实验8.20
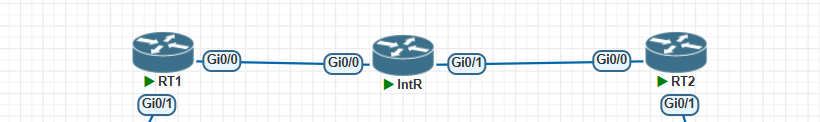
二、试验配置
1、静态路由实现GRE
RT1配置:
Int e1/0
Ip add 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
Int e0/0
Ip add 172.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
Ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.1.1.1
rt1(config)#interface tunnel 0
rt1(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
rt1(config-if)#tunnel source ethernet 0/0
rt1(config-if)#tunnel destination 172.1.2.2
rt1(config-if)#exit
rt1(config)#ip route 192.168.36.0 255.255.255.0 tunnel 0
RT2配置:
Int e1/0
Ip add 192.168.36.1 255.255.255.0
Int e0/0
Ip add 172.1.2.2 255.255.255.0
Ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.1.2.1
rt2(config)#interface tunnel 0
rt2(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
rt2(config-if)#tunnel source ethernet 0/0
rt2(config-if)#tunnel destination 172.1.1.2
rt2(config-if)#exit
rt2(config)#ip route 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0 tunnel 0
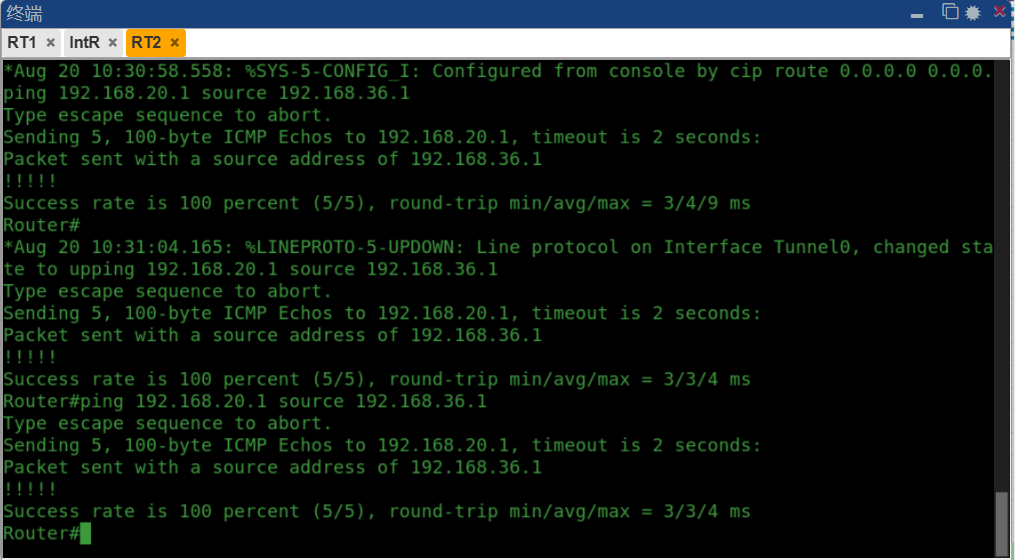
RT2pingRT1:
rt2#ping 192.168.20.1 source 192.168.36.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.36.1
..!!!
Success rate is 60 percent (3/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 96/118/136 ms
本试验现象:
在ping包过程中的数据包没有加密
2、OSPF over GRE
RT1配置:
rt1(config)#interface tunnel 0
rt1(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
rt1(config-if)#tunnel source ethernet 0/0
rt1(config-if)#tunnel destination 172.1.2.2
rt1(config-if)#exit
rt1(config)#no ip route 192.168.36.0 255.255.255.0 tunnel 0 删除之前的静态路由
rt1(config)#router ospf 1
rt1(config-router)#network 192.168.20.0 0.0.0.255 a 0
rt1(config-router)#network 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 a 0
rt1(config-router)#exit
RT2配置:
rt2(config)#interface tunnel 0
rt2(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
rt2(config-if)#tunnel source ethernet 0/0
rt2(config-if)#tunnel destination 172.1.1.2
rt2(config-if)#exit
rt2(config)#no ip route 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0 tunnel 0 删除之前的静态路由
rt2(config)#router ospf 1
rt2(config-router)#network 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 a 0
rt2(config-router)#network 192.168.36.0 0.0.0.255 a 0
rt2(config-router)#exit
本试验现象:
OSPF邻居通过tunnel隧道建立,ospf数据包来触发GRE,OSPF数据报文承载在GRE数据包中,学习到对方的私网路由(之前是静态配置)
3、GRE over Ipsecend
RT1配置:
rt1(config)#interface tunnel 0
rt1(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
rt1(config-if)#tunnel source ethernet 0/0
rt1(config-if)#tunnel destination 172.1.2.2
rt1(config-if)#exit
rt1(config)#crypto isakmp enable
rt1(config)#crypto isakmp policy 1
rt1(config-isakmp)#authentication pre-share
rt1(config-isakmp)#hash md5
rt1(config-isakmp)#group 2
rt2(config-isakmp)#encryption des
rt1(config-isakmp)#exit
rt1(config)#crypto isakmp key 0 cisco address 172.1.2.2
rt1(config)#crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac
rt1(cfg-crypto-trans)#exit
rt1(config)#access-list 101 permit ip host 172.1.1.2 host 172.1.2.2
rt1(config)#crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp
rt1(config-crypto-map)#set peer 172.1.2.2
rt1(config-crypto-map)#set transform-set cisco
rt1(config-crypto-map)#match address 101
rt1(config-crypto-map)#exit
rt1(config)#interface ethernet 0/0
rt1(config-if)#crypto map cisco
RT2配置:
rt2(config)#interface tunnel 0
rt2(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
rt2(config-if)#tunnel source ethernet 0/0
rt2(config-if)#tunnel destination 172.1.1.2
rt2(config-if)#exit
rt2(config)#crypto isakmp enable
rt2(config)#crypto isakmp policy 1
rt2(config-isakmp)#encryption des
rt2(config-isakmp)#authentication pre-share
rt2(config-isakmp)#hash md5
rt2(config-isakmp)#group 2
rt2(config-isakmp)#exit
rt2(config)#crypto isakmp key 0 cisco address 172.1.1.2
rt2(config)#crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac
rt2(cfg-crypto-trans)#exit
rt2(config)#access-list 101 permit ip host 172.1.2.2 host 172.1.1.2
rt2(config)#crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp
rt2(config-crypto-map)#set peer 172.1.1.2
rt2(config-crypto-map)#set transform-set cisco
rt2(config-crypto-map)#match address 101
rt2(config-crypto-map)#exit
rt2(config)#interface ethernet 0/0
rt2(config-if)#crypto map cisco
本试验现象:
GRE本身不能解决VPN传输数据的安全性,通过承载在Ipsec VPN中实现安全性的要求,RT2客户端定义感兴趣的流量是公网地址,RT2pingRT1的时候,触发GRE的流量,被GRE封装,打上新的IP头部,这时匹配Ipsec 的流量做IP sec,这样实现的了GRE被IP sec承载,实现了安全性的要求。
