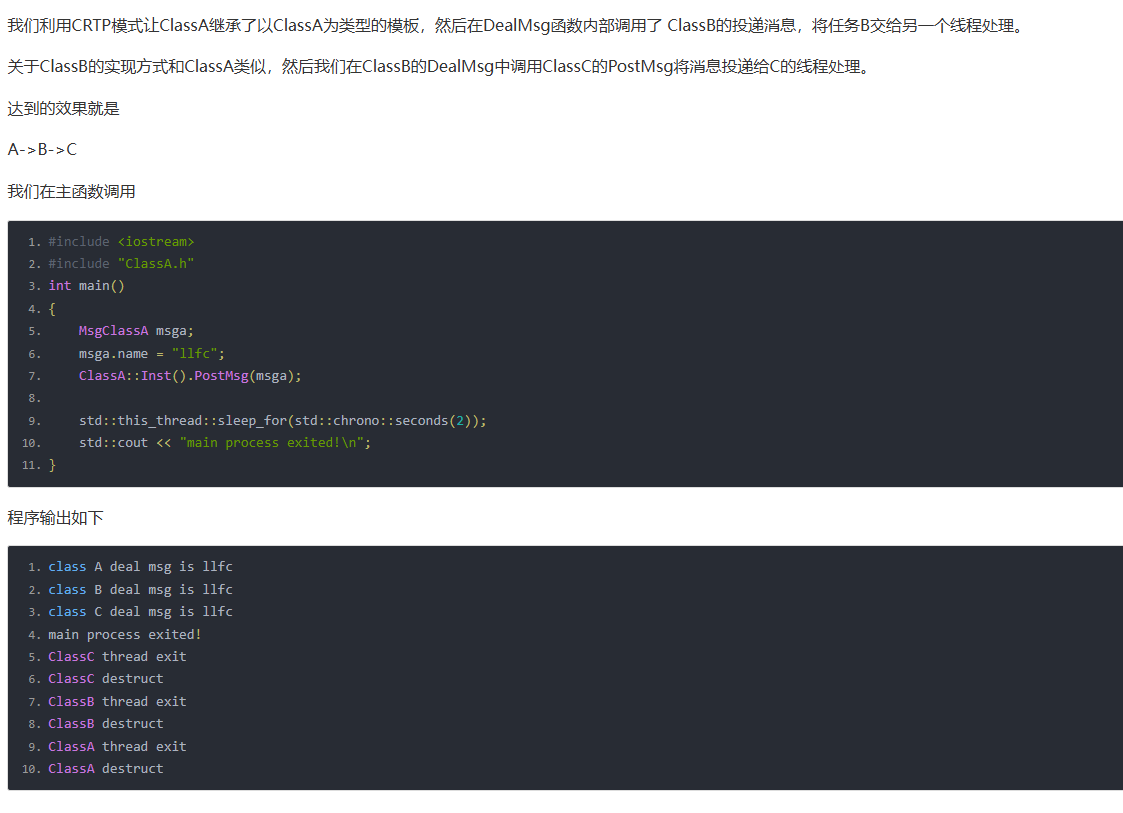
C++并发编程-23. 线程间切分任务的方法
按数量划分
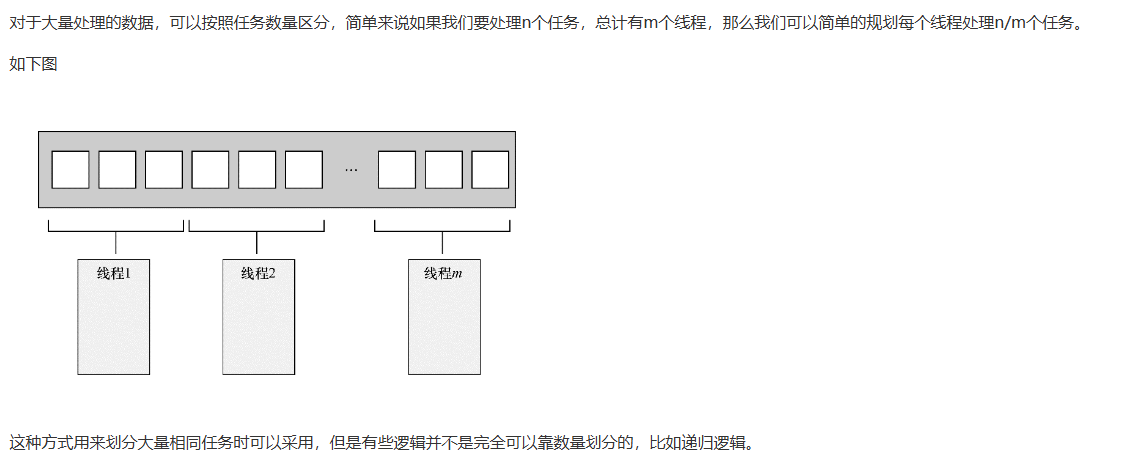
按递归划分

#include <thread>
#include <list>
#include "thread_safe_stack.h"
#include <future>
#include <memory>
template<typename T>
struct sorter //1
{struct chunk_to_sort{std::list<T> data;std::promise<std::list<T> > promise;};thread_safe_stack<chunk_to_sort> chunks; //⇽-- - 2std::vector<std::thread> threads; // ⇽-- - 3unsigned const max_thread_count;std::atomic<bool> end_of_data;sorter() :max_thread_count(std::thread::hardware_concurrency() - 1),end_of_data(false){}~sorter() //⇽-- - 4{end_of_data = true; //⇽-- - 5for (unsigned i = 0; i < threads.size(); ++i){threads[i].join(); //⇽-- - 6}}void try_sort_chunk(){std::shared_ptr<chunk_to_sort> chunk = chunks.try_pop(); //⇽-- - 7if (chunk){sort_chunk(chunk); //⇽-- - 8}}std::list<T> do_sort(std::list<T>& chunk_data) //⇽-- - 9{if (chunk_data.empty()){return chunk_data;}std::list<T> result;result.splice(result.begin(),chunk_data,chunk_data.begin());T const& partition_val = *result.begin();typename std::list<T>::iterator divide_point = //⇽-- - 10std::partition(chunk_data.begin(),chunk_data.end(),[&](T const& val) {return val < partition_val; });chunk_to_sort new_lower_chunk;new_lower_chunk.data.splice(new_lower_chunk.data.end(),chunk_data,chunk_data.begin(),divide_point);std::future<std::list<T> > new_lower =new_lower_chunk.promise.get_future();chunks.push(std::move(new_lower_chunk)); // ⇽-- - 11if (threads.size() < max_thread_count) // ⇽-- - 12{threads.push_back(std::thread(&sorter<T>::sort_thread,this));}std::list<T> new_higher(do_sort(chunk_data));result.splice(result.end(),new_higher);while (new_lower.wait_for(std::chrono::seconds(0)) !=std::future_status::ready) //⇽-- - 13{try_sort_chunk(); // ⇽-- - 14}result.splice(result.begin(),new_lower.get());return result;}void sort_chunk(std::shared_ptr<chunk_to_sort > const& chunk){chunk->promise.set_value(do_sort(chunk->data)); //⇽-- - 15}void sort_thread(){while (!end_of_data) //⇽-- - 16{try_sort_chunk(); // ⇽-- - 17//交出时间片std::this_thread::yield(); //⇽-- - 18}}
};
我们实现一个函数调用上面的封装快速排序
template<typename T>
std::list<T> parallel_quick_sort(std::list<T> input) //⇽-- - 19
{if (input.empty()){return input;}sorter<T> s;return s.do_sort(input); //⇽-- - 20
}
本例中,parallel_quick_sort()函数(19处)把绝大部分功能委托给sorter类(1处),后者通过栈容器管理待排序的数据段(2处),并集中管控多个线程以并发执行任务(3处),从而以便捷的操作方式给出了代码实现。
本例中,主要工作由成员函数do_sort()负责(9处),它借标准库的std::partition()函数完成数据分段(10处)。
do_sort()将新划分出来的数据段压入栈容器(11处),但没有为每个数据段都专门生成新线程,而仅当仍存在空闲的处理器时(12处)才生成新线程。
因为划分出的前半部分数据可能会由别的线程处理,所以我们需要等待它完成排序而进入就绪状态(13处)。
如果当前线程是整个程序中仅有的线程,或者其他线程都正忙于别的任务,那么这一等待行为则需妥善处理,在当前线程的等待期间,我们让它试着从栈容器取出数据进行处理(14处)。
try_sort_chunk()先从栈容器弹出一段数据(7处)并对其进行排序(8处),再把结果存入附属该段的promise中(15处),使之准备就绪,以待提取。
向栈容器压入数据段与取出相关结果相互对应,两项操作均由同一个线程先后执行(11和12处)。
只要标志end_of_data没有成立(16处),各线程便反复循环,尝试对栈内数据段进行排序17。
每个线程在两次检测标志之间进行让步(18处),好让别的线程有机会向栈容器添加数据段。这段代码由sorter类的析构函数汇合各个线程(4处)。
do_sort()将在全部数据段都完成排序后返回(即便许多工作线程仍在运行),主线程进而从parallel_quick_sort()的调用返回20,并销毁sorter对象。其析构函数将设置标志end_of_data成立(5处),然后等待全部线程结束(6处)。标志的成立使得线程函数内的循环终止(16处)。
按工作类别划分

CRTP(Curiously Recurring Template Pattern,奇特递归模板模式)
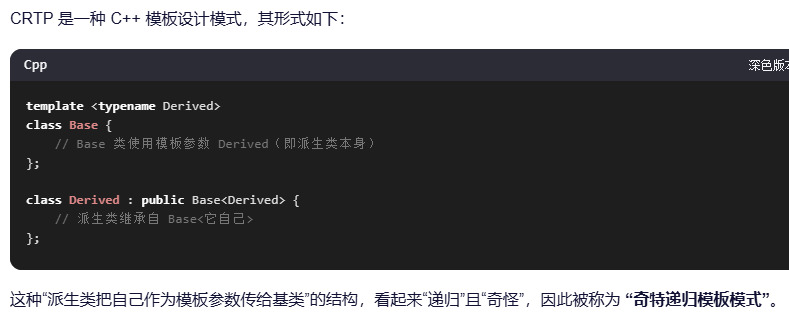
template <typename Derived>
class Shape {
public:void draw() {// 将 this 转换为派生类指针,调用具体实现static_cast<Derived*>(this)->draw();}double area() {return static_cast<Derived*>(this)->area();}
};class Circle : public Shape<Circle> {
public:void draw() {std::cout << "Drawing a circle\n";}double area() {return 3.14159 * 10 * 10;}
};class Rectangle : public Shape<Rectangle> {
public:void draw() {std::cout << "Drawing a rectangle\n";}double area() {return 10 * 20;}
};
模板单例类包含了原子变量_bstop控制线程是否停止
包含了_que用来存储要处理的信息,这是一个线程安全的队列。
_thread是要处理任务的线程。
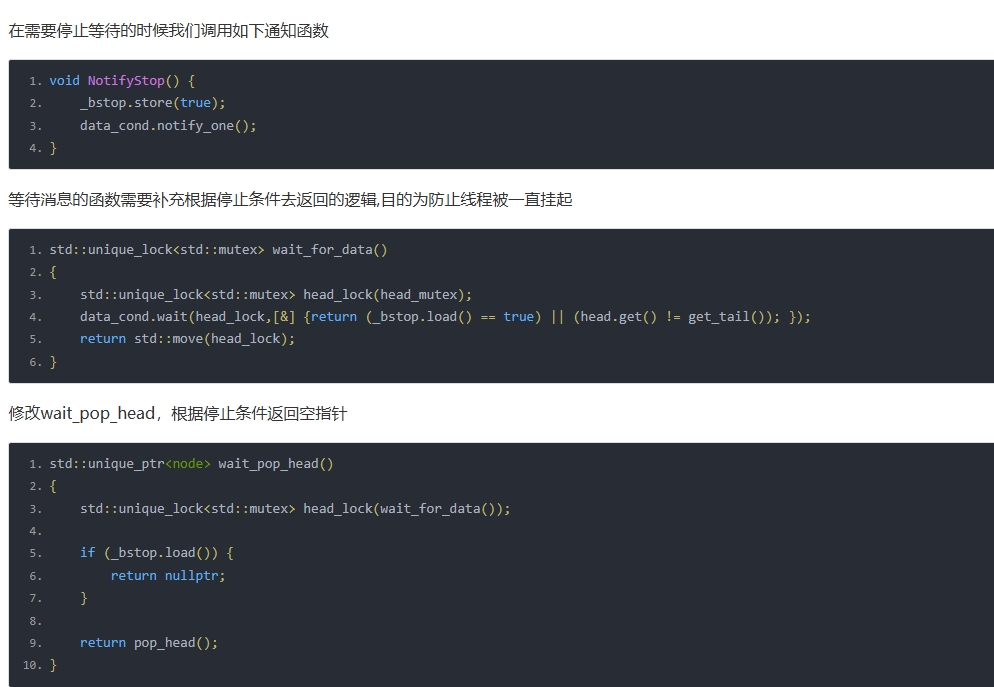
线程安全队列我们之前有实现过,但是还需要稍微改进下以满足接受外部停止的通知。
我们给ThreadSafeQue添加一个原子变量_bstop表示线程停止的标记
在需要停止等待的时候我们调用如下通知函数

比如我们要实现一个ClassA 处理A类任务,可以这么做
#include "ActorSingle.h"
#include "ClassB.h"
struct MsgClassA {std::string name;friend std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& os, const MsgClassA& ca) {os << ca.name;return os;}
};
class ClassA : public ActorSingle<ClassA, MsgClassA> {friend class ActorSingle<ClassA, MsgClassA>;
public:~ClassA() {_bstop = true;_que.NotifyStop();_thread.join();std::cout << "ClassA destruct " << std::endl;}void DealMsg(std::shared_ptr<MsgClassA> data) {std::cout << "class A deal msg is " << *data << std::endl;MsgClassB msga;msga.name = "llfc";ClassB::Inst().PostMsg(msga);}
private:ClassA(){_thread = std::thread([this]() {for (; (_bstop.load() == false);) {std::shared_ptr<MsgClassA> data = _que.WaitAndPop();if (data == nullptr) {continue;}DealMsg(data);}std::cout << "ClassA thread exit " << std::endl;});}
};