0903 C++类的运算符重载、静态成员与继承
Part 1.梳理思维导图
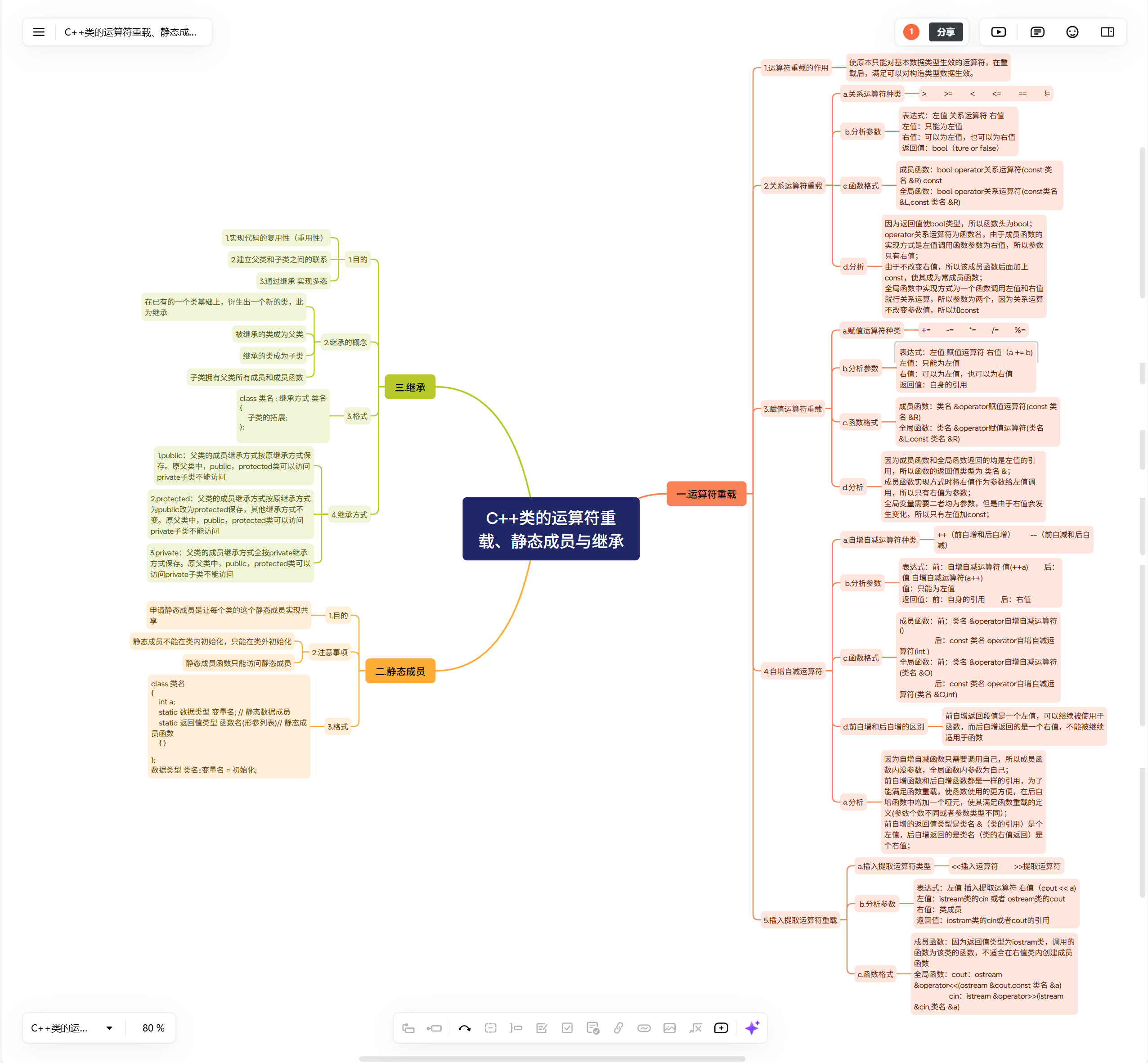
一.运算符重载
1.运算符重载的作用
使原本只能对基本数据类型生效的运算符,在重载后,满足可以对构造类型数据生效。
2.关系运算符重载
a.关系运算符种类
> >= < <= == !=
b.分析参数
表达式:左值 关系运算符 右值
左值:只能为左值
右值:可以为左值,也可以为右值
返回值:bool(ture or false)
c.函数格式
成员函数:bool operator关系运算符(const 类名 &R) const
全局函数:bool operator关系运算符(const类名 &L,const 类名 &R)
d.分析
因为返回值使bool类型,所以函数头为bool;
operator关系运算符为函数名,由于成员函数的实现方式是左值调用函数参数为右值,所以参数只有右值;
由于不改变右值,所以该成员函数后面加上const,使其成为常成员函数;
全局函数中实现方式为一个函数调用左值和右值就行关系运算,所以参数为两个,因为关系运算不改变参数值,所以加const
e.例子
以关系运算符>为例,当需要全局函数实现时,需要在类内添加友元
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class num
{
// friend const num operator+(const num &L,const num &R);
// friend bool operator>(const num &L,const num &R);
private:int a;int b;
public:num(){}num(int a,int b):a(a),b(b){}const num operator+(const num &R) const{num temp;temp.a = a + R.a;temp.b = b + R.b;return temp;}//成员函数实现bool operator>(const num &R) const{if(a > R.a && b < R.b)return true;elsereturn false;}void show(){cout << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;}
};//const num operator+(const num &L,const num &R)
//{
// num temp;
// temp.a = L.a + R.a;
// temp.b = L.b + R.b;
// return temp;
//}//全局函数实现,需要在类内添加友元
//bool operator>(const num &L,const num &R)
//{
// if(L.a > R.a && L.b < R.b)
// return true;
// else
// return false;
//}ostream & operator<<(ostream &cout,const num &n)
{cout << n.a << " " << n.b << endl;return cout;
}istream & operator>>(istream &cin,num &n)
{cin >> n.a >> n.b;return cin;
}int main()
{num n1(2,3);num n2(3,4);num n3 = n1+n2;n3.show();if(n1 > n2)cout << "n1 > n2" << endl;elsecout << "n1 < n2" << endl;return 0;
}
3.赋值运算符重载
a.赋值运算符种类
+= -= *= /= %=
b.分析参数
表达式:左值 赋值运算符 右值(a += b)
左值:只能为左值
右值:可以为左值,也可以为右值
返回值:自身的引用
c.函数格式
成员函数:类名 &operator赋值运算符(const 类名 &R)
全局函数:类名 &operator赋值运算符(类名 &L,const 类名 &R)
d.分析
因为成员函数和全局函数返回的均是左值的引用,所以函数的返回值类型为 类名 &;
成员函数实现方式时将右值作为参数给左值调用,所以只有右值为参数;
全局变量需要二者均为参数,但是由于右值会发生变化,所以只有左值加const;
e.例子
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class num
{
// friend const num operator+(const num &L,const num &R);
// friend bool operator>(const num &L,const num &R);
// friend num & operator+=(num &L,const num &R);private:int a;int b;
public:num(){}num(int a,int b):a(a),b(b){}const num operator+(const num &R) const{num temp;temp.a = a + R.a;temp.b = b + R.b;return temp;}bool operator>(const num &R) const{if(a > R.a && b < R.b)return true;elsereturn false;}//成员函数实现num &operator+=(const num &R){a = a + R.a;b = b + R.b;return *this;}void show(){cout << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;}
};//const num operator+(const num &L,const num &R)
//{
// num temp;
// temp.a = L.a + R.a;
// temp.b = L.b + R.b;
// return temp;
//}//bool operator>(const num &L,const num &R)
//{
// if(L.a > R.a && L.b < R.b)
// return true;
// else
// return false;
//}//全局函数实现
//num & operator+=(num &L,const num &R)
//{
// L.a = L.a + R.a;
// L.b = L.b + R.b;
// return L;
//}int main()
{num n1(2,3);num n2(3,4);num n3 = n1+n2;n3.show();// if(n1 > n2)
// cout << "n1 > n2" << endl;
// else
// cout << "n1 < n2" << endl;n1 += n2 += n3;n1.show();n2.show();n3.show();return 0;
}
4.自增自减运算符
a.自增自减运算符种类
++(前自增和后自增) --(前自减和后自减)
b.分析参数
表达式:前:自增自减运算符 值(++a) 后:值 自增自减运算符(a++)
值:只能为左值
返回值:前:自身的引用 后:右值
c.函数格式
成员函数:前:类名 &operator自增自减运算符()
后:const 类名 operator自增自减运算符(int )
全局函数:前:类名 &operator自增自减运算符(类名 &O)
后:const 类名 operator自增自减运算符(类名 &O,int)
d.前自增和后自增的区别
前自增返回段值是一个左值,可以继续被使用于函数,而后自增返回的是一个右值,不能被继续适用于函数
e.分析
因为自增自减函数只需要调用自己,所以成员函数内没参数,全局函数内参数为自己;
前自增函数和后自增函数都是一样的引用,为了能满足函数重载,使函数使用的更方便,在后自增函数中增加一个哑元,使其满足函数重载的定义(参数个数不同或者参数类型不同);
前自增的返回值类型是类名 &(类的引用)是个左值,后自增返回的是类名(类的右值返回)是个右值;
f.例子
因为后自增是返回没自增前的值,所以需要定义一个新的临时类成员,用于返回
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class num
{
// friend const num operator+(const num &L,const num &R);
// friend bool operator>(const num &L,const num &R);
// friend num & operator+=(num &L,const num &R);
// friend num &operator++(num &L);
// friend const num operator++(num &L,int);
private:int a;int b;
public:num(){}num(int a,int b):a(a),b(b){}const num operator+(const num &R) const{num temp;temp.a = a + R.a;temp.b = b + R.b;return temp;}bool operator>(const num &R) const{if(a > R.a && b < R.b)return true;elsereturn false;}num &operator+=(const num &R){a = a + R.a;b = b + R.b;return *this;}//成员函数实现前自增num &operator++(){a++;b++;return *this;}//成员函数实现后自增const num operator++(int){num temp;temp.a = a++;temp.b = b++;return temp;}void show(){cout << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;}
};//const num operator+(const num &L,const num &R)
//{
// num temp;
// temp.a = L.a + R.a;
// temp.b = L.b + R.b;
// return temp;
//}//bool operator>(const num &L,const num &R)
//{
// if(L.a > R.a && L.b < R.b)
// return true;
// else
// return false;
//}//num & operator+=(num &L,const num &R)
//{
// L.a = L.a + R.a;
// L.b = L.b + R.b;
// return L;
//}//全局函数实现前自增
//num &operator++(num &L)
//{
// ++L.a;
// ++L.b;
// return L;
//}//全局函数实现后自增
//const num operator++(num &L,int)
//{
// num temp;
// temp.a = L.a++;
// temp.b = L.b++;
// return temp;
//}int main()
{num n1(2,3);num n2(3,4);num n3 = n1+n2;n3.show();// if(n1 > n2)
// cout << "n1 > n2" << endl;
// else
// cout << "n1 < n2" << endl;// n1 += n2 += n3;
// n1.show();
// n2.show();
// n3.show();cout << "++++++++++++++++++" << endl;n1.show();++n1;n1.show();cout << "++++++++++++++++++" << endl;n1.show();n2.show();n2 = n1++;n1.show();n2.show();return 0;
}
5.插入提取运算符重载
a.插入提取运算符类型
<<插入运算符 >>提取运算符
b.分析参数
表达式:左值 插入提取运算符 右值(cout << a)
左值:istream类的cin 或者 ostream类的cout
右值:类成员
返回值:iostram类的cin或者cout的引用
c.函数格式
成员函数:因为返回值类型为iostram类,调用的函数为该类的函数,不适合在右值类内创建成员函数
全局函数:cout:ostream &operator<<(ostream &cout,const 类名 &a)
cin:istream &operator>>(istream &cin,类名 &a)
d.例子
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class num
{
// friend const num operator+(const num &L,const num &R);
// friend bool operator>(const num &L,const num &R);
// friend num & operator+=(num &L,const num &R);
// friend num &operator++(num &L);
// friend const num operator++(num &L,int);friend ostream & operator<<(ostream &cout,const num &n);friend istream & operator>>(istream &cin,num &n);
private:int a;int b;
public:num(){}num(int a,int b):a(a),b(b){}const num operator+(const num &R) const{num temp;temp.a = a + R.a;temp.b = b + R.b;return temp;}bool operator>(const num &R) const{if(a > R.a && b < R.b)return true;elsereturn false;}num &operator+=(const num &R){a = a + R.a;b = b + R.b;return *this;}num &operator++(){a++;b++;return *this;}const num operator++(int){num temp;temp.a = a++;temp.b = b++;return temp;}void show(){cout << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;}
};//const num operator+(const num &L,const num &R)
//{
// num temp;
// temp.a = L.a + R.a;
// temp.b = L.b + R.b;
// return temp;
//}//bool operator>(const num &L,const num &R)
//{
// if(L.a > R.a && L.b < R.b)
// return true;
// else
// return false;
//}//num & operator+=(num &L,const num &R)
//{
// L.a = L.a + R.a;
// L.b = L.b + R.b;
// return L;
//}//num &operator++(num &L)
//{
// ++L.a;
// ++L.b;
// return L;
//}//const num operator++(num &L,int)
//{
// num temp;
// temp.a = L.a++;
// temp.b = L.b++;
// return temp;
//}//全局函数实现<<
ostream & operator<<(ostream &cout,const num &n)
{cout << n.a << " " << n.b << endl;return cout;
}//全局函数实现>>
istream & operator>>(istream &cin,num &n)
{cin >> n.a >> n.b;return cin;
}int main()
{num n1(2,3);num n2(3,4);num n3 = n1+n2;n3.show();// if(n1 > n2)
// cout << "n1 > n2" << endl;
// else
// cout << "n1 < n2" << endl;// n1 += n2 += n3;
// n1.show();
// n2.show();
// n3.show();cout << "++++++++++++++++++" << endl;n1.show();++n1;n1.show();cout << "++++++++++++++++++" << endl;n1.show();n2.show();n2 = n1++;n1.show();n2.show();return 0;
}
二.静态成员
1.目的
申请静态成员是让每个类的这个静态成员实现共享
2.注意事项
静态成员不能在类内初始化,只能在类外初始化
静态成员函数只能访问静态成员
3.格式
class 类名
{int a;static 数据类型 变量名; // 静态数据成员static 返回值类型 函数名(形参列表)// 静态成员函数{ }};数据类型 类名::变量名 = 初始化;4.例子
该函数为模拟银行存储,balance为余额,rate为利率,静态成员利率会在函数外改变,并使每一个账户成员利率一起改,静态函数static double getrate()只能调用静态成员rate,static double getmenory(Bankaccent &accent)静态函数为了调用非静态成员balance,只能调用类对象再调用
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Bankaccent
{
private:double balance;static double rate;
public:Bankaccent(){}Bankaccent(double balance):balance(balance){};static double getrate(){return rate;}static void setrate(double setrate){rate = setrate;}static double getmenory(Bankaccent &accent){return accent.balance*(1+rate);}};double Bankaccent::rate = 0.05;int main()
{Bankaccent accent1(1000);cout << Bankaccent::getrate() << endl;Bankaccent::setrate(0.06);cout << Bankaccent::getrate() << endl;cout << Bankaccent::getmenory(accent1) << endl;return 0;
}
三.继承
1.目的
1.实现代码的复用性(重用性)
2.建立父类和子类之间的联系
3.通过继承 实现多态
2.继承的概念
在已有的一个类基础上,衍生出一个新的类,此为继承
被继承的类成为父类
继承的类成为子类
子类拥有父类所有成员和成员函数
3.格式
class 类名 : 继承方式 类名
{子类的拓展;
};
4.继承方式
1.public:父类的成员继承方式按原继承方式保存。原父类中,public,protected类可以访问private子类不能访问
2.protected:父类的成员继承方式按原继承方式为public改为protected保存,其他继承方式不变。原父类中,public,protected类可以访问private子类不能访问
3.private:父类的成员继承方式全按private继承方式保存。原父类中,public,protected类可以访问private子类不能访问
Part 2.程序
搭建一个货币的场景,创建一个名为 RMB 的类,该类具有整型私有成员变量 yuan(元)、jiao(角)和 fen(分),并且具有以下功能:
(1)重载算术运算符 + 和 -,使得可以对两个 RMB 对象进行加法和减法运算,并返回一个新的 RMB 对象作为结果。
(2)重载关系运算符 >,判断一个 RMB 对象是否大于另一个 RMB 对象,并返回 true 或 false。
(3)重载前置减减运算符 --,使得每次调用时 RMB 对象的 yuan、jiao 和 fen 分别减 1
(4)重载后置减减运算符 --,使得每次调用时 RMB 对象的 yuan、jiao 和 fen 分别减 1
(5)另外, RMB 类还包含一个静态整型成员变量 count,用于记录当前已创建的 RMB 对象的数量。每当创建一个新的 RMB 对象时,count 应该自增 1;每当销毁一个 RMB 对象时,count 应该自减 1。
要求,需要在main 函数中测试上述RMB 类的功能
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class RMB
{
private:int yuan;int jiao;int fen;static int count;
public:RMB(){countplus();}RMB(int yuan,int jiao,int fen):yuan(yuan),jiao(jiao),fen(fen){countplus();}RMB(const RMB& other):yuan(other.yuan),jiao(other.jiao),fen(other.fen){countplus();}~RMB(){countdecrease();}const RMB operator+(const RMB &R){RMB temp;temp.yuan = yuan+R.yuan;temp.jiao = jiao+R.jiao;temp.fen = fen+R.fen;return temp;}const RMB operator-(const RMB &R){RMB temp;temp.yuan = yuan-R.yuan;temp.jiao = jiao-R.jiao;temp.fen = fen-R.fen;return temp;}bool operator>(const RMB &R){if(yuan > R.yuan)return true;elsereturn false;}RMB &operator--(){--yuan;--jiao;--fen;return *this;}const RMB operator--(int){RMB temp;temp.yuan = yuan--;temp.jiao = jiao--;temp.fen = fen--;return temp;}static void countplus(){count++;}static void countdecrease(){count--;}static int countshow(){return count;}void show(){cout << yuan << " " << jiao << " " << fen << endl;}
};int RMB::count = 0;int main()
{{cout << RMB::countshow() << endl;RMB r1(100,99,88);cout << RMB::countshow() << endl;RMB r2(55,101,76);cout << RMB::countshow() << endl;cout << "算数运算符+" << endl;r1 = r1+r2;r1.show();cout << "算数运算符-" << endl;r1 = r1-r2;r1.show();cout << "关系运算符>" << endl;bool a = r1 > r2;cout << a << endl;cout << "前自减运算符--" << endl;--r1;r1.show();cout << "后自减运算符--" << endl;RMB r3 = r2--;r3.show();r2.show();}cout << RMB::countshow() << endl;return 0;
}
