Java集合---Collection接口和Map接口
目录
一、Java集合框架概述
二、Collection接口
2.1 List接口(可重复元素)
ArrayList实现类
Vector实现类
LinkedList实现类
2.2 Set接口(不可重复元素)
HashSet
TreeSet
LinkedHashSet
三、Map接口
3.1 HashMap
3.2 Hashtable
3.3 ConcurrentHashMap
一、Java集合框架概述
Java集合框架主要分为三大类:
-
Collection接口 - 存储单个元素的集合
-
Map接口 - 存储键值对的集合
-
队列 - 特殊的集合类型
二、Collection接口
2.1 List接口(可重复元素)
List接口允许存储重复元素,并保持插入顺序。
ArrayList实现类
特点:
-
底层使用数组实现,初始大小为空
-
线程非同步
-
随机访问速度快,增删改相对较慢
// ArrayList示例
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(20);
list1.add(30);
System.out.println("ArrayList元素: " + list1);输出结果:
ArrayList元素: [20, 30]Vector实现类
特点:
-
底层使用数组实现,初始化大小默认为10
-
线程同步(全部锁住)
-
与ArrayList相比性能较低
// Vector示例
Vector<Integer> v1 = new Vector<>();
v1.add(20);
v1.add(30);
System.out.println("Vector元素: " + v1);输出结果:
Vector元素: [20, 30]Vector的线程安全性:
// Vector线程安全测试
public class Test implements Runnable {static Vector<Integer> lists = new Vector<>();CountDownLatch cd;public Test(CountDownLatch cd) {this.cd = cd;}public void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {lists.add(i);}cd.countDown();}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {CountDownLatch cd = new CountDownLatch(3);Test t = new Test(cd);new Thread(t).start();new Thread(t).start();new Thread(t).start();cd.await();System.out.println("最后三个线程的总和为: " + lists.size());}
}输出结果:
最后三个线程的总和为: 300LinkedList实现类
特点:
-
底层使用双向链表实现
-
增删改速度快,随机访问相对较慢
-
可以用迭代器遍历,速度快
public static void main(String[] args) {//LinkedList也可以使用栈的数据结构特点//栈:先进后出,后进先出LinkedList lists =new LinkedList();lists.push(10);lists.push(20);lists.push(30);lists.add(10);lists.add(20);lists.add(30);while(!lists.isEmpty()){System.out.println(lists.pop());}}输出结果:
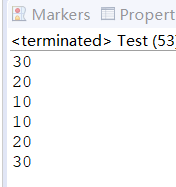
使用迭代器遍历LinkedList:
package com.demo4;import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;public class Test1 {public static void queryData1(LinkedList lists) {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < lists.size(); i++) {// 获取lists.get(i);}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("遍历花费的时间为:" + (endTime - startTime));}public static void queryData2(LinkedList lists) {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//迭代器遍历Iterator its = lists.iterator();while(its.hasNext()){its.next();}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("遍历花费的时间为:" + (endTime - startTime));}public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList lists1 = new LinkedList();for (int i = 0; i < 200000; i++) {lists1.add(i);}//queryData1(lists1);//一般for遍历花费的时间大约30秒queryData2(lists1);//迭代器遍历 遍历花费的时间为:10毫秒}}实现List接口去重:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> lists =new ArrayList<String>();lists.add("花露水");lists.add("花露水");lists.add("茉莉");//List集合本身是不能过滤重复的,现在要实现过滤重复List<String> lists1 =new ArrayList<String>();for(String s:lists){if(!lists1.contains(s)){lists1.add(s);}}System.out.println(lists1);}}输出结果:
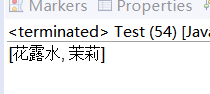
2.2 Set接口(不可重复元素)
Set接口不允许存储重复元素。
HashSet
-
基于HashMap实现
-
不保证顺序
HashSet中自定义对象的去重
必须重写Object类的hashCode和equals方法:
-
hashCode():快速定位,提高查找效率(索引) -
equals():精确比较,确认是否真正相同
下面这段代码的目的是测试和演示HashSet如何判断对象是否重复,并对比了自定义类(User) 和Java内置类(String) 在其中的不同表现。它主要验证了一个关键机制:HashSet 依靠对象的 hashCode() 和 equals() 方法来确保元素的唯一性。
package com.demo6;public class User {public User(int uid, String name) {super();this.uid = uid;this.uname = name;}private int uid;private String uname;public int getUid() {return uid;}public void setUid(int uid) {this.uid = uid;}public String getName() {return uname;}public void setName(String uname) {this.uname = uname;}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {// 重写hashCode()后,哈希码的行为改变了:它现在基于字段值的组合,而不是对象身份。// 因此,只要拼接字符串相同,哈希码就相同,即使对象不同。return (this.uid+this.uname).hashCode();}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object obj) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubif(this == obj){return true;}else if(obj instanceof User){User u =(User)obj;return (this.uid+this.uname).equals(u.uid+u.uname);}return false;}}package com.demo6;import java.util.HashSet;public class Test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {HashSet set1 = new HashSet();User u1 = new User(100,"茉莉");User u2 = new User(100,"茉莉");System.out.println("u1: "+u1.hashCode());System.out.println("u2: "+u2.hashCode());//自定义类型判断重复的算法是由:重写Object类的hashCode的值,通过equals来决定的//在Java中,如果没有重写hashCode()方法,每个对象会使用Object类的默认实现,该实现基于对象的内存地址生成哈希码。//因此,两个不同的对象(即使字段值相同)通常会有不同的哈希码。set1.add(u1);set1.add(u2);//set过滤自定义类型是否重复失效了System.out.println(set1.size());System.out.println("------------------");//String类已经天然正确重写了hashCode()和equals()方法HashSet set2 =new HashSet();String s1 = new String("123");String s2 = new String("123");set2.add(s1);set2.add(s2);//HashSet通过d对String类型的分析:判断了hashCode的值,通过equals判断值System.out.println(set2.size());System.out.println("s1: "+s1.hashCode());System.out.println("s2: "+s2.hashCode());System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));}}输出结果:
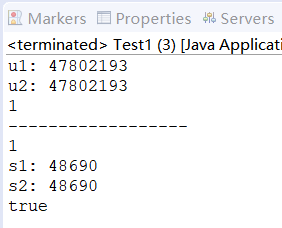
TreeSet
-
基于TreeMap实现
-
元素按自然顺序或自定义比较器排序
下面这段代码的核心目的是演示如何使用TreeSet对中文姓名按拼音首字母进行排序。它利用pinyin4j库将中文转换为拼音,然后基于拼音的首字母来实现自定义的排序规则。
package com.demo7;import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;import net.sourceforge.pinyin4j.PinyinHelper;public class Test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeSet ts = new TreeSet();String name ="花露水"; String[] arrs= PinyinHelper.toHanyuPinyinStringArray(name.substring(0, 1).toCharArray()[0]);System.out.println(arrs[0]);//TreeSet放入元素的时候一定要排序ts.add(new Stu("魔芋爽",48));ts.add(new Stu("鹿鹿",20));ts.add(new Stu("西瓜",18));//System.out.println(ts);Iterator rs = ts.iterator();while(rs.hasNext()){Stu s =(Stu) rs.next();System.out.println(s.getName()+","+s.getAge());}}
}
package com.demo7;import com.mysql.cj.PingTarget;import net.sourceforge.pinyin4j.PinyinHelper;public class Stu implements Comparable {public Stu(String name, int age) {super();this.name = name;this.age = age;}private String name; private int age ;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}// 排序方法 规则由业务决定的// 返回负数:当前对象排在前面 // 返回0:两个对象相等(不会重复添加)// 返回正数:参数对象排在前面public int compareTo(Object o) {// TODO Auto-generated method stub//return ((Stu)o).age- this.age ; // 取姓名的第一个字,转为字符数组取第一个字符,然后取拼音数组的第一个拼音。// 示例:"魔" → ["mo2", "mo4"] → 取"mo2"String currentChar1 =PinyinHelper.toHanyuPinyinStringArray(this.name.substring(0, 1).toCharArray()[0])[0];String currentChar2 =PinyinHelper.toHanyuPinyinStringArray(((Stu)o).name.substring(0, 1).toCharArray()[0])[0];System.out.println("1"+currentChar1);System.out.println("2"+currentChar2);return currentChar1.compareTo(currentChar2);}
}
-
TreeSet会自动对添加的元素进行排序
-
排序规则由Stu类的
compareTo()方法决定 -
这里按姓名首字的拼音字母顺序排序
输出结果:

LinkedHashSet
-
基于LinkedHashMap实现
-
保持插入顺序
package com.demo5;import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedHashSet<String> set = new LinkedHashSet<String>();set.add("one");set.add("two");set.add("three");set.add("four");System.out.println(set);System.out.println("-------------");HashSet<String> set1 = new HashSet<String>();set1.add("one");set1.add("two");set1.add("three");set1.add("four");System.out.println(set1);}}输出结果:

三、Map接口
Map接口是一个存储键值对的集合,每个键对应一个值,键不能重复。
3.1 HashMap
-
线程非同步
-
允许null键和null值
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
// HashMap键和值都可以为null
map1.put(null, null);
map1.put(null, 10); // 键唯一,会覆盖前一个值
System.out.println("Map大小: " + map1.size());
System.out.println("null键的值: " + map1.get(null));输出结果:
Map大小: 1
null键的值: 10遍历方式:
package com.demo1;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;public class Test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap map1 = new HashMap();map1.put("a", "茉莉1");map1.put("b", "茉莉2");map1.put("c", "茉莉3");//单个值 通过key找值System.out.println(map1.get("a"));// 遍历key找值for (Object key : map1.keySet()) {System.out.println("map集合中每个元素的值为:" + map1.get(key));}System.out.println("----------------------");// 找值for (Object value : map1.values()) {System.out.println("map集合中每个元素的值为:" + value);}System.out.println("----------------------");//key和value的Set集合Set<Entry> entrys = map1.entrySet(); for (Entry e : entrys) {System.out.println(e.getKey() + "," + e.getValue());}System.out.println("----------------------");}}
输出结果:

HashMap的线程不安全问题
package com.demo3;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;public class Test {public static void testHashMap(){HashMap<Integer,Integer> maps = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();CountDownLatch cd = new CountDownLatch(100);Lock lock =new ReentrantLock();for(int i= 0;i<100;i++){new MapThread(maps,cd,lock).start();}try {cd.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("HashMap的大小为:"+maps.size());}public static void main(String[] args) {for(int i=0;i<10;i++){testHashMap();}}}package com.demo3;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;public class MapThread extends Thread{HashMap<Integer,Integer> maps;CountDownLatch cd;Lock lock ;public MapThread( HashMap<Integer,Integer> maps , CountDownLatch cd,Lock lock ){this.maps = maps;this.cd =cd;this.lock =lock;}public void run(){for(int i=0;i<100;i++){// synchronized (Thread.class) {
// this.maps.put(i, i);
// }lock.lock();this.maps.put(i, i);lock.unlock();}this.cd.countDown();}}输出结果:
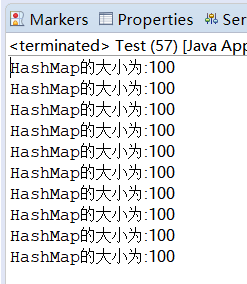
3.2 Hashtable
-
线程安全(所有方法都用synchronized修饰)
-
不允许null键和null值
-
性能较低(全部加锁)
// Hashtable键和值都不能为null
Hashtable map2 = new Hashtable();
// map2.put(null, null); // 会抛出NullPointerException
// map2.put("key", null); // 会抛出NullPointerException3.3 ConcurrentHashMap
-
线程安全(分段锁机制)
-
不允许null键和null值
-
性能优化
ConcurrentHashMap map3 = new ConcurrentHashMap();
// map3.put(null, null); // 会抛出NullPointerException