ofile.Close()enc := json.NewEncoder(ofile)err := enc.Encode(&kvs)if err != nil {DPrintf("Error when encoding kv: %v\n", err)}}DPrintf("Finish saving map result.\n")
}
处理 Reduce 任务
和处理 Map 任务的思路一致——周期性尝试获取一个 Reduce 任务 ➡️ 处理 Reduce 任务 ➡️ 保存 Reduce 结果 ➡️ 向 coordinator 提交结果:
// Do the Reduce task
for !reduceDone {reduceTask := ReduceTask{WorkerID: workerID}DPrintf("<%s> ask for a reduce task...\n", workerID)call("Coordinator.WorkerGetReduceTask", workerID, &reduceTask)DPrintf("<%s> get reduceID: %s\n", workerID, reduceTask.ReduceID)if !reduceTask.AllReduceDone {// Get Map result files to be Reducedpattern := fmt.Sprintf(`^mr-.*-%s.json$`, regexp.QuoteMeta(reduceTask.ReduceID))re := regexp.MustCompile(pattern)files, err := os.ReadDir(".")if err != nil {fmt.Println("Error reading directory:", err)return}var toReduceFiles []stringfor _, file := range files {if !file.IsDir() && re.MatchString(file.Name()) {toReduceFiles = append(toReduceFiles, file.Name())}}// Do the reduce jobdoReduce(toReduceFiles, reducef, reduceTask.TempResFile)DPrintf("<%s> finish reduce job, res to %s.\n", workerID, reduceTask.TempResFile)var reply stringcall("Coordinator.WorkerGiveReduceRes", reduceTask, &reply)DPrintf("<%s> reduce res save to %s.\n", workerID, reply)} else {reduceDone = trueDPrintf("All reduce done.\n")}time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
}
其中负责执行 Reduce 的方法 doReduce 主要参考 mrsequential.go 实现:
func doReduce(toReduceFiles []string, reducef func(string, []string) string, oname string) {ofile, _ := os.Create(oname)defer ofile.Close()intermediate := []KeyValue{}for _, toReduceFile := range toReduceFiles {file, _ := os.Open(toReduceFile)dec := json.NewDecoder(file)kva := []KeyValue{}if err := dec.Decode(&kva); err != nil {DPrintf("Error when json decode: %v\n", err)return}intermediate = append(intermediate, kva...)file.Close()}sort.Sort(ByKey(intermediate))i := 0for i < len(intermediate) {j := i + 1for j < len(intermediate) && intermediate[j].Key == intermediate[i].Key {j++}values := []string{}for k := i; k < j; k++ {values = append(values, intermediate[k].Value)}output := reducef(intermediate[i].Key, values)fmt.Fprintf(ofile, "%v %v\n", intermediate[i].Key, output)i = j}
}
实验结果
手动测试并打印中间过程(在 worker.go 中将 Debug 设置为 true ):

运行测试脚本 mr-test.sh :
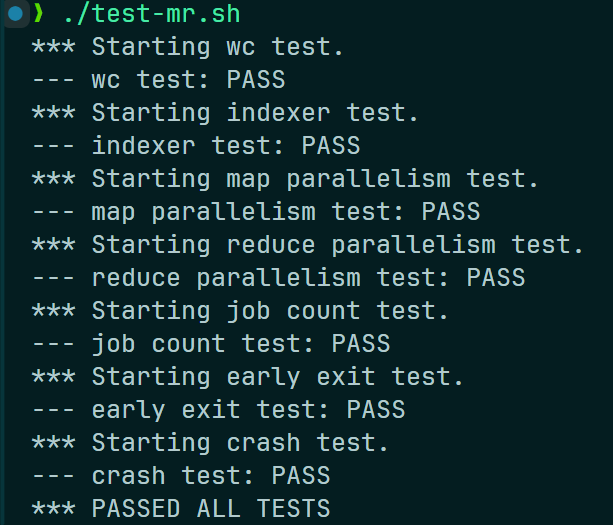
测试通过。
踩坑记录/建议
-
用
DPrintf打印日志能发现大部分 bug,但是可能有些细节需要用打断点调试,如果是 vscode 的话需要配置一下:-
例如,对于 worker,要断点调试
wc任务,需要在.vscode/launch.json中添加配置:{"name": "mrworker-wc","type": "go","request": "launch","mode": "exec","program": "${workspaceFolder}/6.5840/src/main/mrworker","args": ["wc.so"],"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}/6.5840/src/main" }, -
对于 coordinator,可以配置:
{"name": "debug mrcoordinator","type": "go","request": "launch","mode": "auto","program": "${workspaceFolder}/6.5840/src/main/mrcoordinator.go","args": ["pg-being_ernest.txt","pg-dorian_gray.txt","pg-frankenstein.txt","pg-grimm.txt","pg-huckleberry_finn.txt","pg-metamorphosis.txt","pg-sherlock_holmes.txt","pg-tom_sawyer.txt"] }具体参数可以根据任务调整,不懂的多问 AI。
-
-
本 lab 实现的是一个 MapReduce 框架 ,也就是说具体的 Map 任务和 Reduce 任务 不是一定的 ——我一开始以为只有单词计数(
src/mrapps/wc.go),所以傻了吧唧地搬运mrsequential.go的代码,但实际上最后测试的任务有很多,都在src/mrapps/下。最后跑test-mr.sh的时候,也可以根据出错任务到src/mrapps/中看看对应任务代码,可能有所启发。 -
RPC 函数,不仅 函数名 要 首字母大写 ,如果参数是结构体,则该结构体中的 成员变量也要首字母大写
否则你可能会像我一样,发现
reply中有些成员被更新了、有些没有,非常诡异 🤷♂ -
仔细阅读官方实验手册的
Hints,很有用。比如前一条,其实
Hints中就有提到:“Go RPC sends only struct fields whose names start with capital letters. Sub-structures must also have capitalized field names.”
-
注意采用合理方法保存 Map 任务的中间结果,便于之后 Reduce 任务读取。
Hints中的建议是:“A reasonable naming convention for intermediate files is
mr-X-Y, where X is the Map task number, and Y is the reduce task number.” -
注意给 coordinator 上锁,防止多 worker 的读写冲突。
如果你觉得有帮助,欢迎去 我的代码仓库 点个 star ⭐️ : )
