【C++】哈希
目录
一、unordered系列关联式容器
1.1 unordered_map
1.1.1 unordered_map的文档介绍
1.1.2 unordered_map的接口说明
1.2 unordered_set
1.3 在线OJ
二、底层结构
2.1 哈希概念
2.2 哈希冲突
2.3 哈希函数
2.4 哈希冲突解决
2.4.1 闭散式
2.4.2 开散式
三、模拟实现
一、unordered系列关联式容器
在C++98中,STL提供了底层为红黑树结构的一系列关联式容器,在查询时效率可达到$log_2N$,即最差情况下需要比较红黑树的高度次,当树中的节点非常多时,查询效率也不理想。最好的查询是,进行很少的比较次数就能够将元素找到,因此在C++11中,STL又提供了4个unordered系列的关联式容器,这四个容器与红黑树结构的关联式容器使用方式基本类似,只是其底层结构不同,本文中只对unordered_map和unordered_set进行介绍,unordered_multimap和unordered_multiset可查看文档介绍。(unordered_multimap,unordered_multiset)
1.1 unordered_map
1.1.1 unordered_map的文档介绍
- unordered_map是存储<key, value>键值对的关联式容器,其允许通过keys快速的索引到与其对应的value。
- 在unordered_map中,键值通常用于惟一地标识元素,而映射值是一个对象,其内容与此键关联。键和映射值的类型可能不同。
- 在内部, unordered_map没有对<kye, value>按照任何特定的顺序排序, 为了能在常数范围内找到key所对应的value,unordered_map将相同哈希值的键值对放在相同的桶中。
- unordered_map容器通过key访问单个元素要比map快,但它通常在遍历元素子集的范围迭代方面效率较低。
- unordered_maps实现了直接访问操作符(operator[]),它允许使用key作为参数直接访问value。
- 它的迭代器至少是前向迭代器。
1.1.2 unordered_map的接口说明
1. unordered_map的构造
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| unordered_map | 构造不同格式的unordered_map对象 |
2. unordered_map的容量
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| bool empty() const | 检测unordered_map是否为空,是返回true,否返回false |
| size_type size() const | 获取unordered_map的有效元素个数 |
3. unordered_map的迭代器
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| iterator begin() | 返回unordered_map第一个元素的迭代器 |
| iterator end() | 返回unordered_map最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
| const_iterator cbegin() const | 返回unordered_map第一个元素的const迭代器 |
| const_iterator cend() const | 返回unordered_map最后一个元素下一个位置的const迭代器 |
4. unordered_map的元素访问
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| operator[] | 返回与key对应的value,没有一个默认值 |
5. unordered_map的查询
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| iterator find ( const key_type& k ) | 返回key在哈希桶中的位置 |
| size_type count ( const key_type& k ) const | 返回哈希桶中关键码为key的键值对的个数 |
6. unordered_map的修改操作
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| insert | 向容器中插入键值对 |
| erase | 删除容器中的键值对 |
| clear | 清空容器中有效元素个数 |
| swap | 交换两个容器中的元素 |
7. unordered_map的桶操作
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| size_type bucket_count() const | 返回哈希桶中桶的总个数 |
| size_type bucket_size ( size_type n ) const | 返回n号桶中有效元素的总个数 |
| size_type bucket ( const key_type& k ) const | 返回元素key所在的桶号 |
1.2 unordered_set
1. unordered_set的构造
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| unordered_set | 构造不同格式的unordered_set对象 |
2. unordered_set的容量
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| bool empty() const | 检测unordered_set是否为空,是返回true,否返回false |
| size_type size() const | 获取unordered_set的有效元素个数 |
3. unordered_set的迭代器
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| iterator begin() | 返回unordered_set第一个元素的迭代器 |
| iterator end() | 返回unordered_set最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
| const_iterator cbegin() const | 返回unordered_set第一个元素的const迭代器 |
| const_iterator cend() const | 返回unordered_set最后一个元素下一个位置的const迭代器 |
4. unordered_set的查询
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| iterator find ( const key_type& k ) | 返回key在哈希桶中的位置 |
| size_type count ( const key_type& k ) const | 返回哈希桶中关键码为key的键值对的个数 |
5. unordered_set的修改操作
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| insert | 在unordered_set中插入新元素 |
| clear | 从unordered_set容器中删除单个元素或一系列元素 |
| clear | unordered_set容器中的所有元素都被删除 |
| swap | 将容器的内容交换为 ust 的内容,ust 是另一个包含相同类型元素的unordered_set对象 |
6. unordered_set的桶操作
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
| size_type bucket_count() const | 返回哈希桶中桶的总个数 |
| size_type bucket_size ( size_type n ) const | 返回n号桶中有效元素的总个数 |
| size_type bucket ( const key_type& k ) const | 返回元素key所在的桶号 |
1.3 在线OJ
在长度 2N 的数组中找出重复 N 次的元素
class Solution {
public:int repeatedNTimes(vector<int>& nums) {unordered_map<int, int> m;for(auto i : nums){if(m.find(i) != m.end()) return i;m[i] = i;}return 0;}
};两个数组的交集
class Solution {
public:vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {// 用unordered_set对nums1中的元素去重unordered_set<int> s1;for (auto e : nums1)s1.insert(e);// 用unordered_set对nums2中的元素去重unordered_set<int> s2;for (auto e : nums2)s2.insert(e);// 遍历s1,如果s1中某个元素在s2中出现过,即为交集vector<int> vRet;for (auto e : s1) {if (s2.find(e) != s2.end())vRet.push_back(e);}return vRet;}
};二、底层结构
unordered系列的关联式容器之所以效率比较高,是因为其底层使用了哈希结构。
2.1 哈希概念
顺序结构以及平衡树中,元素关键码与其存储位置之间没有对应的关系,因此在查找一个元素时,必须要经过关键码的多次比较。顺序查找时间复杂度为O(N),平衡树中为树的高度,即O($log_2 N$),搜索的效率取决于搜索过程中元素的比较次数。
理想的搜索方法:可以不经过任何比较,一次直接从表中得到要搜索的元素。如果构造一种存储结构,通过某种函数(hashFunc)使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立一一映射的关系,那么在查找时通过该函数可以很快找到该元素。
当向该结构中:
该方式即为哈希(散列)方法,哈希方法中使用的转换函数称为哈希(散列)函数,构造出来的结构称为哈希表(Hash Table)(或者称散列表)。
例如:数据集合{4,5,9,33,66,21,78}
哈希函数设置为:hash(key) = key % capacity;capacity为存储元素底层空间的总大小。
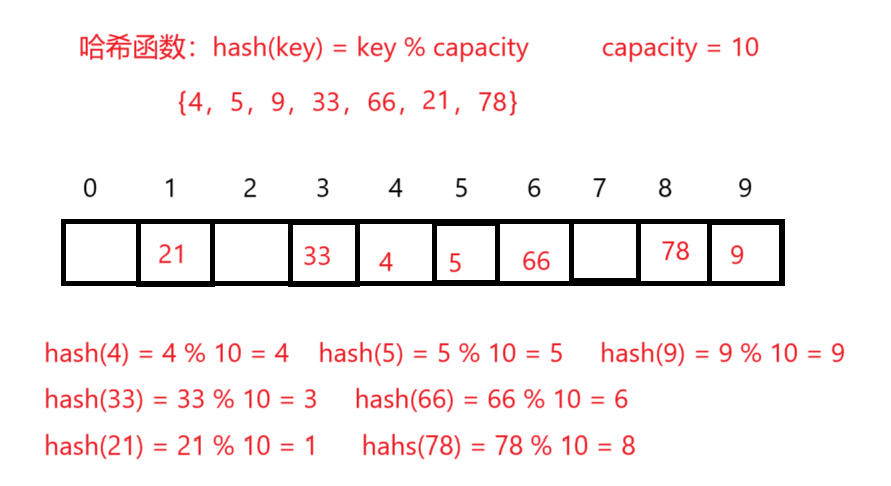
用该方法进行搜索不必进行多次关键码的比较,因此搜索的速度比较快
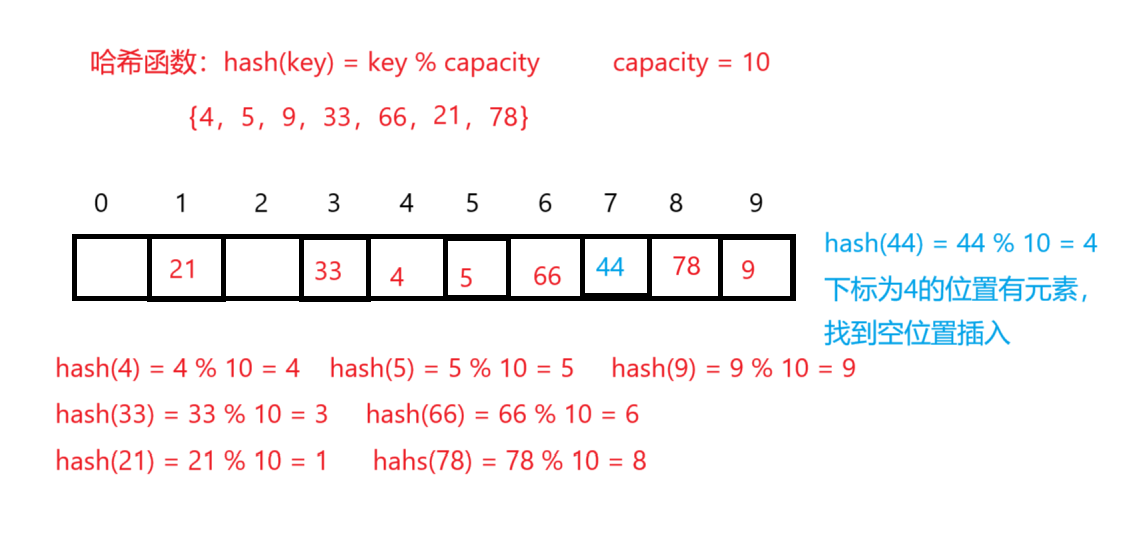
问题:按照上述哈希方式,向集合中插入元素44,会出现什么问题?
- 插入元素:根据待插入元素的关键码,以此函数计算出该元素的存储位置并按此位置进行存放
- 搜索元素:对元素的关键码进行同样的计算,把求得的函数值当做元素的存储位置,在结构中按此位置取元素比较,若关键码相等,则搜索成功
2.2 哈希冲突
对于两个数据元素的关键字$k_i$和 $k_j$(i != j),有$k_i$ != $k_j$,但有:Hash($k_i$) ==Hash($k_j$),即:不同关键字通过相同哈希哈数计算出相同的哈希地址,该种现象称为哈希冲突或哈希碰撞。
把具有不同关键码而具有相同哈希地址的数据元素称为“同义词”。
发生哈希冲突该如何处理呢?
2.3 哈希函数
引起哈希冲突的一个原因可能是:哈希函数设计不够合理。
哈希函数设计原则:
- 哈希函数的定义域必须包括需要存储的全部关键码,而如果散列表允许有m个地址时,其值域必须在0到m-1之间
- 哈希函数计算出来的地址能均匀分布在整个空间中
- 哈希函数应该比较简单
常见哈希函数:
1. 直接定址法 --- (常用)
取关键字的某个线性函数为散列地址:hash(key) = A*key + B
优点:简单,均匀
缺点:需要事先知道关键字的分布情况
使用场景:适合查找比较小且连续的情况
2. 除留余数法 --- (常用)
设散列表中允许的地址数为m,取一个不大于m,但最接近或者等于m的质数p作为除数,按照哈希函数:hash(key) = key % p (p <= m),将关键码转换成哈希地址。
4. 折叠法 --- (了解)
折叠法是将关键字从左到右分割成位数相等的几部分(最后一部分位数可以短些),然后将这几部分叠加求和,并按散列表表长,取后几位作为散列地址。
折叠法适合事先不需要知道关键字的分布,适合关键字位数比较多的情况
5. 随机数法 --- (了解)
选择一个随机函数,取关键字的随机函数值为它的哈希地址,即H(key) = random(key), 其中random为随机数函数。
通常应用于关键字长度不等时采用此法
6. 数学分析法--(了解)
设有n个d位数,每一位可能有r种不同的符号,这r种不同的符号在各位上出现的频率不一定相同,可能在某些位上分布比较均匀,每种符号出现的机会均等,在某些位上分布不均匀只有某几种符号经常出现。可根据散列表的大小,选择其中各种符号分布均匀的若干位作为散列地址。例如:假设要存储某家公司员工登记表,如果用手机号作为关键字,那么极有可能前7位都是 相同的,那么我们可以选择后面的四位作为散列地址,如果这样的抽取工作还容易出现 冲突,还可以对抽取出来的数字进行反转(如1234改成4321)、右环位移(如1234改成4123)、左环移位、前两数与后两数叠加(如1234改成12 + 34 = 46)等方法。
数字分析法通常适合处理关键字位数比较大的情况,如果事先知道关键字的分布且关键字的若干位分布较均匀的情况
注意:哈希函数设计的越精妙,产生哈希冲突的可能性就越低,但是无法避免哈希冲突
2.4 哈希冲突解决
解决哈希冲突两种常见的方法是:闭散列和开散列
2.4.1 闭散式
闭散列:也叫开放定址法,当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有空位置,那么可以把key存放到冲突位置中的“下一个”空位置中去。那么如何寻找下一个空位置呢?
1. 线性探测
比如2.1中的场景,现在需要插入元素44,先通过哈希函数计算哈希地址,哈希地址为4,因此44理论应该插入到4的位置,但是该位置已经放了值为4的元素,即发生哈希冲突。
线性探测:从发生冲突的位置开始,依次向后探测,知道寻找到下一个空位置为止。
a. 插入
- 通过哈希函数获取待插入元素在哈希表中的位置
- 如果该位置中没有元素,则直接插入元素,如果该位置中有元素发生了哈希冲突,使用线性探测找到下一个空位置,插入新元素
b. 删除
采用闭散列处理哈希冲突时,不能随便物理删除哈希表中已有元素,若直接删除元素会影响其他元素的搜索。比如删除元素4,如果直接删除掉,44查找起来可能会受到影响。因此,线性探测采用标记的伪删除法来删除一个元素。
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}
};// 特化
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t hash = 0;for (auto& c : key){hash *= 31;hash += c;}return hash;}
};namespace my
{enum State
{EMPTY,EXIST,DELETE
};template<class K, class V>
struct HashData
{pair<K, V> _kv;State _state = EMPTY;
};template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:HashTable(){_table.resize(10);}bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (find(kv.first))return false;if (_size * 10 / _table.capacity() >= 7){HashTable<K, V, Hash> newhash;newhash._table.resize(_table.capacity() * 2);for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.capacity(); ++i)if (_table[i]._state == EXIST)newhash.insert(_table[i]._kv); // 复用代码_table.swap(newhash._table);}Hash h;size_t k = h(kv.first) % _table.capacity();while (_table[k]._state == EXIST){++k;k %= _table.capacity();}_table[k]._kv = kv;_table[k]._state = EXIST;++_size;return true;}HashData<K, V>* find(const K& key){Hash h;size_t k = h(key) % _table.capacity();while (_table[k]._state != EMPTY) // 必定会有空位置{if (_table[k]._state == EXIST && _table[k]._kv.first == key)return &_table[k];++k;k %= _table.capacity();}return nullptr;}bool erase(const K& key){HashData<K, V>* pdata = find(key);if (pdata){pdata->_state = DELETE;_size--;return true;}elsereturn false;}
private:vector<HashData<K, V>> _table;size_t _size = 0;
};
}测试代码:
void TestHT1()
{HashTable<int, int> ht;int a[] = { 11,21,4,14,24,15,9 };for (auto e : a){ht.insert({ e,e });}ht.insert({ 19,19 });ht.insert({ 19,190 });ht.insert({ 19,1900 });ht.insert({ 39,1900 });if (ht.find(24))cout << "找到了24" << endl;elsecout << "not find" << endl;ht.erase(4);if (ht.find(4))cout << "找到了4" << endl;elsecout << "not find" << endl;
}
线性探测优点:实现非常简单
线性探测缺点:一旦发生哈希冲突,所有的冲突连在一起,容易产生数据“堆积”,即:不同关键码占据了可利用的空位置,使得寻找某关键码的位置需要许多次比较,导致搜索效率降低。如何缓解呢?
2. 二次探测
线性探测的缺陷是产生冲突的数据堆积在一块,这与其找下一个空位置有关系,因为找空位置的方式就是挨着往后逐个去找,因此二次探测为了避免该问题,找下一个空位置的方法为:H_i = (H_0 + i ^ 2) % m, 或者:H_i = (H_0 - i ^ 2) % m。其中:i =1, 2, 3…, H_0是通过散列函数Hash(x)对元素的关键码 key 进行计算得到的位置,m是表的大小。
研究表明:当表的长度为质数且表装载因子a不超过0.5时,新的表项一定能够插入,而且任何一个位置都不会被探查两次。因此只要表中有一半的空位置,就不会存在表满的问题。在搜索时可以不考虑表装满的情况,但在插入时必须确保表的装载因子a不超过0.5,如果超出必须考虑增容。
因此:闭散列最大的缺陷就是空间利用率比较低,这也是哈希的缺陷。
2.4.2 开散式
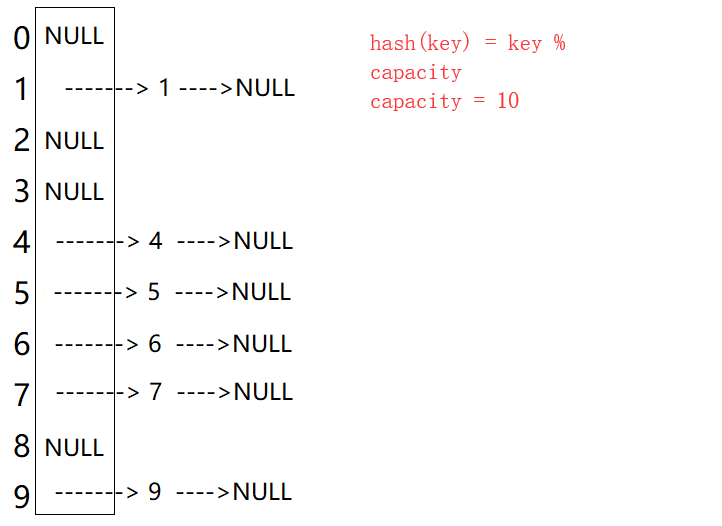
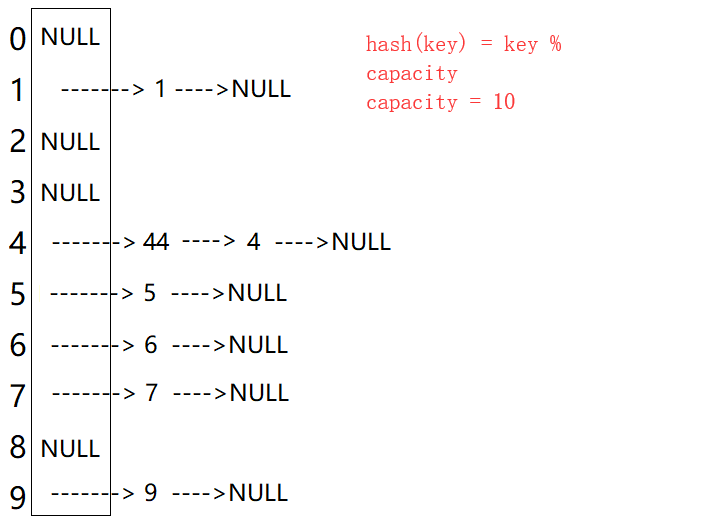
从上图可以看出,开散列每个桶中放的都是发生哈希冲突的元素。
namespace my_open
{template<class T>struct HashNode{T _data;HashNode<T>* _next;HashNode(const T& data):_data(data),_next(nullptr){ }};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class HashTable{typedef HashNode<T> Node;public:HashTable(){_table.resize(10, nullptr);}~HashTable(){for (int i = 0; i < _table.capacity(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = next;}_table[i] = nullptr;}}bool insert(const T& data){KeyOfT kot;if (find(kot(data)))return false;Hash ha;// 负载因子 == 1 扩容if (_size == _table.capacity()){vector<Node*> newtable(_table.capacity() * 2, nullptr);for (int i = 0; i < _table.capacity(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;size_t hashi = ha(kot(cur->_data)) % newtable.capacity();cur->_next = newtable[hashi]; // 头插newtable[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}}_table.swap(newtable);}size_t hashi = ha(kot(data)) % _table.capacity();Node* node = new Node(data);node->_next = _table[hashi];_table[hashi] = node;++_size;return true;}Node* find(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Hash ha;size_t hashi = ha(key) % _table.capacity();Node* cur = _table[hashi];while (cur){if (key == kot(cur->_data))return cur;cur = cur->_next;}return nullptr;}bool erase(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Hash ha;size_t hashi = ha(key) % _table.capacity();Node* cur = _table[hashi], prev = nullptr;while (cur){if (key == kot(cur->_data)){if (prev == nullptr)_table[hashi] = cur->_next;elseprev->_next = cur->_next;delete cur;_size--;return true;}prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}return false;}private:vector<Node*> _table;size_t _size = 0;};
}开散列与闭散列比较
应用链地址法处理溢出,需要增设链接指针,似乎增加了存储开销。事实上:由于开地址法必须保持大量的空闲空间以确保搜索效率,如二次探查法要求装载因子a <=0.7,而表项所占空间又比指针大的多,所以使用链地址法反而比开地址法节省存储空间。
三、模拟实现
1. 哈希表的改造
namespace my_open
{template<class T>struct HashNode{T _data;HashNode<T>* _next;HashNode(const T& data):_data(data),_next(nullptr){ }};// 前置声明template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>class HashTable;template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>struct HashIterator{typedef HashNode<T> Node;typedef HashIterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, KeyOfT, Hash> Self;Node* _node;const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* _ptable;HashIterator(Node* node, HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* ptable):_node(node),_ptable(ptable){ }Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_next){_node = _node->_next;}else{Hash ha;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = ha(kot(_node->_data)) % _ptable->_table.capacity();++hashi;while (hashi < _ptable->_table.capacity()){if (_ptable->_table[hashi])break;++hashi;}if (hashi < _ptable->_table.capacity())_node = _ptable->_table[hashi];else_node = nullptr;}return *this;}};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>class HashTable{typedef HashNode<T> Node;// 友元声明,需要使用到私有成员template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>friend struct HashIterator;public:typedef HashIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> Iterator;typedef HashIterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyOfT, Hash> ConstIterator;Iterator begin(){if (_size == 0)return end();for (int i = 0; i < _table.capacity(); i++)if (_table[i])return Iterator(_table[i], this);}Iterator end(){return Iterator(nullptr, this);}ConstIterator begin() const {if (_size == 0)return end();for (int i = 0; i < _table.capacity(); i++)if (_table[i])return ConstIterator(_table[i], this);}ConstIterator end() const {return ConstIterator(nullptr, this);}HashTable(){_table.resize(10, nullptr);}~HashTable(){for (int i = 0; i < _table.capacity(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;delete cur;cur = next;}_table[i] = nullptr;}}size_t capacity(){return _table.capacity();}pair<Iterator, bool> insert(const T& data){KeyOfT kot;Iterator it = find(kot(data));if (it != end())return make_pair(it, false);Hash ha;// 负载因子 == 1 扩容if (_size == _table.capacity()){vector<Node*> newtable(_table.capacity() * 2, nullptr);for (int i = 0; i < _table.capacity(); i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;size_t hashi = ha(kot(cur->_data)) % newtable.capacity();cur->_next = newtable[hashi]; // 头插newtable[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}}_table.swap(newtable);}size_t hashi = ha(kot(data)) % _table.capacity();Node* node = new Node(data);node->_next = _table[hashi];_table[hashi] = node;++_size;return make_pair(Iterator(node, this), true);}Iterator find(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Hash ha;size_t hashi = ha(key) % _table.capacity();Node* cur = _table[hashi];while (cur){if (key == kot(cur->_data))return Iterator(cur, this);cur = cur->_next;}return end();}bool erase(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Hash ha;size_t hashi = ha(key) % _table.capacity();Node* cur = _table[hashi], prev = nullptr;while (cur){if (key == kot(cur->_data)){if (prev == nullptr)_table[hashi] = cur->_next;elseprev->_next = cur->_next;delete cur;_size--;return true;}prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}return false;}private:vector<Node*> _table;size_t _size = 0;};
}
2. unordered_map封装
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{template<class K, class V>struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};
public:typedef typename HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT<K, V>, Hash>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT<K, V>, Hash>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}const_iterator begin() const {return _ht.begin();}const_iterator end() const {return _ht.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _ht.insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> p = _ht.insert(make_pair(key, V()));return p.first->second;}iterator find(const K& key){return _ht.find(key);}bool erase(const K& key){return _ht.erase(key);}
private:HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT<K, V>, Hash> _ht;
};测试代码:
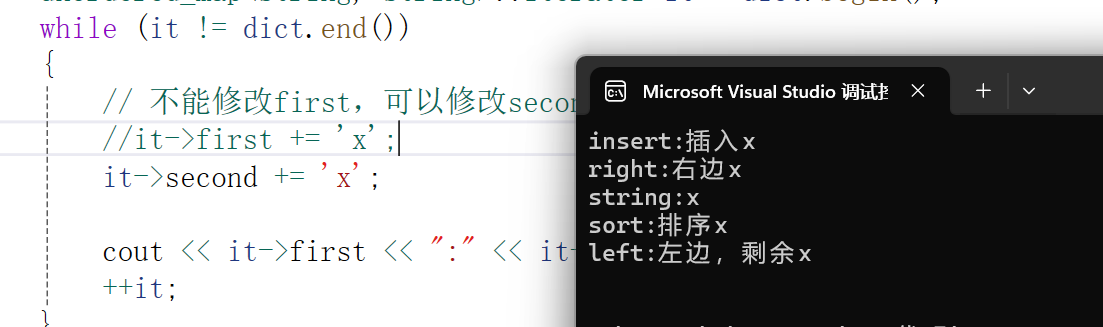
void test_map()
{unordered_map<string, string> dict;dict.insert({ "sort", "排序" });dict.insert({ "left", "左边" });dict.insert({ "right", "右边" });dict["left"] = "左边,剩余";dict["insert"] = "插入";dict["string"];unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();while (it != dict.end()){// 不能修改first,可以修改second//it->first += 'x';it->second += 'x';cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;++it;}cout << endl;
}
3. unordered_set封装
template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{template<class K>struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};
public:typedef typename HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT<K>, Hash>::Iterator iterator;typedef typename HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT<K>, Hash>::ConstIterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}const_iterator begin() const {return _ht.begin();}const_iterator end() const {return _ht.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){return _ht.insert(key);}iterator find(const K& key){return _ht.find(key);}bool erase(const K& key){return _ht.erase(key);}
private:HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT<K>, Hash> _ht;
};测试代码:
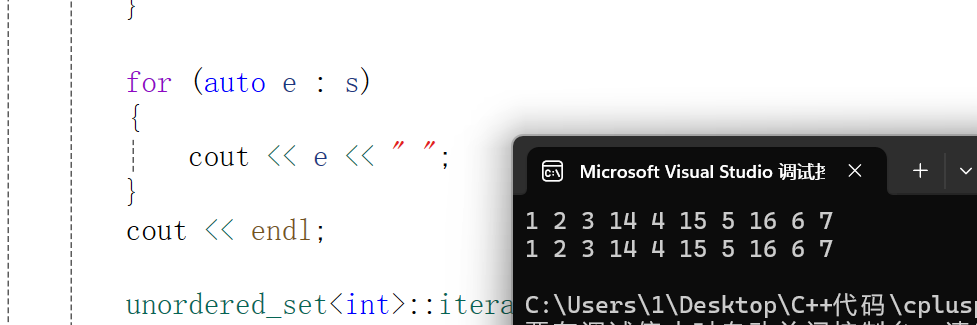
void test_set()
{unordered_set<int> s;int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14, 3,3,15 };for (auto e : a){s.insert(e);}for (auto e : s){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){//*it += 1;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;
}