《P3623 [APIO2008] 免费道路》
题目描述
新亚(New Asia)王国有 N 个村庄,由 M 条道路连接。其中一些道路是鹅卵石路,而其它道路是水泥路。保持道路免费运行需要一大笔费用,并且看上去王国不可能保持所有道路免费。为此亟待制定一个新的道路维护计划。
国王已决定保持尽可能少的道路免费,但是两个不同的村庄之间都应该一条且仅由一条免费道路的路径连接。同时,虽然水泥路更适合现代交通的需要,但国王也认为走在鹅卵石路上是一件有趣的事情。所以,国王决定保持刚好 K 条鹅卵石路免费。
举例来说,假定新亚王国的村庄和道路如图 3(a) 所示。如果国王希望保持两 条鹅卵石路免费,那么可以如图 3(b) 中那样保持道路 (1,2),(2,3),(3,4) 和 (3,5) 免费。该方案满足了国王的要求,因为:
- 两个村庄之间都有一条由免费道路组成的路径。
- 免费的道路已尽可能少。
- 方案中刚好有两条鹅卵石道路 (2,3) 和 (3,4)。
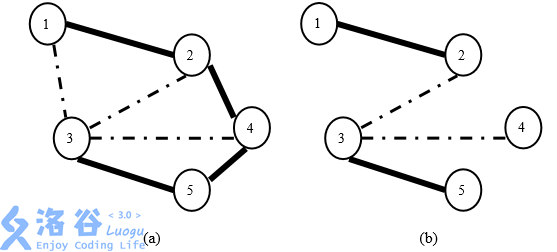
图 3:(a) 新亚王国中村庄和道路的一个示例。实线标注的是水泥路,虚线标注的是鹅卵石路。(b) 一个保持两条鹅卵石路免费的维护方案。图中仅标出了免费道路。
给定一个关于新亚王国村庄和道路的述以及国王决定保持免费的鹅卵石道路数目,写一个程序确定是否存在一个道路维护计划以满足国王的要求,如果存在则任意输出一个方案。
输入格式
输入第一行包含三个由空格隔开的整数:
N,村庄的数目 (1≤N≤2×104);
M,道路的数目 (1≤M≤105);
K,国王希望保持免费的鹅卵石道路数目 (0≤K≤N−1)。
此后 M 行述了新亚王国的道路,编号分别为 1 到 M。第 (i+1) 行述了第 i 条道路的情况。用 3 个由空格隔开的整数述:
ui 和 vi,为第 i 条道路连接的两个村庄的编号,村庄编号为 1 到 N;
ci,表示第 i 条道路的类型。ci=0 表示第 i 条道路是鹅卵石路,ci=1 表示第 i 条道路是水泥路。
输入数据保证一对村庄之间至多有一条道路连接。
输出格式
如果满足国王要求的道路维护方案不存在,你的程序应该在输出第一行打印 no solution。 否则,你的程序应该输出一个符合要求的道路维护方案,也就是保持免费的道路列表。按照输入中给定的那样输出免费的道路。如果有多种合法方案,你可以任意输出一种。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
5 7 2 1 3 0 4 5 1 3 2 0 5 3 1 4 3 0 1 2 1 4 2 1
输出 #1复制
3 2 0 4 3 0 5 3 1 1 2 1
说明/提示
数据范围
对于 100% 的数据。保证 1≤N≤2×104,1≤M≤105,0≤K≤N−1。
代码实现:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// 定义点对类型
typedef pair<int, int> PointPair;
#define firstPoint first
#define secondPoint second
#define makePointPair make_pair
// 常量定义
const int MAX_NODE = 200000;
// 道路结构
struct Road
{
int start; // 起点
int end; // 终点
};
// 全局变量
int parent[MAX_NODE]; // 并查集父节点数组
int totalNodes; // 总节点数
int totalRoads; // 总道路数
int requiredCobblestone; // 要求的鹅卵石路数量
int cementCount; // 水泥路数量
int cobblestoneCount; // 鹅卵石路数量
int usedCement[MAX_NODE]; // 标记水泥路是否被使用
int usedCobblestone[MAX_NODE]; // 标记鹅卵石路是否被使用
// 并查集查找函数(带路径压缩)
int findSet(int node)
{
return parent[node] == node ? node : parent[node] = findSet(parent[node]);
}
int main()
{
// 读取输入
scanf("%d%d%d", &totalNodes, &totalRoads, &requiredCobblestone);
// 存储两种类型的道路
Road cementRoads[MAX_NODE], cobblestoneRoads[MAX_NODE];
for (int i = 1; i <= totalRoads; i++)
{
int u, v, type;
scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &type);
if (type == 0)
// 鹅卵石路(type=0)
cobblestoneRoads[++cobblestoneCount] = (Road){u, v};
else
// 水泥路(type=1)
cementRoads[++cementCount] = (Road){u, v};
}
// 检查鹅卵石路数量是否足够
if (cobblestoneCount < requiredCobblestone)
return puts("no solution"), 0;
// 初始化并查集
for (int i = 1; i <= totalNodes; i++)
parent[i] = i;
// 先加入所有水泥路
for (int i = 1; i <= cementCount; i++)
{
int root1 = findSet(cementRoads[i].start);
int root2 = findSet(cementRoads[i].end);
if (root1 != root2)
parent[root1] = root2;
}
// 计算必须使用的鹅卵石路数量
int usedCobble = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= cobblestoneCount; i++)
{
int root1 = findSet(cobblestoneRoads[i].start);
int root2 = findSet(cobblestoneRoads[i].end);
if (root1 != root2)
{
usedCobblestone[i] = 1;
usedCobble++;
parent[root1] = root2;
}
}
// 必须使用的鹅卵石路超过要求,无解
if (usedCobble > requiredCobblestone)
return puts("no solution"), 0;
// 检查图是否连通
for (int i = 1; i < totalNodes; i++)
if (findSet(i) != findSet(i + 1))
return puts("no solution"), 0;
// 重新初始化并查集,准备构建最终方案
for (int i = 1; i <= totalNodes; i++)
parent[i] = i;
// 先加入必须使用的鹅卵石路
for (int i = 1; i <= cobblestoneCount; i++)
if (usedCobblestone[i])
{
int root1 = findSet(cobblestoneRoads[i].start);
int root2 = findSet(cobblestoneRoads[i].end);
parent[root1] = root2;
}
// 补充鹅卵石路直到达到要求数量
for (int i = 1; i <= cobblestoneCount && usedCobble < requiredCobblestone; i++)
{
if (!usedCobblestone[i])
{
int root1 = findSet(cobblestoneRoads[i].start);
int root2 = findSet(cobblestoneRoads[i].end);
if (root1 != root2)
{
usedCobblestone[i] = 1;
usedCobble++;
parent[root1] = root2;
}
}
}
// 检查是否达到要求的鹅卵石路数量
if (usedCobble < requiredCobblestone)
return puts("no solution"), 0;
// 加入水泥路使图连通
for (int i = 1; i <= cementCount; i++)
{
int root1 = findSet(cementRoads[i].start);
int root2 = findSet(cementRoads[i].end);
if (root1 != root2)
{
usedCement[i] = 1;
parent[root1] = root2;
}
}
// 输出结果
for (int i = 1; i <= cementCount; i++)
if (usedCement[i])
printf("%d %d %d\n", cementRoads[i].start, cementRoads[i].end, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= cobblestoneCount; i++)
if (usedCobblestone[i])
printf("%d %d %d\n", cobblestoneRoads[i].start, cobblestoneRoads[i].end, 0);
return 0;
}
