8.25作业
双向循环链表主要带代码
#include"link.h"
//创建双向链表
node_p create_link()
{node_p H = (node_p)malloc(sizeof(node));if (H==NULL){printf("空间申请失败\n");return NULL;}H->len=0;H->next=H;H->pre=H;return H;}
//创建节点
node_p create_node(int element)
{node_p new = (node_p)malloc(sizeof(node));if (new==NULL){printf("空间申请失败\n");return NULL;}new->data=element;new->next=NULL;new->pre=NULL;return new;}
//判空
int kong(node_p H)
{if (H==NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return -1;}return H->next==H;
}//尾插
void insert_rear(node_p H,int element)
{if (H==NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return;}node_p s=create_node(element);node_p p = H->pre;s->next=H;s->pre=p;p->next=s;H->pre=s;H->len++;
}//头删
void delete_head(node_p H)
{if (H==NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return;}if (kong(H)){printf("表为空,无法删除\n");return;}node_p del=H->next;H->next=del->next;del->next->pre=H;free(del);H->len--;
}//按位置插入
void insert_pos(node_p H,int pos,int element)
{if (H==NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return;}node_p s=create_node(element);node_p p= H;for (int i=0; i<pos-1; i++){p=p->next;if (p==H){printf("位置不合理\n");return;}}s->next=p->next;s->pre=p;p->next=s;s->next->pre=s;H->len++;}//按位置删除
void delete_pos(node_p H,int pos)
{if (H==NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return;}if (kong(H)){printf("表为空,无法删除\n");return;}int i;node_p p=H;for (i=0; i<pos-1; i++){ p=p->next;if (p==H){printf("位置不合理\n");return;}}node_p del=p->next;p->next=del->next;del->next->pre=p;free(del);H->len--;}//输出
void output(node_p H)
{if (H==NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return;}if (kong(H)){printf("表为空,无需输出\n");return;}node_p p = H->next;while (p!=H){printf("%d ",p->data);p=p->next;}printf("\n");}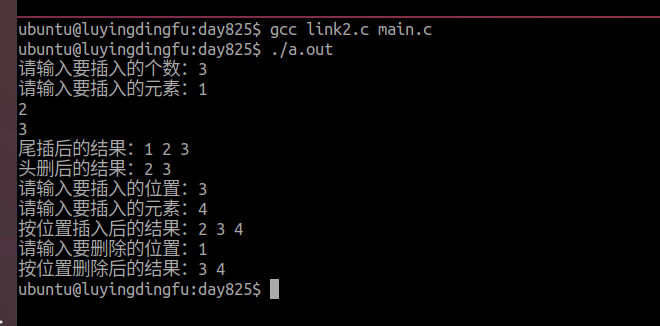
栈
stack.c
#include"stack.h"stack_p create_seq_stack()
{stack_p S = (stack_p)malloc(sizeof(seq_stack));if(S==NULL){printf("申请空间失败\n");return NULL;}S->top = -1; //栈顶位置的初始值bzero(S,sizeof(S->data));return S;
}
//2、将数据压入栈
void push_stack(stack_p S,int value)
{if(S==NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return;}//先加再压//先加栈顶位置,再将元素压入栈S->data[++(S->top)] = value;
}
//3、判空
int empty_stack(stack_p S)
{if(S==NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return -1;}return S->top==-1;
}
//4、判满
int full_stack(stack_p S)
{if(S==NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return -1;}return S->top==MAX-1;
}
//5、弹栈/出栈,需要返回出栈的元素
int pop_stack(stack_p S)
{if(S==NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return -1;}return S->data[S->top--];
}
// 输出栈(从栈顶到栈底)
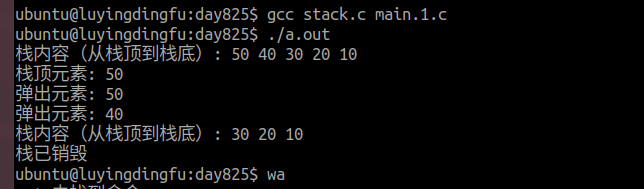
void show_stack(stack_p S)
{if(S == NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return;}if(empty_stack(S)){printf("栈为空,无需输出\n");return;}printf("栈内容(从栈顶到栈底): ");for(int i = S->top; i >= 0; i--){printf("%d ", S->data[i]);}printf("\n");
}// 销毁栈
void destroy_stack(stack_p S)
{if(S == NULL){printf("入参为空,请检查\n");return;}free(S);printf("栈已销毁\n");
}stack.h
#ifndef __STACK_H__
#define __STACK_H__
#include<myhead.h>#define MAX 7typedef struct node
{int data[MAX];int top;
}seq_stack,*stack_p;stack_p create_seq_stack();
void push_stack(stack_p S,int value);
int empty_stack(stack_p S);
int full_stack(stack_p S);
int pop_stack(stack_p S);void show_stack(stack_p S);
void destroy_stack(stack_p S);int peek_stack(stack_p S);#endifmain.1.c
#include"stack.h"
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{stack_p stack = create_seq_stack();// 压入一些元素for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){push_stack(stack, i * 10);}// 显示栈内容show_stack(stack);// 查看栈顶元素printf("栈顶元素: %d\n", peek_stack(stack));// 弹出一些元素printf("弹出元素: %d\n", pop_stack(stack));printf("弹出元素: %d\n", pop_stack(stack));// 再次显示栈内容show_stack(stack);// 销毁栈destroy_stack(stack);return 0;
}
总结顺序表和链表的区别和优缺点
顺序表使用连续内存空间,支持快速随机访问但插入删除效率低;
链表使用非连续内存空间,插入删除高效但只能顺序访问。
顺序表适合查询多、增删少的固定大小场景;链表适合频繁增删、动态变化的场景。
