基于遗传编程的自动程序生成
这里写目录标题
- 核心概念与工作原理
- 1. 个体表示:树结构
- 2. 初始化种群
- 3. 适应度评估
- 4. 选择
- 5. 遗传操作(繁殖)
- 6. 新一代种群形成
- 7. 终止条件
- 基于遗传编程的符号回归示例
- 问题示例
- GP实现符号回归(Deap)
- GP实现符号回归(Pure Python)
- GP典型应用领域
- 遗传编程的关键特点与优势
- 关键特点、挑战与局限性
遗传编程(Genetic Programming, GP)是一种进化计算技术,属于进化算法的一个分支。它的核心思想是模拟达尔文的自然选择过程(“物竞天择,适者生存”)来自动地、进化地在程序空间(或算法空间中)搜索,进而生成计算机程序或数学表达式,以解决特定的问题。简单来说,遗传编程的目标是:让计算机自己“发明”出解决问题的程序或公式,而不是由人类程序员手动编写。
核心概念与工作原理
1. 个体表示:树结构
- GP中的每个“个体”(候选解)是一棵树。
- 节点类型:
- 内部节点(非叶节点):代表函数或运算符。例如:
+,-,*,/,sin,cos,log,if,while等数学、逻辑或程序控制结构。 - 叶节点(终端节点):代表输入变量(如
x,y)、常数(如3.14,5)或无参函数(如随机数生成器)。
- 内部节点(非叶节点):代表函数或运算符。例如:
- 树的含义:从根节点开始,按照树的结构递归地执行内部节点的函数,最终得到一个输出值或执行一系列操作。这棵树就是一个完整的程序或表达式。
- 示例:例如,下图图展示了使用语法树表示程序/函数: max(x+3∗y,x+x)\max(x + 3 * y, x + x)max(x+3∗y,x+x)。对于这棵树以及接下来的示例,树的叶节点(绿色部分)被称为终端节点,而内部节点(红色部分)被称为函数节点(运算符/函数)。终端节点分为两种子类型:常量和参数。常量在整个演化过程中保持不变,而参数是程序的输入。对于上述树结构,参数是变量 xxx 和 yyy,常量是数字 333。
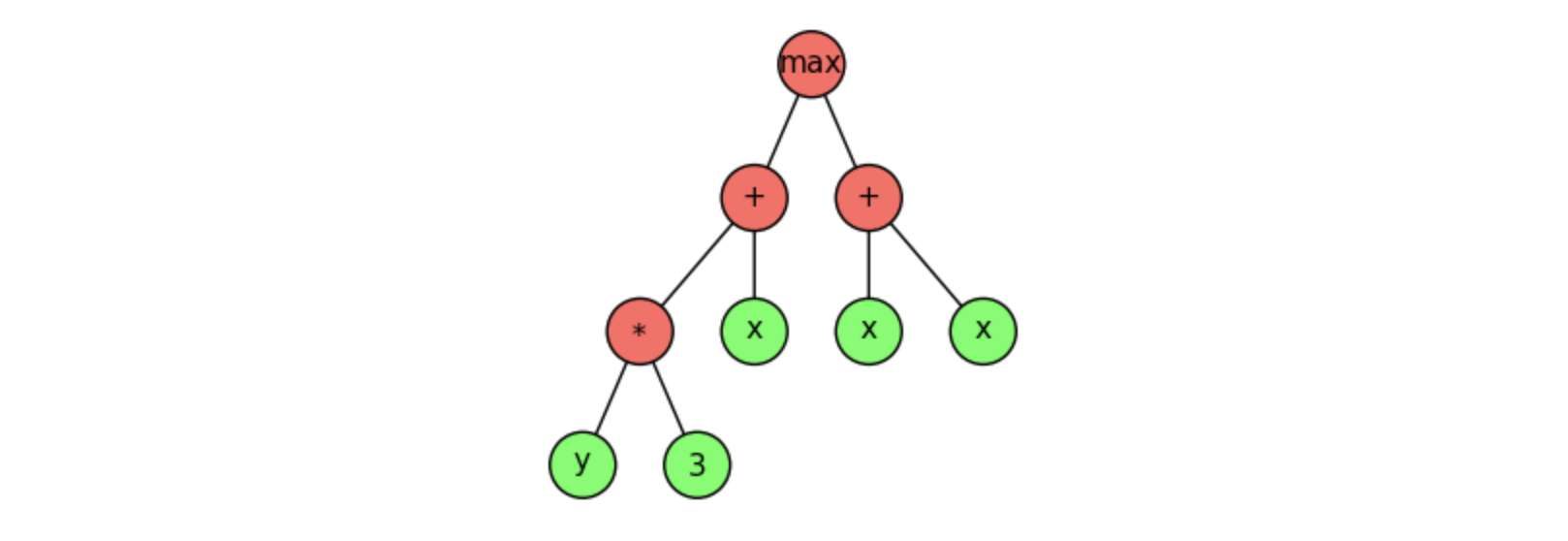
- 示例:例如,下图图展示了使用语法树表示程序/函数: max(x+3∗y,x+x)\max(x + 3 * y, x + x)max(x+3∗y,x+x)。对于这棵树以及接下来的示例,树的叶节点(绿色部分)被称为终端节点,而内部节点(红色部分)被称为函数节点(运算符/函数)。终端节点分为两种子类型:常量和参数。常量在整个演化过程中保持不变,而参数是程序的输入。对于上述树结构,参数是变量 xxx 和 yyy,常量是数字 333。
2. 初始化种群
- 随机生成一个包含大量(例如几百或几千个)不同树结构的初始种群。
- 生成方法通常有:Grow、Full、Ramped half-and-half
3. 适应度评估
- 对种群中的**每一个个体(每一棵树/程序)**进行评估,衡量其解决问题的好坏程度。
- 评估方法取决于具体问题:
- 符号回归:用树计算一组输入数据对应的输出,与目标输出比较(如均方误差MSE)。误差越小,适应度越高。
- 分类问题:用树对数据点进行分类,计算准确率、F1分数等。准确率越高,适应度越高。
- 自动编程/控制:在模拟环境中运行树代表的程序,评估其完成任务的能力(如机器人走迷宫的步数、完成时间)。性能越好,适应度越高。
- 适应度函数是GP成功的关键,它必须准确反映解的质量。
4. 选择
- 根据适应度,从当前种群中选择“父代”个体,用于繁殖下一代。
- 选择策略:
- 轮盘赌选择:适应度高的个体被选中的概率更大。
- 锦标赛选择:随机挑选几个个体,其中适应度最高的胜出。这是最常用、最鲁棒的选择方法。
- 目的:让“好”的解有更多机会将其“基因”(树结构的一部分)传递给下一代。
5. 遗传操作(繁殖)
- 对选出的父代个体应用遗传操作,产生新的子代个体。核心操作是:
- 交叉:
- 从两个父代树中随机各选一个节点(子树)。
- 交换这两个子树。
- 结果是两棵新的子代树,它们分别继承了两个父代的部分结构。
- 这是GP中创造新解的主要方式,模拟生物的基因重组。
- 变异:
- 在单个父代树中随机选择一个节点(子树)。
- 用随机生成的新子树替换掉选中的子树。
- 新子树可以是随机生成的函数或终端节点。
- 目的是引入新的多样性,防止算法陷入局部最优,模拟生物的基因突变。
- 交叉:
- 其他操作:有时也会使用复制(直接复制父代)、排列(交换子节点顺序)等操作。
6. 新一代种群形成
- 将通过遗传操作产生的子代个体组成新的种群。
- 通常会采用精英保留策略:直接将当前种群中适应度最高的少数几个个体(精英)不经操作复制到下一代,确保最优解不会丢失。
7. 终止条件
- 重复步骤3-6(评估、选择、繁殖),直到满足某个终止条件:
- 找到满足精度要求的解。
- 达到预设的最大进化代数。
- 适应度 improvement停滞(长时间没有显著提升)。
- 耗尽计算资源(时间或内存)。
基于遗传编程的符号回归示例
问题示例
遗传编程(GP)在自动程序设计领域的一个经典应用是符号回归(Symbolic Regression),即自动发现拟合数据的数学公式。这是一个例子:假设我们有一组实验数据,描述一个物体在重力作用下的自由落体运动(忽略空气阻力)。我们不知道背后的物理公式,但希望通过GP自动生成一个函数 h = f(t),其中 h 是高度,t 是时间。
观测数据(训练集)
时间 t (秒) | 高度 h (米) |
|---|---|
| 0.0 | 100.0 |
| 1.0 | 95.1 |
| 2.0 | 80.4 |
| 3.0 | 55.9 |
| 4.0 | 21.6 |
真实物理公式(GP需要发现的解):
h(t) = 100 - 4.9 * t²
(其中 100 是初始高度,4.9 是 0.5 * g,g ≈ 9.8 m/s²)
GP自动生成函数的步骤如下:
1. 定义GP组件
-
终端集(Terminals):程序的基本构建块
- 变量:
t(时间) - 常数:随机生成的小数(如
0.5,2.7,4.9…) - 特殊常数:
ERC(Ephemeral Random Constant,在树生成时随机创建,如3.14)
- 变量:
-
函数集(Functions):组合终端的操作
- 算术运算:
+,-,*,/(保护性除法,避免除以0) - 数学函数:
sin,cos,log,exp(可选) - 控制结构:
IF(如IF(t>2 THEN ... ELSE ...))
- 算术运算:
-
适应度函数:评估程序好坏
- 计算预测值与真实值的误差(如均方误差 MSE)
- 适应度 =
1 / (1 + MSE)(值越大越好)
-
遗传操作:
- 交叉:交换两个父代树的子树
- 变异:随机修改节点(如
+→*,或t→5.2)
2. 进化过程示例
初始种群(随机生成):
个体1: (+ t 1.0) # h = t + 1.0
个体2: (* t t) # h = t²
个体3: (- 100 (* t 5.0)) # h = 100 - 5.0*t
个体4: (/ 1.0 t) # h = 1.0/t
适应度计算(以个体2 h = t² 为例):
t | 真实 h | 预测 h=t² | 误差² |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 10000 |
| 1.0 | 95.1 | 1.0 | 8836 |
| 2.0 | 80.4 | 4.0 | 5856 |
| 3.0 | 55.9 | 9.0 | 2209 |
| 4.0 | 21.6 | 16.0 | 31 |
| MSE = (10000+8836+5856+2209+31)/5 = 5386.4 → 适应度 ≈ 0.0002 |
3. 进化迭代(关键步骤)
第1代:
- 选择高适应度个体(如个体3
h=100-5t适应度较高) - 交叉:个体3与个体2交叉 → 生成新个体
(- 100 (* t t))
(即h = 100 - t²,接近真实解!) - 变异:个体1的
+变异为*→(* t 1.0)→h = t
第2代:
-
评估新个体
h = 100 - t²:t真实 h预测 h=100-t²误差² 0.0 100.0 100.0 0 1.0 95.1 99.0 15.2 2.0 80.4 96.0 243 3.0 55.9 91.0 1232 4.0 21.6 84.0 3894 MSE = 1077 → 适应度 ≈ 0.0009(优于初始种群)
第N代:
- 通过持续交叉/变异,可能生成:
(- 100 (* 4.9 (* t t)))
即h = 100 - 4.9 * t²(完美匹配真实公式!) - 此时适应度接近
1.0(误差≈0)
最终生成的函数(代码)
GP输出一个可直接执行的树结构程序:
(-)/ \100 (*)/ \4.9 (*)/ \t t
等价代码(Python函数):
def height(t):return 100 - 4.9 * (t * t)
注:GP 也可能得到 近似表达式/近似解。
总结:遗传编程通过模拟自然进化,实现了从“问题描述”到“可执行程序”的自动化生成,尤其擅长发现人类难以设计的复杂关系或算法。符号回归是其最成功的应用之一,展现了机器自动创造科学定律的潜力。
关键结论:
GP通过**“结构进化 + 参数稠密逼近”** 的双重机制,在实数空间中找到精确值。它不直接搜索4.9,而是进化出能生成4.9的运算组合(如9.8 / 2),同时优化公式结构(如发现t²项)。
GP实现符号回归(Deap)
import operator
import math
import random
import numpy as np
from deap import base, creator, tools, gp, algorithms# --------------------------
# 1. 构造训练数据 (假设真实 h0=100, g=9.8)
# --------------------------
h0 = 1000.0
g = 9.8
X = np.linspace(0, 10, 900) # 时间点
Y = h0 - 0.5 * g * X**2 # 对应高度
print(X)
print(Y)
# --------------------------
# 2. 定义函数集和终端集
# --------------------------
pset = gp.PrimitiveSet("MAIN", 1) # 输入只有一个变量 t
pset.renameArguments(ARG0="t")# 基本运算符
pset.addPrimitive(operator.add, 2)
pset.addPrimitive(operator.sub, 2)
pset.addPrimitive(operator.mul, 2)
# 保护性除法,避免除以零
pset.addPrimitive(lambda x, y: x / y if abs(y) > 1e-6 else 1.0, 2, name="safe_div")# 常量和变量
pset.addTerminal(1.0)
pset.addTerminal(2.0)
pset.addTerminal(3.0)
pset.addTerminal(9.8)
pset.addTerminal(100.0)# --------------------------
# 3. 定义GP个体和适应度
# --------------------------
creator.create("FitnessMin", base.Fitness, weights=(-1.0,)) # 最小化误差
creator.create("Individual", gp.PrimitiveTree, fitness=creator.FitnessMin)toolbox = base.Toolbox()
toolbox.register("expr", gp.genHalfAndHalf, pset=pset, min_=1, max_=3)
toolbox.register("individual", tools.initIterate, creator.Individual, toolbox.expr)
toolbox.register("population", tools.initRepeat, list, toolbox.individual)# --------------------------
# 4. 适应度函数 (MSE)
# --------------------------
def evalSymbReg(individual):func = toolbox.compile(expr=individual)predictions = [func(t) for t in X]mse = np.mean((np.array(predictions) - Y) ** 2)return (mse,)toolbox.register("compile", gp.compile, pset=pset)
toolbox.register("evaluate", evalSymbReg)
toolbox.register("select", tools.selTournament, tournsize=3)
toolbox.register("mate", gp.cxOnePoint) # 子树交叉
toolbox.register("mutate", gp.mutUniform, expr=toolbox.expr, pset=pset)toolbox.decorate("mate", gp.staticLimit(key=len, max_value=20))
toolbox.decorate("mutate", gp.staticLimit(key=len, max_value=20))# --------------------------
# 5. 进化过程
# --------------------------
def main():pop = toolbox.population(n=100)hof = tools.HallOfFame(1) # 保存最优个体stats = tools.Statistics(lambda ind: ind.fitness.values)stats.register("avg", np.mean)stats.register("min", np.min)pop, log = algorithms.eaSimple(pop, toolbox, cxpb=0.5, mutpb=0.2, ngen=40, stats=stats, halloffame=hof, verbose=True)return pop, log, hofif __name__ == "__main__":pop, log, hof = main()print("Best individual:", hof[0])func = toolbox.compile(expr=hof[0])print("Test prediction:", [func(t) for t in [0,1,2,3,4]])pengkangzhen@MacBook-Air demo % poetry run python src/demo/gp/main_deap.py
gen nevals avg min
0 100 9.6654e+07 42582.1
1 58 7.75984e+06 42582.1
2 69 1.08566e+11 20161
3 59 7.14814e+06 20161
4 64 1.07493e+08 20161
5 59 1.33134e+07 37315.2
6 54 1.04653e+08 23750.4
7 53 1.00963e+08 23750.4
8 55 1.00794e+08 11635.4
9 56 7.3922e+06 22018.3
10 52 3.69273e+13 21722.1
11 63 1.89782e+08 21722.1
12 64 2.08932e+08 22018.3
13 55 2.47054e+08 22018.3
14 66 2.60462e+08 22014.8
15 59 3.1163e+09 22018.3
16 58 1.85385e+08 21825
17 63 2.57881e+08 21825
18 56 1.02048e+08 22014.8
19 59 9.92879e+06 5826.42
20 54 9.63558e+07 5826.42
21 66 9.88217e+07 5826.42
22 56 1.73167e+08 5826.42
23 72 6.94483e+06 16582.5
24 68 1.92449e+08 15624.4
25 60 2.90454e+06 15624.4
26 63 7.94306e+07 15105.3
27 67 8.83195e+06 15105.3
28 57 1.67198e+06 14500.4
29 54 2.94928e+06 14500.4
30 50 1.54439e+06 14500.4
31 62 4.33627e+06 10349.1
32 54 3.15992e+06 10349.1
33 63 2.95055e+06 9017.27
34 58 3.387e+06 8804.64
35 59 1.78313e+06 8804.64
36 67 426506 4996.66
37 69 9.47825e+07 5245.22
38 50 2.0105e+08 4732.09
39 63 787600 4732.09
40 74 1.37935e+06 3182.91
Best individual: sub(mul(sub(sub(100.0, mul(t, 3.0)), sub(100.0, sub(100.0, t))), 9.8), mul(sub(t, 9.8), 3.0))
Test prediction: [1009.4000000000001, 967.2, 925.0, 882.8000000000001, 840.6]
pengkangzhen@MacBook-Air demo %
将运行结果中的Best individual进行简化:
989.8 + t - 5.0t²
两次的拟合曲线可视化:
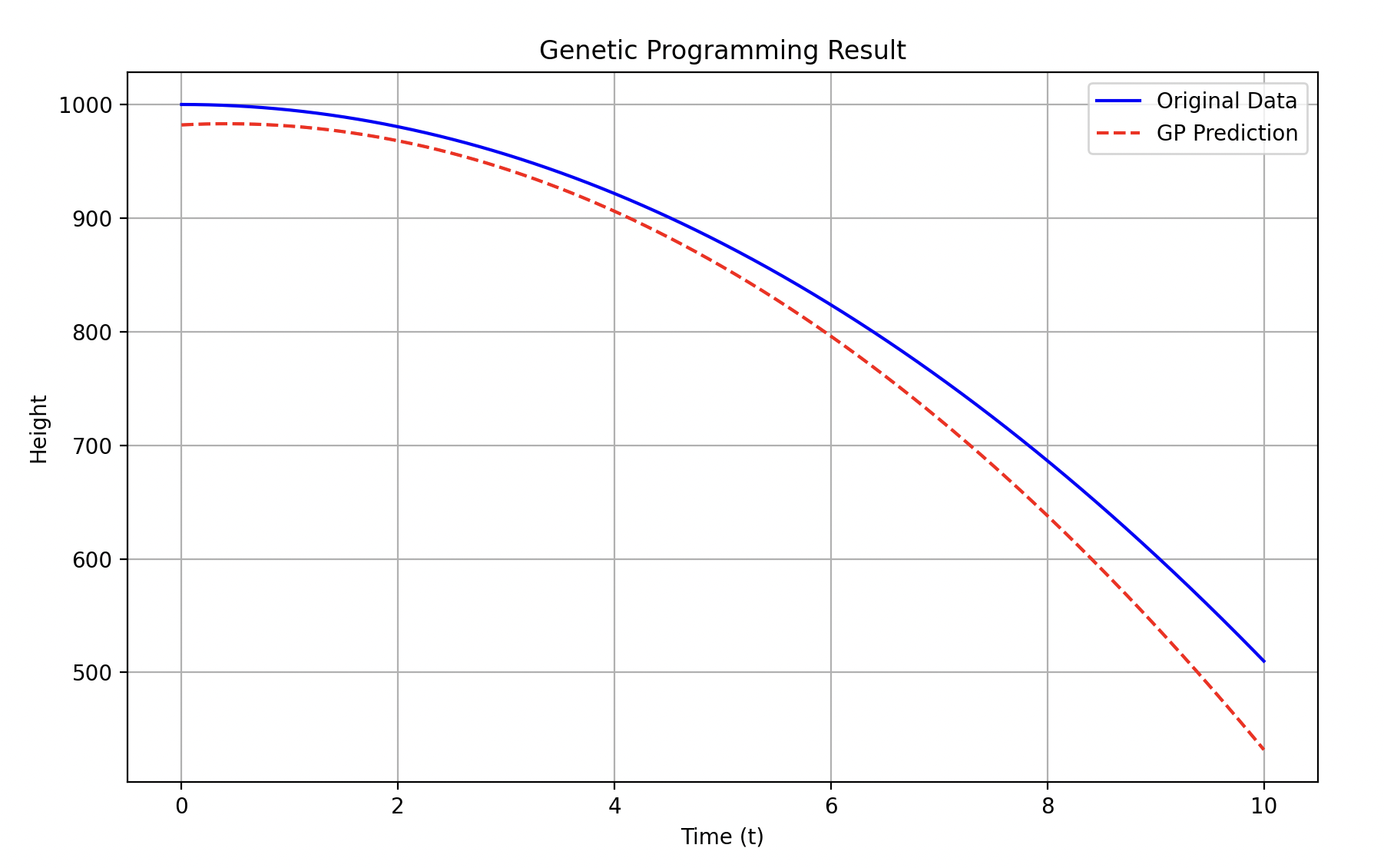
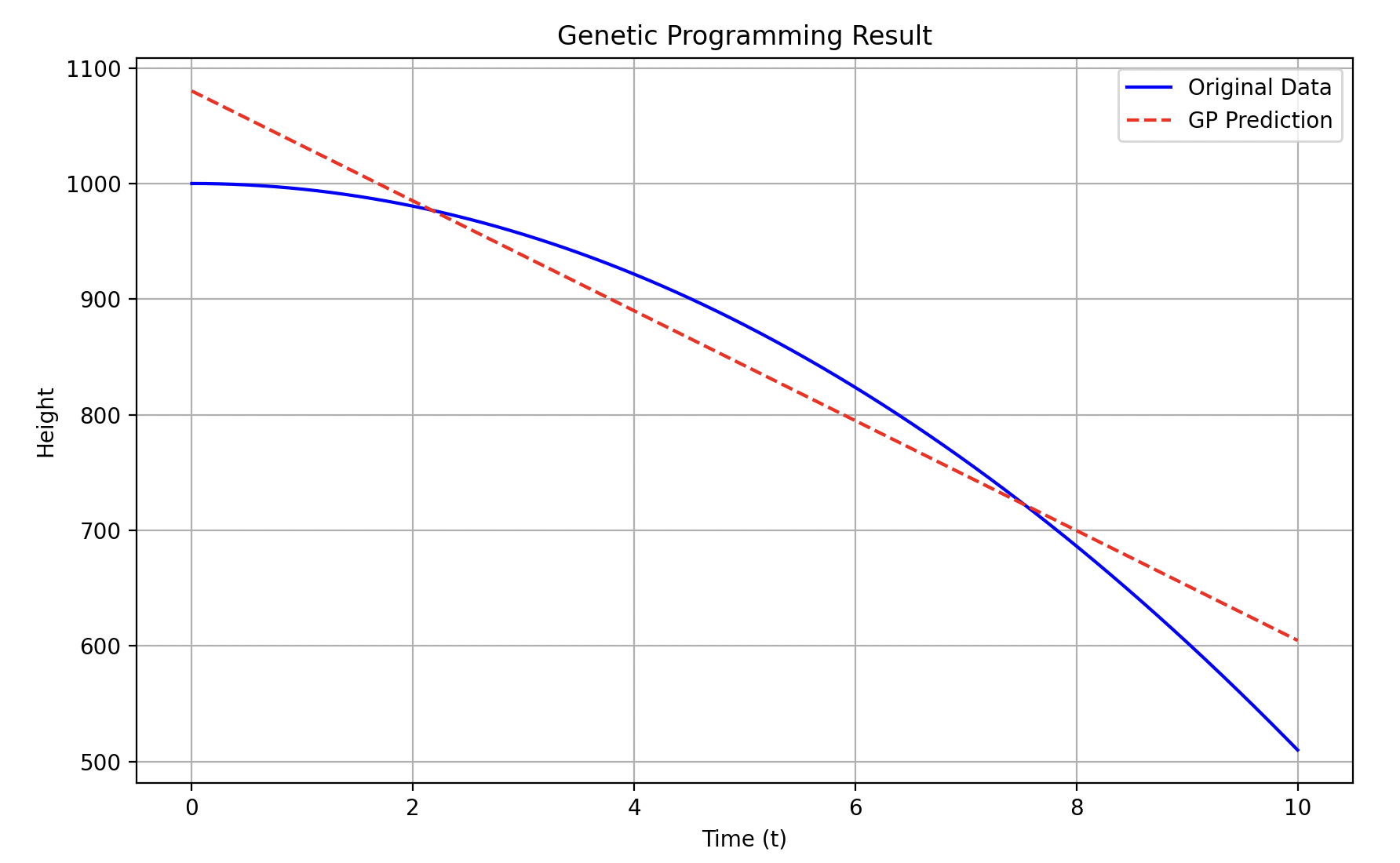
GP实现符号回归(Pure Python)
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
工业级遗传编程(GP)系统
用于拟合自由落体公式 h = h0 - 0.5*g*t^2作者: GP System
版本: 1.0
"""import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import copy
import math
from typing import List, Tuple, Dict, Any, Optional, Callable
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
import warnings
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor
import multiprocessing as mp# 忽略数值警告
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore', category=RuntimeWarning)@dataclass
class GPConfig:"""遗传编程配置类"""population_size: int = 500max_generations: int = 100max_depth: int = 6min_depth: int = 2crossover_prob: float = 0.8mutation_prob: float = 0.2tournament_size: int = 7elitism_size: int = 10parsimony_coefficient: float = 0.001max_evaluations: int = 50000target_fitness: float = 1e-6use_multiprocessing: bool = Truerandom_seed: Optional[int] = Nonedef __post_init__(self):"""配置验证"""if self.population_size <= 0:raise ValueError("种群大小必须大于0")if self.max_generations <= 0:raise ValueError("最大世代数必须大于0")if not 0 <= self.crossover_prob <= 1:raise ValueError("交叉概率必须在[0,1]范围内")if not 0 <= self.mutation_prob <= 1:raise ValueError("变异概率必须在[0,1]范围内")class Node:"""表达式树节点基类"""def __init__(self, value: Any, children: List['Node'] = None):self.value = valueself.children = children or []self.fitness = float('inf')self.depth = 0self.size = 1self._update_properties()def _update_properties(self):"""更新节点属性"""if self.children:self.depth = max(child.depth for child in self.children) + 1self.size = sum(child.size for child in self.children) + 1else:self.depth = 0self.size = 1def copy(self) -> 'Node':"""深拷贝节点"""new_children = [child.copy() for child in self.children]new_node = Node(self.value, new_children)new_node.fitness = self.fitnessreturn new_nodedef evaluate(self, variables: Dict[str, float]) -> float:"""评估节点值"""try:if isinstance(self.value, str):if self.value in variables:return variables[self.value]elif self.value in FUNCTION_SET:func = FUNCTION_SET[self.value]args = [child.evaluate(variables) for child in self.children]return func(*args)else:return 0.0else:return float(self.value)except (ZeroDivisionError, OverflowError, ValueError, TypeError):return float('inf')def to_string(self) -> str:"""转换为字符串表示"""if not self.children:return str(self.value)elif len(self.children) == 1:return f"{self.value}({self.children[0].to_string()})"elif len(self.children) == 2:return f"({self.children[0].to_string()} {self.value} {self.children[1].to_string()})"else:args = ', '.join(child.to_string() for child in self.children)return f"{self.value}({args})"def get_all_nodes(self) -> List['Node']:"""获取所有子节点"""nodes = [self]for child in self.children:nodes.extend(child.get_all_nodes())return nodes# 函数集合定义
def safe_divide(a: float, b: float) -> float:"""安全除法"""if abs(b) < 1e-10:return 1.0return a / bdef safe_sqrt(x: float) -> float:"""安全开方"""return math.sqrt(abs(x))def safe_log(x: float) -> float:"""安全对数"""return math.log(abs(x) + 1e-10)def safe_exp(x: float) -> float:"""安全指数"""try:if x > 700: # 防止溢出return float('inf')return math.exp(x)except OverflowError:return float('inf')def safe_power(a: float, b: float) -> float:"""安全幂运算"""try:if abs(a) < 1e-10 and b < 0:return 1.0if abs(b) > 100: # 防止过大的指数return 1.0return pow(abs(a), b) if a >= 0 else -pow(abs(a), b)except (OverflowError, ValueError):return 1.0# 函数集合
FUNCTION_SET = {'+': lambda a, b: a + b,'-': lambda a, b: a - b,'*': lambda a, b: a * b,'/': safe_divide,'pow': safe_power,'sqrt': safe_sqrt,'log': safe_log,'exp': safe_exp,'sin': math.sin,'cos': math.cos,
}# 终端集合
TERMINAL_SET = ['t', 'const']# 函数元数
FUNCTION_ARITY = {'+': 2, '-': 2, '*': 2, '/': 2, 'pow': 2,'sqrt': 1, 'log': 1, 'exp': 1, 'sin': 1, 'cos': 1
}class TreeGenerator:"""表达式树生成器"""def __init__(self, config: GPConfig):self.config = configself.rng = random.Random(config.random_seed)def generate_random_tree(self, max_depth: int, method: str = 'grow') -> Node:"""生成随机树"""if method == 'grow':return self._grow_method(max_depth)elif method == 'full':return self._full_method(max_depth)else:return self._ramped_half_and_half(max_depth)def _grow_method(self, max_depth: int) -> Node:"""Grow方法生成树"""if max_depth <= 0 or (max_depth > 0 and self.rng.random() < 0.1): # 减少终端概率,鼓励更复杂的树return self._create_terminal()else:return self._create_function(max_depth - 1)def _full_method(self, max_depth: int) -> Node:"""Full方法生成树"""if max_depth <= 0:return self._create_terminal()else:return self._create_function(max_depth - 1)def _ramped_half_and_half(self, max_depth: int) -> Node:"""Ramped half-and-half方法"""if self.rng.random() < 0.5:return self._grow_method(max_depth)else:return self._full_method(max_depth)def _create_terminal(self) -> Node:"""创建终端节点"""if self.rng.random() < 0.7: # 增加变量t的概率return Node('t')else:# 生成常数,偏向于物理意义的值const_value = self.rng.choice([self.rng.uniform(-1000, 1000), # 一般常数self.rng.uniform(0.1, 20), # 小正数(可能是重力加速度相关)self.rng.uniform(0, 2), # 0-2之间(可能是系数)0.5, # 常见系数1.0, # 单位2.0, # 常见系数9.8, # 重力加速度1000.0, # 初始高度])return Node(const_value)def _create_function(self, max_depth: int) -> Node:"""创建函数节点"""func_name = self.rng.choice(list(FUNCTION_SET.keys()))arity = FUNCTION_ARITY[func_name]children = []for _ in range(arity):if max_depth > 0:child = self._grow_method(max_depth)else:child = self._create_terminal()children.append(child)node = Node(func_name, children)node._update_properties()return nodeclass FitnessEvaluator:"""适应度评估器"""def __init__(self, X: np.ndarray, Y: np.ndarray, config: GPConfig):self.X = Xself.Y = Yself.config = configself.evaluation_count = 0def evaluate(self, individual: Node) -> float:"""评估个体适应度"""self.evaluation_count += 1try:predictions = np.array([individual.evaluate({'t': x}) for x in self.X])# 检查无效值if np.any(np.isnan(predictions)) or np.any(np.isinf(predictions)):return 1e10 # 使用大数值而不是无穷大# 限制预测值范围predictions = np.clip(predictions, -1e6, 1e6)# 计算均方误差mse = np.mean((predictions - self.Y) ** 2)# 添加复杂度惩罚(简约性)complexity_penalty = self.config.parsimony_coefficient * individual.sizefitness = mse + complexity_penalty# 确保适应度在合理范围内if not np.isfinite(fitness) or fitness > 1e10:fitness = 1e10fitness = max(fitness, 1e-10) # 避免返回0或负值individual.fitness = fitnessreturn fitnessexcept Exception:return 1e10def batch_evaluate(self, population: List[Node]) -> List[float]:"""批量评估"""fitness_scores = []for individual in population:fitness = self.evaluate(individual)# 确保适应度值在合理范围内fitness = min(fitness, 1e10)fitness_scores.append(fitness)return fitness_scoresdef _parallel_evaluate(self, population: List[Node]) -> List[float]:"""并行评估"""try:with ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers=mp.cpu_count()) as executor:futures = [executor.submit(self._evaluate_individual, ind) for ind in population]results = [future.result() for future in futures]return resultsexcept Exception:# 如果并行失败,回退到串行return [self.evaluate(ind) for ind in population]def _evaluate_individual(self, individual: Node) -> float:"""单个个体评估(用于并行)"""try:predictions = np.array([individual.evaluate({'t': x}) for x in self.X])if np.any(np.isnan(predictions)) or np.any(np.isinf(predictions)):return float('inf')mse = np.mean((predictions - self.Y) ** 2)complexity_penalty = self.config.parsimony_coefficient * individual.sizereturn mse + complexity_penaltyexcept Exception:return float('inf')class SelectionOperator:"""选择算子"""def __init__(self, config: GPConfig):self.config = configself.rng = random.Random(config.random_seed)def tournament_selection(self, population: List[Node]) -> Node:"""锦标赛选择"""tournament = self.rng.sample(population, min(self.config.tournament_size, len(population)))return min(tournament, key=lambda x: x.fitness)def select_parents(self, population: List[Node], num_parents: int) -> List[Node]:"""选择父代"""return [self.tournament_selection(population) for _ in range(num_parents)]class CrossoverOperator:"""交叉算子"""def __init__(self, config: GPConfig):self.config = configself.rng = random.Random(config.random_seed)def subtree_crossover(self, parent1: Node, parent2: Node) -> Tuple[Node, Node]:"""子树交叉"""offspring1 = parent1.copy()offspring2 = parent2.copy()# 获取所有节点nodes1 = offspring1.get_all_nodes()nodes2 = offspring2.get_all_nodes()if len(nodes1) <= 1 or len(nodes2) <= 1:return offspring1, offspring2# 选择交叉点(避免根节点)crossover_point1 = self.rng.choice(nodes1[1:]) if len(nodes1) > 1 else nodes1[0]crossover_point2 = self.rng.choice(nodes2[1:]) if len(nodes2) > 1 else nodes2[0]# 找到父节点并交换子树self._swap_subtrees(offspring1, crossover_point1, crossover_point2)self._swap_subtrees(offspring2, crossover_point2, crossover_point1)# 更新属性offspring1._update_properties()offspring2._update_properties()# 检查深度限制if offspring1.depth > self.config.max_depth:offspring1 = parent1.copy()if offspring2.depth > self.config.max_depth:offspring2 = parent2.copy()return offspring1, offspring2def _swap_subtrees(self, root: Node, old_subtree: Node, new_subtree: Node):"""交换子树"""def find_and_replace(node: Node) -> bool:for i, child in enumerate(node.children):if child is old_subtree:node.children[i] = new_subtree.copy()return Trueif find_and_replace(child):return Truereturn Falsefind_and_replace(root)class MutationOperator:"""变异算子"""def __init__(self, config: GPConfig, tree_generator: TreeGenerator):self.config = configself.tree_generator = tree_generatorself.rng = random.Random(config.random_seed)def subtree_mutation(self, individual: Node) -> Node:"""子树变异"""mutant = individual.copy()nodes = mutant.get_all_nodes()if not nodes:return mutant# 选择变异点mutation_point = self.rng.choice(nodes)# 生成新子树max_depth = min(self.config.max_depth - mutation_point.depth, 3)new_subtree = self.tree_generator.generate_random_tree(max_depth, 'grow')# 替换子树if mutation_point is mutant:return new_subtreeelse:self._replace_subtree(mutant, mutation_point, new_subtree)mutant._update_properties()return mutantdef point_mutation(self, individual: Node) -> Node:"""点变异"""mutant = individual.copy()nodes = mutant.get_all_nodes()if not nodes:return mutantmutation_point = self.rng.choice(nodes)if isinstance(mutation_point.value, (int, float)):# 常数变异mutation_point.value += self.rng.gauss(0, abs(mutation_point.value) * 0.1 + 0.1)elif mutation_point.value in FUNCTION_SET and mutation_point.children:# 函数变异same_arity_functions = [f for f, arity in FUNCTION_ARITY.items() if arity == len(mutation_point.children)]if same_arity_functions:mutation_point.value = self.rng.choice(same_arity_functions)return mutantdef _replace_subtree(self, root: Node, old_subtree: Node, new_subtree: Node):"""替换子树"""def find_and_replace(node: Node) -> bool:for i, child in enumerate(node.children):if child is old_subtree:node.children[i] = new_subtreereturn Trueif find_and_replace(child):return Truereturn Falsefind_and_replace(root)class GPEvolutionEngine:"""遗传编程演化引擎"""def __init__(self, config: GPConfig, X: np.ndarray, Y: np.ndarray):self.config = configself.X = Xself.Y = Y# 初始化组件self.tree_generator = TreeGenerator(config)self.fitness_evaluator = FitnessEvaluator(X, Y, config)self.selection_operator = SelectionOperator(config)self.crossover_operator = CrossoverOperator(config)self.mutation_operator = MutationOperator(config, self.tree_generator)# 统计信息self.generation = 0self.best_fitness_history = []self.avg_fitness_history = []self.best_individual = None# 设置随机种子if config.random_seed is not None:random.seed(config.random_seed)np.random.seed(config.random_seed)def initialize_population(self) -> List[Node]:"""初始化种群"""population = []# 使用ramped half-and-half方法depth_range = range(self.config.min_depth, self.config.max_depth + 1)individuals_per_depth = self.config.population_size // len(depth_range)for depth in depth_range:for _ in range(individuals_per_depth):individual = self.tree_generator.generate_random_tree(depth, 'ramped')population.append(individual)# 补充剩余个体while len(population) < self.config.population_size:depth = random.choice(list(depth_range))individual = self.tree_generator.generate_random_tree(depth, 'ramped')population.append(individual)return populationdef evolve(self) -> Tuple[Node, List[float], List[float]]:"""执行演化过程"""print("初始化种群...")population = self.initialize_population()print("开始演化过程...")for generation in range(self.config.max_generations):self.generation = generation# 评估适应度fitnesses = self.fitness_evaluator.batch_evaluate(population)for ind, fitness in zip(population, fitnesses):ind.fitness = fitness# 排序种群population.sort(key=lambda x: x.fitness)# 更新最佳个体if self.best_individual is None or population[0].fitness < self.best_individual.fitness:self.best_individual = population[0].copy()# 记录统计信息best_fitness = population[0].fitnessvalid_fitnesses = [ind.fitness for ind in population if ind.fitness != float('inf') and ind.fitness <= 1e10]avg_fitness = np.mean(valid_fitnesses) if valid_fitnesses else 1e10self.best_fitness_history.append(min(best_fitness, 1e10))self.avg_fitness_history.append(avg_fitness)# 打印进度if generation % 10 == 0 or generation == self.config.max_generations - 1:print(f"世代 {generation}: 最佳适应度 = {best_fitness:.6f}, 平均适应度 = {avg_fitness:.6f}")print(f"最佳个体: {population[0].to_string()}")# 检查终止条件if best_fitness < self.config.target_fitness:print(f"达到目标适应度,在第 {generation} 世代停止")breakif self.fitness_evaluator.evaluation_count > self.config.max_evaluations:print(f"达到最大评估次数,停止演化")break# 生成下一代new_population = self._create_next_generation(population)population = new_populationreturn self.best_individual, self.best_fitness_history, self.avg_fitness_historydef _create_next_generation(self, population: List[Node]) -> List[Node]:"""创建下一代种群"""new_population = []# 精英保留elite_size = min(self.config.elitism_size, len(population))elites = population[:elite_size]new_population.extend([elite.copy() for elite in elites])# 生成剩余个体while len(new_population) < self.config.population_size:if len(new_population) + 1 < self.config.population_size and random.random() < self.config.crossover_prob:# 交叉操作parent1 = self.selection_operator.tournament_selection(population)parent2 = self.selection_operator.tournament_selection(population)offspring1, offspring2 = self.crossover_operator.subtree_crossover(parent1, parent2)# 变异if random.random() < self.config.mutation_prob:offspring1 = self.mutation_operator.subtree_mutation(offspring1)if random.random() < self.config.mutation_prob:offspring2 = self.mutation_operator.point_mutation(offspring2)new_population.extend([offspring1, offspring2])else:# 仅变异parent = self.selection_operator.tournament_selection(population)if random.random() < 0.5:offspring = self.mutation_operator.subtree_mutation(parent)else:offspring = self.mutation_operator.point_mutation(parent)new_population.append(offspring)# 截断到指定大小return new_population[:self.config.population_size]class GPVisualizer:"""遗传编程可视化器"""def __init__(self, X: np.ndarray, Y: np.ndarray):self.X = Xself.Y = Yplt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei', 'Arial Unicode MS', 'DejaVu Sans']plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = Falsedef plot_fitness_evolution(self, best_fitness: List[float], avg_fitness: List[float]):"""绘制适应度演化图"""# 清理无效值best_fitness_clean = [f if f != float('inf') and not np.isnan(f) else 1e10 for f in best_fitness]avg_fitness_clean = [f if f != float('inf') and not np.isnan(f) else 1e10 for f in avg_fitness]plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)generations = range(len(best_fitness_clean))plt.plot(generations, best_fitness_clean, 'b-', label='最佳适应度', linewidth=2)plt.plot(generations, avg_fitness_clean, 'r--', label='平均适应度', linewidth=1)plt.xlabel('世代')plt.ylabel('适应度')plt.title('适应度演化过程')plt.legend()plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)# 只有当数值合理时才使用对数刻度min_val = min(min(best_fitness_clean), min(avg_fitness_clean))if min_val > 0 and min_val < 1e8:plt.yscale('log')# 绘制最后几代的详细视图plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)if len(best_fitness_clean) > 20:start_gen = len(best_fitness_clean) - 20plt.plot(generations[start_gen:], best_fitness_clean[start_gen:], 'b-', label='最佳适应度', linewidth=2)plt.plot(generations[start_gen:], avg_fitness_clean[start_gen:], 'r--', label='平均适应度', linewidth=1)else:plt.plot(generations, best_fitness_clean, 'b-', label='最佳适应度', linewidth=2)plt.plot(generations, avg_fitness_clean, 'r--', label='平均适应度', linewidth=1)plt.xlabel('世代')plt.ylabel('适应度')plt.title('最后20代适应度详情')plt.legend()plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)plt.tight_layout()plt.show()def plot_fitting_result(self, best_individual: Node, title: str = "拟合结果"):"""绘制拟合结果"""plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))# 生成预测值predictions = np.array([best_individual.evaluate({'t': x}) for x in self.X])# 清理无效预测值valid_mask = np.isfinite(predictions) & ~np.isnan(predictions)if not np.any(valid_mask):print("警告: 所有预测值都无效,跳过可视化")return# 限制预测值范围以避免绘图问题predictions = np.clip(predictions, -1e6, 1e6)# 主图:拟合结果对比plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)plt.scatter(self.X, self.Y, alpha=0.6, color='blue', label='真实数据', s=20)plt.plot(self.X, predictions, 'r-', label='GP拟合', linewidth=2)plt.xlabel('时间 t')plt.ylabel('高度 h')# 截断过长的表达式expr_str = best_individual.to_string()if len(expr_str) > 50:expr_str = expr_str[:47] + "..."plt.title(f'{title}\n最佳个体: {expr_str}')plt.legend()plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)# 残差图plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)residuals = predictions - self.Yresiduals = np.clip(residuals, -1e6, 1e6) # 限制残差范围plt.scatter(self.X, residuals, alpha=0.6, color='green', s=20)plt.axhline(y=0, color='red', linestyle='--', alpha=0.7)plt.xlabel('时间 t')plt.ylabel('残差')plt.title('残差分布')plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)# 预测值 vs 真实值plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)plt.scatter(self.Y, predictions, alpha=0.6, color='purple', s=20)# 安全计算范围y_min, y_max = self.Y.min(), self.Y.max()pred_min, pred_max = np.min(predictions), np.max(predictions)if np.isfinite(pred_min) and np.isfinite(pred_max):min_val = min(y_min, pred_min)max_val = max(y_max, pred_max)plt.plot([min_val, max_val], [min_val, max_val], 'r--', alpha=0.7)plt.xlabel('真实值')plt.ylabel('预测值')plt.title('预测值 vs 真实值')plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)# 统计信息plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)# 安全计算统计指标try:mse = np.mean((predictions - self.Y) ** 2)rmse = np.sqrt(mse) if mse >= 0 else float('inf')mae = np.mean(np.abs(predictions - self.Y))ss_res = np.sum((self.Y - predictions) ** 2)ss_tot = np.sum((self.Y - np.mean(self.Y)) ** 2)r2 = 1 - (ss_res / ss_tot) if ss_tot != 0 else 0# 格式化数值显示mse_str = f"{mse:.6f}" if mse < 1e6 else f"{mse:.2e}"rmse_str = f"{rmse:.6f}" if rmse < 1e6 else f"{rmse:.2e}"mae_str = f"{mae:.6f}" if mae < 1e6 else f"{mae:.2e}"fitness_str = f"{best_individual.fitness:.6f}" if best_individual.fitness < 1e6 else f"{best_individual.fitness:.2e}"except Exception:mse_str = rmse_str = mae_str = fitness_str = "N/A"r2 = 0stats_text = f"""统计指标:
MSE: {mse_str}
RMSE: {rmse_str}
MAE: {mae_str}
R²: {r2:.6f}个体信息:
深度: {best_individual.depth}
大小: {best_individual.size}
适应度: {fitness_str}"""plt.text(0.1, 0.5, stats_text, transform=plt.gca().transAxes, fontsize=10, verticalalignment='center',bbox=dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='lightgray', alpha=0.8))plt.axis('off')plt.tight_layout()plt.show()def main():"""主函数"""print("=" * 60)print("遗传编程系统 - 自由落体公式拟合")print("=" * 60)# 构造训练数据print("\n1. 构造训练数据...")h0 = 1000.0g = 9.8X = np.linspace(0, 10, 100) # 时间点Y = h0 - 0.5 * g * X**2 # 对应高度print(f"数据范围: t ∈ [0, 10], h ∈ [{Y.min():.2f}, {Y.max():.2f}]")print(f"真实参数: h0 = {h0}, g = {g}")print(f"真实公式: h = {h0} - 0.5 * {g} * t²")# 配置GP参数print("\n2. 配置遗传编程参数...")config = GPConfig(population_size=300,max_generations=50,max_depth=6,min_depth=2,crossover_prob=0.8,mutation_prob=0.2,tournament_size=7,elitism_size=5,parsimony_coefficient=0.001,target_fitness=1e-6,use_multiprocessing=True,random_seed=42)print(f"种群大小: {config.population_size}")print(f"最大世代数: {config.max_generations}")print(f"最大树深度: {config.max_depth}")print(f"交叉概率: {config.crossover_prob}")print(f"变异概率: {config.mutation_prob}")# 创建GP引擎print("\n3. 创建遗传编程引擎...")gp_engine = GPEvolutionEngine(config, X, Y)# 执行演化print("\n4. 执行演化过程...")best_individual, best_fitness_history, avg_fitness_history = gp_engine.evolve()# 输出结果print("\n" + "=" * 60)print("演化完成!")print("=" * 60)print(f"最佳个体表达式: {best_individual.to_string()}")print(f"最佳适应度: {best_individual.fitness:.8f}")print(f"个体深度: {best_individual.depth}")print(f"个体大小: {best_individual.size}")print(f"总评估次数: {gp_engine.fitness_evaluator.evaluation_count}")# 计算拟合统计predictions = np.array([best_individual.evaluate({'t': x}) for x in X])mse = np.mean((predictions - Y) ** 2)rmse = np.sqrt(mse)mae = np.mean(np.abs(predictions - Y))r2 = 1 - np.sum((Y - predictions) ** 2) / np.sum((Y - np.mean(Y)) ** 2)print(f"\n拟合统计:")print(f"MSE: {mse:.8f}")print(f"RMSE: {rmse:.8f}")print(f"MAE: {mae:.8f}")print(f"R²: {r2:.8f}")# 可视化结果print("\n5. 生成可视化结果...")visualizer = GPVisualizer(X, Y)# 绘制适应度演化visualizer.plot_fitness_evolution(best_fitness_history, avg_fitness_history)# 绘制拟合结果visualizer.plot_fitting_result(best_individual, "遗传编程拟合自由落体公式")print("\n程序执行完成!")return best_individual, best_fitness_history, avg_fitness_historyif __name__ == "__main__":# 运行主程序best_solution, fitness_history, avg_fitness_history = main()
GP典型应用领域
- 符号回归:这是GP最经典的应用。给定一组输入输出数据点,自动发现拟合这些数据的最佳数学表达式(如物理定律、经验公式)。例如,从行星轨道数据发现开普勒定律。
- 自动编程:生成解决特定任务的小型计算机程序(如排序算法、字符串处理、游戏策略)。
- 机器学习:
- 分类器设计:进化决策树或规则集。
- 特征构造:为其他机器学习算法(如SVM、神经网络)自动创建更有效的输入特征。
- 模型结构优化:进化神经网络的拓扑结构或超参数。
- 控制与优化:设计控制器(如机器人行走路径、倒立摆平衡、无人机飞行策略)、优化工业过程参数。
- 电子设计自动化:进化电路设计(如模拟滤波器、数字逻辑电路)。
- 金融建模:发现交易策略、预测市场趋势、风险评估模型。
- 生物信息学:分析基因序列数据、预测蛋白质结构、发现生物标志物。
遗传编程的关键特点与优势
- 自动程序生成:这是GP最核心、最独特的优势。它能自动发现解决问题的程序结构、算法或数学公式,无需人类预先指定形式。
- 灵活性:树结构可以表示极其复杂的程序、控制流、逻辑和数学表达式,适用范围非常广。
- 解决“黑箱”问题:当问题内在的数学关系或解决方案结构未知时,GP是强大的探索工具。
- 特征工程:在机器学习中,GP可以自动从原始特征中构造出更有预测能力的新特征(即生成新的数学表达式组合特征)。
- 符号可解释性:与神经网络等“黑箱”模型不同,GP最终生成的树结构(程序或公式)通常是人类可读的,便于理解和分析解的内在逻辑(虽然复杂的树也可能难以解读)。
关键特点、挑战与局限性
- 计算开销大:评估大量复杂树结构的适应度通常非常耗时,尤其是当问题涉及模拟或大数据集时。
- 代码膨胀:进化过程中,树的规模(深度、节点数)往往会无限制地增长,导致计算成本剧增和过拟合(解变得过于复杂,泛化能力下降)。需要采用限制树深度、节点数或引入惩罚项等策略来控制。
- 过拟合风险:和所有机器学习方法一样,GP容易在训练数据上表现很好,但在新数据上表现差。需要仔细设计适应度函数(如加入复杂度惩罚)和验证策略。
- 参数敏感:GP的性能对参数设置(种群大小、最大深度、交叉/变异概率、选择压力等)比较敏感,需要调优。
- 结果解释性:虽然树结构本身是符号化的,但进化出的最优解可能非常庞大和复杂,难以被人类完全理解。
- 收敛问题:可能过早收敛到局部最优解,或者收敛速度很慢。
- 随机性:结果具有随机性,多次运行可能得到不同的解。
总结:遗传编程是一种强大的、受生物进化启发的自动化程序合成与问题求解技术。它通过进化代表程序或公式的树结构,利用选择、交叉、变异等操作,在巨大的搜索空间中自动探索和发现高质量的解决方案。其核心优势在于自动发现解的结构,尤其适用于那些解的形式未知或难以手动设计的问题(如符号回归、自动编程、特征工程)。尽管存在计算开销大、膨胀、过拟合等挑战,GP在科学研究、工程优化、机器学习等领域仍展现出独特的价值和潜力,是进化计算领域一个非常重要且活跃的研究方向。
参考:https://deap.readthedocs.io/en/master/tutorials/advanced/gp.html
