利用Qwen大模型进行c++11并发库的学习,与时俱进!!!!
文章目录
- 1、学习新的东西可以借助ai和官方文档
-
- 1.1 会问问题
- 异步编程教程
-
- 1. std::future
- 2. std::shared_future
- 3、std::promise
- 4、4. std::packaged_task
- 5. std::async
- 6. std::future_status 和等待函数
- 综合代码
- 总结
1、学习新的东西可以借助ai和官方文档
因为别人写的有可能会写错或者水平不高
1.1 会问问题
eg:
这样写可能会讲的不清晰并且会少讲函数接口等
你可以这样问
这样就会清晰很多。
后续不懂最好是问ai,再参考官方文档。
异步编程教程

1. std::future
std::future 是一个模板类,用于访问异步操作的结果。它提供了一种机制来获取异步操作(可能在另一个线程中执行)的返回值。
常用接口
get(): 获取结果,如果结果未准备好则阻塞
valid(): 检查 future 是否拥有共享状态
wait(): 等待结果变为可用
wait_for(): 等待一段时间
wait_until(): 等待直到某个时间点
#include <iostream>
#include <future>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>int calculate() {std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(2)); // 模拟耗时计算return 42;
}int main() {// 使用 async 启动异步任务,返回 futurestd::future<int> fut = std::async(std::launch::async, calculate);std::cout << "正在计算结果..." << std::endl;// get() 会阻塞直到结果可用int result = fut.get();std::cout << "结果是: " << result << std::endl;// 再次调用 get() 会导致异常,因为共享状态已被消费// int result2 = fut.get(); // 错误!return 0;
}
2. std::shared_future
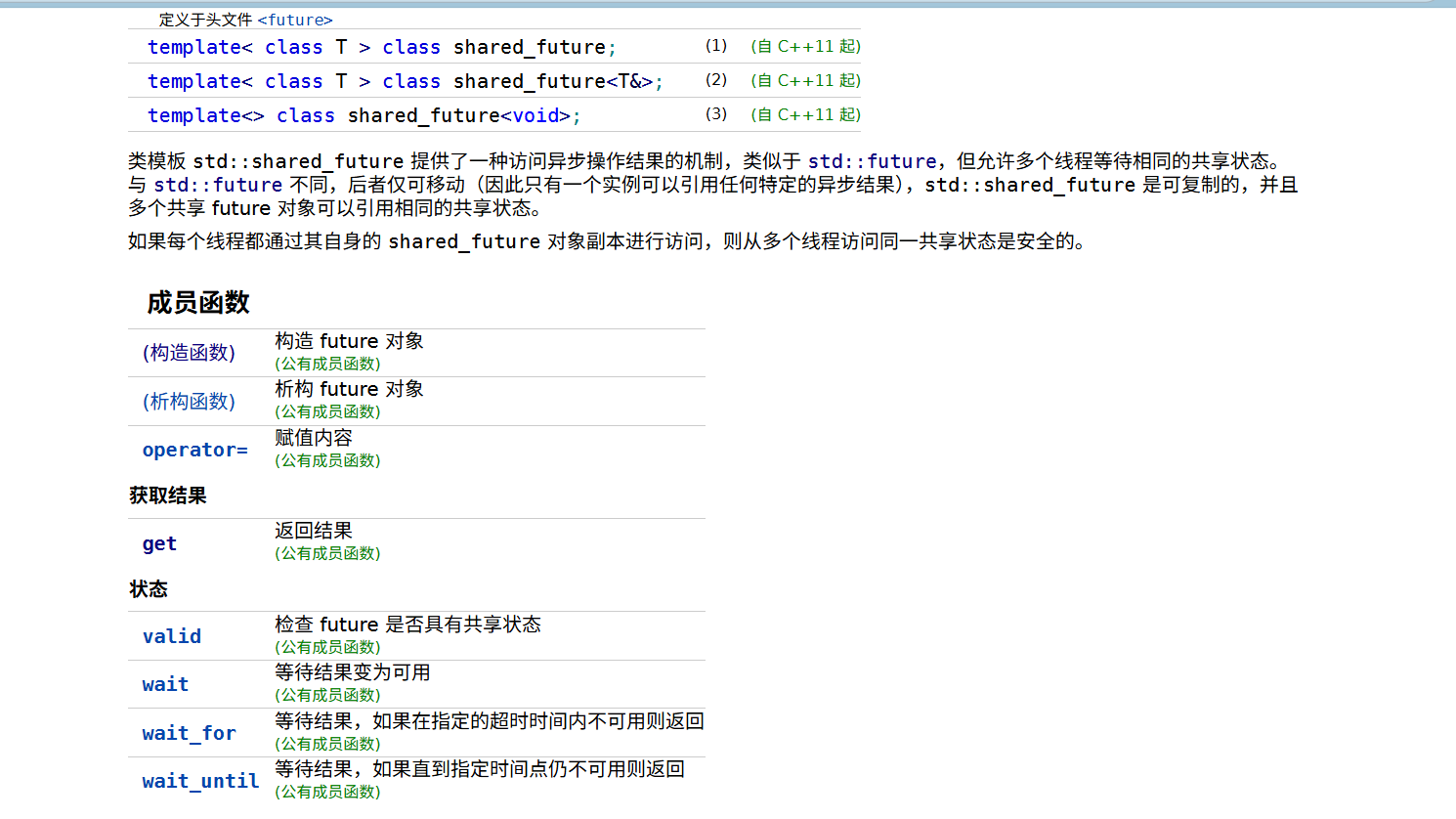
std::shared_future 类似于 std::future,但可以被多次访问(允许多个线程等待同一个结果)。
常用接口
与 std::future 类似,但可以多次调用 get()
#include <iostream>
#include <future>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>void worker(std::shared_future<int> fut) {// 每个线程都可以安全地获取结果int result = fut.get();std::cout << "Worker got result: " << result << std::endl;
}int main() {// 创建一个 promise 对象std::promise<int> prom;// 从 promise 获取 futurestd::future<int> fut = prom.get_future();// 将 future 转换为 shared_futurestd::shared_future<int> shared_fut = fut.share();// 创建多个线程共享同一个结果std::vector<std::thread> threads;for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {threads.emplace_back(worker, shared_fut);}// 设置 promise 的值prom.set_value(42);// 等待所有线程完成for (auto& t : threads) {t.join();}return 0;
}
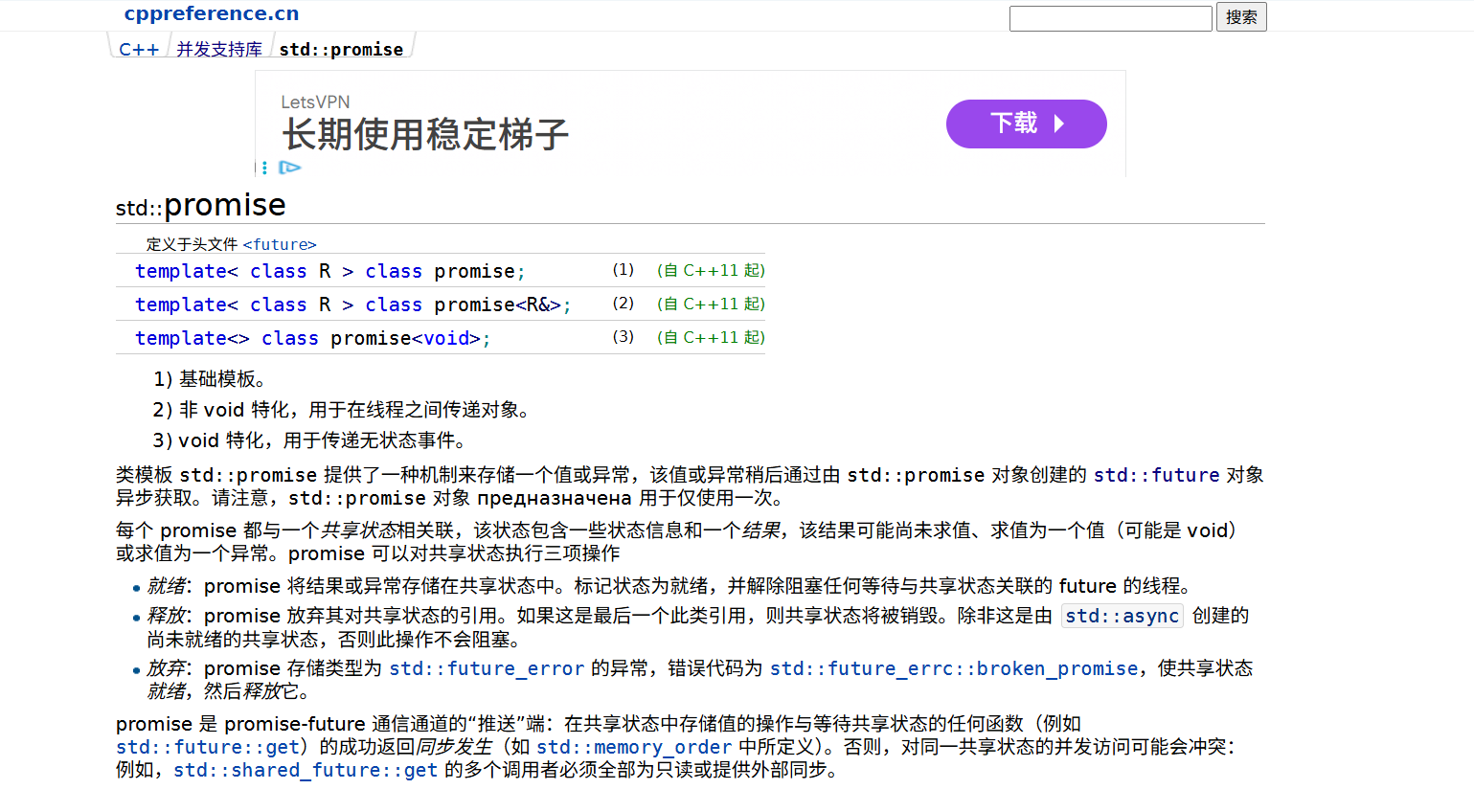
3、std::promise
std::promise 是一个模板类,用于存储一个值或异常,稍后可以通过与之关联的 std::future 对象获取。
常用接口
get_future(): 获取与 promise 关联的 future
set_value(): 设置结果值
set_exception(): 设置异常
set_value_at_thread_exit(): 在线程退出时设置值
set_exception_at_thread_exit(): 在线程退出时设置异常

#include <iostream>
#include <future>
#include <thread>
#include <stdexcept>void calculate(std::promise<int> prom) {try {// 模拟计算std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));int result = 42;// 设置结果值prom.set_value(result);} catch (...) {// 捕获所有异常并存储在 promise 中prom.set_exception(std::current_exception(