【Java开发日记】我们来讲一讲 Channel 和 FileChannel
目录
Channel
FileChannel
打开 FileChannel
从 FileChannel 读数据
写数据到 FileChannel
关闭 FileChannel
示例
读数据
写数据
Channel
在 NIO 中,Channel 和 Buffer 是相辅相成的,只能从 Channel 读取数据到 Buffer 中,或者从 Buffer 写入数据到 Channle,如下图:
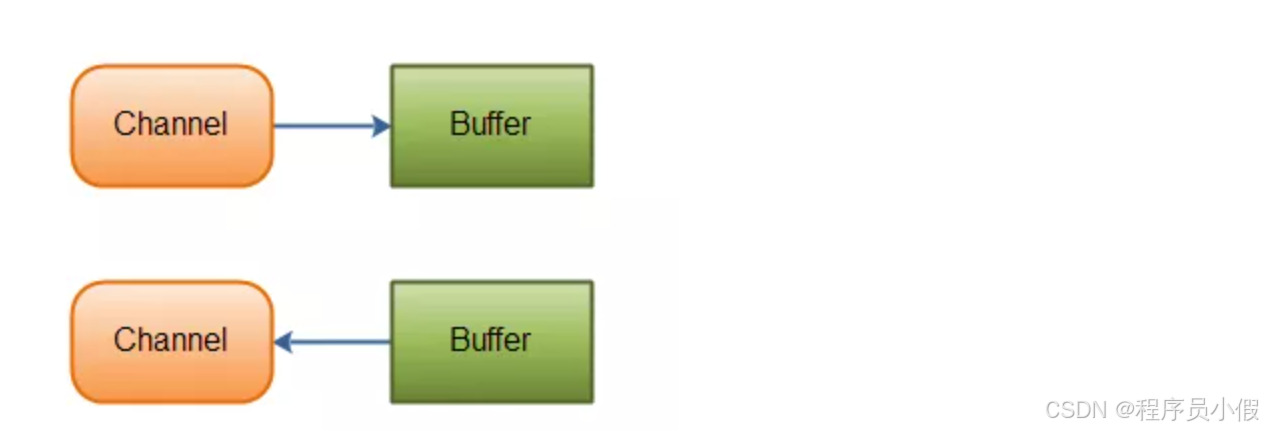
Channel 类似于 OIO 中的流(Stream),但是又有所区别:
- 流是单向的,但 Channel 是双向的,可读可写。
- 流是阻塞的,但 Channle 可以异步读写。
- 流中的数据可以选择性的先读到缓存中,而 Channel 的数据总是要先读到一个 Buffer 中,或从 Buffer 中写入,如上图。
NIO 中通过 Channel 封装了对数据源的操作,通过 Channel 可以操作数据源,但是又不必关注数据源的具体物理结构,这个数据源可以是文件,也可以是socket。
Channel 的接口定义如下:
publicinterface Channel extends Closeable {public boolean isOpen();public void close() throws IOException;
}Channel 接口仅定义两个方法:
isOpen():Channel 是否打开close():关闭 Channel
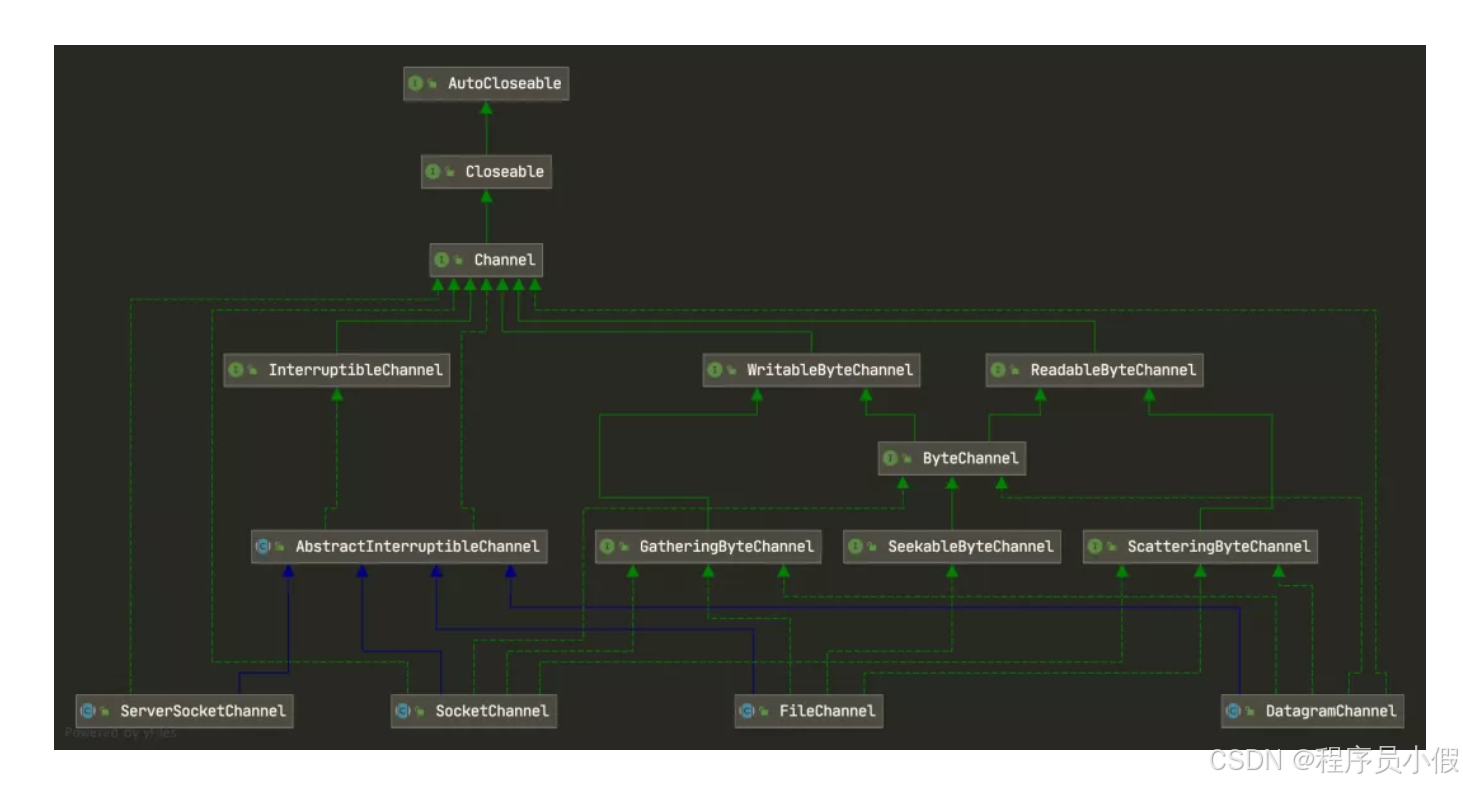
它的主要实现有:
FileChannel:文件通道,用于文件的数据读写。SocketChannel:套接字通道,能通过 TCP 读写网络中的数据。ServerSocketChannel:服务器套接字通道,监听新进来的 TCP 连接,像 web 服务器那样,对每一个新进来的连接都会创建一个SocketChannel。DatagramChannel:数据报通道,能通过 UDP 读写网络中的数据。
基本类图如下:
FileChannel
FileChannel 主要是用来读写和映射一个系统文件的 Channel,它是一个抽象类,具体由 FileChannelImpl 来实现。
定义如下:
package java.nio.channels;
publicabstractclass FileChannelextends AbstractInterruptibleChannelimplements SeekableByteChannel, GatheringByteChannel, ScatteringByteChannel{/*** 初始化一个无参构造器.*/protected FileChannel() { }//打开或创建一个文件,返回一个文件通道来访问文件public static FileChannel open(Path path,Set<? extends OpenOption> options,FileAttribute<?>... attrs)throws IOException{FileSystemProvider provider = path.getFileSystem().provider();return provider.newFileChannel(path, options, attrs);}privatestaticfinal FileAttribute<?>[] NO_ATTRIBUTES = new FileAttribute[0];//打开或创建一个文件,返回一个文件通道来访问文件public static FileChannel open(Path path, OpenOption... options)throws IOException{Set<OpenOption> set = new HashSet<OpenOption>(options.length);Collections.addAll(set, options);return open(path, set, NO_ATTRIBUTES);}//从这个通道读入一个字节序列到给定的缓冲区public abstract int read(ByteBuffer dst) throws IOException;//从这个通道读入指定开始位置和长度的字节序列到给定的缓冲区public abstract long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts, int offset, int length)throws IOException;/*** 从这个通道读入一个字节序列到给定的缓冲区*/public final long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts) throws IOException {return read(dsts, 0, dsts.length);}/*** 从给定的缓冲区写入字节序列到这个通道*/public abstract int write(ByteBuffer src) throws IOException;/*** 从给定缓冲区的子序列向该信道写入字节序列*/public abstract long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs, int offset, int length)throws IOException;/*** 从给定的缓冲区写入字节序列到这个通道*/public final long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs) throws IOException {return write(srcs, 0, srcs.length);}/*** 返回通道读写缓冲区中的开始位置*/public abstract long position() throws IOException;/*** 设置通道读写缓冲区中的开始位置*/public abstract FileChannel position(long newPosition) throws IOException;/*** 返回此通道文件的当前大小*/public abstract long size() throws IOException;/*** 通过指定的参数size来截取通道的大小*/public abstract FileChannel truncate(long size) throws IOException;/*** 强制将通道中的更新文件写入到存储设备(磁盘等)中*/public abstract void force(boolean metaData) throws IOException;/*** 将当前通道中的文件写入到可写字节通道中* position就是开始写的位置,long就是写的长度*/public abstract long transferTo(long position, long count,WritableByteChannel target)throws IOException;/*** 将当前通道中的文件写入可读字节通道中* position就是开始写的位置,long就是写的长度*/public abstract long transferFrom(ReadableByteChannel src,long position, long count)throws IOException;/*** 从通道中读取一系列字节到给定的缓冲区中* 从指定的读取开始位置position处读取*/public abstract int read(ByteBuffer dst, long position) throws IOException;/*** 从给定的缓冲区写入字节序列到这个通道* 从指定的读取开始位置position处开始写*/public abstract int write(ByteBuffer src, long position) throws IOException;// -- Memory-mapped buffers --/*** 一个文件映射模式类型安全枚举*/publicstaticclass MapMode {//只读映射模型publicstaticfinal MapMode READ_ONLY= new MapMode("READ_ONLY");//读写映射模型publicstaticfinal MapMode READ_WRITE= new MapMode("READ_WRITE");/*** 私有模式(复制在写)映射*/publicstaticfinal MapMode PRIVATE= new MapMode("PRIVATE");privatefinal String name;private MapMode(String name) {this.name = name;}}/*** 将该通道文件的一个区域直接映射到内存中*/public abstract MappedByteBuffer map(MapMode mode,long position, long size)throws IOException;/*** 获取当前通道文件的给定区域上的锁* 区域就是从position处开始,size长度 * shared为true代表获取共享锁,false代表获取独占锁*/public abstract FileLock lock(long position, long size, boolean shared)throws IOException;/*** 获取当前通道文件上的独占锁*/public final FileLock lock() throws IOException {return lock(0L, Long.MAX_VALUE, false);}/*** 尝试获取给定的通道文件区域上的锁* 区域就是从position处开始,size长度 * shared为true代表获取共享锁,false代表获取独占锁*/public abstract FileLock tryLock(long position, long size, boolean shared)throws IOException;/*** 尝试获取当前通道文件上的独占锁*/public final FileLock tryLock() throws IOException {return tryLock(0L, Long.MAX_VALUE, false);}
}打开 FileChannel
在使用 FileChannle 之前必须要先打开它,但是无法直接打开一个 FileChannel,需要通过使用一个 InputStream、OutputStream、RandomAcessFile 来获取一个 FileChannel 实例,如下:
RandomAccessFile accessFile = new RandomAccessFile("/Users/chenssy/Documents/FileChannel.txt","rw");
FileChannel fileChannel = accessFile.getChannel();调用 getChannel() 即可获取 FileChannel 实例,源码如下:
public final FileChannel getChannel() {synchronized (this) {if (channel == null) {channel = FileChannelImpl.open(fd, path, true, rw, this);}return channel;}
}getChnnel() 方法很简单,直接调用 FileChannelImpl 的静态方法 open():
public static FileChannel open(Path path,Set<? extends OpenOption> options,FileAttribute<?>... attrs) throws IOException{FileSystemProvider provider = path.getFileSystem().provider();return provider.newFileChannel(path, options, attrs);
}从 FileChannel 读数据
调用 FileChannel 的 read() 方法即可从 FileChannel 中获取数据,当然不是直接获取,而是需要先写入到 Buffer 中,所以调用 read() 之前,需要分配一个 Buffer,然后调用 read() ,该方法返回 int 表示有多少数据读取到了 Buffer 中了,如果返回 -1 表示已经到文件末尾了。
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readCount = fileChannel.read(buffer);FileChannel 仅定义了方法,具体实现在 FileChannelImpl,如下:
public int read(ByteBuffer dst) throws IOException {ensureOpen();if (!readable)thrownew NonReadableChannelException();// 加锁synchronized (positionLock) {int n = 0;int ti = -1;try {begin();ti = threads.add();if (!isOpen())return0;do {// 通过IOUtil.read实现n = IOUtil.read(fd, dst, -1, nd);} while ((n == IOStatus.INTERRUPTED) && isOpen());return IOStatus.normalize(n);} finally {threads.remove(ti);end(n > 0);assert IOStatus.check(n);}}
}- 首先确保该 Channel 是打开的
- 然后加锁,主要是因为写入缓冲区需要保证线程安全
-
最后通过
IOUtils.read()实现static int read(FileDescriptor fd, ByteBuffer dst, long position, NativeDispatcher nd) throws IOException{// 1 申请一块临时堆外DirectByteBufferByteBuffer bb = Util.getTemporaryDirectBuffer(dst.remaining());try {// 2 先往DirectByteBuffer写入数据,提高效率int n = readIntoNativeBuffer(fd, bb, position, nd);bb.flip();if (n > 0)// 3 再拷贝到传入的bufferdst.put(bb);return n;} finally {Util.offerFirstTemporaryDirectBuffer(bb);} } -
首先申请一块临时的堆外
DirectByteBuffer - 然后先往
DirectByteBuffer写入数据,因为这样能够提高效率,为什么会提高效率,后文分析。 -
最后拷贝到
ByteBuffer中写数据到 FileChannel
read()方法是从 FileChannel 中读取数据,那write()方法则是从ByteBuffer中读取数据写入到 Channel 中。调用write()需要先申请一个ByteBuffer,如下:ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); fileChannel.write(buffer);同样,实现是在 FileChannelImpl 中。
public int write(ByteBuffer src) throws IOException {ensureOpen();if (!writable)thrownew NonWritableChannelException();synchronized (positionLock) {int n = 0;int ti = -1;try {begin();ti = threads.add();if (!isOpen())return0;do {n = IOUtil.write(fd, src, -1, nd);} while ((n == IOStatus.INTERRUPTED) && isOpen());return IOStatus.normalize(n);} finally {threads.remove(ti);end(n > 0);assert IOStatus.check(n);}} }与
read()方法实现一模一样,先确定该 Channel 是打开的,然后加锁,最后调用 IOUtil 的write()。static int write(FileDescriptor fd, ByteBuffer src, long position, NativeDispatcher nd)throws IOException{if (src instanceof DirectBuffer)return writeFromNativeBuffer(fd, src, position, nd);int pos = src.position();int lim = src.limit();assert (pos <= lim);int rem = (pos <= lim ? lim - pos : 0);// 2 否则构造一块跟传入缓冲区一样大小的DirectBufferByteBuffer bb = Util.getTemporaryDirectBuffer(rem);try {bb.put(src);bb.flip();src.position(pos);// 3 调用writeFromNativeBuffer读取int n = writeFromNativeBuffer(fd, bb, position, nd);if (n > 0) {// now update srcsrc.position(pos + n);}return n;} finally {Util.offerFirstTemporaryDirectBuffer(bb);} } -
首先判断传入的 Buffer 是否为
DirectBuffer,如果是的话,就直接写入 - 否则则构造一块跟传入 Buffer 一样大小的
DirectBuffer -
最后调用
writeFromNativeBuffer()关闭 FileChannel
保持好习惯,用完了一定要记得关闭:
close()。public final void close() throws IOException {synchronized (closeLock) {if (!open)return;open = false;implCloseChannel();} }调用
implCloseChannel()释放 Channel。protected void implCloseChannel() throws IOException {// 释放文件锁if (fileLockTable != null) {for (FileLock fl: fileLockTable.removeAll()) {synchronized (fl) {if (fl.isValid()) {//释放锁nd.release(fd, fl.position(), fl.size());((FileLockImpl)fl).invalidate();}}}}// 通知当前通道所有被阻塞线程threads.signalAndWait();if (parent != null) {((java.io.Closeable)parent).close();} else {nd.close(fd);} }关闭 FileChannel 时,需要释放所有锁和文件流。
示例
读数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {RandomAccessFile accessFile = new RandomAccessFile("/Users/chenssy/Documents/FileChannel.txt","rw");FileChannel fileChannel = accessFile.getChannel();ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);fileChannel.read(buffer);System.out.println(new String(buffer.array()));fileChannel.close(); }写数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {String fileContent = "写入数据";RandomAccessFile accessFile = new RandomAccessFile("/Users/chenssy/Documents/FileChannel.txt","rw");FileChannel fileChannel = accessFile.getChannel();ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);buffer.put(fileContent.getBytes("UTF-8"));buffer.flip();fileChannel.write(buffer);fileChannel.close(); }
如果小假的内容对你有帮助,请点赞,评论,收藏。创作不易,大家的支持就是我坚持下去的动力!

