玳瑁的嵌入式日记D24-0823(数据结构)
散列表(哈希表)
![]()


typedef int DATATYPE;
typedef struct {
DATATYPE *head;
int tlen;
}HS_Table;
HS_Table *CreateHsTable(int len)
{
HS_Table *hs = (HS_Table *)malloc(sizeof(HS_Table)); //分配 HS_Table 结构体的内存空间
if(NULL == hs)
{
perror("malloc1 error\n");
return NULL;
}
hs->head = (DATATYPE *)malloc(sizeof(DATATYPE) * len); //为存储数据的数组分配内存空间
if(NULL == hs->head)
{
perror("malloc2 error\n");
return NULL;
}
hs->tlen = len;
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
hs->head[i] = -1;
} //将数组所有元素初始化为 -1,表示空位置
return hs;
}
/**
* @brief 根据需要存储的数据,计算下标
* FUN 1.计算过程尽可能简单 2.下标均匀分布
*/
int HS_Fun(HS_Table *h, DATATYPE *data)
{
return *data % h->tlen;
} //使用除留余数法计算数据在表中的位置
int HS_Insert(HS_Table *h, DATATYPE *data)
{
int ind = HS_Fun(h, data);
//hash表的空间,一定要大于等于需要存储的数据的个数
while(h->head[ind] != -1)
{
printf("data:%d ind:%d\n",*data, ind);
ind = (ind + 1) % h->tlen; // 如果当前位置已被占用,则检查下一个位置(循环方式)
}
memcpy(&h->head[ind], data, sizeof(DATATYPE));
return 0;
}
int HS_Search(HS_Table*h,DATATYPE* data)
{
int ind = HS_Fun(h, data);
int old_ind = ind;
while(h->head[ind] != *data)
{
ind = (ind + 1) % h->tlen;
if(ind == old_ind) //如果回到起始位置仍未找到,说明数据不存在,返回 -1
{
return -1;
}
}
return ind;
}
int HS_Destroy(HS_Table *h)
{
free(h->head);
free(h);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
HS_Table *hs = CreateHsTable(12);
int array[12] = {12,67,56,16,25,37,22,29,15,47,48,34};
for(int i = 0; i < 12; i++)
{
HS_Insert(hs, &array[i]);
}
int want_num = 22;
int ret = HS_Search(hs, &want_num);
if(ret == -1)
{
printf("not find %d\n",want_num);
}
else
{
printf("find %d\n", want_num);
}
HS_Destroy(hs);
//system("pause");
return 0;
}
排序
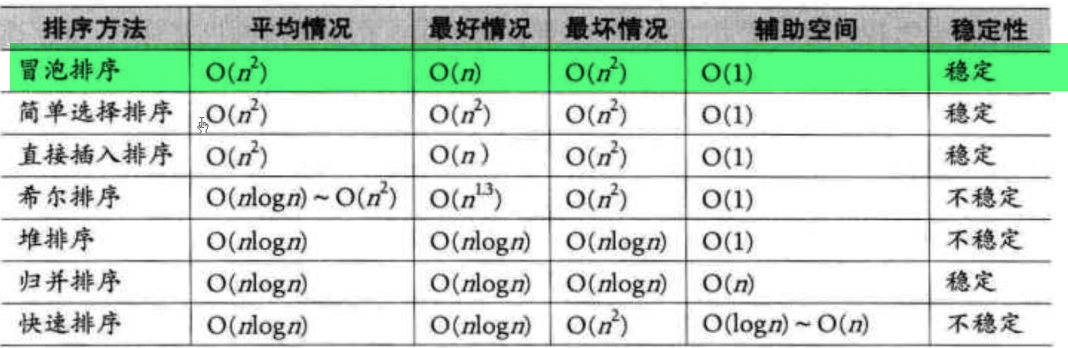
快速排序
设左指针 left 指向数组起始位置,右指针 right 指向数组末尾。
左指针向右移动,直到找到大于等于基准值的元素。
右指针向左移动,直到找到小于等于基准值的元素。
交换两个指针指向的元素,重复步骤 2-3,直到 left ≥ right。
交换基准值与 right 指针指向的元素(此时基准值被放到正确位置)。
#include <stdio.h>
// 交换两个元素的值
void swap(int* a, int* b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// 分区函数:返回基准值最终位置
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[low]; // 选择最左侧元素作为基准值
int left = low; // 左指针
int right = high; // 右指针
while (left < right)
{
// 左指针向右移动,直到找到大于等于基准值的元素
while (arr[left] < pivot)
{
left++;
}
// 右指针向左移动,直到找到小于等于基准值的元素
while (arr[right] > pivot)
{
right--;
}
// 交换左右指针指向的元素
if (left < right) {
swap(&arr[left], &arr[right]);
}
}
// 将基准值放到正确位置(与右指针交换)
swap(&arr[low], &arr[right]);
return right; // 返回基准值位置
}
// 快速排序递归函数
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// 划分区间,获取基准值位置
int pivotPos = partition(arr, low, high);
// 递归排序左侧子数组
quickSort(arr, low, pivotPos - 1);
// 递归排序右侧子数组
quickSort(arr, pivotPos + 1, high);
}
}
KLIST 内核链表(Kernel Linked List)

#include "list.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/**
* @brief 这个是内核链表的一个demo
* 1. 第一自己需要的数据类型 ,其中必须包含一个 struct list_head 的变量
2. 定义头节点,并初始化
3. 增加结点,malloc自己的结构体,填入自己需要的数据 调用list_add,把当前结点加入链表
4. 遍历所有元素list_for_each_entry_safe,
*/
typedef struct {
int id;
char name[20];
struct list_head node;
}PER;
int add_per(struct list_head *head, int id, char *name)
{
PER *per = malloc(sizeof(PER));
if(NULL == per)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return -1;
}
per->id = id;
strcpy(per->name, name);
//list_add(&per->node, head);
list_add_tail(&per->node, head);
return 0;
}
int show(struct list_head *head)
{
PER *tmp;
PER *next;
list_for_each_entry_safe(tmp, next, head, node)
{
printf("id:%d, name:%s\n", tmp->id, tmp->name);
}
return 0;
}
int del_per(struct list_head *head, int id)
{
PER *tmp;
PER *next;
list_for_each_entry_safe(tmp, next, head, node)
{
if (tmp->id == id)
{
list_del(&tmp->node);
free(tmp);
}
}
return 0;
}
int find_per(struct list_head *head, int id)
{
PER *tmp;
PER *next;
list_for_each_entry_safe(tmp, next, head, node)
{
if(tmp->id == id)
{
printf("find id:%d, name:%s\n", tmp->id, tmp->name);
}
}
return 0;
}
int modify_per(struct list_head *head, int id,char *new_name,int new_id)
{
PER *tmp;
PER *next;
list_for_each_entry_safe(tmp, next, head, node)
{
if(tmp->id == id)
{
if(new_name)
{
strcpy(tmp->name, new_name);
}
id = new_id;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
struct list_head head;
//双向循环链表,当前结点的prev,next 都指向自己
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&head);
add_per(&head, 1, "zhagnsan");
add_per(&head, 2, "lisi");
add_per(&head, 3, "wangmazi");
add_per(&head, 4, "guanerge");
add_per(&head, 5, "liubei ");
show(&head);
del_per(&head, 1);
printf("------------del--------------\n");
modify_per(&head, 2, "lisi2",5);
show(&head);
//system("pause");
return 0;
}
