android View详解—动画
旋转动画
一、使用 XML 方式(推荐)
1. 创建动画文件
在 res/anim 目录下新建一个 XML 文件,例如:rotate_animation.xml
?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<rotate xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:duration="1000" <!-- 动画持续时间,毫秒 -->android:fromDegrees="0" <!-- 起始角度 -->android:toDegrees="360" <!-- 结束角度 -->android:pivotX="50%" <!-- 旋转中心点 X 坐标 -->android:pivotY="50%" <!-- 旋转中心点 Y 坐标 -->android:repeatCount="infinite" <!-- 重复次数,infinite 表示无限循环 -->android:repeatMode="restart" <!-- 重复模式,restart 表示每次都重新开始 -->
android:interpolator="@android:anim/linear_interpolator" /> <!-- 插值器 -->2. 在代码中使用动画
mageView imageView = findViewById(R.id.imageView);
Animation rotateAnimation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this, R.anim.rotate_animation);
imageView.startAnimation(rotateAnimation);二、使用代码动态创建动画
ImageView imageView = findViewById(R.id.imageView);RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = new RotateAnimation(0f, 360f, // 起始角度,结束角度Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, // 旋转中心点 X 坐标Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f // 旋转中心点 Y 坐标
);rotateAnimation.setDuration(1000); // 动画持续时间
rotateAnimation.setRepeatCount(Animation.INFINITE); // 无限循环
rotateAnimation.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator()); // 线性插值器imageView.startAnimation(rotateAnimation);三、使用属性动画(更灵活,推荐)
ImageView imageView = findViewById(R.id.imageView);ObjectAnimator rotateAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView, "rotation", 0f, 360f);
rotateAnimator.setDuration(1000);
rotateAnimator.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);
rotateAnimator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
rotateAnimator.start();四、暂停与恢复动画(属性动画)
// 暂停动画
rotateAnimator.pause();// 恢复动画
rotateAnimator.resume();五、注意事项与建议:
性能优化:如果动画只是简单的旋转,推荐使用 XML 或属性动画。
重复次数:repeatCount 设置为 Animation.INFINITE 或 ValueAnimator.INFINITE 表示无限循环。
插值器选择:
LinearInterpolator:匀速旋转
AccelerateInterpolator:加速旋转
DecelerateInterpolator:减速旋转
AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator:先加速后减速旋转
动画停止:
使用 Animation 时调用 animation.cancel();
使用属性动画时调用 animator.cancel()。
平移动画
一、XML 视图动画(传统方式,最简单)
1. 创建动画文件
res/anim/translate_left_to_right.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<translate xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:duration="800"android:fromXDelta="-100%"android:toXDelta="0%"android:fromYDelta="0%"android:toYDelta="0%"
android:fillAfter="true" /> <!-- 动画结束后停在终点 -->
fromXDelta / toXDelta:水平方向位移,可用具体数值(dp、px)或百分比(相对自身或父容器)。
fromYDelta / toYDelta:垂直方向位移,同上。
fillAfter="true":动画结束后停留在最终位置(否则控件会闪回起点)2. 使用动画
Animation anim = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(context, R.anim.translate_left_to_right);
view.startAnimation(anim);二、代码动态创建视图动画
TranslateAnimation anim = new TranslateAnimation(Animation.RELATIVE_TO_PARENT, -1.0f, // fromXAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_PARENT, 0.0f, // toXAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_PARENT, 0.0f, // fromYAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_PARENT, 0.0f); // toY
anim.setDuration(800);
anim.setFillAfter(true);
view.startAnimation(anim);三、属性动画(ObjectAnimator,API 11+,最推荐)
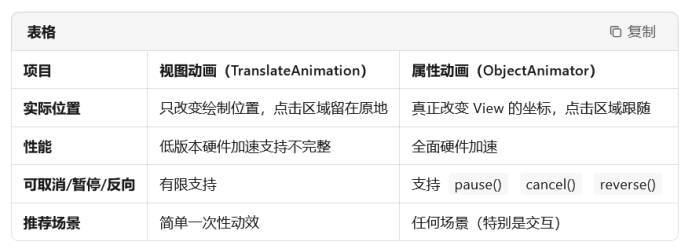
优势:真正改变 View 的坐标,不会出现视图动画“点击区域还在原地”的问题;
兼容硬件加速,性能更好。
1. 水平位移
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "translationX", -view.getWidth(), 0f).setDuration(800).start();2. 垂直位移
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, "translationY", 0f, 200f).setDuration(800).start();3. 组合位移(X+Y)
Path path = new Path();
path.moveTo(0f, 0f);
path.lineTo(200f, 100f);
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, View.X, View.Y, path).setDuration(800).start();四、常用扩展技巧
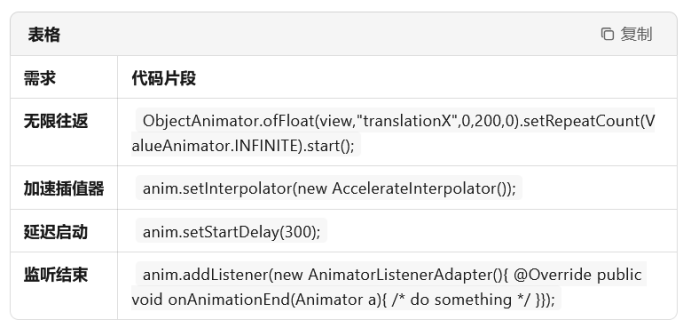
五、视图动画 vs 属性动画(避坑)
缩放动画
XML 视图动画
在 res/anim/scale_center.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<scale xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:duration="400"android:fromXScale="1.0"android:toXScale="1.5"android:fromYScale="1.0"android:toYScale="1.5"android:pivotX="50%" <!-- 中心点:水平中点 -->android:pivotY="50%" <!-- 中心点:垂直中点 -->
android:fillAfter="true" /> <!-- 动画结束后保持最终大小 -->使用:
Animation anim = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(context, R.anim.scale_center);
imageView.startAnimation(anim);代码动态创建视图动画
ScaleAnimation anim = new ScaleAnimation(1f, 1.5f, // 起始/结束 X 缩放1f, 1.5f, // 起始/结束 Y 缩放Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, // 中心点 XAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f); // 中心点 Y
anim.setDuration(400);
anim.setFillAfter(true);
imageView.startAnimation(anim);属性动画(ObjectAnimator
真正改变 View 的 scaleX/scaleY,点击区域同步放大/缩小
imageView.setPivotX(imageView.getWidth() / 2f); // 中心点
imageView.setPivotY(imageView.getHeight() / 2f);ObjectAnimator scaleX = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView, "scaleX", 1f, 1.5f);
ObjectAnimator scaleY = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView, "scaleY", 1f, 1.5f);AnimatorSet set = new AnimatorSet();
set.playTogether(scaleX, scaleY);
set.setDuration(400);
set.start();ViewPropertyAnimator(一行代码链式调用)
imageView.animate().scaleX(1.5f).scaleY(1.5f).setDuration(400).start();常见需求速查表
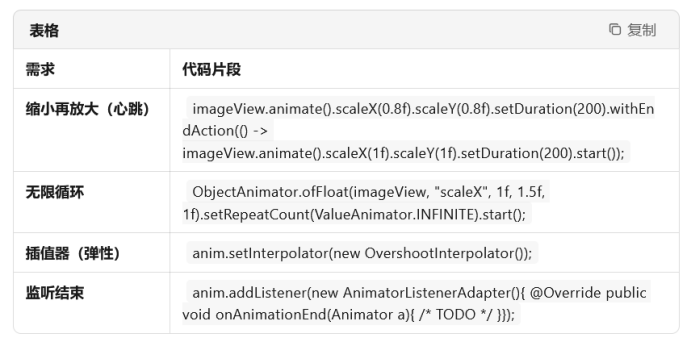
注意点
视图动画(ScaleAnimation) 只改变绘制大小,点击区域不变。
属性动画(ObjectAnimator / View.animate) 会真正改变 View 的大小和触控区域,推荐优先使用。
若需兼容 API < 11,可引入 NineOldAndroids(已过时)或保留 XML 视图动画。
淡入淡出
XML 视图动画
在 res/anim/fade_in.xml(淡入)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<alpha xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:duration="1000"android:fromAlpha="0.0"android:toAlpha="1.0"
android:fillAfter="true" />res/anim/fade_out.xml(淡出)
<alpha xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:duration="1000"android:fromAlpha="1.0"android:toAlpha="0.0"
android:fillAfter="true" />使用:
Animation in = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(context, R.anim.fade_in);
Animation out = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(context, R.anim.fade_out);view.startAnimation(in); // 淡入
view.startAnimation(out); // 淡出代码动态创建视图动画
// 淡入
AlphaAnimation fadeIn = new AlphaAnimation(0f, 1f);
fadeIn.setDuration(1000);
fadeIn.setFillAfter(true);
view.startAnimation(fadeIn);// 淡出
AlphaAnimation fadeOut = new AlphaAnimation(1f, 0f);
fadeOut.setDuration(1000);
fadeOut.setFillAfter(true);
view.startAnimation(fadeOut);属性动画(ObjectAnimator,推荐)
// 淡入
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, View.ALPHA, 0f, 1f).setDuration(1000).start();// 淡出
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(view, View.ALPHA, 1f, 0f).setDuration(1000).start();ViewPropertyAnimator(一行链式)
view.animate().alpha(1f) // 淡入.setDuration(1000).start();view.animate().alpha(0f) // 淡出.setDuration(1000)
.start();交叉淡入淡出(两个 View 场景切换)
View oldView = findViewById(R.id.old);
View newView = findViewById(R.id.new);// 先把新 View 设为透明
newView.setAlpha(0f);
newView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);oldView.animate().alpha(0f).setDuration(500).withEndAction(() -> {oldView.setVisibility(View.GONE);newView.animate().alpha(1f).setDuration(500).start();}).start();常见需求速查表

视图动画(AlphaAnimation) 只改变绘制透明度,不触发 setVisibility() 事件;如需隐藏,记得手动 setVisibility(GONE)。
属性动画(ObjectAnimator / View.animate) 会真正修改 View.ALPHA,可配合 setVisibility() 实现更复杂的场景切换。
交叉淡入淡出时,两个 View 必须位于同一个父布局,且新 View 初始 visibility = VISIBLE + alpha = 0。
动画插值器
LinearInterpolator 匀速 旋转加载圈
AccelerateInterpolator 越来越快 页面滑出
DecelerateInterpolator 越来越慢 页面滑入
AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator 两头慢中间快 默认效果
AnticipateInterpolator 先回拉再前进 弹出菜单
OvershootInterpolator 冲过头再回弹 点赞放大
AnticipateOvershootInterpolator 回拉 + 冲过头 卡片翻转
BounceInterpolator 落地弹跳 掉落按钮
CycleInterpolator(float cycles) 正弦循环 抖动提示
FastOutSlowInInterpolator Material 默认 所有 Material 动效
LinearOutSlowInInterpolator 先快后慢 Snackbar 滑出
FastOutLinearInInterpolator 先慢后快 返回按钮
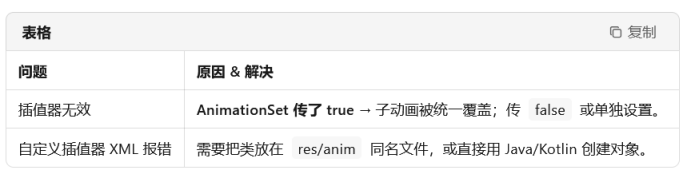
设置插值器
setInterpolator
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_decelerate_interpolator"
AnimationListener视图动画
AnimationListener 是 视图动画(View Animation) 专用的回调接口,用来监听 Animation 的生命周期事件。
当使用 AlphaAnimation、ScaleAnimation、TranslateAnimation、RotateAnimation、AnimationSet 等旧版补间动画时,通过它可以在动画开始、结束、重复时执行额外逻辑。
Animation anim = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(context, R.anim.fade_in);anim.setAnimationListener(new Animation.AnimationListener() {@Overridepublic void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) {Log.d("TAG", "动画开始");}@Overridepublic void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) {Log.d("TAG", "动画结束");view.setVisibility(View.GONE); // 常见操作}@Overridepublic void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) {Log.d("TAG", "动画重复");}
});view.startAnimation(anim);AnimatorListener属性动画
Android 属性动画(ObjectAnimator、ValueAnimator、AnimatorSet 等)的监听器接口叫 AnimatorListener,位于
包 android.animation.Animator.AnimatorListener。它与“视图动画”的 AnimationListener 不同,后者只适用于旧版补间动画。
- 接口方法一览
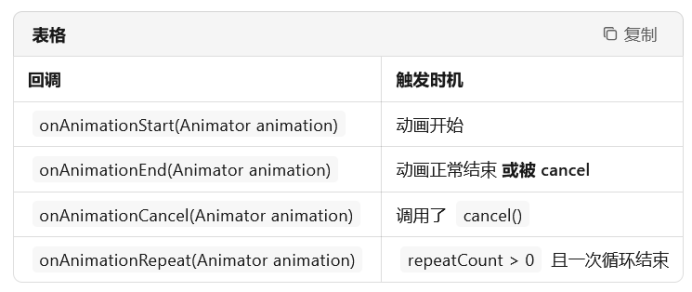
AnimatorUpdateListener属性动画
Android 属性动画体系里,AnimatorUpdateListener 是 ValueAnimator(包括其子类 ObjectAnimator、AnimatorSet)提供的“帧级”回调接口。
它会在每一帧刷新时调用一次,让你拿到「当前这一帧算出来的值」并手动刷新 UI,是自定义动画的核心手段。
ValueAnimator valueAnim = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0f, 100f); // 值区间
valueAnim.setDuration(1000);valueAnim.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {@Overridepublic void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {// 1. 取出当前帧值float curValue = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();// 2. 手动赋给任意属性textView.setTranslationX(curValue);// 3. 如需要,可刷新自定义 View// invalidate();}
});valueAnim.start();Android 动画类型
一、视图动画(View Animation,API 1+)
子类:Tween Animation(补间动画)和 Frame Animation(逐帧动画)。
特点:只改绘制矩阵,不改真实属性;点击区域不跟随;兼容所有版本。
典型使用:AlphaAnimation、ScaleAnimation、TranslateAnimation、RotateAnimation、AnimationDrawable。
二、属性动画(Property Animation,API 11+)
核心类:ValueAnimator、ObjectAnimator、AnimatorSet。
特点:真正改变对象属性值;支持可暂停、可逆、可插值;点击区域同步。
兼容低版本:NineOldAndroids(已弃用),或使用 AndroidX Core 的 ViewCompat.animate()。
三、转场动画(Transition Framework,API 19+)
包路径:android.transition.*
适用场景:Activity/Fragment 切换、布局内容变化(如列表→详情)。
核心 API:
· Explode、Slide、Fade
· TransitionManager.beginDelayedTransition()
共享元素:ActivityOptions.makeSceneTransitionAnimation()
特点:自动捕捉起始/结束状态并执行补间;与属性动画底层打通。
四、矢量动画(Animated Vector Drawable / Vector Animation,API 21+)
文件格式:res/drawable/animated_vector.xml
使用:
静态矢量图 vector
动画指令 objectAnimator 嵌入到 <target> 节点
场景:图标动效、加载动画、路径变形(path morphing)
兼容:使用 AnimatedVectorDrawableCompat(API 14+)
五、物理动画(Physics-based Animation,API 16+)
框架 androidx.dynamicanimation:dynamicanimation
子类:
SpringAnimation(弹簧)
FlingAnimation(甩动/惯性滑动)
特点:基于物理模型(阻尼、刚度、摩擦),真实自然;无需指定时长和终止值。