JUC之虚拟线程
文章目录
- 一、虚拟线程核心概念
- 1.1 概述
- 1.2 虚拟线程 vs 平台线程
- 1.3 虚拟线程的核心优势
- 1.3.1 解决传统并发瓶颈
- 1.3.2 虚拟线程的解决方案
- 二、虚拟线程的创建方式
- 2.1 Thread.startVirtualThread
- 2.2 Thread.ofVirtual
- 2.3 使用ThreadFactory
- 2.4 使用Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()
- 三、虚拟线程的高级特性
- 3.1 虚拟线程的线程局部变量
- 3.2 虚拟线程与异常编程
- 3.3 虚拟线程的状态与生命周期
- 3.4 虚拟线程的工作原理
- 3.5 虚拟线程的异常处理
- 四、虚拟线程的核心应用场景
- 4.1 IO密集型场景
- 4.2 高并发网络请求处理
- 4.3 并行数据处理
- 4.4 与结构化并发结合使用
- 4.5 高并发Web服务器
- 4.6 实时数据流处理
- 五、最佳实践与注意事项
- 5.1 虚拟线程最佳实践
- 5.2 性能调优与监控
- 5.3 虚拟线程与传统线程对比
- 5.4 何时使用虚拟线程
- 5.5 虚拟线程的核心价值
- 5.6 虚拟线程的限制与注意事项
- 5.7 与其它并发模型对比
一、虚拟线程核心概念
1.1 概述
虚拟线程是 Java 19 中引入的预览特性(JEP 425),并在 Java 21 中成为正式特性(JEP 444)。由 JVM 进行调度和管理,而不是操作系统。旨在显著提高高并发场景下的性能和资源利用率。

它们与传统平台线程(操作系统线程)的关键区别在于:
- 轻量级:内存占用极小(初始约几百字节)
- 高密度:可创建数百万个虚拟线程
- JVM 管理:由 JVM 调度而不是操作系统
- 低成本:创建和销毁开销极小
1.2 虚拟线程 vs 平台线程
| 特性 | 平台线程 | 虚拟线程 |
|---|---|---|
| 资源消耗 | 大量内存(~1MB/线程) | 极少内存(~几百字节/线程) |
| 创建数量 | 数百至数千 | 数百万 |
| 调度方式 | 操作系统内核调度 | JVM 调度 |
| 阻塞成本 | 高(上下文切换昂贵) | 低(几乎为零) |
| 适用场景 | CPU 密集型任务 | I/O 密集型任务 |
1.3 虚拟线程的核心优势
1.3.1 解决传统并发瓶颈
传统线程模型的"一个请求一个线程"模式无法应对高并发场景:
// 传统方式 - 每个请求一个平台线程
public class TraditionalWebServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);while (true) {// 每个新连接创建一个新线程 - 资源消耗大!Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();new Thread(() -> handleRequest(clientSocket)).start();}}private static void handleRequest(Socket clientSocket) {// 处理请求逻辑// 线程在此阻塞等待I/O操作,浪费资源}
}
1.3.2 虚拟线程的解决方案
// 使用虚拟线程 - 每个请求一个虚拟线程
public class VirtualThreadWebServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);try (var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {while (true) {Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();// 为每个请求提交一个虚拟线程任务executor.submit(() -> handleRequest(clientSocket));}}}private static void handleRequest(Socket clientSocket) {// 处理请求逻辑// 虚拟线程在I/O阻塞时自动释放载体线程}
}
二、虚拟线程的创建方式
2.1 Thread.startVirtualThread
- 创建一个虚拟线程来执行任务并计划其执行, 此方法相当于:
Thread.ofVirtual().start(task);
public static Thread startVirtualThread(Runnable task) {Objects.requireNonNull(task);var thread = ThreadBuilders.newVirtualThread(null, null, 0, task);thread.start();return thread;
}
示例代码:
static void main() throws InterruptedException {// 1. 方式一: Thread t1 = Thread.startVirtualThread(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread(), " Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread());try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});t1.join();
}

Thread.startVirtualThread()直接创建并启动虚拟线程。Thread.sleep()会自动挂起虚拟线程,不阻塞平台线程。
2.2 Thread.ofVirtual
- 返回用于创建虚拟 Thread 线程或 ThreadFactory 创建虚拟线程的构建器
public static Builder.OfVirtual ofVirtual() {return new ThreadBuilders.VirtualThreadBuilder();
}// Builder.OfVirtual相关代码
sealed interface OfVirtual extends Builderpermits ThreadBuilders.VirtualThreadBuilder {@Override OfVirtual name(String name); // 设置线程名称/*** @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}*/@Override OfVirtual name(String prefix, long start);@Override OfVirtual inheritInheritableThreadLocals(boolean inherit);@Override OfVirtual uncaughtExceptionHandler(UncaughtExceptionHandler ueh);
}
- API使用说明
// 启动虚拟线程以运行任务。
Thread thread = Thread.ofVirtual().start(runnable);
// 创建虚拟线程的 ThreadFactory
ThreadFactory factory = Thread.ofVirtual().factory();
// 方式二: Thread.ofVirtual()
Thread t2 = Thread.ofVirtual().name("tc-virtual-thread-", 0) // 配置虚拟线程名称.start(() -> { // 启动虚拟线程System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread(), " 虚拟线程t2: " + Thread.currentThread());try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});
2.3 使用ThreadFactory
// 方式三: ThreadFactory
ThreadFactory factory = Thread.ofVirtual().factory();
Thread t3 = factory.newThread(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread(), "");try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(3000);}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}
});
2.4 使用Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()
// 方式四: 使用Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor() (推荐)
try (var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {int taskId = i;Future<String> future = executor.submit(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread(), "");try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100 * (taskId + 1));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "任务 " + taskId + " 完成!";});System.out.println(future.get());}
} catch (ExecutionException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
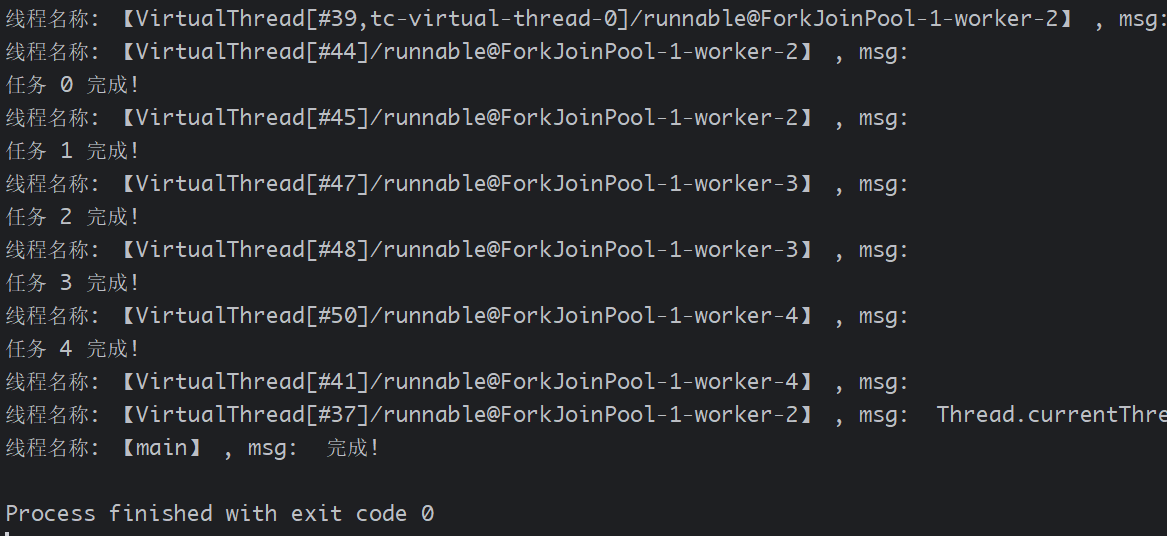
关键点:
newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()为每个任务分配独立虚拟线程。- 线程池自动释放资源,无需手动管理。
三、虚拟线程的高级特性
3.1 虚拟线程的线程局部变量
public class VirtualThreadLocals {private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> userId = new ThreadLocal<>();private static final ThreadLocal<String> requestId = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> "REQ-" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "-" + Thread.currentThread().threadId());public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {try (var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {int finalI = i;executor.submit(() -> {// 设置线程局部变量userId.set(finalI);// 模拟处理请求processRequest();return null;});}}}private static void processRequest() {System.out.println("处理请求: " + requestId.get() + ", 用户ID: " + userId.get() +", 线程: " + Thread.currentThread());// 注意: 虚拟线程中应谨慎使用大量ThreadLocal,因为创建数量可能极大}
}
3.2 虚拟线程与异常编程
public class VirtualThreadAsync {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();try (var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {// 并行执行多个异步任务Future<String> userFuture = executor.submit(() -> fetchUserData());Future<String> productFuture = executor.submit(() -> fetchProductData());Future<String> inventoryFuture = executor.submit(() -> fetchInventoryData());// 等待所有任务完成并获取结果String userData = userFuture.get();String productData = productFuture.get();String inventoryData = inventoryFuture.get();// 组合结果String result = processResults(userData, productData, inventoryData);System.out.println("最终结果: " + result);} catch (ExecutionException e) {System.err.println("任务执行失败: " + e.getCause().getMessage());}long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;System.out.println("总执行时间: " + duration + "ms");}private static String fetchUserData() throws InterruptedException {Thread.sleep(200); // 模拟网络I/Oreturn "用户数据";}private static String fetchProductData() throws InterruptedException {Thread.sleep(300); // 模拟网络I/Oreturn "产品数据";}private static String fetchInventoryData() throws InterruptedException {Thread.sleep(250); // 模拟网络I/Oreturn "库存数据";}private static String processResults(String user, String product, String inventory) {return String.format("整合结果: %s, %s, %s", user, product, inventory);}
}
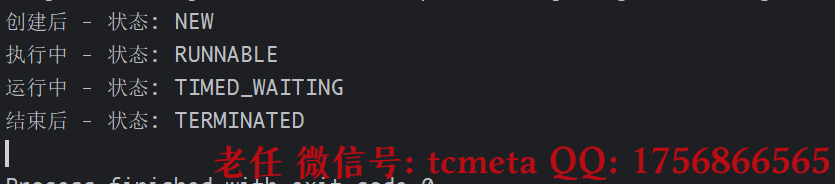
3.3 虚拟线程的状态与生命周期
虚拟线程与平台线程共享相同的 Thread.State 枚举,但内部实现不同:
package cn.tcmeta.usevirtualthread;public class VirtualThreadLifecycle {static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread vt = Thread.ofVirtual().name("lifecycle-vt").unstarted(() -> {try {System.out.println("执行中 - 状态: " + Thread.currentThread().getState());Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}});System.out.println("创建后 - 状态: " + vt.getState()); // NEWvt.start();Thread.sleep(20);System.out.println("运行中 - 状态: " + vt.getState()); // RUNNABLEvt.join();System.out.println("结束后 - 状态: " + vt.getState()); // TERMINATED}
}
3.4 虚拟线程的工作原理
虚拟线程的高效性源于其独特的调度机制:
- 非阻塞 I/O 协作:当虚拟线程执行阻塞 I/O 操作时,JVM 会暂停虚拟线程并释放载体线程,允许其他虚拟线程运行
- 栈内存管理:虚拟线程的栈采用惰性分配和动态增长,初始内存占用极小
- M:N 调度:JVM 维护的调度器将大量虚拟线程映射到少量平台线程
3.5 虚拟线程的异常处理
public class VirtualThreadExceptionHandling {public static void main(String[] args) {// 虚拟线程的未捕获异常处理Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler((thread, exception) -> {System.err.println("线程 " + thread + " 发生未捕获异常: " + exception.getMessage());});Thread vThread = Thread.startVirtualThread(() -> {System.out.println("虚拟线程开始执行");// 模拟异常if (true) {throw new RuntimeException("虚拟线程中的模拟异常");}System.out.println("这行代码不会执行");});try {vThread.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}System.out.println("主线程继续执行");}
}
四、虚拟线程的核心应用场景
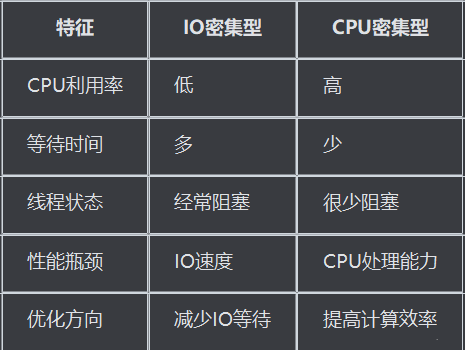
4.1 IO密集型场景
CPU密集型(CPU Bound)
定义:程序运行过程中,大部分时间花费在执行CPU计算上,很少等待IO操作。
- 特点:
- CPU使用率很高,几乎满负荷运行
- 大量时间消耗在数学计算、数据处理、图像处理等计算任务上
- 线程很少阻塞,一直在进行计算工作
- 常见场景:
- 大量数学计算(科学计算、加密解密)
- 图像和视频处理
- 数据压缩和解压缩
- 复杂的数据分析和处理
IO密集型(I/O Bound)
定义:
程序运行过程中,大部分时间花费在等待输入/输出操作完成上,而不是执行CPU计算。
- 特点:
- CPU使用率较低,经常处于等待状态
- 大量时间消耗在磁盘读写、网络请求、数据库查询等操作上
- 线程经常处于阻塞状态,等待IO操作完成
- 常见场景:
- 文件读写操作
- 网络请求(HTTP、FTP等)
- 数据库查询和更新
- 用户输入等待
4.2 高并发网络请求处理
虚拟线程特别适合处理大量并发网络请求,如 API 服务、爬虫等:
package cn.tcmeta.usevirtualthread;import java.net.URI;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;/*** 使用虚拟线程处理大量并发HTTP请求*/
public class HttpRequestsDemo {private static final HttpClient client = HttpClient.newBuilder().connectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(10)).build();static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 要请求的URL列表List<String> urls = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {urls.add("https://httpbin.org/get?num=" + i);}// 使用虚拟线程池处理所有请求long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();try (ExecutorService executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {List<Future<String>> futures = new ArrayList<>();for (String url : urls) {futures.add(executor.submit(() -> fetchUrl(url)));}// 等待所有请求完成并统计结果int successCount = 0;for (Future<String> future : futures) {try {String result = future.get();if (result.contains("\"status\": 200")) {successCount++;}} catch (ExecutionException e) {// 处理单个请求失败System.err.println("请求失败: " + e.getCause().getMessage());}}System.out.printf("完成 %d 个请求, 成功: %d, 失败: %d%n",urls.size(), successCount, urls.size() - successCount);}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.printf("总耗时: %d ms%n", endTime - startTime);}// 发送HTTP请求并返回响应private static String fetchUrl(String url) throws Exception {HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder().uri(URI.create(url)).timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(5)).GET().build();HttpResponse<String> response = client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());return response.body();}
}
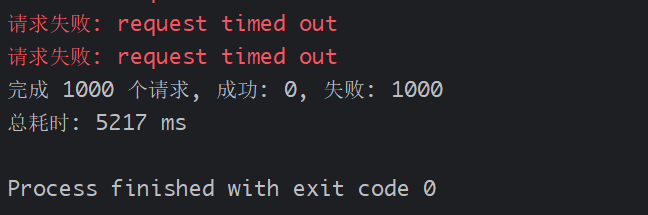
优势分析:
- 轻松处理数千甚至数万个并发请求
- 内存占用远低于使用平台线程池
- 无需复杂的异步回调代码,保持同步编程模型
4.3 并行数据处理
虚拟线程可以高效处理需要并行执行的计算任务,尤其是 I/O 与计算混合的场景:
package cn.tcmeta.usevirtualthread;import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;/*** 使用虚拟线程并行处理数据*/
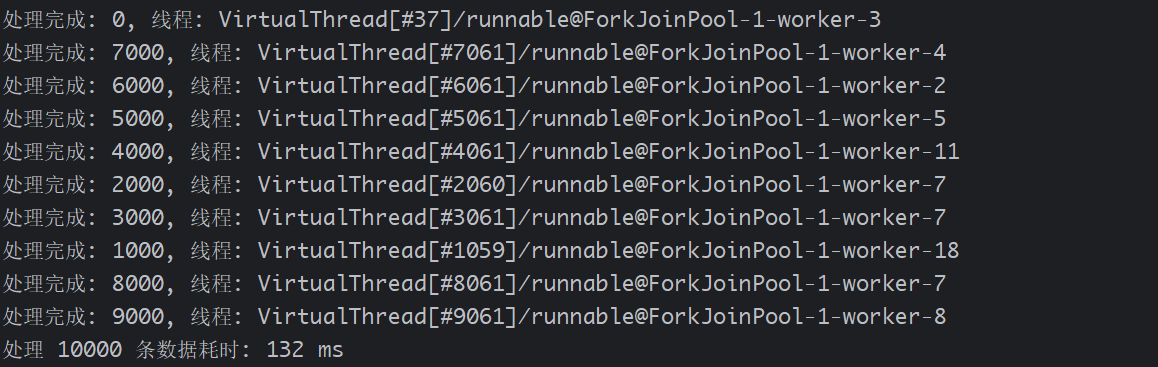
public class DataProcessingDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 生成大量数据List<Integer> data = IntStream.range(0, 10_000).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();// 使用虚拟线程池并行处理try (ExecutorService executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {data.forEach(num -> executor.submit(() -> processData(num)));}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.printf("处理 %d 条数据耗时: %d ms%n",data.size(), endTime - startTime);}// 处理单个数据项(包含计算和模拟I/O)private static void processData(int num) {try {// 模拟CPU计算int result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {result += (num * i) % 13;}// 模拟I/O操作(如写入数据库)if (num % 100 == 0) { // 每100条数据模拟一次I/OThread.sleep(10);}// 每1000条数据输出一次进度if (num % 1000 == 0) {System.out.printf("处理完成: %d, 线程: %s%n",num, Thread.currentThread().getName());}} catch (InterruptedException e) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}}
}
4.4 与结构化并发结合使用
虚拟线程与结构化并发(Structured Concurrency)结合可获得最佳效果:
package cn.tcmeta.usevirtualthread;import java.util.concurrent.StructuredTaskScope;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;/*** 虚拟线程与结构化并发结合使用*/
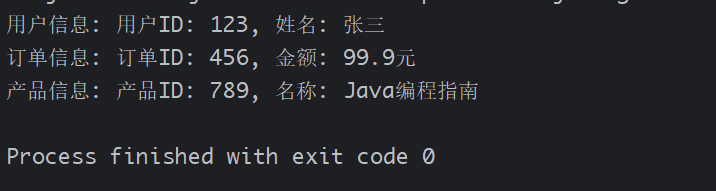
public class StructuredWithVirtualThreads {public static void main(String[] args) {try {// 创建使用虚拟线程的结构化任务范围var threadFactory = Thread.ofVirtual().factory();try (var scope = new StructuredTaskScope.ShutdownOnFailure("task",threadFactory)) {// 并行执行多个任务StructuredTaskScope.Subtask<String> userFuture = scope.fork(() -> fetchUser("123"));StructuredTaskScope.Subtask<String> orderFuture = scope.fork(() -> fetchOrder("456"));StructuredTaskScope.Subtask<String> productFuture = scope.fork(() -> fetchProduct("789"));// 等待所有任务完成scope.join();scope.throwIfFailed();// 处理结果System.out.println("用户信息: " + userFuture.get());System.out.println("订单信息: " + orderFuture.get());System.out.println("产品信息: " + productFuture.get());}} catch (Exception e) {System.err.println("处理失败: " + e.getMessage());}}private static String fetchUser(String id) throws InterruptedException {Thread.sleep(2000); // 模拟网络请求return "用户ID: " + id + ", 姓名: 张三";}private static String fetchOrder(String id) throws InterruptedException {Thread.sleep(3000); // 模拟网络请求return "订单ID: " + id + ", 金额: 99.9元";}private static String fetchProduct(String id) throws InterruptedException {Thread.sleep(2500); // 模拟网络请求return "产品ID: " + id + ", 名称: Java编程指南";}
}
4.5 高并发Web服务器
场景:基于Netty或Spring WebFlux的高并发HTTP服务。记得引入Netty依赖
package cn.tcmeta.usevirtualthread;import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;public class NettyServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();try {ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {ch.pipeline().addLast(new VirtualThreadHandler());}}).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128).childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);ChannelFuture f = b.bind(8080).sync();f.channel().closeFuture().sync();} finally {workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();}}
}class VirtualThreadHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {@Overrideprotected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) {Thread.ofVirtual().start(() -> {try {// 处理请求ctx.writeAndFlush("Response from virtual thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}});}
}
优势:
- 每个请求由独立虚拟线程处理,避免阻塞。
- 支持高并发连接,资源消耗极低
Web服务器并发处理
public class VirtualThreadWebServer {private static final int PORT = 8080;private static final ExecutorService virtualThreadExecutor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor();public static void startServer() throws IOException {try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(PORT)) {System.out.println("服务器启动,端口: " + PORT);while (true) {Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();// 为每个连接使用虚拟线程处理virtualThreadExecutor.execute(() -> handleClient(clientSocket));}} finally {virtualThreadExecutor.shutdown();}}private static void handleClient(Socket clientSocket) {try (clientSocket;var in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(clientSocket.getInputStream()));var out = new PrintWriter(clientSocket.getOutputStream(), true)) {// 读取请求String request = in.readLine();System.out.println("收到请求: " + request + ", 线程: " + Thread.currentThread());// 模拟处理时间Thread.sleep(50);// 发送响应out.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");out.println("Content-Type: text/plain");out.println();out.println("Hello from virtual thread: " + Thread.currentThread().threadId());} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {System.err.println("处理客户端请求时出错: " + e.getMessage());}}public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {startServer();}
}
4.6 实时数据流处理
场景:处理传感器数据流或金融交易数据。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;public class DataStreamProcessing {public static void main(String[] args) {try (var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {IntStream.range(0, 1_000_000).forEach(i -> {executor.submit(() -> {// 模拟数据处理double value = Math.random() * 1000;if (value > 990) {System.out.println("High value detected: " + value);}return value;});});}}
}
优势:
- 轻量级线程适合高频数据处理。
- 阻塞操作(如日志写入)不影响其他任务。
五、最佳实践与注意事项
5.1 虚拟线程最佳实践
package cn.tcmeta.usevirtualthread;import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;public class ApiAggregatorService {private final HttpClient httpClient = HttpClient.newHttpClient();public record UserProfile(String userInfo, String orders, String recommendations) {}public CompletableFuture<UserProfile> getUserProfile(String userId) {try (var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {// 并行调用多个微服务Future<String> userInfoFuture = executor.submit(() ->fetchFromUserService(userId));Future<String> ordersFuture = executor.submit(() ->fetchFromOrderService(userId));Future<String> recommendationsFuture = executor.submit(() ->fetchFromRecommendationService(userId));// 等待所有结果return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {String userInfo = userInfoFuture.get();String orders = ordersFuture.get();String recommendations = recommendationsFuture.get();return new UserProfile(userInfo, orders, recommendations);} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {throw new RuntimeException("获取用户资料失败", e);}}, executor);}}private String fetchFromUserService(String userId) throws IOException, InterruptedException {HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder().uri(URI.create("http://user-service/users/" + userId)).timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(5)).build();HttpResponse<String> response = httpClient.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());return response.body();}private String fetchFromOrderService(String userId) throws IOException, InterruptedException {// 类似实现...return "订单数据";}private String fetchFromRecommendationService(String userId) throws IOException, InterruptedException {// 类似实现...return "推荐数据";}
}
5.2 性能调优与监控
public class ApiAggregatorService {private final HttpClient httpClient = HttpClient.newHttpClient();public record UserProfile(String userInfo, String orders, String recommendations) {}public CompletableFuture<UserProfile> getUserProfile(String userId) {try (var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {// 并行调用多个微服务Future<String> userInfoFuture = executor.submit(() -> fetchFromUserService(userId));Future<String> ordersFuture = executor.submit(() -> fetchFromOrderService(userId));Future<String> recommendationsFuture = executor.submit(() -> fetchFromRecommendationService(userId));// 等待所有结果return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {String userInfo = userInfoFuture.get();String orders = ordersFuture.get();String recommendations = recommendationsFuture.get();return new UserProfile(userInfo, orders, recommendations);} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {throw new RuntimeException("获取用户资料失败", e);}}, executor);}}private String fetchFromUserService(String userId) throws IOException, InterruptedException {HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder().uri(URI.create("http://user-service/users/" + userId)).timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(5)).build();HttpResponse<String> response = httpClient.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());return response.body();}private String fetchFromOrderService(String userId) throws IOException, InterruptedException {// 类似实现...return "订单数据";}private String fetchFromRecommendationService(String userId) throws IOException, InterruptedException {// 类似实现...return "推荐数据";}
}
5.3 虚拟线程与传统线程对比
| 特性 | 传统线程 | 虚拟线程 |
|---|---|---|
| 内存开销 | ~1MB/线程 | 4KB/线程(可扩展) |
| 上下文切换开销 | 内核级,昂贵 | 用户级,廉价 |
| 最大并发数 | 数千 | 百万级 |
| 阻塞处理 | 阻塞整个线程 | 自动挂起,释放资源 |
| 调度模型 | 1:1(1线程=1OS线程) | M:N(多虚拟线程=少OS线程) |
5.4 何时使用虚拟线程
- 高并发 I/O 操作:Web 服务器、微服务、API 网关
- 批量数据处理:ETL 流程、文件处理、数据导入导出
- 并行任务处理:聚合多个数据源、并行计算
- 异步编程:替代复杂的回调地狱,保持代码清晰性
| 适用场景 | 不适用场景 |
|---|---|
| I/O 密集型任务(网络请求、数据库操作) | 长时间运行的 CPU 密集型任务 |
| 高并发服务(API、微服务) | 需要大量同步代码块的场景 |
| 服务器端应用 | 依赖 ThreadLocal 的旧代码 |
| 处理大量并发任务的场景 | 依赖线程本地状态的场景 |
5.5 虚拟线程的核心价值
- 极高的并发能力:支持百万级并发连接
- 简化的编程模型:保持同步编程风格的简单性,获得异步性能
- 优秀的资源利用率:极大减少内存消耗和上下文切换开销
- 无缝集成:与现有 Java 并发 API 完全兼容
5.6 虚拟线程的限制与注意事项
- 不适合 CPU 密集型任务:
- 虚拟线程在 CPU 密集型任务上没有优势
- 大量 CPU 密集型虚拟线程会导致频繁调度,降低性能
- 同步代码块的影响:
- 虚拟线程在同步代码块(synchronized)中阻塞时,可能不会释放载体线程
- 建议使用 ReentrantLock 替代 synchronized
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;public class SynchronizationDemo {private static final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); // 推荐// private static final Object lock = new Object(); // 不推荐用于虚拟线程public void criticalSection() {// 推荐: 使用ReentrantLock,虚拟线程阻塞时会释放载体线程lock.lock();try {// 临界区代码Thread.sleep(100); // 阻塞时释放载体线程} catch (InterruptedException e) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();} finally {lock.unlock();}// 不推荐: 使用synchronized,虚拟线程阻塞时可能不释放载体线程/*synchronized (lock) {try {Thread.sleep(100); // 可能不会释放载体线程} catch (InterruptedException e) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}}*/}
}
5.7 与其它并发模型对比
| 特性 | 虚拟线程 | 平台线程 | CompletableFuture | 反应式编程 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 资源效率 | 极高 | 低 | 中 | 高 |
| 编程模型 | 同步(简单) | 同步(简单) | 异步(复杂) | 异步(复杂) |
| 最大并发数 | 数百万 | 数千 | 数千 | 数万 |
| 学习曲线 | 低 | 低 | 中 | 高 |
| 适用场景 | I/O 密集型高并发 | 简单并发场景 | 异步任务链 | 响应式应用 |