使用Rag 命中用户feedback提升triage agent 准确率
简述
使用 RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation),提升 Triage Agent 对用户反馈的处理准确率。这个方案的背景源于当前系统服务多个租户,各租户在业务场景、问题描述方式、术语使用习惯等方面存在极大差异,导致通用模型难以在所有租户场景下保持一致的分类准确率。同时,部分租户出于数据安全、成本或维护复杂性的考虑,明确表示不接受通过机器学习模型训练或 LoRA 微调等需要长期迭代和算力投入的方式进行个性化适配。
在此约束下,项目选择以大语言模型(LLM)的基座能力为核心,通过 API 调用快速实现 Triage Agent 的功能落地,确保在最短时间内为用户提供可用的智能分诊服务。现阶段的目标并非追求绝对精准,而是先让 AI 基于其通用理解能力对用户反馈进行初步判断,形成可运行的闭环。
在此基础上,引入 RAG 机制作为关键增强手段:将历史已标注的用户反馈(包括问题描述、分类结果、人工修正记录等)构建成向量知识库。当新反馈进入系统时,RAG 首先检索与之语义相似的历史案例,并将这些高相关性上下文注入到 LLM 的提示词中,引导其参考过往经验进行推理与分类。这种方式无需修改模型参数,即可实现“类记忆”效果,显著提升模型在特定租户语境下的判断准确性与一致性。
随着用户反馈数据的持续积累,系统将进一步构建“反馈闭环”——通过分析用户对 AI 分类结果的修正行为,动态优化检索库中的标注质量与向量表示,并探索轻量化的模型演进路径(如定向 prompt 优化、小样本学习或增量式微调),逐步推动 LLM 朝着更贴合实际业务需求的方向持续演进。当前阶段的 RAG 方案,既是快速交付的务实选择,也为后续智能化升级奠定了可扩展的数据与架构基础。
原型方案设计
为了让方案能尽可能快的方式呈现,我选择使用了 MaxKB 作为核心框架,充分利用其开箱即用的可视化知识库管理、RAG 流程支持和轻量级部署优势,显著缩短了从开发到上线的周期。MaxKB 支持灵活的文档导入、切片策略配置和检索测试功能,使得在多租户环境下能快速为每个租户独立配置专属知识空间,满足数据隔离与个性化分诊的需求。
向量数据库方面,选择使用 PostgreSQL 的扩展 pgvector,主要基于以下几点考虑:
- 技术栈统一:项目已使用 PostgreSQL 作为主业务数据库,引入
pgvector无需额外维护独立的向量数据库(如 Milvus 或 Pinecone),降低运维复杂度; - 数据一致性保障:用户反馈、工单记录与向量索引可共存于同一事务体系,确保数据同步的实时性与可靠性;
- 成本可控:避免引入新组件带来的资源开销和学习成本,适合现阶段快速验证与中小规模部署;
- 兼容性强:MaxKB 支持自定义向量数据库对接,通过简单配置即可集成
pgvector,实现无缝替换。
详细设计
1) 将feedback的ticket , triage result 结构为纯文本可以轻易chrunk化的结构
import json# 读取JSON文件
with open('../sample/Billing_Codes.json', 'r') as f:data = json.load(f)# 转换格式
output_lines = []
billing_codes = set() # 用于存储唯一的billing codes# 修改:为每个item添加编号
for index, item in enumerate(data, 1):title = item['title']description = item['description']billing_code = item['fields_value_name']# 收集唯一的billing codesbilling_codes.add(billing_code)# 创建格式化文本,包含编号formatted_text = f"{index}. text: {title} {description}, billing codes: {billing_code}"output_lines.append(formatted_text)# 用###分割子项目
output_text = "\n######\n".join(output_lines)# 输出结果
print(output_text)# 输出billing code类别总数
print(f"\n总共有 {len(billing_codes)} 类别的billing code")print('billing_codes', "\n".join(billing_codes))with open('./Billing_Codes_output.txt', 'w') as f:f.write(output_text)f.write(f"\n\n总共有 {len(billing_codes)} 类别的billing code")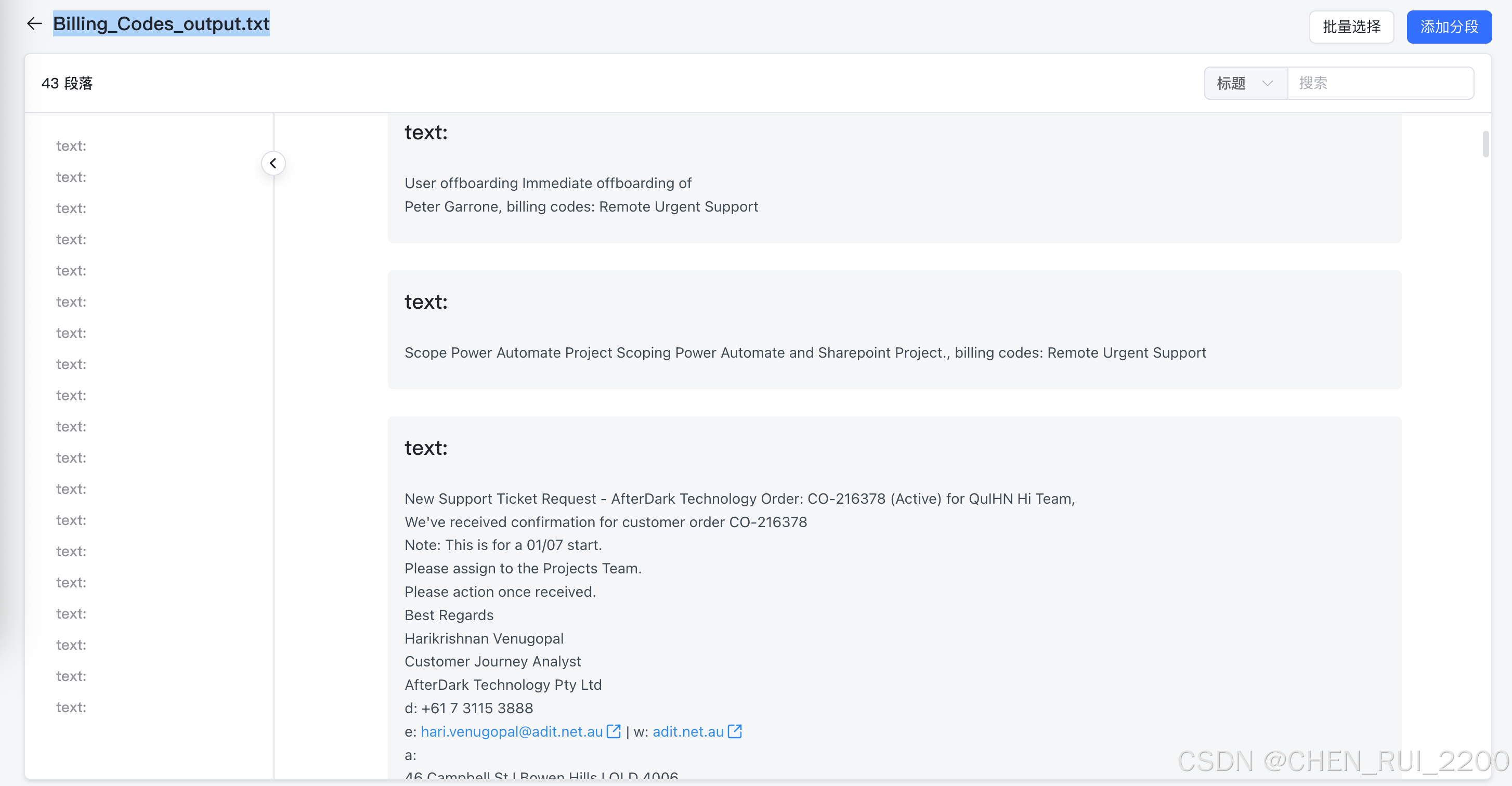
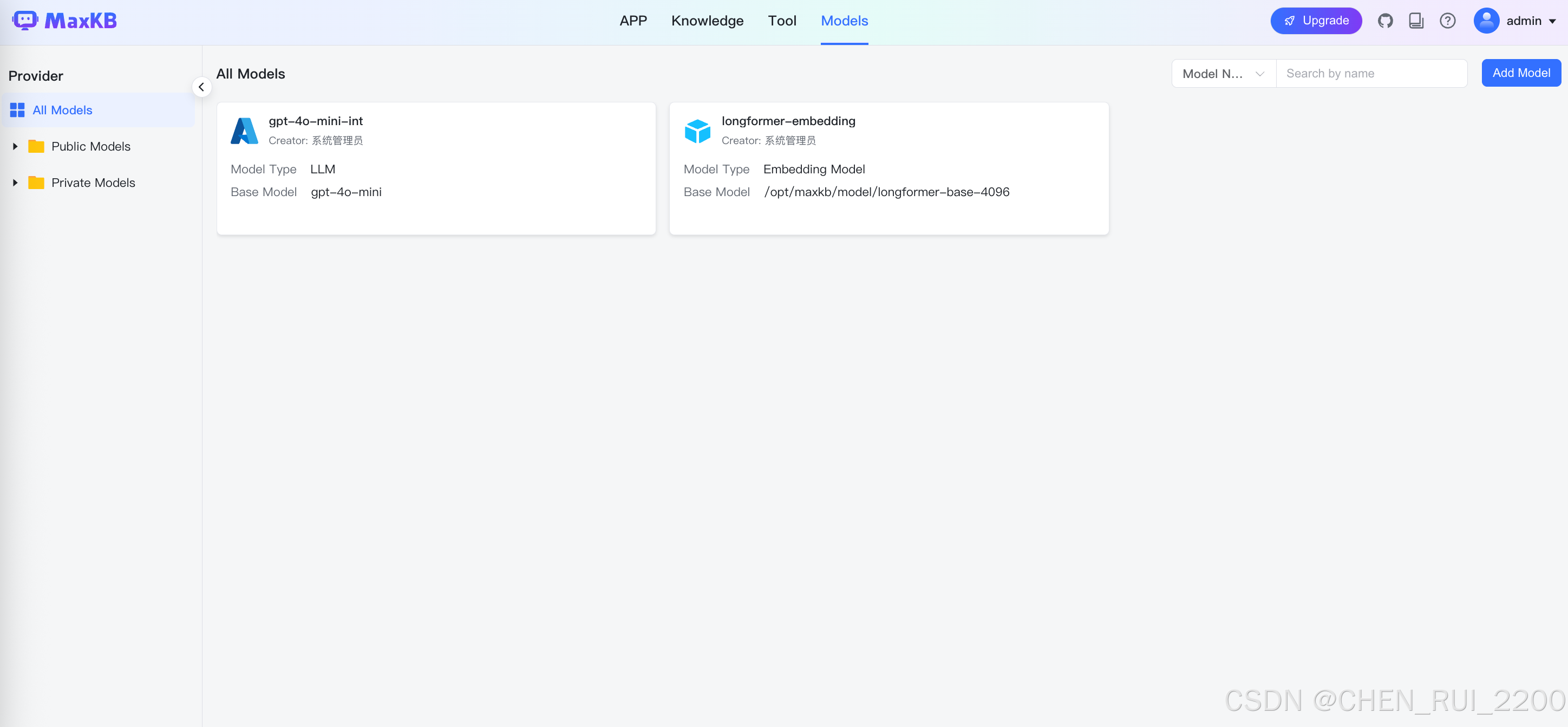
每个ticket 单独trunk一个片段,为了让嵌入模型能尽可能处理多的token, 我选择使用之前利用的longformer-4096-base模型, 配置文件修改
# 模型路径 如果EMBEDDING_MODEL_NAME是绝对路径则无效,反之则会从https://huggingface.co/下载模型到当前目录
EMBEDDING_MODEL_PATH: /opt/maxkb/model/
# 模型名称 如果模型名称是绝对路径 则会加载目录下的模型,如果是模型名称,则会在https://huggingface.co/下载模型 模型的下载位置为EMBEDDING_MODEL_PATH
EMBEDDING_MODEL_NAME: /opt/maxkb/model/longformer-base-4096调试过程里发现虽然配置了
但是分段嵌入一直失败,调试代码发现embedding 的调用方式走了web访问的方式
需要在tools.py里修改下面方法,如果provider携带使用local字符,use_local设置为true
def get_model_(provider, model_type, model_name, credential, model_id, use_local=False, **kwargs):"""获取模型实例@param provider: 供应商@param model_type: 模型类型@param model_name: 模型名称@param credential: 认证信息@param model_id: 模型id@param use_local: 是否调用本地模型 只适用于本地供应商@return: 模型实例"""if 'local' in provider:use_local = Truemodel = get_provider(provider).get_model(model_type,model_name,json.loads(rsa_long_decrypt(credential)),model_id=model_id,use_local=use_local,streaming=True, **kwargs)return model2)先检索ticket相似度,返回相似度高的
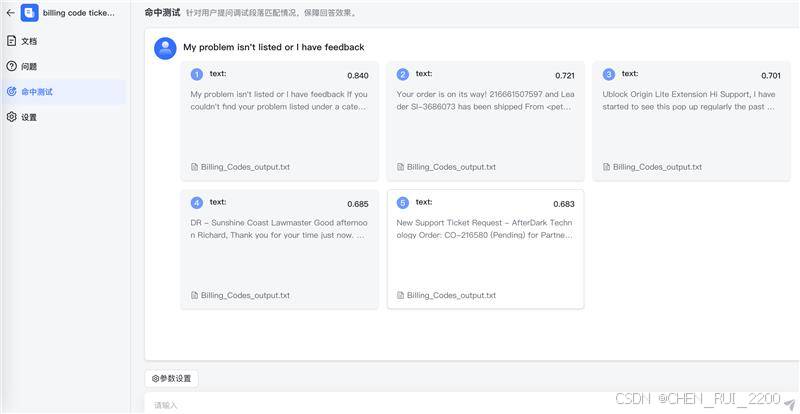
maxkb使用/hit_test接口走命中测试
def hit_test(self):self.is_valid()vector = VectorStore.get_embedding_vector()exclude_document_id_list = [str(document.id) for document in QuerySet(Document).filter(knowledge_id=self.data.get('knowledge_id'), is_active=False)]model = get_embedding_model_by_knowledge_id(self.data.get('knowledge_id'))# 向量库检索hit_list = vector.hit_test(self.data.get('query_text'),[self.data.get('knowledge_id')],exclude_document_id_list,self.data.get('top_number'),self.data.get('similarity'),SearchMode(self.data.get('search_mode')),model)hit_dict = reduce(lambda x, y: {**x, **y}, [{hit.get('paragraph_id'): hit} for hit in hit_list], {})p_list = list_paragraph([h.get('paragraph_id') for h in hit_list])return [{**p,'similarity': hit_dict.get(p.get('id')).get('similarity'),'comprehensive_score': hit_dict.get(p.get('id')).get('comprehensive_score')} for p in p_list]在maxkb页面进行命中测试
3) 将相似度高的ticket作为提示词中的参考用例子给llm进行推理
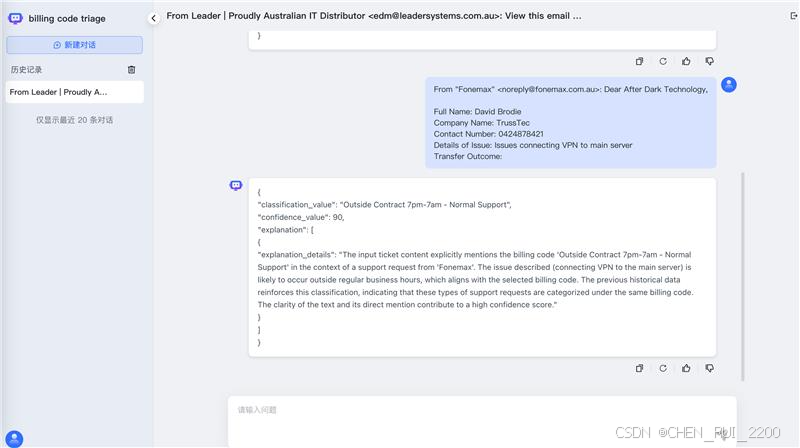
这里使用之前预测率偏低的billing code做试验
1)每个ticke content + billing codes 结果做trunk, 通过嵌入模型编码,制作知识库
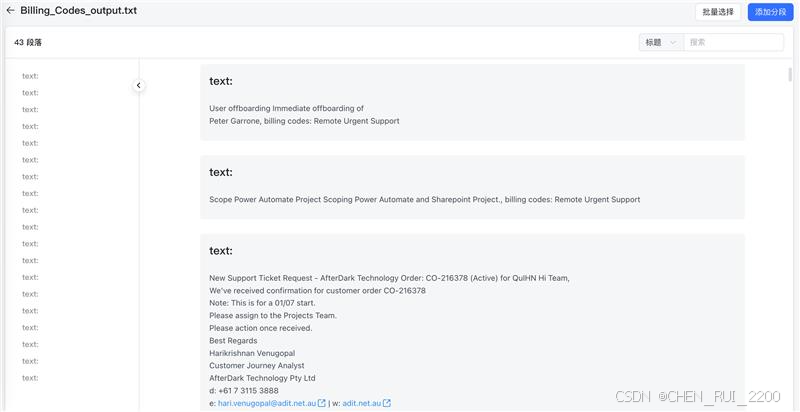
2)flow 工具集成了知识库+ llm, 问题先在知识库上做命中,然后传入llm作为推理依据,这就是一般说的谜底在谜面上
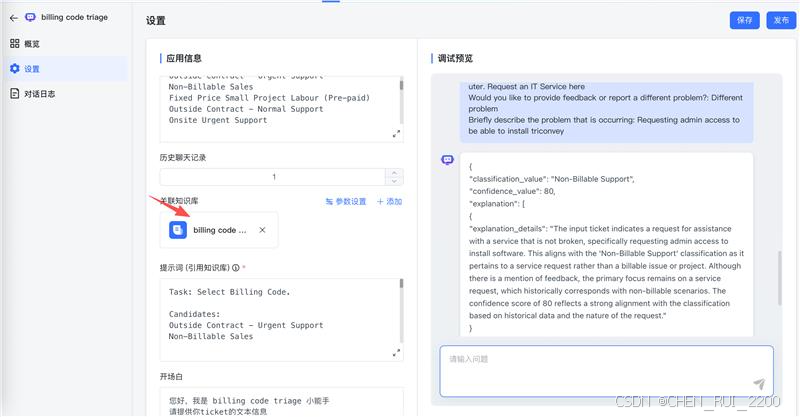
提示词修改为下面,其中{data}就是文本相似命中的chrunk
Task: Select Billing Code.
Candidates:
Fixed Price Small Project Labour (Pre-paid)
Remote Urgent Support
Non-Billable Sales
Onsite Normal Support
Onsite Urgent Support
Outside Contract - Urgent Support
Non-Billable Support
Contract Labour - GST
Remote Normal Support
Development Support
Outside Contract 7pm-7am - Normal Support
Outside Contract - Normal SupportInput ticket content:
{question}Experience:
Find the best matching triage result from the following experience
{data}Output Json Format:
Generate a raw JSON response containing the predicted classification value for the given ticket text. Do not include any Markdown code block markers (e.g., ```json), comments, or additional formatting. Output only the JSON object:
1 classification_value Assign full Billing Code name
2 confidence_value Estimate confidence score, [0~100], number based on clarity of text and dimension alignment
3 ref_ticket Assign the billing code experience ticket
4 ref_result Assign the billing code pointed to by the reference triage experience3)ouput格式输出
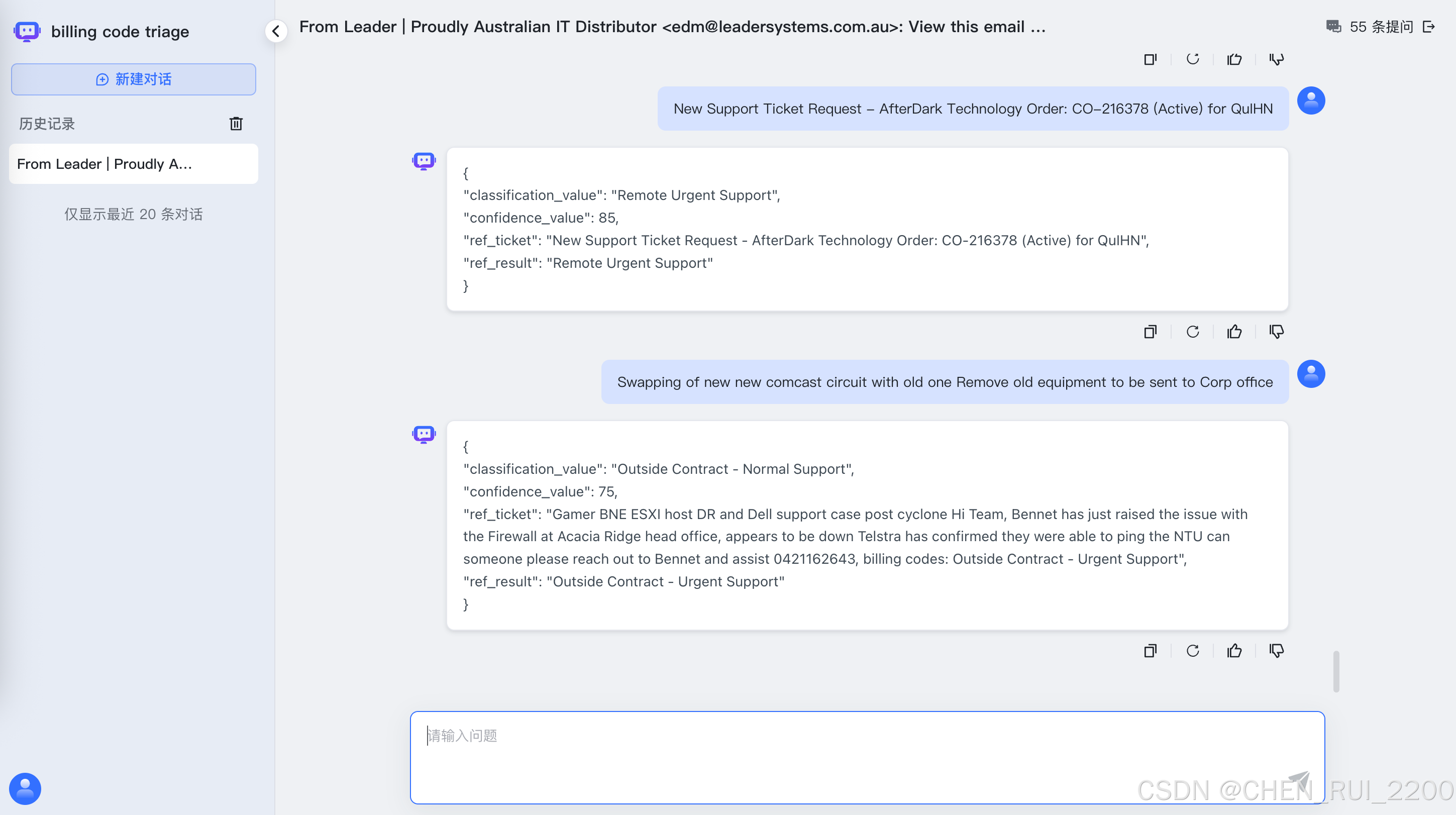
测试
使用maxkb的接口进行测试
HEADERS = {'accept': '*/*','Authorization': 'Bearer application-fe728b15cbd1949fb6c555f2ac821da1','Content-Type': 'application/json','X-CSRFTOKEN': 'My7YR2pbk6XVNnpTjOqHv2V49ke11CAJY9BdeQbj0DOljUwWNSFJNjIS9DByQj5V'
}def call_api(message: str, retries: int = 3, delay: int = 10) -> dict:"""调用分类 API with retry logic"""payload = {"message": message,"stream": False,"re_chat": True}for attempt in range(retries):try:response = requests.post(API_URL, headers=HEADERS, json=payload)response.raise_for_status()return response.json()except RequestException as e:print(f"API 调用失败 (尝试 {attempt + 1}/{retries}): {e}")if attempt < retries - 1:sleep(delay)continuereturn {}def extract_classification(data: dict) -> str:"""从 API 返回中提取 classification_value"""try:if 'data' not in data or 'content' not in data['data']:print(f"Invalid response structure: {data}")return ""content = data['data']['content']print(f"Raw content: {content}") # Log the raw contentparsed_content = json.loads(content)classification = parsed_content.get('classification_value', '').strip()return classificationexcept json.JSONDecodeError as e:print(f"JSON 解析错误: {content}, 错误: {e}")return ""except Exception as e:print(f"从 {content} 里解析 classification_value 失败: {e}")return ""def main():# 读取 JSON 文件with open(FILE_PATH, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:records: List[Dict] = json.load(f)total = len(records)correct = 0results = []print(f"开始处理 {total} 条记录...\n")for i, record in enumerate(records):title = record.get('title', '').strip()description = record.get('description', '').strip()expected = record.get('fields_value_name', '').strip()# 构造 messagemessage = f"{title} {description}".replace('\n', ' ').replace('\r', ' ').replace('\t', ' ')# 调用 APIprint(f"[{i+1}/{total}] 正在处理:\n {message},\nexpected: {expected}")api_response = call_api(message)# 修改:即使API调用失败也继续处理,而不是跳过if not api_response:print(f" API调用失败,记录预测为空")predicted = ""else:predicted = extract_classification(api_response)# 比较is_correct = predicted == expectedif is_correct:correct += 1# 保存结果results.append({"title": title,"description": description,"expected": expected,"predicted": predicted,"is_correct": is_correct})print(f" 预测: '{predicted}' -> {'✅ 正确' if is_correct else '❌ 错误'}\n")# 输出统计结果accuracy = correct / total if total > 0 else 0print(f"✅ 处理完成!")print(f"总数: {total}")print(f"正确: {correct}")print(f"准确率: {accuracy:.2%}")# 可选:保存结果到文件with open('evaluation_results.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:json.dump(results, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)print(f"详细结果已保存到 evaluation_results.json")if __name__ == '__main__':main()# message = "My problem isn't listed or I have feedback If you couldn't find your problem listed under a category or you would like to submit feedback for the support portal Details ----------------------------------------- Requesting an IT Service: Service Requests are for things that aren't broken but IT need to help with, like changing mailbox access or setting up a computer. Request an IT Service here Would you like to provide feedback or report a different problem?: Different problem Briefly describe the problem that is occurring: Requesting admin access to be able to install triconvey,"# api_response = call_api(message)# predicted = extract_classification(api_response)下面是试验结果,结果好的有点让人兴奋了
开始处理 43 条记录...
[1/43] 正在处理: Remote Urgent Support
预测: 'Remote Urgent Support' -> ✅ 正确
[2/43] 正在处理: Remote Urgent Support
预测: 'Remote Urgent Support' -> ✅ 正确
[3/43] 正在处理: Remote Urgent Support
预测: 'Remote Urgent Support' -> ✅ 正确
[4/43] 正在处理: Remote Urgent Support
预测: 'Remote Urgent Support' -> ✅ 正确
[5/43] 正在处理: Non-Billable Sales
预测: 'Non-Billable Sales' -> ✅ 正确
[6/43] 正在处理: Non-Billable Sales
预测: 'Non-Billable Sales' -> ✅ 正确
[7/43] 正在处理: Non-Billable Sales
预测: 'Non-Billable Sales' -> ✅ 正确
[8/43] 正在处理: Non-Billable Sales
预测: 'Non-Billable Sales' -> ✅ 正确
[9/43] 正在处理: Non-Billable Sales
预测: 'Non-Billable Sales' -> ✅ 正确
[10/43] 正在处理: Non-Billable Support
预测: 'Non-Billable Support' -> ✅ 正确
[11/43] 正在处理: Non-Billable Support
预测: 'Non-Billable Support' -> ✅ 正确
[12/43] 正在处理: Non-Billable Support
预测: 'Non-Billable Support' -> ✅ 正确
[13/43] 正在处理: Non-Billable Support
预测: 'Non-Billable Support' -> ✅ 正确
[14/43] 正在处理: Non-Billable Support
预测: 'Non-Billable Support' -> ✅ 正确
[15/43] 正在处理: Onsite Urgent Support
预测: 'Onsite Urgent Support' -> ✅ 正确
[16/43] 正在处理: Onsite Normal Support
预测: 'Onsite Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[17/43] 正在处理: Onsite Normal Support
预测: 'Onsite Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[18/43] 正在处理: Onsite Normal Support
预测: 'Onsite Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[19/43] 正在处理: Onsite Normal Support
预测: 'Onsite Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[20/43] 正在处理: Remote Normal Support
预测: 'Remote Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[21/43] 正在处理: Remote Normal Support
预测: 'Remote Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[22/43] 正在处理: Remote Normal Support
预测: 'Remote Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[23/43] 正在处理: Remote Normal Support
预测: 'Remote Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[24/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract 7pm-7am - Normal Support
预测: 'Outside Contract 7pm-7am - Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[25/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract 7pm-7am - Normal Support
预测: 'Outside Contract 7pm-7am - Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[26/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract 7pm-7am - Normal Support
预测: 'Outside Contract 7pm-7am - Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[27/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract 7pm-7am - Normal Support
预测: 'Outside Contract 7pm-7am - Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[28/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract 7pm-7am - Normal Support
预测: 'Outside Contract 7pm-7am - Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[29/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract - Normal Support
预测: 'Outside Contract - Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[30/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract - Normal Support
预测: 'Outside Contract - Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[31/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract - Normal Support
预测: 'Outside Contract - Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[32/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract - Normal Support
预测: 'Outside Contract - Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[33/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract - Normal Support
预测: 'Outside Contract - Normal Support' -> ✅ 正确
[34/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract - Urgent Support
预测: 'Outside Contract - Urgent Support' -> ✅ 正确
[35/43] 正在处理: Outside Contract - Urgent Support
预测: 'Outside Contract - Urgent Support' -> ✅ 正确
[36/43] 正在处理: Development Support
预测: 'Development Support' -> ✅ 正确
[37/43] 正在处理: Development Support
预测: 'Development Support' -> ✅ 正确
[38/43] 正在处理: Fixed Price Small Project Labour (Pre-paid)
预测: 'Fixed Price Small Project Labour (Pre-paid)' -> ✅ 正确
[39/43] 正在处理: Fixed Price Small Project Labour (Pre-paid)
预测: 'Fixed Price Small Project Labour (Pre-paid)' -> ✅ 正确
[40/43] 正在处理: Fixed Price Small Project Labour (Pre-paid)
预测: 'Fixed Price Small Project Labour (Pre-paid)' -> ✅ 正确
[41/43] 正在处理: Fixed Price Small Project Labour (Pre-paid)
预测: 'Fixed Price Small Project Labour (Pre-paid)' -> ✅ 正确
[42/43] 正在处理: Fixed Price Small Project Labour (Pre-paid)
预测: 'Fixed Price Small Project Labour (Pre-paid)' -> ✅ 正确
[43/43] 正在处理: Contract Labour - GST
预测: 'Contract Labour - GST' -> ✅ 正确
✅ 处理完成!
总数: 43
正确: 43
准确率: 100%
总结
在构建基于大模型的智能系统(如客服机器人、企业知识助手等)时,“使用向量知识库” vs “LoRA 微调” 是一个非常关键的技术选型问题。
下面从多个维度全面对比这两种方案,帮助你根据业务场景做出最优选择。
🆚 对比总览
全称 | Retrieval-Augmented Generation | Low-Rank Adaptation |
核心思想 | 检索外部知识 + 生成答案 | 修改模型参数以适应任务 |
是否修改模型 | ❌ 不修改原始模型 | ✅ 修改部分权重 |
数据依赖 | 知识文档(文本) | 标注数据(问题-答案对) |
更新成本 | ⭐ 极低(增删文档即可) | ⭐⭐⭐ 高(需重新训练) |
推理延迟 | ⭐⭐ 稍高(检索+生成) | ⭐ 低(直接生成) |
准确性 | 依赖检索质量 | 依赖训练数据质量 |
可解释性 | ✅ 高(能溯源) | ❌ 低(黑盒) |
适合场景 | 动态知识、多变内容 | 固定风格、固定任务 |
维护难度 | 低 | 中高 |
一、向量知识库(RAG)
✅ 原理
- 将企业文档切片 → 向量化 → 存入向量数据库(如 FAISS、Pinecone、Milvus);
- 用户提问时,先检索最相关的知识片段;
- 把知识片段作为上下文输入给大模型,生成答案。
✅ 优点
🔁知识更新快 | 只需更新文档库,无需重新训练 |
💾节省算力 | 不需要 GPU 训练,部署成本低 |
📚支持长文本/大量知识 | 可处理百万字文档 |
🔍可溯源 | 能返回“答案来自哪份文档”,适合审计 |
🛠️调试简单 | 查检索结果即可定位问题 |
❌ 缺点
⏱️延迟略高 | 多一步检索过程(通常增加 200~800ms) |
🔎依赖检索质量 | 如果检索不准,答案可能“幻觉” |
🧩上下文长度限制 | 拼接知识后可能超 |
📉对复杂推理支持弱 | 依赖模型自身推理能力 |
✅ 适用场景
- 企业知识库问答(如 IT 支持、HR 政策)
- 法律、医疗等需要可解释性的领域
- 知识频繁更新(如产品手册、公告)
- 缺乏标注数据,但有大量原始文档
二、LoRA 微调
✅ 原理
- 在预训练大模型基础上,使用少量标注数据(如 100~1000 条 QA 对);
- 使用 LoRA 技术只训练低秩矩阵,冻结大部分参数;
- 得到一个“定制化”的模型,能按你的风格/知识回答问题。
✅ 优点
⚡推理速度快 | 直接生成,无额外检索开销 |
🎯任务定制性强 | 可学习特定话术、格式、风格 |
🤖减少幻觉 | 模型“内化”了知识,不易胡说 |
📦部署轻量 | LoRA 仅增加几 MB 参数 |
❌ 缺点
🔄更新困难 | 知识变更需重新收集数据 + 训练 |
💰训练成本高 | 需要 GPU(如 A100),训练时间长 |
📉过拟合风险 | 数据少时容易记住样本,泛化差 |
🔒不可解释 | 不知道答案是“学来的”还是“编的” |
📚知识容量有限 | 无法承载海量知识(如整本书) |
✅ 适用场景
- 固定任务(如工单分类、话术生成)
- 强调响应风格一致(如客服语气)
- 有高质量标注数据
- 知识稳定、不常变(如产品功能)
🧩 三、如何选择决策
你的知识会频繁更新吗?
├── 是 → 用 向量知识库(RAG)
└── 否└── 你有高质量标注数据(>200条)吗?├── 是 → 可考虑 LoRA 微调└── 否 → 用 向量知识库(RAG)你希望答案可溯源吗?
├── 是 → 用 向量知识库(RAG)
└── 否 → 可考虑 LoRA你对延迟敏感吗?(要求 <500ms)
├── 是 → 考虑 LoRA(更快)
└── 否 → RAG 也可接受你想让模型学会“说话风格”吗?
├── 是 → LoRA 更擅长
└── 否 → RAG 足够🌟 四、高级方案:RAG + LoRA 混合
✅RAG + LoRA | 用 LoRA 让模型学会“怎么答”,用 RAG 提供“答什么” |
示例 | LoRA 学习客服话术风格,RAG 提供产品知识 |
这是当前最前沿的做法,兼顾准确性与可控性。
✅ 五、推荐组合策略
初创项目、知识多变 | ✅ 向量知识库(RAG) |
成熟产品、风格统一 | ✅ LoRA 微调 + RAG 检索 |
缺少标注数据 | ✅ RAG |
有标注数据 + 稳定知识 | ✅ LoRA |
高合规要求(金融、医疗) | ✅ RAG(可溯源) |
✅ 总结
🔹用向量知识库,适合“知识在变”的场景 |
