Pytorch Yolov11目标检测+window部署+推理封装 留贴记录
本节主要记录使用Yolov11 进行目标检测 + Windows LibTorch 部署调用 + 动态库封装及调用
侧重点主要是记录下部署过程,主要是为了备份和记录,也希望帮助到正在学习的小伙伴…
1.首先先训练一个目标检测的模型
1.1 安装pytorch见博客【Tensorflow-gpu搭建,转载备忘】,最后面有两行命令,直接就安装好了,前提是我这个版本的GPU
1.2 先下载代码+标注+训练+python直接调用预测,这个直接看我上一篇博客【YOLO v11 目标检测+关键点检测 实战记录】
区别是:上一篇是目标检测+关键点检测,标样本不标关键点即可,把json转txt代码关键点部分注释掉即可,流程全部一模一样,就不再赘述了
https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics yolo源码下载
2.导出libtorch可以用的格式
导出一个.torchscript格式的权重文件,影像大小为640*640,设备0【GPU】,batch = 1
#---------------------模型导出------------------------------
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO("best.pt")
# Export the model
model.export(format="torchscript",imgsz = 640,device = 0,batch = 1)
3.开始安装libtorch
3.1 安装的版本要和训练用到的版本一致,我也没有测不一致的情况是否可行
conda activate pytorch 进入虚拟环境
conda list 查询安装的版本
我这里安装的是 pytorch 1.12.1 cuda版本是11.3
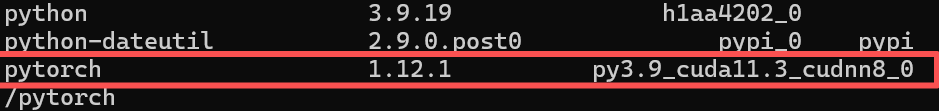
下载连接如下(找不到看这里):
cpu: https://download.pytorch.org/libtorch/cpu/libtorch-shared-with-deps-1.12.1%2Bcpu.zip
cuda11.3: https://download.pytorch.org/libtorch/cu113/libtorch-shared-with-deps-1.12.1%2Bcu113.zip
下载完解压,我们重点只关注include lib文件夹
3.2 编译Opencv 这个我就不赘述了,网上资料一大堆
3.3 编译器选择
最低选择VS2017以上,我2013 2015都试过不行,要求C++14,2017 2022 亲试都可以,自行选择吧
OpenCV编译版本,要和自己VS版本一致,
3.4 VS中需要设置的一些东西
都是踩坑的心血,靠,全部列在下面
我也不一个问题一个解决方案的列出了,直接按我的全部设置,如果还有问题,再自己查吧
3.4.1 配置libtorch和opencv的包含目录和库目录,常规操作

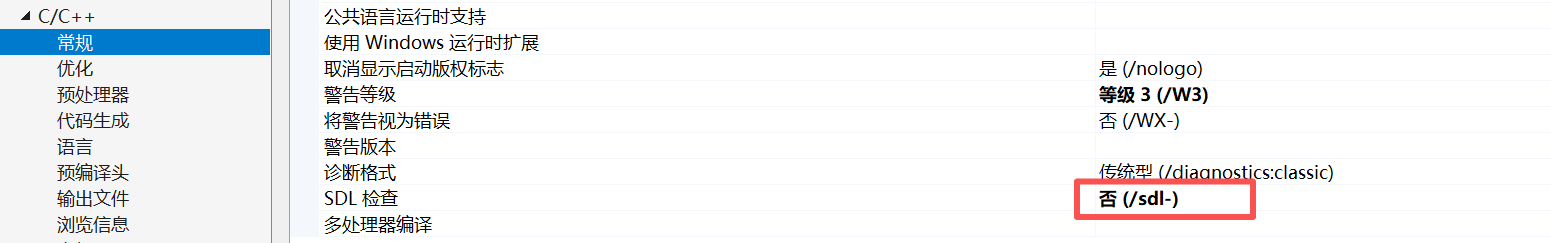
3.4.2 SDL检查为否
3.4.3 符合模式 否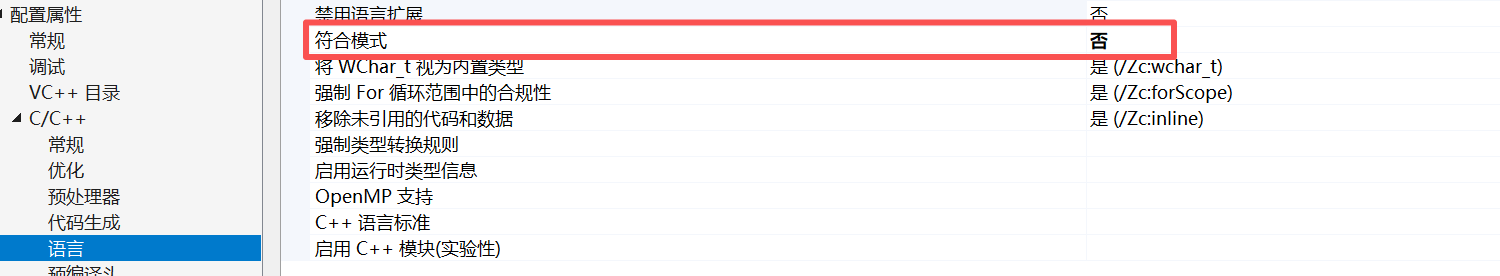
3.4.4 库依赖项,我的是GPU版本,CPU应该没这么多
c10.lib
asmjit.lib
c10_cuda.lib
caffe2_nvrtc.lib
clog.lib
cpuinfo.lib
dnnl.lib
fbgemm.lib
kineto.lib
libprotobuf.lib
libprotobuf-lite.lib
libprotoc.lib
pthreadpool.lib
torch.lib
torch_cpu.lib
torch_cuda.lib
torch_cuda_cpp.lib
torch_cuda_cu.lib
XNNPACK.lib
opencv_world453.lib
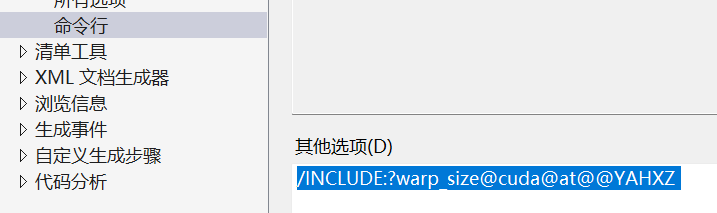
3.4.5 命令行加这一条信息,不加的话用不了GPU
/INCLUDE:?warp_size@cuda@at@@YAHXZ 复制即可
不加的话用不了GPU,torch::Device device(torch::cuda::is_available() ? torch::kCUDA : torch::kCPU);返回0
4.测试配置情况
到目前为止,应该是配置差不多了,可以加代码调试一下,看还报不报错
4.1 代码在哪里呢?
人家已经写过了,何不拿来直接用
ultralytics-main\examples\YOLOv8-LibTorch-CPP-Inference\main.cc
你们可以直接拷贝,我针对我的项目做了些修改,你们可以对照这俩文件区别,没啥差别其实
如果说区别点:
1.修改了类别种类
2.添加了以下代码
//这个放置位置一定在前面各种函数之后,要么还得改函数,我也不知道为什么
#include<windows.h>
//加载模型前,先LoadLibraryA一下
LoadLibraryA("ATen_cuda.dll");
LoadLibraryA("c10_cuda.dll");
LoadLibraryA("torch_cuda.dll");
LoadLibraryA("torchvision.dll");
yolo_model = torch::jit::load(model_path, device);
//非极大抑制函数里面
//auto[conf, j] = cls.max(1, true);//注释掉了,换成了下面的
std::tuple<torch::Tensor, torch::Tensor> result = cls.max(1, true);
torch::Tensor conf = std::get<0>(result);
torch::Tensor j = std::get<1>(result);
调用源码
#include <iostream>#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp>
#include <torch/torch.h>
#include <torch/script.h>using torch::indexing::Slice;
using torch::indexing::None;float generate_scale(cv::Mat& image, const std::vector<int>& target_size) {int origin_w = image.cols;int origin_h = image.rows;int target_h = target_size[0];int target_w = target_size[1];float ratio_h = static_cast<float>(target_h) / static_cast<float>(origin_h);float ratio_w = static_cast<float>(target_w) / static_cast<float>(origin_w);float resize_scale = std::min(ratio_h, ratio_w);return resize_scale;
}float letterbox(cv::Mat &input_image, cv::Mat &output_image, const std::vector<int> &target_size) {if (input_image.cols == target_size[1] && input_image.rows == target_size[0]) {if (input_image.data == output_image.data) {return 1.;}else {output_image = input_image.clone();return 1.;}}float resize_scale = generate_scale(input_image, target_size);int new_shape_w = std::round(input_image.cols * resize_scale);int new_shape_h = std::round(input_image.rows * resize_scale);float padw = (target_size[1] - new_shape_w) / 2.;float padh = (target_size[0] - new_shape_h) / 2.;int top = std::round(padh - 0.1);int bottom = std::round(padh + 0.1);int left = std::round(padw - 0.1);int right = std::round(padw + 0.1);cv::resize(input_image, output_image,cv::Size(new_shape_w, new_shape_h),0, 0, cv::INTER_AREA);cv::copyMakeBorder(output_image, output_image, top, bottom, left, right,cv::BORDER_CONSTANT, cv::Scalar(114., 114., 114));return resize_scale;
}torch::Tensor xyxy2xywh(const torch::Tensor& x) {auto y = torch::empty_like(x);y.index_put_({ "...", 0 }, (x.index({ "...", 0 }) + x.index({ "...", 2 })).div(2));y.index_put_({ "...", 1 }, (x.index({ "...", 1 }) + x.index({ "...", 3 })).div(2));y.index_put_({ "...", 2 }, x.index({ "...", 2 }) - x.index({ "...", 0 }));y.index_put_({ "...", 3 }, x.index({ "...", 3 }) - x.index({ "...", 1 }));return y;
}torch::Tensor xywh2xyxy(const torch::Tensor& x) {auto y = torch::empty_like(x);auto dw = x.index({ "...", 2 }).div(2);auto dh = x.index({ "...", 3 }).div(2);y.index_put_({ "...", 0 }, x.index({ "...", 0 }) - dw);y.index_put_({ "...", 1 }, x.index({ "...", 1 }) - dh);y.index_put_({ "...", 2 }, x.index({ "...", 0 }) + dw);y.index_put_({ "...", 3 }, x.index({ "...", 1 }) + dh);return y;
}// Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/main/torchvision/csrc/ops/cpu/nms_kernel.cpp
torch::Tensor nms(const torch::Tensor& bboxes, const torch::Tensor& scores, float iou_threshold) {if (bboxes.numel() == 0)return torch::empty({ 0 }, bboxes.options().dtype(torch::kLong));auto x1_t = bboxes.select(1, 0).contiguous();auto y1_t = bboxes.select(1, 1).contiguous();auto x2_t = bboxes.select(1, 2).contiguous();auto y2_t = bboxes.select(1, 3).contiguous();torch::Tensor areas_t = (x2_t - x1_t) * (y2_t - y1_t);auto order_t = std::get<1>(scores.sort(/*stable=*/true, /*dim=*/0, /* descending=*/true));auto ndets = bboxes.size(0);torch::Tensor suppressed_t = torch::zeros({ ndets }, bboxes.options().dtype(torch::kByte));torch::Tensor keep_t = torch::zeros({ ndets }, bboxes.options().dtype(torch::kLong));auto suppressed = suppressed_t.data_ptr<uint8_t>();auto keep = keep_t.data_ptr<int64_t>();auto order = order_t.data_ptr<int64_t>();auto x1 = x1_t.data_ptr<float>();auto y1 = y1_t.data_ptr<float>();auto x2 = x2_t.data_ptr<float>();auto y2 = y2_t.data_ptr<float>();auto areas = areas_t.data_ptr<float>();int64_t num_to_keep = 0;for (int64_t _i = 0; _i < ndets; _i++) {auto i = order[_i];if (suppressed[i] == 1)continue;keep[num_to_keep++] = i;auto ix1 = x1[i];auto iy1 = y1[i];auto ix2 = x2[i];auto iy2 = y2[i];auto iarea = areas[i];for (int64_t _j = _i + 1; _j < ndets; _j++) {auto j = order[_j];if (suppressed[j] == 1)continue;auto xx1 = std::max(ix1, x1[j]);auto yy1 = std::max(iy1, y1[j]);auto xx2 = std::min(ix2, x2[j]);auto yy2 = std::min(iy2, y2[j]);auto w = std::max(static_cast<float>(0), xx2 - xx1);auto h = std::max(static_cast<float>(0), yy2 - yy1);auto inter = w * h;auto ovr = inter / (iarea + areas[j] - inter);if (ovr > iou_threshold)suppressed[j] = 1;}}return keep_t.narrow(0, 0, num_to_keep);
}torch::Tensor non_max_suppression(torch::Tensor& prediction, float conf_thres = 0.25, float iou_thres = 0.45, int max_det = 300) {auto bs = prediction.size(0);auto nc = prediction.size(1) - 4;auto nm = prediction.size(1) - nc - 4;auto mi = 4 + nc;auto xc = prediction.index({ Slice(), Slice(4, mi) }).amax(1) > conf_thres;prediction = prediction.transpose(-1, -2);prediction.index_put_({ "...", Slice({None, 4}) }, xywh2xyxy(prediction.index({ "...", Slice(None, 4) })));std::vector<torch::Tensor> output;for (int i = 0; i < bs; i++) {output.push_back(torch::zeros({ 0, 6 + nm }, prediction.device()));}for (int xi = 0; xi < prediction.size(0); xi++) {auto x = prediction[xi];x = x.index({ xc[xi] });auto x_split = x.split({ 4, nc, nm }, 1);auto box = x_split[0], cls = x_split[1], mask = x_split[2];//auto[conf, j] = cls.max(1, true);std::tuple<torch::Tensor, torch::Tensor> result = cls.max(1, true);torch::Tensor conf = std::get<0>(result);torch::Tensor j = std::get<1>(result);x = torch::cat({ box, conf, j.toType(torch::kFloat), mask }, 1);x = x.index({ conf.view(-1) > conf_thres });int n = x.size(0);if (!n) { continue; }// NMSauto c = x.index({ Slice(), Slice{5, 6} }) * 7680;auto boxes = x.index({ Slice(), Slice(None, 4) }) + c;auto scores = x.index({ Slice(), 4 });auto i = nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres);i = i.index({ Slice(None, max_det) });output[xi] = x.index({ i });}return torch::stack(output);
}torch::Tensor clip_boxes(torch::Tensor& boxes, const std::vector<int>& shape) {boxes.index_put_({ "...", 0 }, boxes.index({ "...", 0 }).clamp(0, shape[1]));boxes.index_put_({ "...", 1 }, boxes.index({ "...", 1 }).clamp(0, shape[0]));boxes.index_put_({ "...", 2 }, boxes.index({ "...", 2 }).clamp(0, shape[1]));boxes.index_put_({ "...", 3 }, boxes.index({ "...", 3 }).clamp(0, shape[0]));return boxes;
}torch::Tensor scale_boxes(const std::vector<int>& img1_shape, torch::Tensor& boxes, const std::vector<int>& img0_shape) {auto gain = (std::min)((float)img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], (float)img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]);auto pad0 = std::round((float)(img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2. - 0.1);auto pad1 = std::round((float)(img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2. - 0.1);boxes.index_put_({ "...", 0 }, boxes.index({ "...", 0 }) - pad0);boxes.index_put_({ "...", 2 }, boxes.index({ "...", 2 }) - pad0);boxes.index_put_({ "...", 1 }, boxes.index({ "...", 1 }) - pad1);boxes.index_put_({ "...", 3 }, boxes.index({ "...", 3 }) - pad1);boxes.index_put_({ "...", Slice(None, 4) }, boxes.index({ "...", Slice(None, 4) }).div(gain));return boxes;
}#include<windows.h>int main() {printf("torch::cuda::is_available:%d\n", torch::cuda::is_available());// Device//torch::Device device(torch::cuda::is_available() ? torch::kCUDA : torch::kCPU);torch::Device device(torch::kCUDA);// Note that in this example the classes are hard-codedstd::vector<std::string> classes{ "Target", "Label", "Top" };try {// Load the model (e.g. yolov8s.torchscript)std::string model_path = ".../ultralytics-main/best.torchscript";torch::jit::script::Module yolo_model;//yolo_model = torch::jit::load(model_path, device);LoadLibraryA("ATen_cuda.dll");LoadLibraryA("c10_cuda.dll");LoadLibraryA("torch_cuda.dll");LoadLibraryA("torchvision.dll");yolo_model = torch::jit::load(model_path, device);yolo_model.eval();yolo_model.to(device, torch::kFloat32);for (int ii = 0; ii < 100; ii++) {// Load image and preprocesscv::Mat image = cv::imread("..../ultralytics-main_0829/ultralytics-main/datasets/data0829/images/train/20250829-102246635.jpg");cv::Mat input_image;letterbox(image, input_image, { 640, 640 });cv::cvtColor(input_image, input_image, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);torch::Tensor image_tensor = torch::from_blob(input_image.data, { input_image.rows, input_image.cols, 3 }, torch::kByte).to(device);image_tensor = image_tensor.toType(torch::kFloat32).div(255);image_tensor = image_tensor.permute({ 2, 0, 1 });image_tensor = image_tensor.unsqueeze(0);std::vector<torch::jit::IValue> inputs{ image_tensor };auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();// Inferencetorch::Tensor output = yolo_model.forward(inputs).toTensor().cpu();// NMSauto keep = non_max_suppression(output)[0];auto boxes = keep.index({ Slice(), Slice(None, 4) });keep.index_put_({ Slice(), Slice(None, 4) }, scale_boxes({ input_image.rows, input_image.cols }, boxes, { image.rows, image.cols }));// Show the resultsfor (int i = 0; i < keep.size(0); i++) {int x1 = keep[i][0].item().toFloat();int y1 = keep[i][1].item().toFloat();int x2 = keep[i][2].item().toFloat();int y2 = keep[i][3].item().toFloat();float conf = keep[i][4].item().toFloat();int cls = keep[i][5].item().toInt();std::cout << "Rect: [" << x1 << "," << y1 << "," << x2 << "," << y2 << "] Conf: " << conf << " Class: " << classes[cls] << std::endl;}// 获取当前时间点(结束时间)auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();// 计算时间差std::chrono::duration<double> duration = end - start;// 输出执行时间std::cout << "Execution Time: " << duration.count() << " seconds\n";}}catch (const c10::Error& e) {std::cout << e.msg() << std::endl;}return 0;
}至此算是部署完毕了,小伙伴可以不往后面看了,当然不保证大家有没有问题,有问题可以自己再查查看
涉及项目细节,就不贴图了,识别什么自己可以随意标注样本
5.动态库封装
为了真正用起来,肯定是要封装一个动态库给别人用的,详细展开讲一下
5.1 新建一个动态库VS工程
1.直接把自带的一堆乱七八糟的头文件和cpp删掉,不使用预编译头,自己写

5.2该添加的各种文件和配置还是要和上面一样哈
5.3构建调用接口,使用纯虚函数,只暴漏最基础的接口即可
5.3.1 对外开放的接口函数.h和cpp
#ifndef INJECTIONBAGINFER_EXPORTS
#define INJECTIONBAGINFER_API __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define INJECTIONBAGINFER_API __declspec(dllimport)
#endif#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>
class INJECTIONBAGINFER_API IDetector
{
public://推理函数virtual int doInfer(unsigned char* pData, int height, int width, int nc, float conf_thr, float*& pResult, int& resultNum) = 0;//模型预热virtual void warmUp() = 0;
};
//用于构建检测句柄
INJECTIONBAGINFER_API std::shared_ptr<IDetector> CreateDetector(const std::string weightFolder);
#include "InjectionBagInfer.h"
#include "IDetectorBase.h"std::shared_ptr<IDetector> CreateDetector(const std::string weightFolder) {return std::make_shared<IDetectorBase>(weightFolder);
}
5.3.2 新建一个派生类,继承一下,做具体实现
派生类头文件
#pragma once
#include "InjectionBagInfer.h"
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp>
#include <torch/torch.h>
#include <torch/script.h>
using torch::indexing::Slice;
using torch::indexing::None;
class IDetectorBase :public IDetector
{
public:/*初始化*/IDetectorBase(const std::string& weightFolder);/*推断*/int doInfer(unsigned char* pData, int height, int width, int nc, float conf_thr, float*& pResult, int& resultNum);/*模型预热*/void warmUp();
private:/*模型*/torch::jit::script::Module yolo_model;/*设备*/torch::Device m_device;
};
派生类实现文件
值得注意,模型预热函数,我理解的是,GPU前几张照片有点慢,我加载模型后,直接塞两张空图像,先跑一下,后面就正常了
#include "IDetectorBase.h"
#include <iostream>float generate_scale(cv::Mat& image, const std::vector<int>& target_size) {int origin_w = image.cols;int origin_h = image.rows;int target_h = target_size[0];int target_w = target_size[1];float ratio_h = static_cast<float>(target_h) / static_cast<float>(origin_h);float ratio_w = static_cast<float>(target_w) / static_cast<float>(origin_w);float resize_scale = std::min(ratio_h, ratio_w);return resize_scale;
}
float letterbox(cv::Mat &input_image, cv::Mat &output_image, const std::vector<int> &target_size) {if (input_image.cols == target_size[1] && input_image.rows == target_size[0]) {if (input_image.data == output_image.data) {return 1.;}else {output_image = input_image.clone();return 1.;}}float resize_scale = generate_scale(input_image, target_size);int new_shape_w = std::round(input_image.cols * resize_scale);int new_shape_h = std::round(input_image.rows * resize_scale);float padw = (target_size[1] - new_shape_w) / 2.;float padh = (target_size[0] - new_shape_h) / 2.;int top = std::round(padh - 0.1);int bottom = std::round(padh + 0.1);int left = std::round(padw - 0.1);int right = std::round(padw + 0.1);cv::resize(input_image, output_image,cv::Size(new_shape_w, new_shape_h),0, 0, cv::INTER_AREA);cv::copyMakeBorder(output_image, output_image, top, bottom, left, right,cv::BORDER_CONSTANT, cv::Scalar(114., 114., 114));return resize_scale;
}
torch::Tensor xyxy2xywh(const torch::Tensor& x) {auto y = torch::empty_like(x);y.index_put_({ "...", 0 }, (x.index({ "...", 0 }) + x.index({ "...", 2 })).div(2));y.index_put_({ "...", 1 }, (x.index({ "...", 1 }) + x.index({ "...", 3 })).div(2));y.index_put_({ "...", 2 }, x.index({ "...", 2 }) - x.index({ "...", 0 }));y.index_put_({ "...", 3 }, x.index({ "...", 3 }) - x.index({ "...", 1 }));return y;
}
torch::Tensor xywh2xyxy(const torch::Tensor& x) {auto y = torch::empty_like(x);auto dw = x.index({ "...", 2 }).div(2);auto dh = x.index({ "...", 3 }).div(2);y.index_put_({ "...", 0 }, x.index({ "...", 0 }) - dw);y.index_put_({ "...", 1 }, x.index({ "...", 1 }) - dh);y.index_put_({ "...", 2 }, x.index({ "...", 0 }) + dw);y.index_put_({ "...", 3 }, x.index({ "...", 1 }) + dh);return y;
}
// Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/main/torchvision/csrc/ops/cpu/nms_kernel.cpp
torch::Tensor nms(const torch::Tensor& bboxes, const torch::Tensor& scores, float iou_threshold) {if (bboxes.numel() == 0)return torch::empty({ 0 }, bboxes.options().dtype(torch::kLong));auto x1_t = bboxes.select(1, 0).contiguous();auto y1_t = bboxes.select(1, 1).contiguous();auto x2_t = bboxes.select(1, 2).contiguous();auto y2_t = bboxes.select(1, 3).contiguous();torch::Tensor areas_t = (x2_t - x1_t) * (y2_t - y1_t);auto order_t = std::get<1>(scores.sort(/*stable=*/true, /*dim=*/0, /* descending=*/true));auto ndets = bboxes.size(0);torch::Tensor suppressed_t = torch::zeros({ ndets }, bboxes.options().dtype(torch::kByte));torch::Tensor keep_t = torch::zeros({ ndets }, bboxes.options().dtype(torch::kLong));auto suppressed = suppressed_t.data_ptr<uint8_t>();auto keep = keep_t.data_ptr<int64_t>();auto order = order_t.data_ptr<int64_t>();auto x1 = x1_t.data_ptr<float>();auto y1 = y1_t.data_ptr<float>();auto x2 = x2_t.data_ptr<float>();auto y2 = y2_t.data_ptr<float>();auto areas = areas_t.data_ptr<float>();int64_t num_to_keep = 0;for (int64_t _i = 0; _i < ndets; _i++) {auto i = order[_i];if (suppressed[i] == 1)continue;keep[num_to_keep++] = i;auto ix1 = x1[i];auto iy1 = y1[i];auto ix2 = x2[i];auto iy2 = y2[i];auto iarea = areas[i];for (int64_t _j = _i + 1; _j < ndets; _j++) {auto j = order[_j];if (suppressed[j] == 1)continue;auto xx1 = std::max(ix1, x1[j]);auto yy1 = std::max(iy1, y1[j]);auto xx2 = std::min(ix2, x2[j]);auto yy2 = std::min(iy2, y2[j]);auto w = std::max(static_cast<float>(0), xx2 - xx1);auto h = std::max(static_cast<float>(0), yy2 - yy1);auto inter = w * h;auto ovr = inter / (iarea + areas[j] - inter);if (ovr > iou_threshold)suppressed[j] = 1;}}return keep_t.narrow(0, 0, num_to_keep);
}
torch::Tensor non_max_suppression(torch::Tensor& prediction, float conf_thres = 0.25, float iou_thres = 0.45, int max_det = 300) {auto bs = prediction.size(0);auto nc = prediction.size(1) - 4;auto nm = prediction.size(1) - nc - 4;auto mi = 4 + nc;auto xc = prediction.index({ Slice(), Slice(4, mi) }).amax(1) > conf_thres;prediction = prediction.transpose(-1, -2);prediction.index_put_({ "...", Slice({None, 4}) }, xywh2xyxy(prediction.index({ "...", Slice(None, 4) })));std::vector<torch::Tensor> output;for (int i = 0; i < bs; i++) {output.push_back(torch::zeros({ 0, 6 + nm }, prediction.device()));}for (int xi = 0; xi < prediction.size(0); xi++) {auto x = prediction[xi];x = x.index({ xc[xi] });auto x_split = x.split({ 4, nc, nm }, 1);auto box = x_split[0], cls = x_split[1], mask = x_split[2];//auto[conf, j] = cls.max(1, true);std::tuple<torch::Tensor, torch::Tensor> result = cls.max(1, true);torch::Tensor conf = std::get<0>(result);torch::Tensor j = std::get<1>(result);x = torch::cat({ box, conf, j.toType(torch::kFloat), mask }, 1);x = x.index({ conf.view(-1) > conf_thres });int n = x.size(0);if (!n) { continue; }// NMSauto c = x.index({ Slice(), Slice{5, 6} }) * 7680;auto boxes = x.index({ Slice(), Slice(None, 4) }) + c;auto scores = x.index({ Slice(), 4 });auto i = nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres);i = i.index({ Slice(None, max_det) });output[xi] = x.index({ i });}return torch::stack(output);
}
torch::Tensor clip_boxes(torch::Tensor& boxes, const std::vector<int>& shape) {boxes.index_put_({ "...", 0 }, boxes.index({ "...", 0 }).clamp(0, shape[1]));boxes.index_put_({ "...", 1 }, boxes.index({ "...", 1 }).clamp(0, shape[0]));boxes.index_put_({ "...", 2 }, boxes.index({ "...", 2 }).clamp(0, shape[1]));boxes.index_put_({ "...", 3 }, boxes.index({ "...", 3 }).clamp(0, shape[0]));return boxes;
}
torch::Tensor scale_boxes(const std::vector<int>& img1_shape, torch::Tensor& boxes, const std::vector<int>& img0_shape) {auto gain = (std::min)((float)img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], (float)img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]);auto pad0 = std::round((float)(img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2. - 0.1);auto pad1 = std::round((float)(img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2. - 0.1);boxes.index_put_({ "...", 0 }, boxes.index({ "...", 0 }) - pad0);boxes.index_put_({ "...", 2 }, boxes.index({ "...", 2 }) - pad0);boxes.index_put_({ "...", 1 }, boxes.index({ "...", 1 }) - pad1);boxes.index_put_({ "...", 3 }, boxes.index({ "...", 3 }) - pad1);boxes.index_put_({ "...", Slice(None, 4) }, boxes.index({ "...", Slice(None, 4) }).div(gain));return boxes;
}
/*初始化*///windows.h 必须放在这里
#include<windows.h>
IDetectorBase::IDetectorBase(const std::string& weightFolder) : m_device(torch::cuda::is_available() ? torch::kCUDA : torch::kCPU)
{//1.开始加载模型了//1.1看设备是GPU还是CPU//torch::Device device(torch::cuda::is_available() ? torch::kCUDA : torch::kCPU);///*if (torch::cuda::is_available()) {// m_device = torch::kCUDA;//}//else {// m_device = torch::kCPU;//}*///1.2待区分的类别std::vector<std::string> classes{ "Target", "Label", "Top" };//1.3加载模型try {// Load the model (e.g. yolov8s.torchscript)std::string model_path = weightFolder;//yolo_model = torch::jit::load(model_path, device);LoadLibraryA("ATen_cuda.dll");LoadLibraryA("c10_cuda.dll");LoadLibraryA("torch_cuda.dll");LoadLibraryA("torchvision.dll");yolo_model = torch::jit::load(model_path, m_device);yolo_model.eval();yolo_model.to(m_device, torch::kFloat32);}catch (const c10::Error& e) {std::cout << e.msg() << std::endl;}
}
int IDetectorBase::doInfer(unsigned char* pData, int height, int width, int nc, float conf_thr, float*& pResult, int& resultNum) {//影像进来要变成640 * 640// 将输入数据转换为 cv::Mat 格式cv::Mat input_image(height, width, CV_8UC3, pData);letterbox(input_image, input_image, { 640, 640 });torch::Tensor image_tensor = torch::from_blob(input_image.data, { 640, 640, nc }, torch::kByte).to(m_device);image_tensor = image_tensor.toType(torch::kFloat32).div(255);image_tensor = image_tensor.permute({ 2, 0, 1 });image_tensor = image_tensor.unsqueeze(0);std::vector<torch::jit::IValue> inputs{ image_tensor };// Inferencetorch::Tensor output = yolo_model.forward(inputs).toTensor().cpu();// NMS 置信度auto keep = non_max_suppression(output, conf_thr)[0];auto boxes = keep.index({ Slice(), Slice(None, 4) });keep.index_put_({ Slice(), Slice(None, 4) }, scale_boxes({ 640, 640 }, boxes, { height, width }));// Show the resultsresultNum = keep.size(0);//检测出的结果数量pResult = new float[resultNum * 6];for (int i = 0; i < keep.size(0); i++) {int x1 = keep[i][0].item().toFloat();int y1 = keep[i][1].item().toFloat();int x2 = keep[i][2].item().toFloat();int y2 = keep[i][3].item().toFloat();float conf = keep[i][4].item().toFloat();int cls = keep[i][5].item().toInt();pResult[i * 6 + 0] = static_cast<float>(x1);pResult[i * 6 + 1] = static_cast<float>(y1);pResult[i * 6 + 2] = static_cast<float>(x2);pResult[i * 6 + 3] = static_cast<float>(y2);pResult[i * 6 + 4] = static_cast<float>(conf);pResult[i * 6 + 5] = static_cast<float>(cls);//std::cout << "Rect: [" << x1 << "," << y1 << "," << x2 << "," << y2 << "] Conf: " << conf << " Class: " << classes[cls] << std::endl;}return 0;
}
/*模型预热*/
void IDetectorBase::warmUp() {//模型预热 我直接理解 加载几张照片先让他运行一下int num = 2;for (int ii = 0; ii < num; ii++) {cv::Mat input_image = cv::Mat::zeros(640, 640, CV_8UC3);// 将图像从BGR转换到RGBcv::cvtColor(input_image, input_image, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);torch::Tensor image_tensor = torch::from_blob(input_image.data, { input_image.rows, input_image.cols, 3 }, torch::kByte).to(m_device);image_tensor = image_tensor.toType(torch::kFloat32).div(255);image_tensor = image_tensor.permute({ 2, 0, 1 });image_tensor = image_tensor.unsqueeze(0);std::vector<torch::jit::IValue> inputs{ image_tensor };auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();// Inferencetorch::Tensor output = yolo_model.forward(inputs).toTensor().cpu();// NMSauto keep = non_max_suppression(output)[0];auto boxes = keep.index({ Slice(), Slice(None, 4) });keep.index_put_({ Slice(), Slice(None, 4) }, scale_boxes({ input_image.rows, input_image.cols }, boxes, { input_image.rows, input_image.cols }));}
}
5.3.3 至此应该是完成了模型的封装,直接调用即可
我的模型有三类 注射液的物品位置+瓶口+商标位置
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <time.h>
#include "InjectionBagInfer.h"using namespace std;std::vector<std::string> getfiles(std::string filename)
{std::vector<cv::String> file_names;cv::glob(filename, file_names); //get file namesreturn file_names;
}
void test()
{// 加载模型vector<string> categories = { "Target", "Label", "Top" };vector<cv::Scalar> colors = { cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0),cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0),cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255) };shared_ptr<IDetector> detector = CreateDetector("./weights/best.torchscript");// 预热模型detector->warmUp();std::vector<std::string>imgfilename;imgfilename = getfiles(".../ultralytics-main/datasets/data0829/images_all");printf("++++++++++++++++++++++++++++\n");for (int ii = 0; ii < imgfilename.size(); ii++) {// Load image and preprocesscv::Mat image = cv::imread(imgfilename[ii], cv::IMREAD_COLOR);cv::cvtColor(image, image, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);//printf("++++++++++++++++1++++++++++++\n");int n; // 检测结果数量// 结果数组float* pResult = NULL;// 推理,并把结果写入pResult,// pResult在doInfer中使用new开辟内存,由用户负责释放,// 每个检测结果包含 6 个float,全部检测结果共包含 6*n 个float。clock_t t0 = clock();detector->doInfer(image.data, image.rows, image.cols, 3, 0.4, pResult, n);//printf("+++++++++++++++2+++++++++++++\n");printf("\nDone inference, time cost: %lf\n", ((double)clock() - t0) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);printf("Number of detections: %d\n", n);// 从结果数组中取出目标各项信息for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {float x1 = pResult[j * 6];float y1 = pResult[j * 6 + 1];float x2 = pResult[j * 6 + 2];float y2 = pResult[j * 6 + 3];float score = pResult[j * 6 + 4];float labelId = pResult[j * 6 + 5];printf("%.2f %.2f\n", score, labelId);if (x1 >= 0 && x2 >= 0 && y1 >= 0 && y2 >= 0) {cv::rectangle(image, cv::Point((int)x1, (int)y1), cv::Point((int)x2, (int)y2), colors[(int)labelId], 2);}}//printf("++++++++++++++3++++++++++++++\n");delete[] pResult; // 释放检测结果内存cv::cvtColor(image, image, cv::COLOR_RGB2BGR);size_t dot_pos = imgfilename[ii].find_last_of(".");std::string outstr = imgfilename[ii].substr(0, dot_pos) + "_out.jpg";printf("out: %s\n", outstr);cv::imwrite(outstr, image);}
}int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{test();return 0;
}6.跨平台调用
实际上,我们的推理函数不仅要给VS的工程调用,还要给其他工程调用,我这边接触最多的是QT Mingw,我这边是已经实现了的,给大家提供一个解决思路即可
6.1 本机构建socket实现互通讯,通过socket实现什么时候触发推理或者其他命令
6.2 构建共享内存,用来交互不同平台间的影像数据 + 参数数据
6.3 QT调用推理EXE,通过写入数据到共享内存+socket接收命令方式,识别结束后,把结果返回去,当前也是共享内存
6.4 不用socket也行其实,直接给参数的共享内存放一个标识也行,标识发生变化则触发不同的操作,不过就需要监测了,看大家使用顺手情况吧
6.再附赠一个设置
GPU版本的代码实际跑起来,如果传入的影像连续,够多,识别效率还是挺稳定的,如果采集频率不够,尤其是拍照效率没那么高的情况,测试下来发现效率不稳定,有时候20ms有时候100-300ms,不稳定,需要在window设置一些参数,和代码没关系
完全参考这个文章即可
https://blog.csdn.net/Charwee_/article/details/128155553
为防止链接失效,我截几个图放下面
nvidia-smi -q -d SUPPORTED_CLOCKS
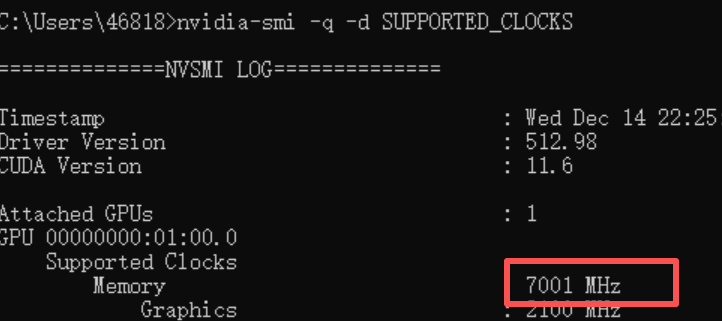
设置一下
nvidia-smi -lgc 7001
显卡驱动设置
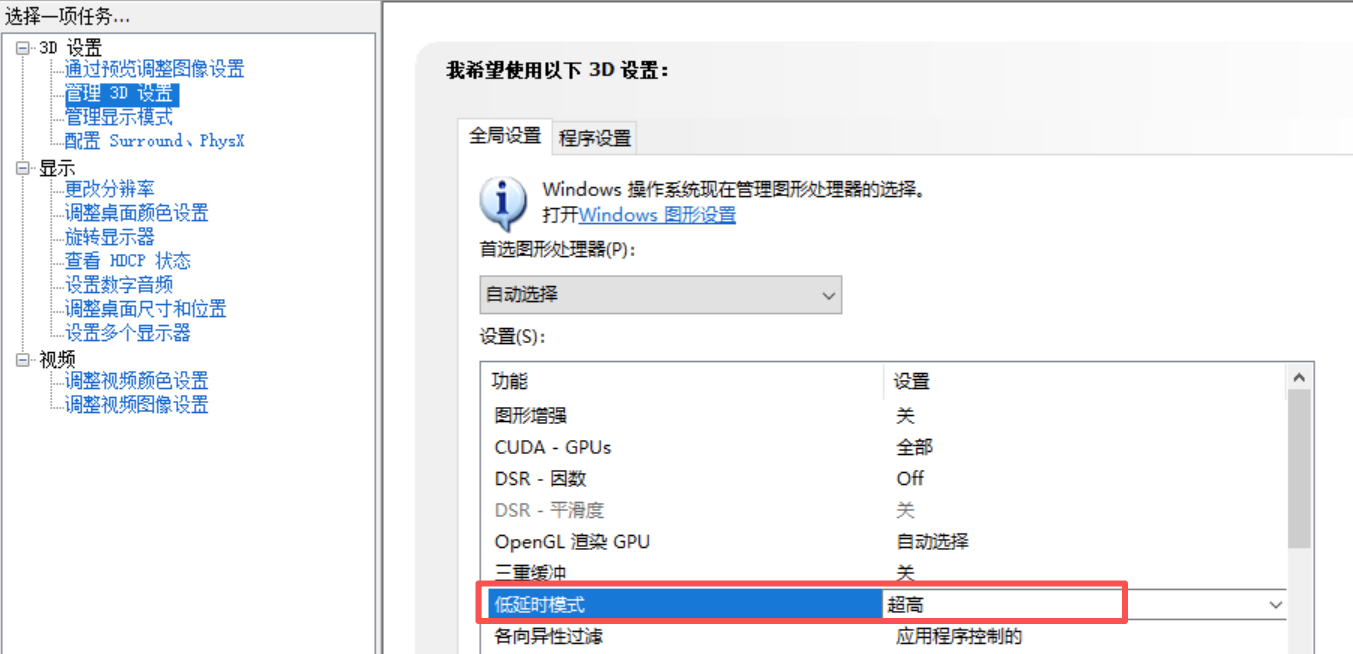
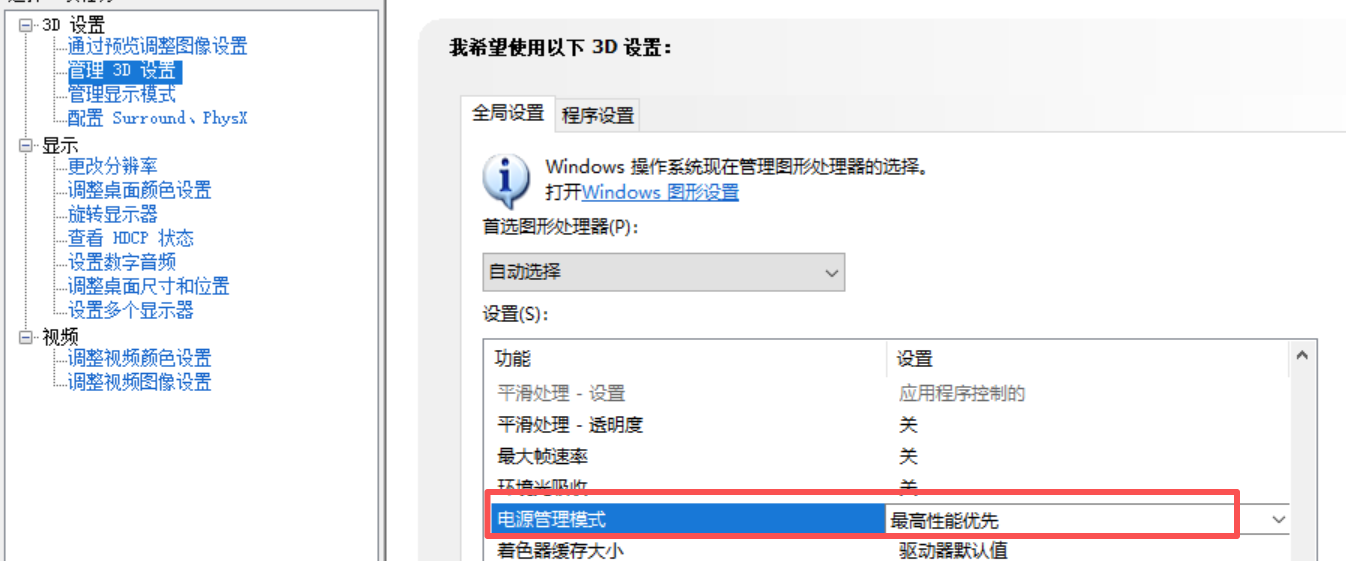
能看到最后面的都是有耐心的小伙伴,如果写的对你有帮助,那就留下点赞和收藏吧
