Springboot和postman的使用
文章目录
- 1.入门
- 2.创建项目
- 3.HTTP
- 4.请求响应
- 5.简单参数的接收
- 6.实体参数的接收
- 7.数组集合参数
- 8.日期参数
- 9.JSON参数
- 10.路径参数
- 11.响应
- 12.分层解耦
1.入门
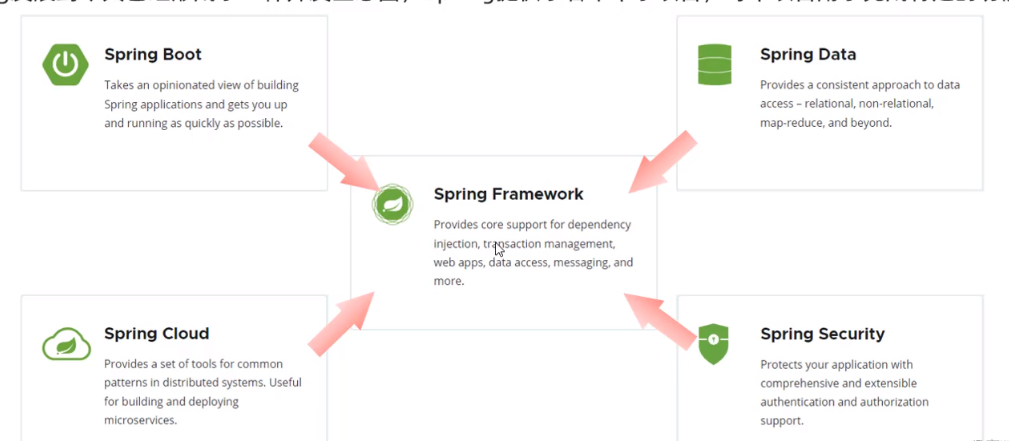
- Spring Boot : 快速方便地构建出一个Spring程序
- Spring Framework :Spring框架,最底层最基础的框架
- Spring Data : 封装了一系列访问数据库的技术
- Spring Cloud : 用来构建微服务项目
- Spring Security : 安全框架
2.创建项目
- 1.
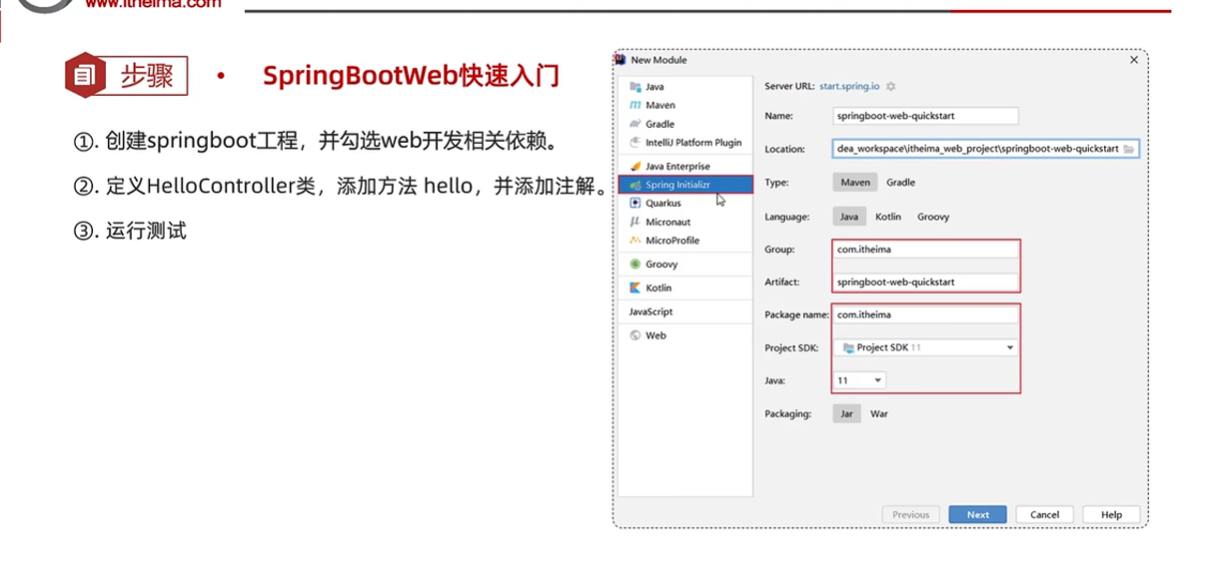
- 2
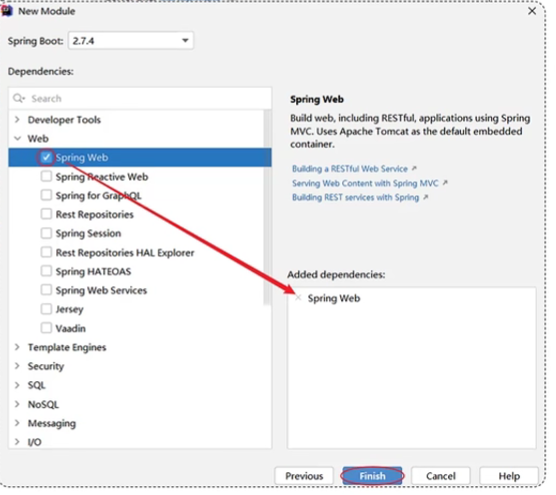

- 3.创建好后,有些文件可以删除
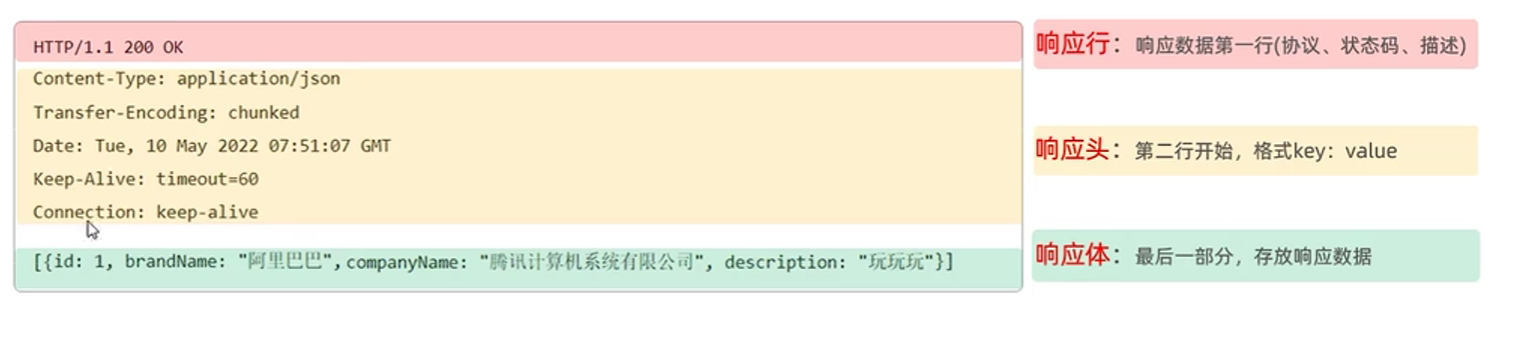
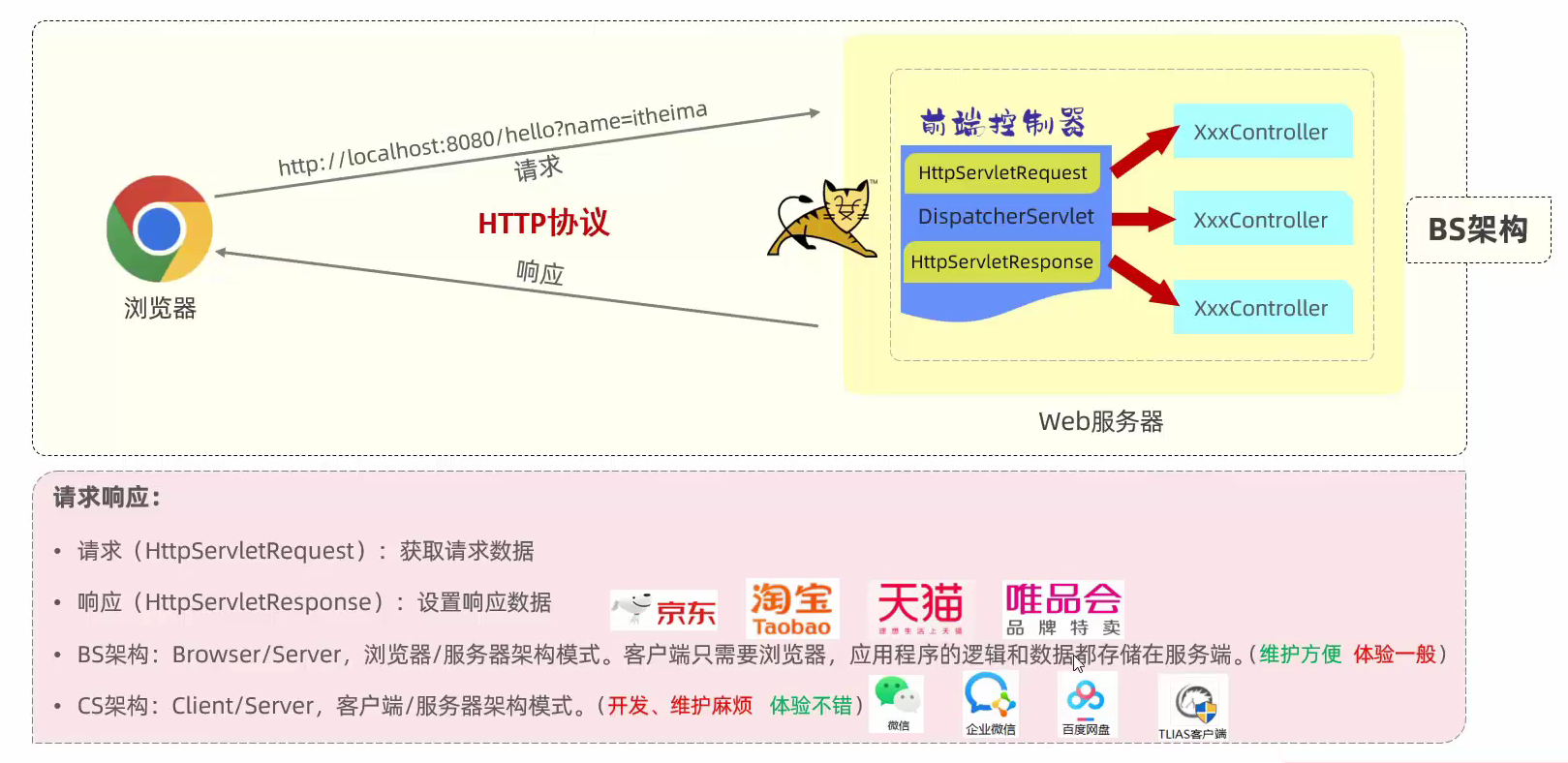
3.HTTP
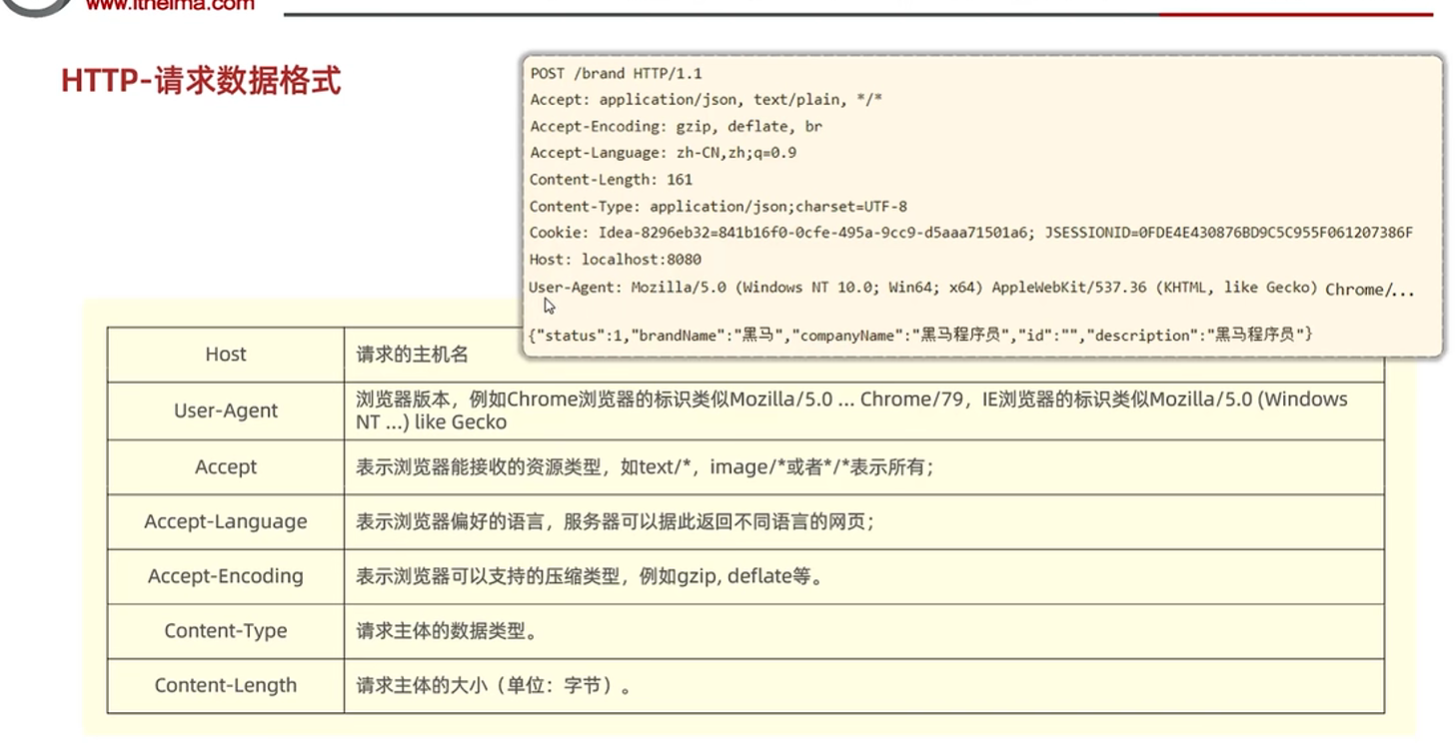
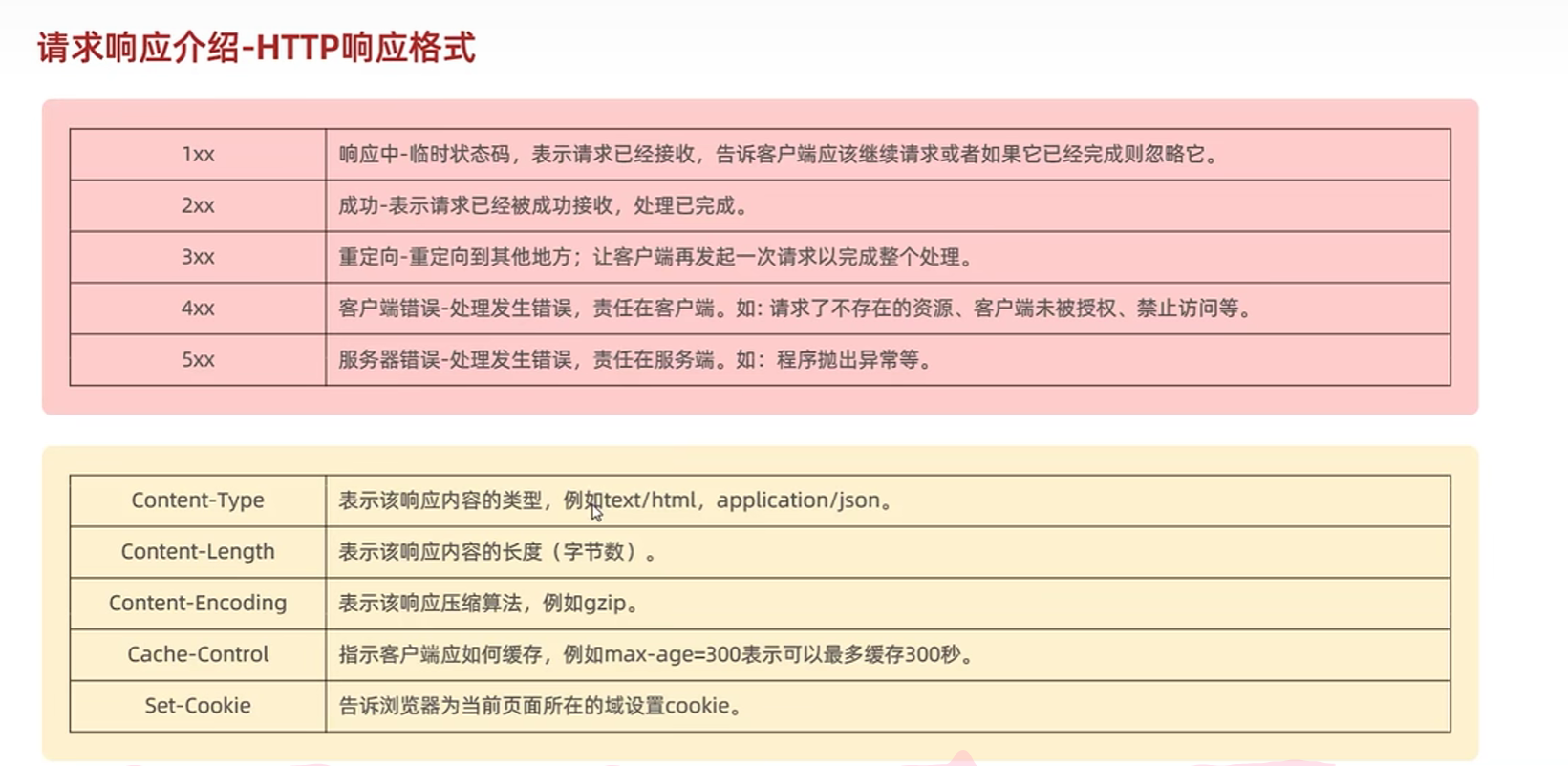
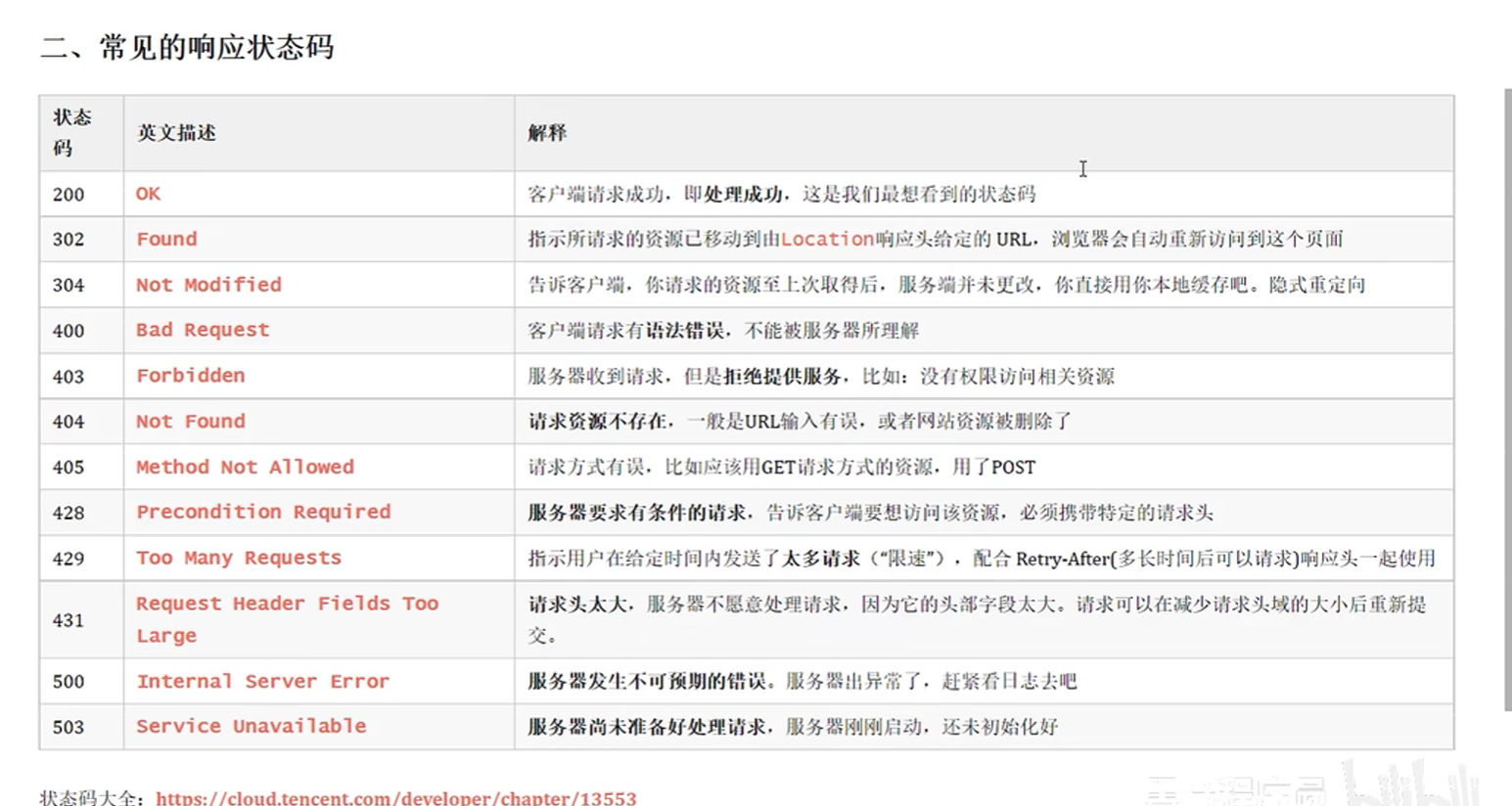
- http协议概述
- 响应协议
-
-
-
-
web服务器

-

-
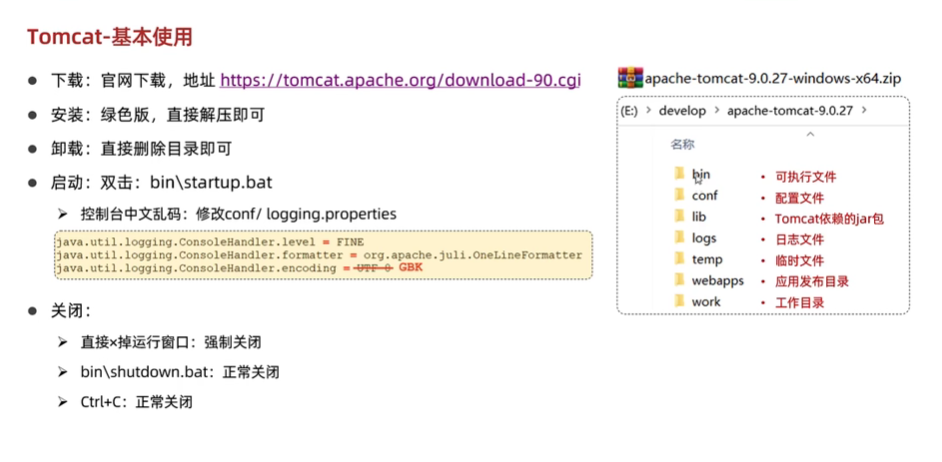
Tomcat介绍
-

-
-
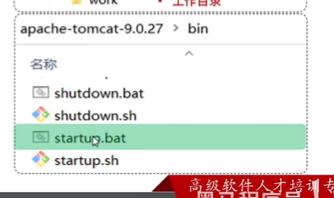
启动
-
打开tomcat出现的问题:
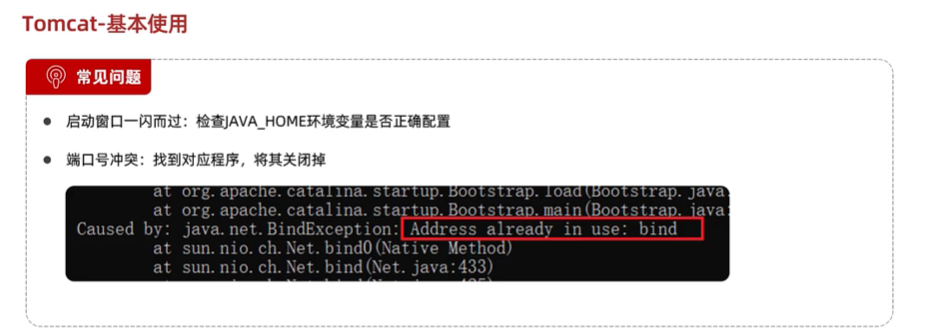
-
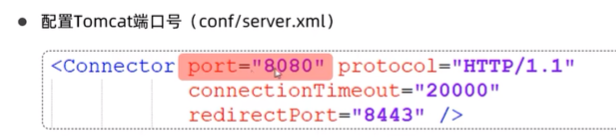

-
双击startup.bat闪退的解决方法
-

-
-


-
-
4.请求响应
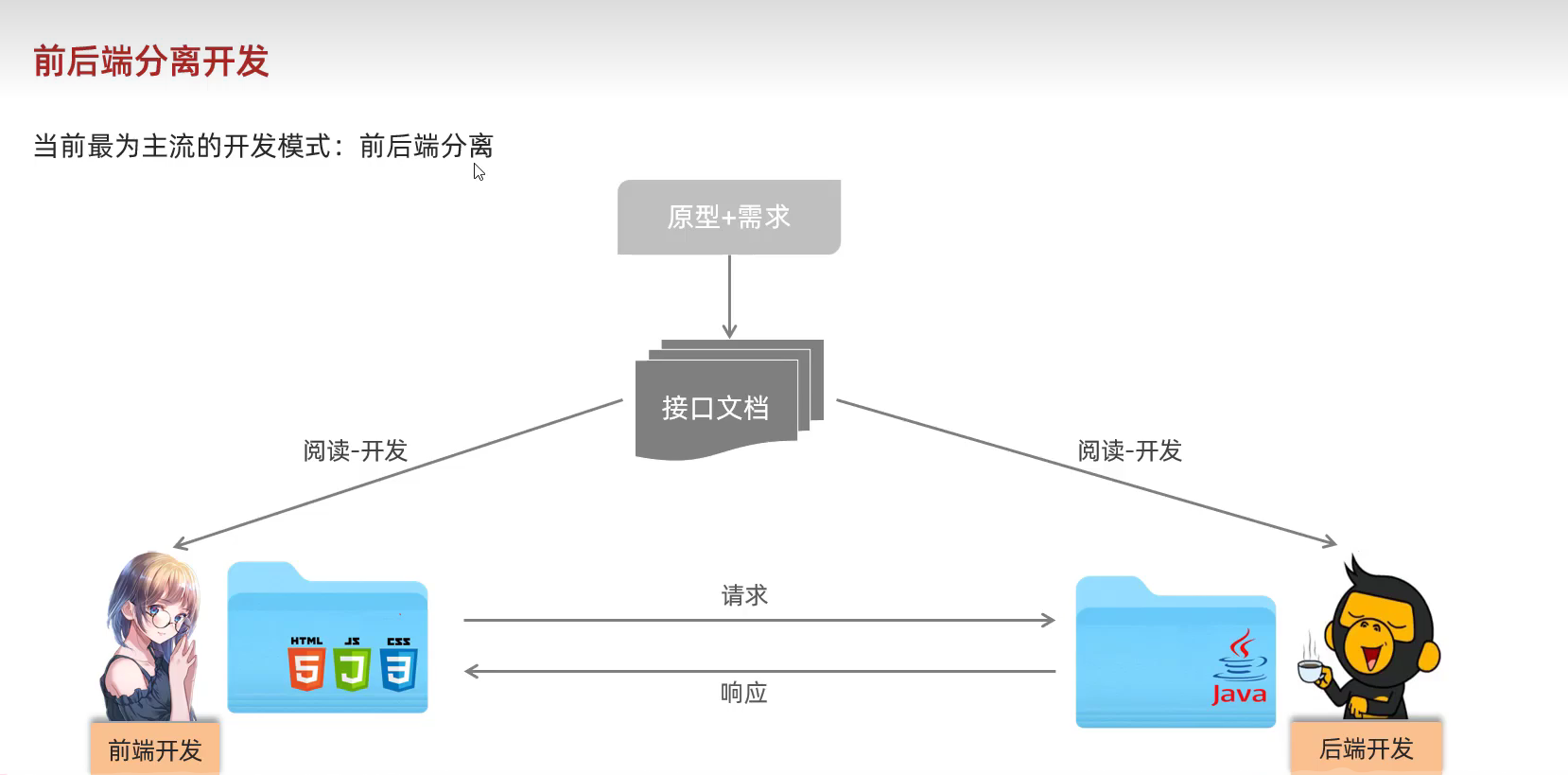
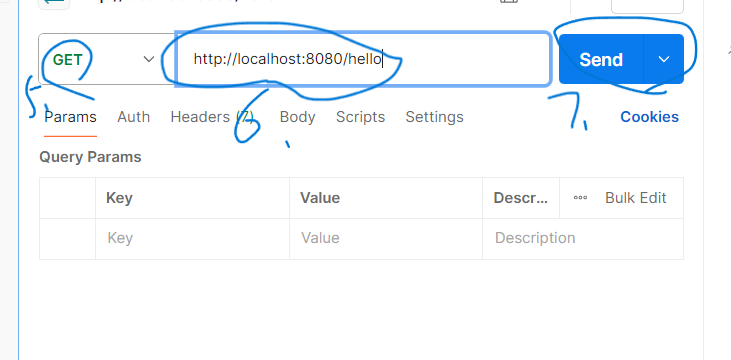
- 工具:postman
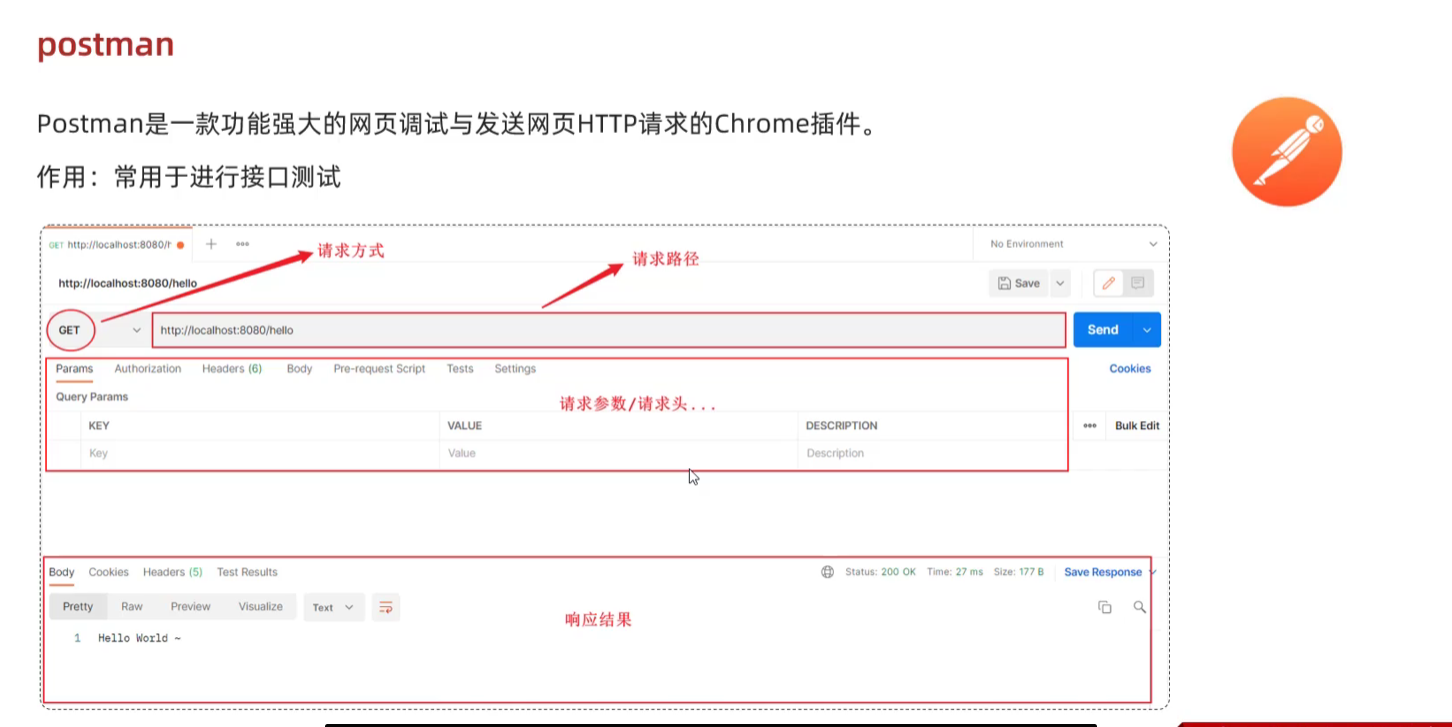
- 安装步骤:可按照该步骤进行
- 创建项目:
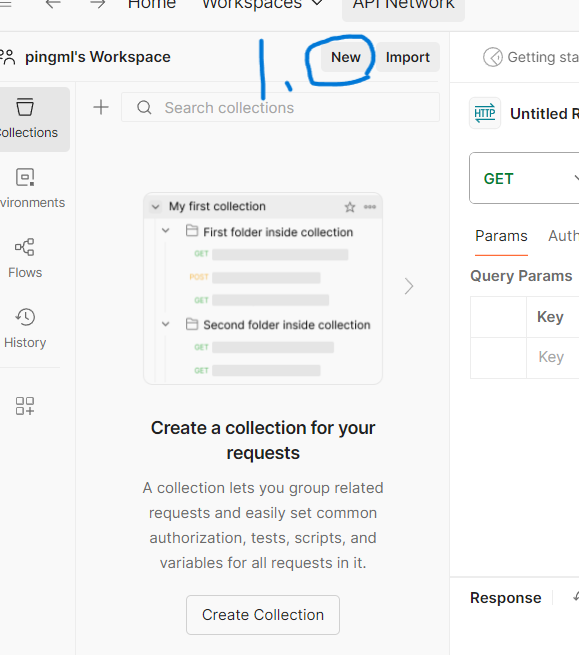
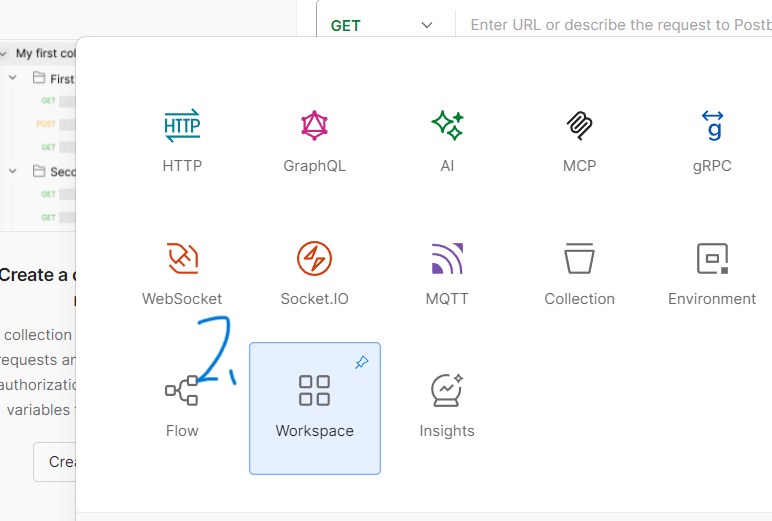
- 创建项目:
- 更改别名,文件夹设置
5.简单参数的接收

- 简单参数
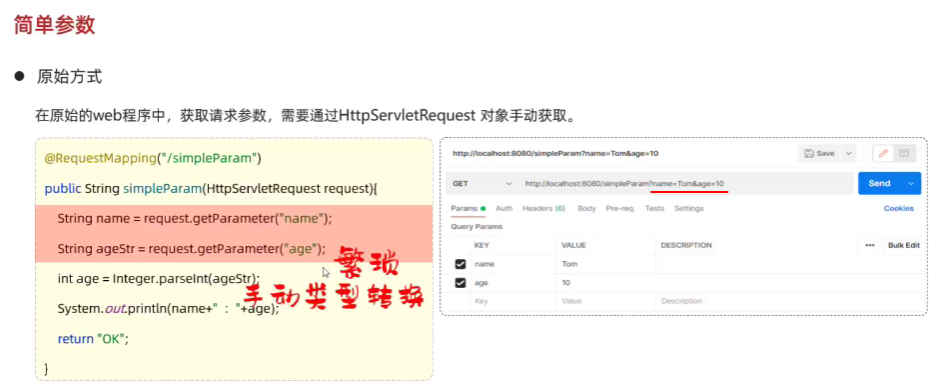
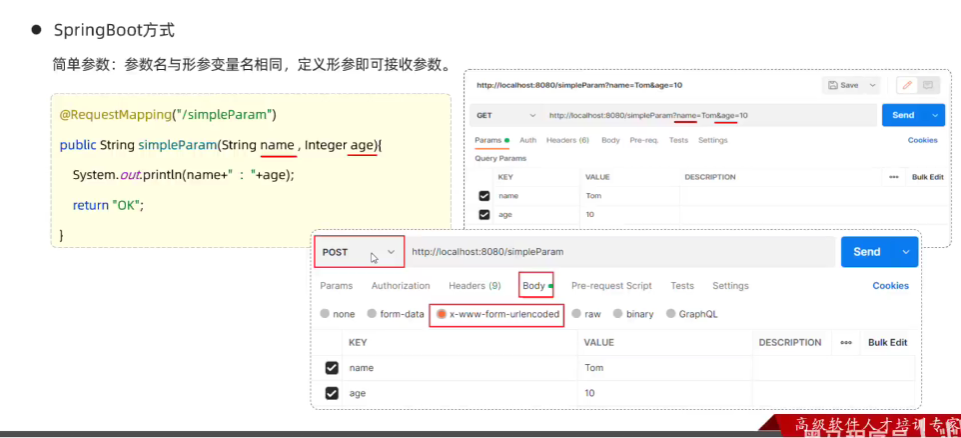
- springboot方式

package com.example.springboot_web_start.controller;import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController
public class RequestController {//springmvc方式
// @RequestMapping("simpleParam")
// public String simpleParam(HttpServletRequest request){
// String name = request.getParameter("name");
// String ageStr = request.getParameter("name");
// int age = Integer.parseInt(ageStr);
// System.out.println(name + " " + age);
// return "success";
// }//#################################################//springboot方式
// @RequestMapping("simpleParam")
// public String simpleParam(String name, Integer age){
//
// System.out.println(name + " " + age);
// return "success";
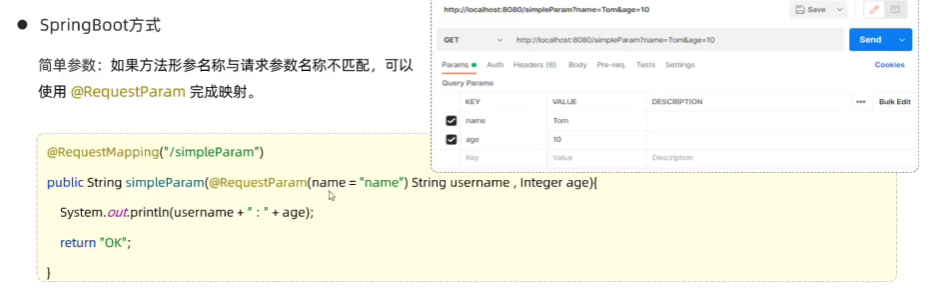
// }//#################################################//当方法形参名称和请求参数名称不匹配的时候,使用@RequestParam注解@RequestMapping("simpleParam")public String simpleParam(@RequestParam(name="name") String username, Integer age){System.out.println(username + " " + age);return "success";}
}6.实体参数的接收
- 规则:请求参数名和形参对象属性名相同
- 简单实体参数
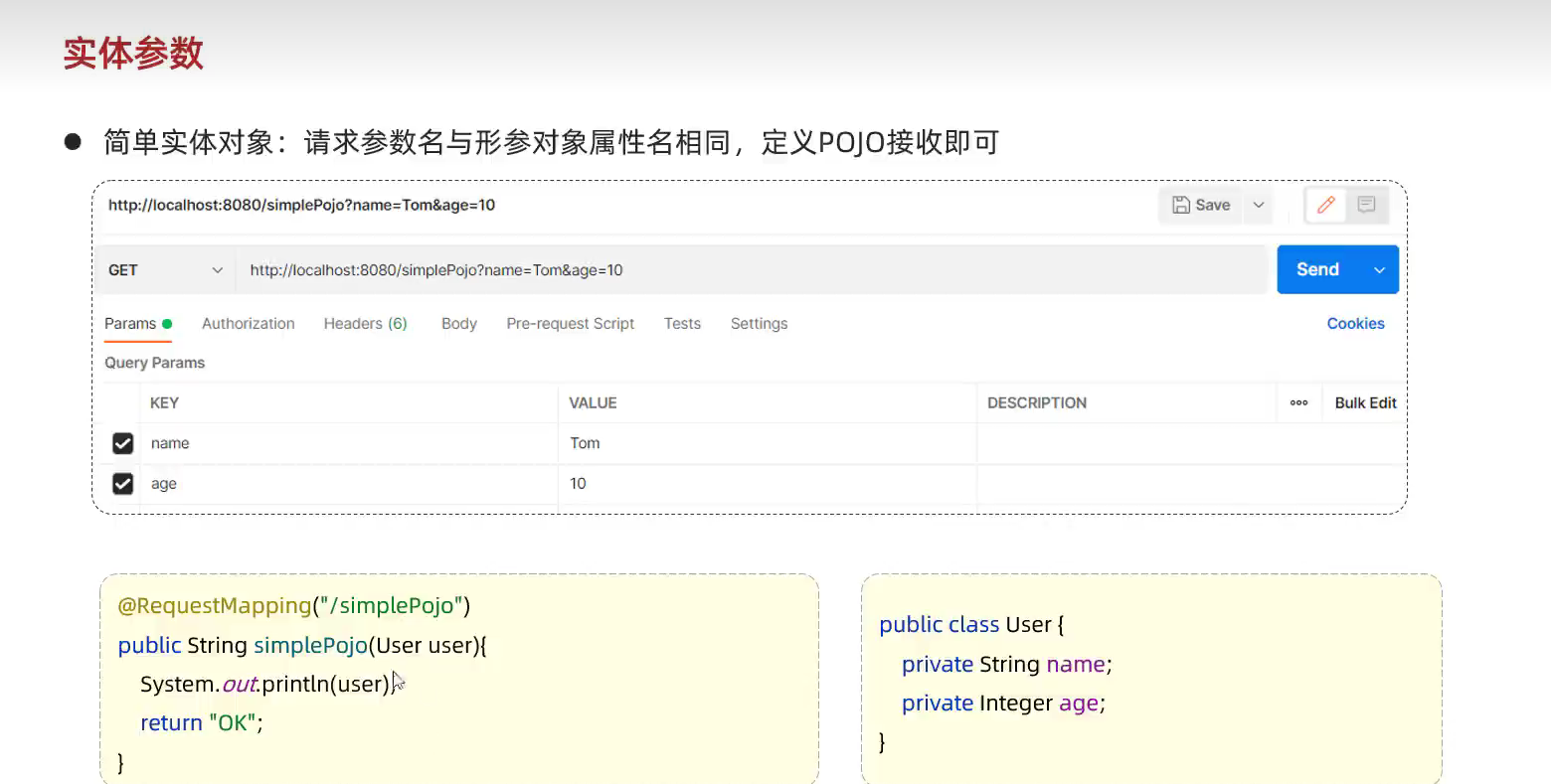
package com.example.springboot_web_start.pojo;public class User {private String name;private int age;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "User{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
package com.example.springboot_web_start.controller;import com.example.springboot_web_start.pojo.User;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController
public class RequestController {//2.实体参数@RequestMapping("simplePojo")public String simplePojo(User user){System.out.println(user);return "success";}
}- 复杂实体参数
package com.example.springboot_web_start.pojo;public class Address {private String address;private String city;public String getAddress() {return address;}public void setAddress(String address) {this.address = address;}public String getCity() {return city;}public void setCity(String city) {this.city = city;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Address{" +"address='" + address + '\'' +", city='" + city + '\'' +'}';}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////package com.example.springboot_web_start.pojo;public class User {private String name;private int age;private Address address;public Address getAddress() {return address;}public void setAddress(Address address) {this.address = address;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "User{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", address=" + address +'}';}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
package com.example.springboot_web_start.controller;import com.example.springboot_web_start.pojo.User;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController
public class RequestController {//复杂实体参数@RequestMapping("complexPojo")public String complexPojo(User user){System.out.println(user);return "success";}
}7.数组集合参数
- 数组:请求参数名和形参中的数组变量名相同,可以直接使用数组封装
- 请求参数名和形参中集合变量名相同,通过@RequestParam绑定参数关系
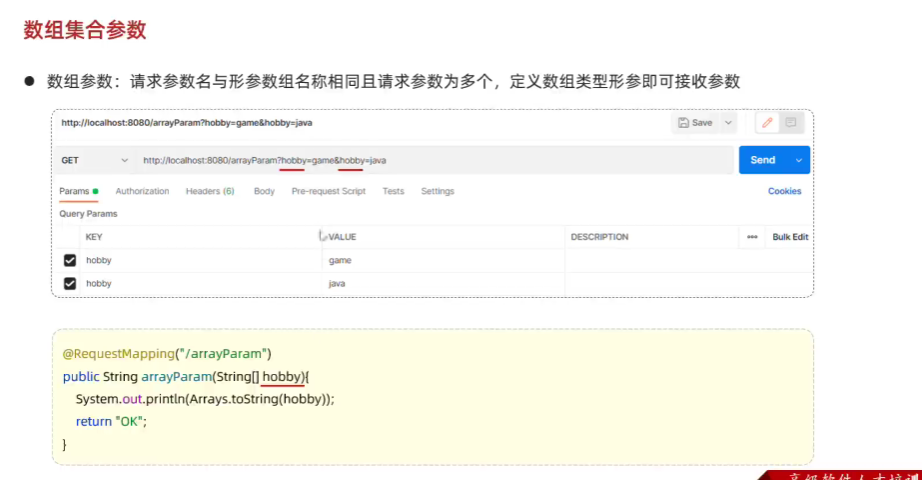
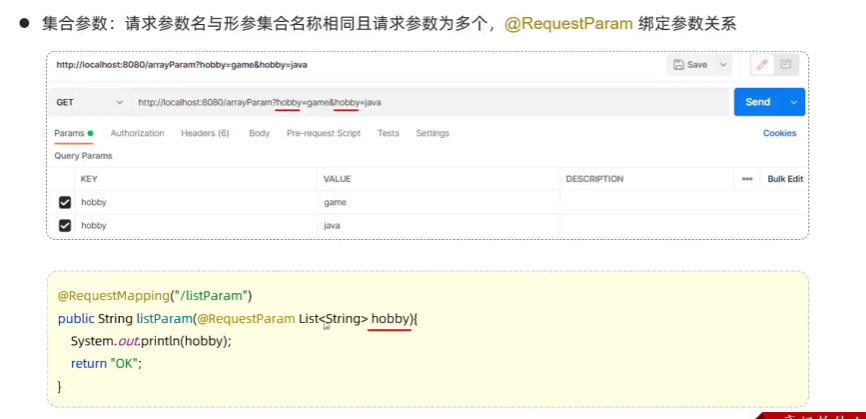
//3.数组参数@RequestMapping("arrayParam")public String arrayParam(String[] hobby){System.out.println(Arrays.toString(hobby));return "success";}//集合参数@RequestMapping("listParam")public String listParam(@RequestParam(name="hobby") List<String> hobby){System.out.println(hobby);return "success";}
8.日期参数
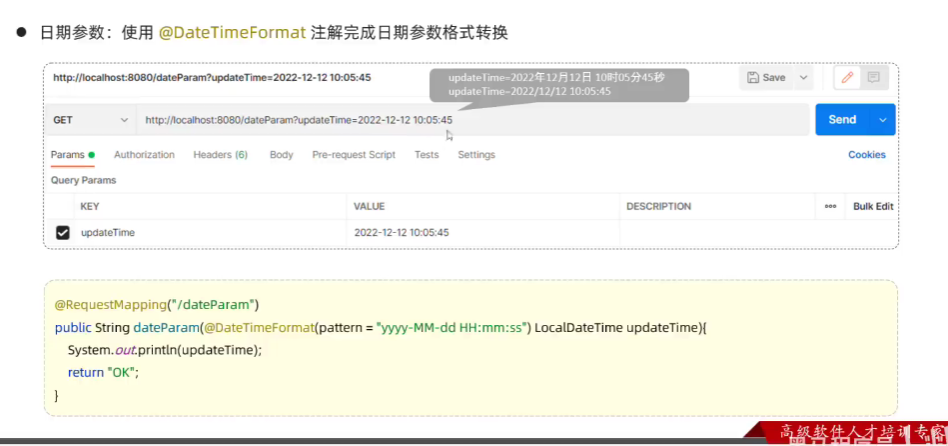
//4.日期时间参数@RequestMapping("dateParam")//指定请求路径public String dateParam(@DateTimeFormat(pattern ="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") LocalDateTime updateTime){System.out.println(updateTime);return "success";}
9.JSON参数
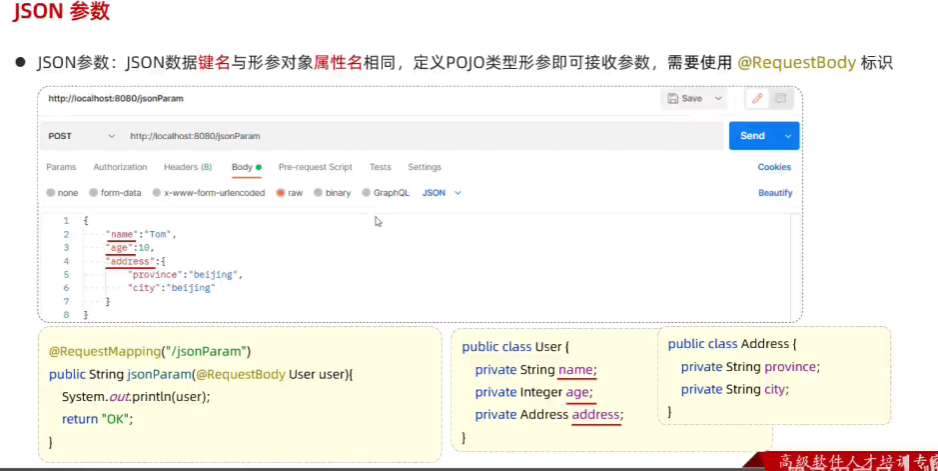
//JSON参数@RequestMapping("jsonParam")public String jsonParam(@RequestBody User user){System.out.println(user);return "success";}
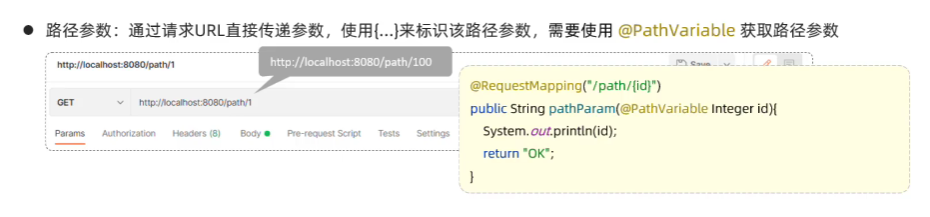
10.路径参数
- 一个参数
- 多个参数
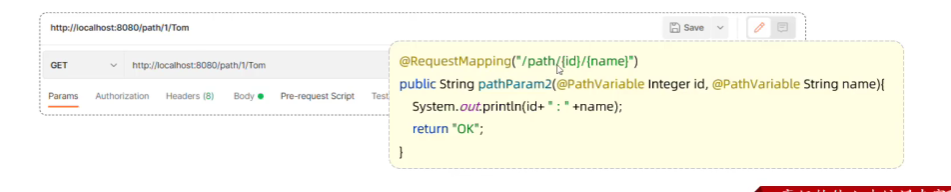
//6.路径参数@RequestMapping("pathVariable/{id}")//指定请求路径public String pathVariable(@PathVariable Integer id){System.out.println(id);return "success";}//多个参数@RequestMapping("pathVariable/{id}/{name}")//指定请求路径public String pathVariable(@PathVariable Integer id, @PathVariable String name){System.out.println(id + " " + name);return "success";}
- 总结

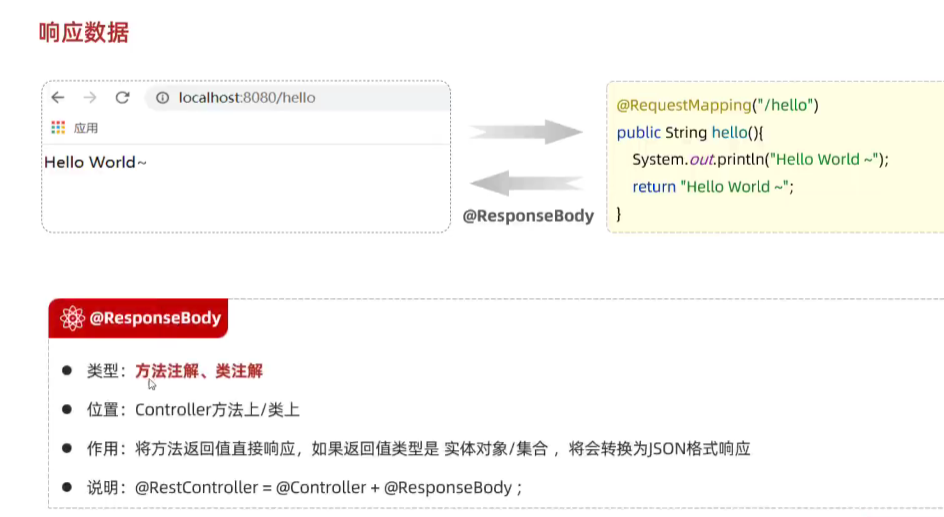
11.响应
- @ResponseBody
- 位置:Controller类上/方法上
- 作用:将方法返回值直接响应,若返回值类型是 实体对象/集合 转JSON格式
- 响应回去的数据没有规范:不方便管理
package com.example.springboot_web_start.controller;import com.example.springboot_web_start.pojo.Address;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;@RestController
public class ResponseController {//返回字符串@RequestMapping("/hello")public String hello(){System.out.println("hell");return "hello";}//返回对象@RequestMapping("/getAddr")public Address getAddr(){Address address = new Address();address.setCity("北京");address.setAddress("长安街");return address;}//返回list集合@RequestMapping("/getAddrList")public List<Address> getAddrList(){List<Address> addressList = new ArrayList<>();Address address1 = new Address();address1.setCity("北京");address1.setAddress("长安街");addressList.add(address1);Address address2 = new Address();address2.setCity("上海");address2.setAddress("南京路");addressList.add(address2);return addressList;}
}- 方法:同一响应结果
- Result(code ,msg ,data)
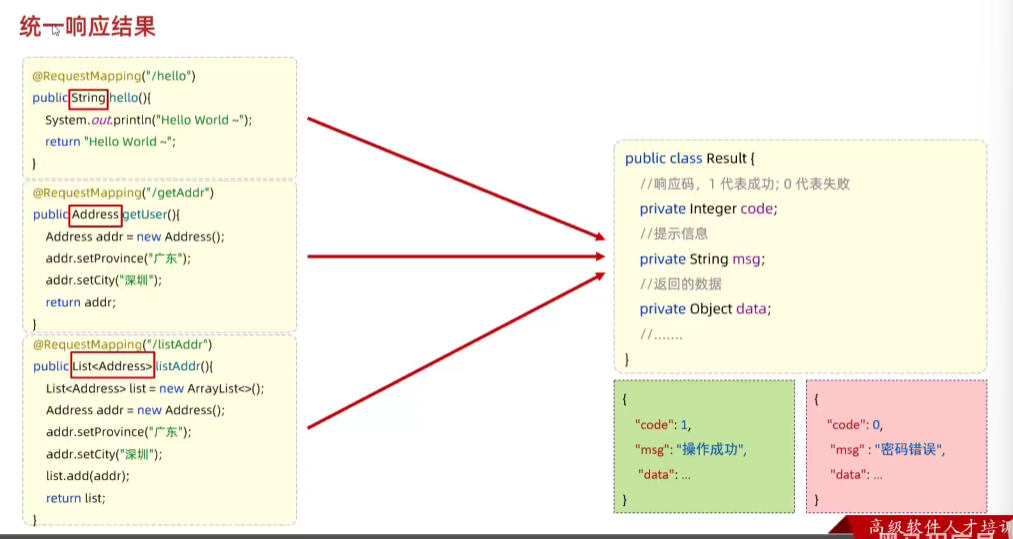
package com.example.springboot_web_start.pojo;
/*
统一响应结果封装类
*/
public class Result {private Integer code;//1 成功 0 失败private String msg;//提示信息private Object data;//返回数据public Result() {}public Result(Integer code, String msg, Object data) {this.code = code;this.msg = msg;this.data = data;}public Integer getCode() {return code;}public void setCode(Integer code) {this.code = code;}public String getMsg() {return msg;}public void setMsg(String msg) {this.msg = msg;}public Object getData() {return data;}public void setData(Object data) {this.data = data;}public static Result success(Object data){return new Result(1,"操作成功",data);}public static Result error(Object data){return new Result(0,"操作失败",null);}public static Result error(String msg,Object data){return new Result(0,msg,null);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Result{" +"code=" + code +", msg='" + msg + '\'' +", data=" + data +'}';}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//返回字符串
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public Result hello(){System.out.println("hell");
// return new Result(1,"success","hello");return Result.success("hello");
}//返回对象@RequestMapping("/getAddr")public Result getAddr(){Address address = new Address();address.setCity("北京");address.setAddress("长安街");return Result.success(address);}//返回list集合@RequestMapping("/getAddrList")public Result getAddrList(){List<Address> addressList = new ArrayList<>();Address address1 = new Address();address1.setCity("北京");address1.setAddress("长安街");addressList.add(address1);Address address2 = new Address();address2.setCity("上海");address2.setAddress("南京路");addressList.add(address2);return Result.success(addressList);}
- 统一响应案例
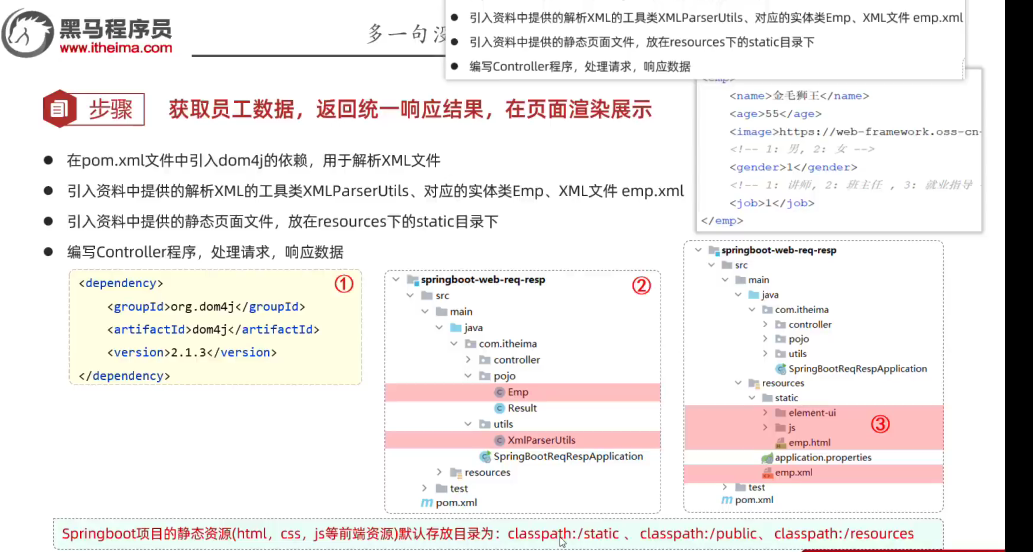
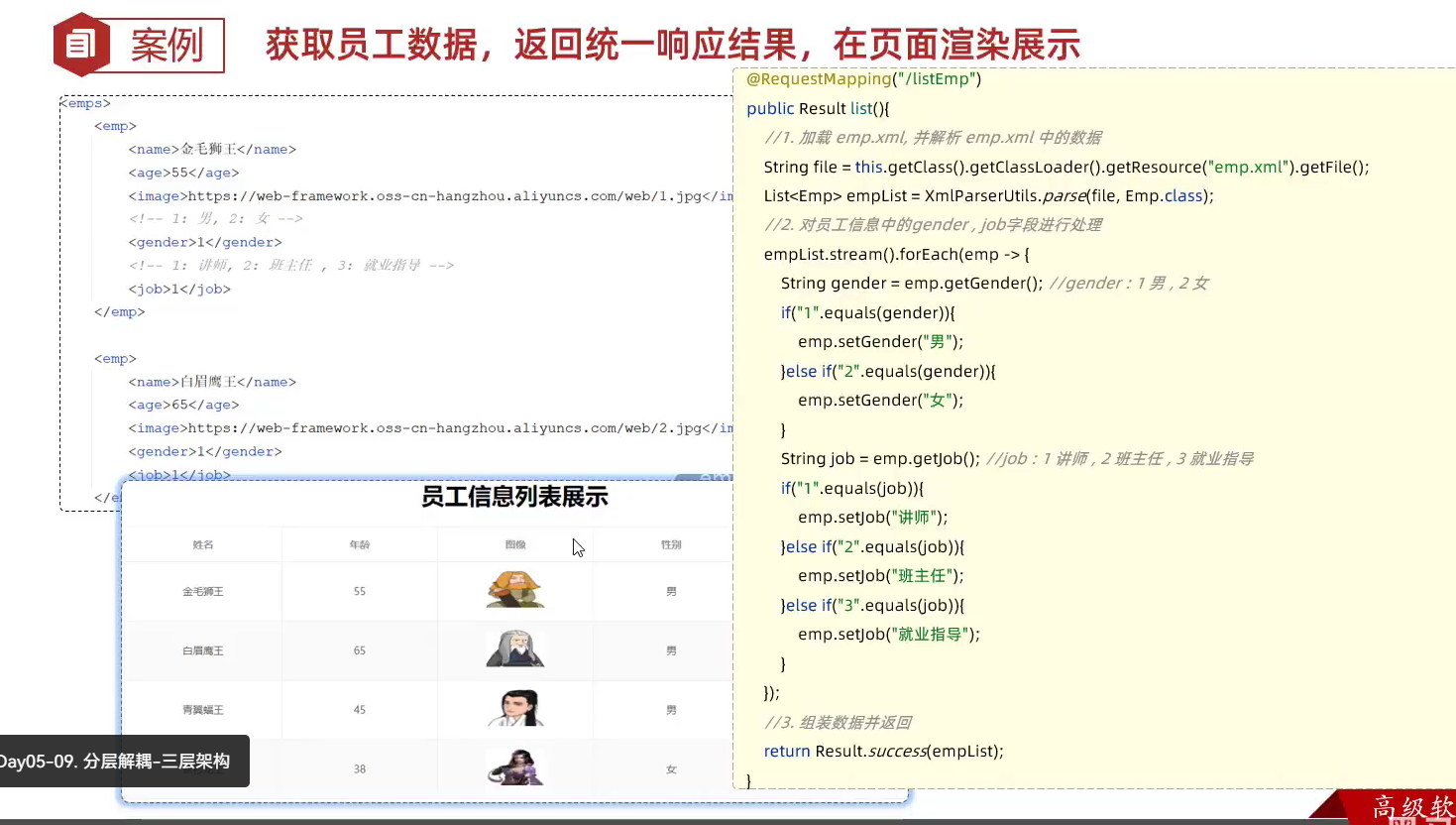
12.分层解耦
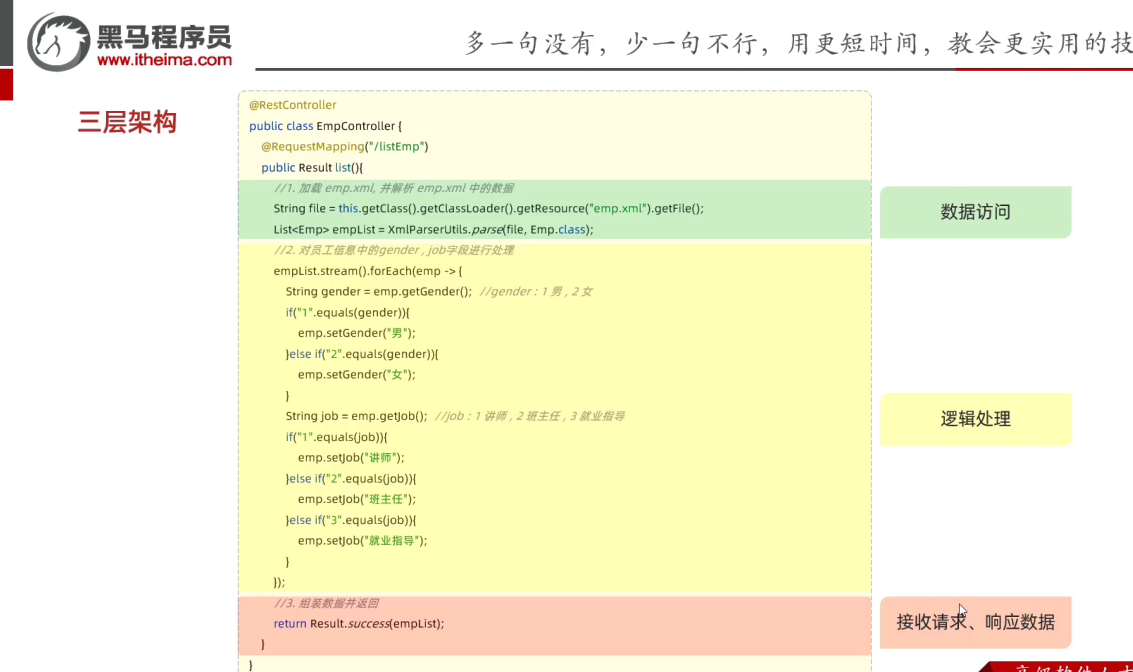
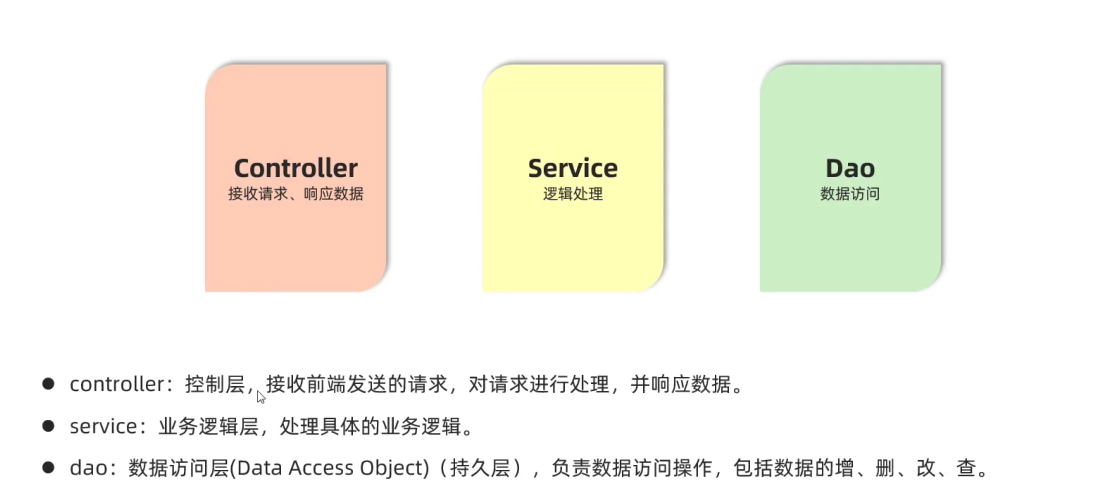
- 分层后代码
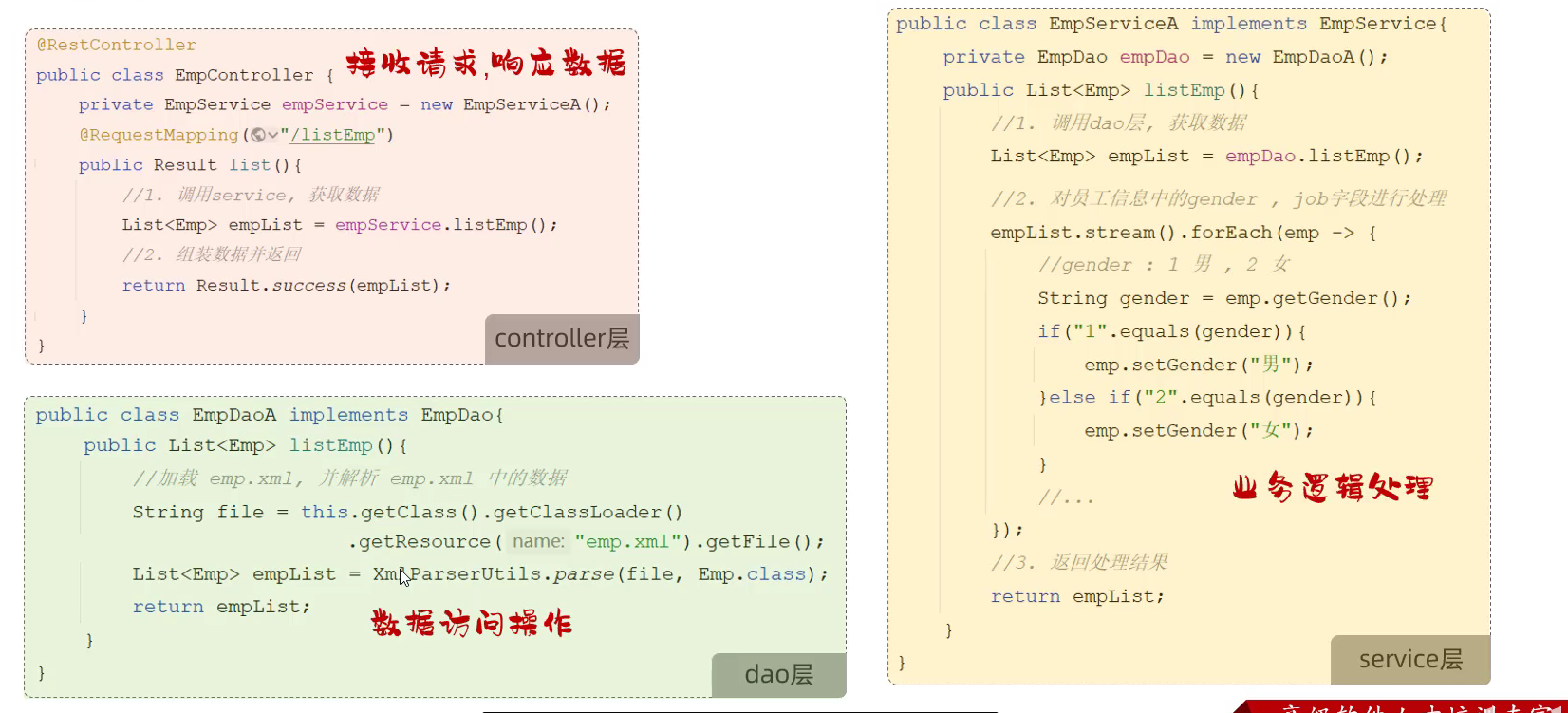
- 内聚:软件中各个功能模块内部的功能联系
- 耦合:衡量软件中各个层/模块之间的依赖,关联的程度
- 软件设计原则:高内聚低耦合
- 高内聚:模块内部的功能联系越紧密越好(在一个模块中只存放与该模块有关的相关处理)
- 低耦合: 降低层与层之间/模块与模块之间的依赖关联
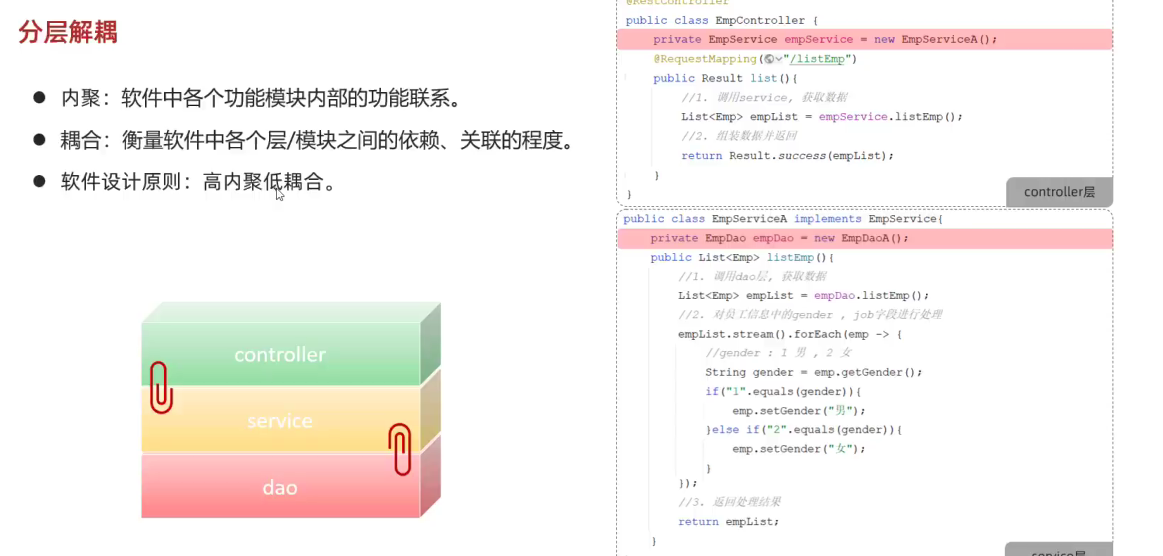
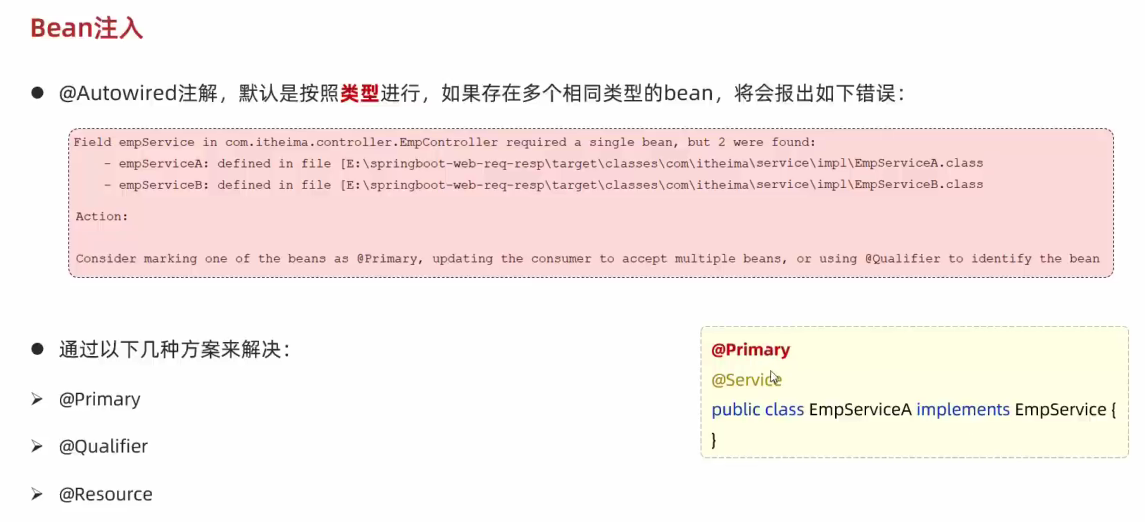
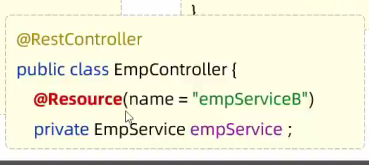
- IOC 与 DI入门
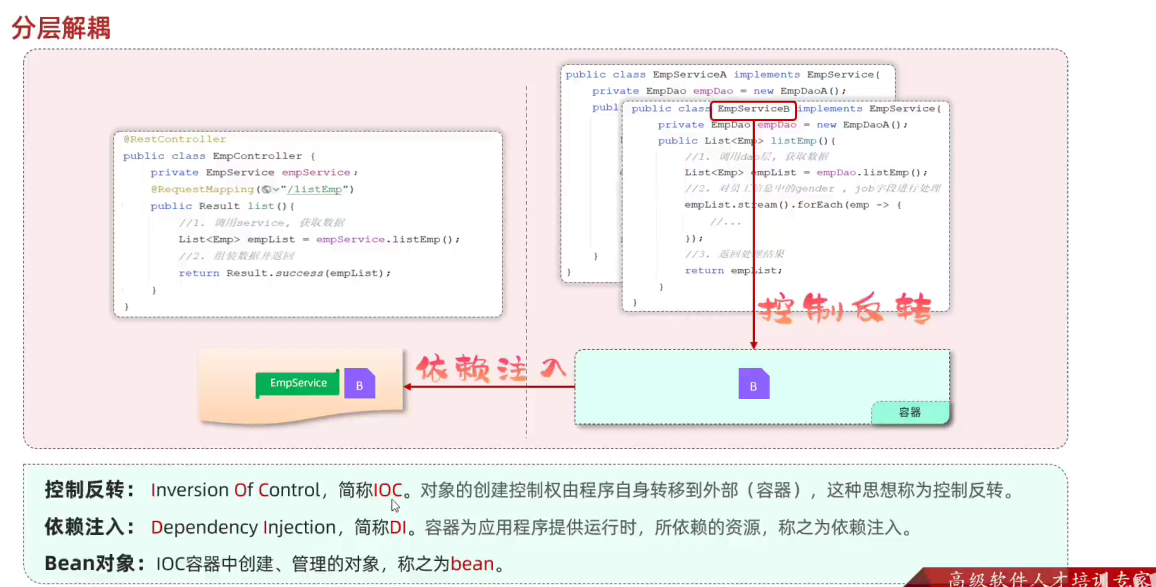
- 解耦例子
- @Component(控制反转) //将当前类交给IOC容器管理,成为IOC容器中的 bean
- @Autowired(依赖注入) //运行时,IOC容器会提供该类型的bean对象,并赋值给该变量

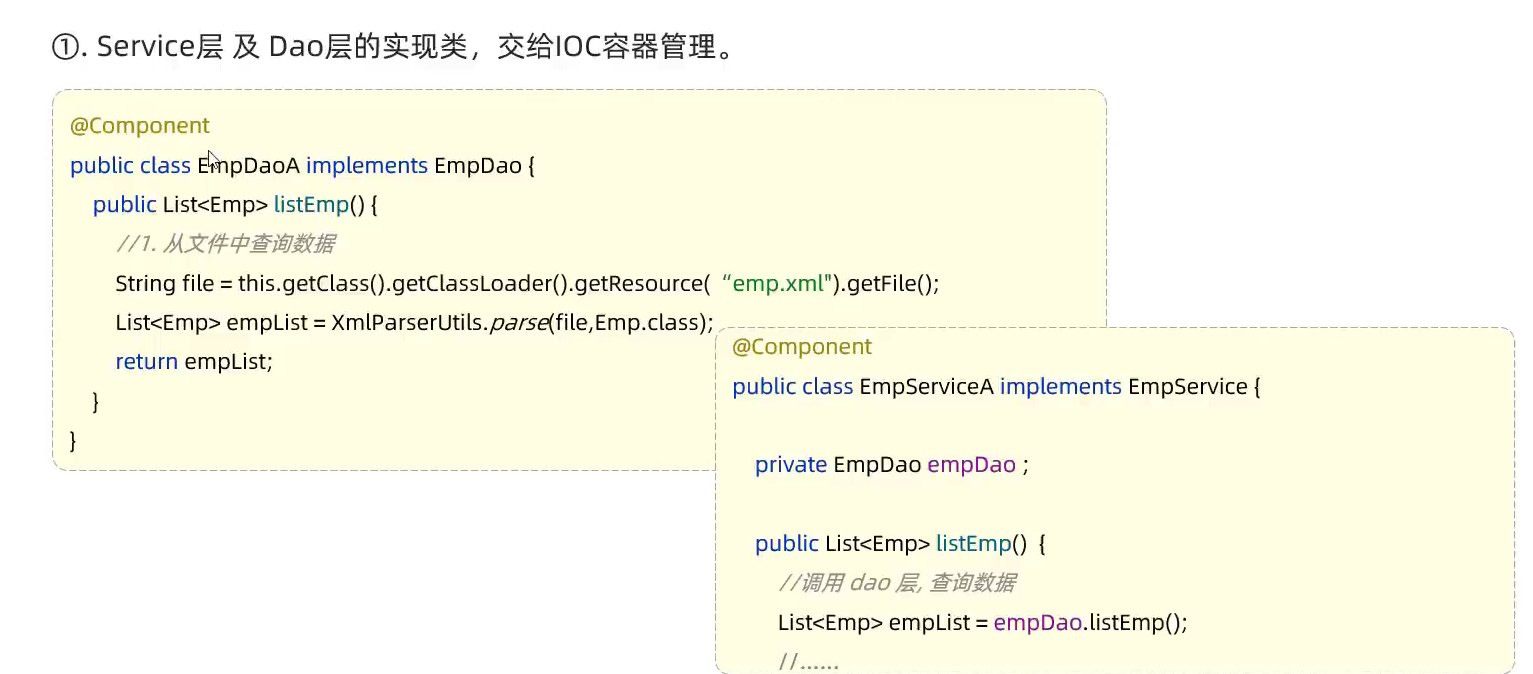

- IOC详解
- 指将对象的控制权交给IOC容器,由IOC容器来创建及管理这些对象,ioc中的对象也称为bean对象,@component可以用来声明一个bean对象
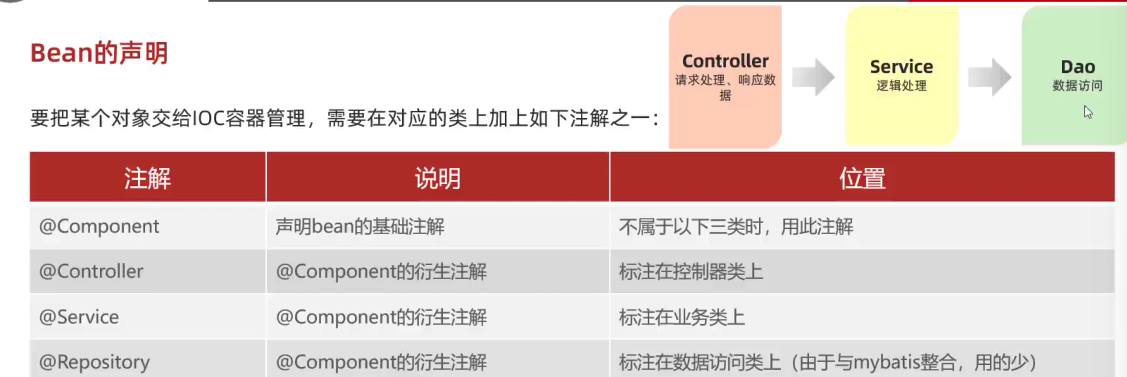
- @Controller,@Service,@Repository 分别对应Controller,Service,Dao层的注解;@Component用于不属于这三个在内的


- DI详解