单例模式与线程池
1. 单例模式
单例模式是一种常用的设计模式,它确保一个类只有一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点来获取这个实例。这种模式在需要控制资源访问、管理共享状态或协调系统行为时非常有用。
单例模式的核心特点:
- 私有构造函数:防止外部通过new关键字创建实例;
- 静态成员函数:提供全局访问点(静态成员函数getInstance());
- 禁止拷贝和赋值:通过delete关键字禁用拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符。
单例模式的应用场景:
- 日志系统:确保所有日志都写入同一个日志文件;
- 配置管理:全局共享一份配置信息;
- 数据库连接池:统一管理数据库连接;
- 设备管理器:如打印机等硬件设备的管理。
需要注意的是,单例模式虽然方便,但也会带来一些问题,如增加代码耦合度、不利于单元测试等,因此在使用时需要权衡利弊。
在 C++ 中,单例模式主要有两种实现方式:饿汉式和懒汉式,它们的核心区别在于实例创建的时机不同。
1.1 饿汉式实现
饿汉式在程序启动时(类加载时)就创建唯一实例,不管后续是否会使用到。
class EagerSingleton {
private:// 私有构造函数,防止外部创建实例EagerSingleton() {}// 禁用拷贝构造和赋值运算EagerSingleton(const EagerSingleton&) = delete;EagerSingleton& operator=(const EagerSingleton&) = delete;// 静态成员变量,程序启动时就初始化static EagerSingleton instance;public:// 提供全局访问点static EagerSingleton& getInstance() {return instance;}
};// 在类外初始化静态成员
EagerSingleton EagerSingleton::instance;饿汉式特点:
- 线程安全:由于实例在程序启动时就创建,不存在多线程竞争问题;
- 可能浪费资源:如果单例从未被使用,也会占用内存;
- 实现简单:不需要考虑线程同步问题。
1.2 懒汉式实现
懒汉式在第一次调用getInstance()方法时才创建实例,实现了 "延迟初始化"。
class LazySingleton {
private:// 私有构造函数LazySingleton() {}// 禁用拷贝构造和赋值运算LazySingleton(const LazySingleton&) = delete;LazySingleton& operator=(const LazySingleton&) = delete;public:// 提供全局访问点,C++11后局部静态变量初始化是线程安全的static LazySingleton& getInstance() {// 第一次调用时才初始化实例static LazySingleton instance;return instance;}
};或者:
class LazySingleton {
private:// 私有构造函数LazySingleton() {}// 私有析构函数~LazySingleton() {instance = nullptr;}// 禁用拷贝构造和赋值运算LazySingleton(const LazySingleton&) = delete;LazySingleton& operator=(const LazySingleton&) = delete;// 使用指针的方式来访问唯一实例static LazySingleton *instance;public:// 此方式无法保证线程安全,应当加锁保护static LazySingleton* const getInstance() {// 第一次调用时才初始化实例if(instance == nullptr)instance = new LazySingleton();return instance;}
};LazySingleton* LazySingleton::instance = nullptr;前者和饿汉式一样,实例在创建之后就不会消失;后者的实例则可以在被销毁之后重新申请。
懒汉式特点:
- 延迟初始化:节省资源,只有在真正需要时才创建实例;
- 线程安全(C++11 及以上):标准保证局部静态变量的初始化是线程安全的;
- 可能影响首次访问性能:第一次调用时需要完成初始化。
1.3 总结
| 饿汉式 | 懒汉式 | |
| 实例创建时机 | 程序启动时 | 首次使用时 |
| 线程安全性 | 天然安全 | C++11 后安全 |
| 资源利用 | 可能浪费 | 更高效 |
| 实现复杂度 | 简单 | 稍复杂(需考虑线程安全) |
实际开发中,懒汉式因为其资源利用效率更高而更常用,尤其是在单例可能不会被使用的场景下。而饿汉式适合在程序启动时就需要初始化的核心组件。
2. 用单例模式设计线程池
2.1 什么是线程池
线程池是一种线程管理机制,它预先创建一定数量的线程,通过复用这些线程来处理多个任务,从而避免频繁创建和销毁线程带来的性能开销,提高系统效率和资源利用率。
线程池包含一个线程队列和一个任务队列:
- 线程队列:存储预先创建的空闲线程,等待处理任务。
- 任务队列:存放待执行的任务,当线程空闲时会从队列中获取任务执行。
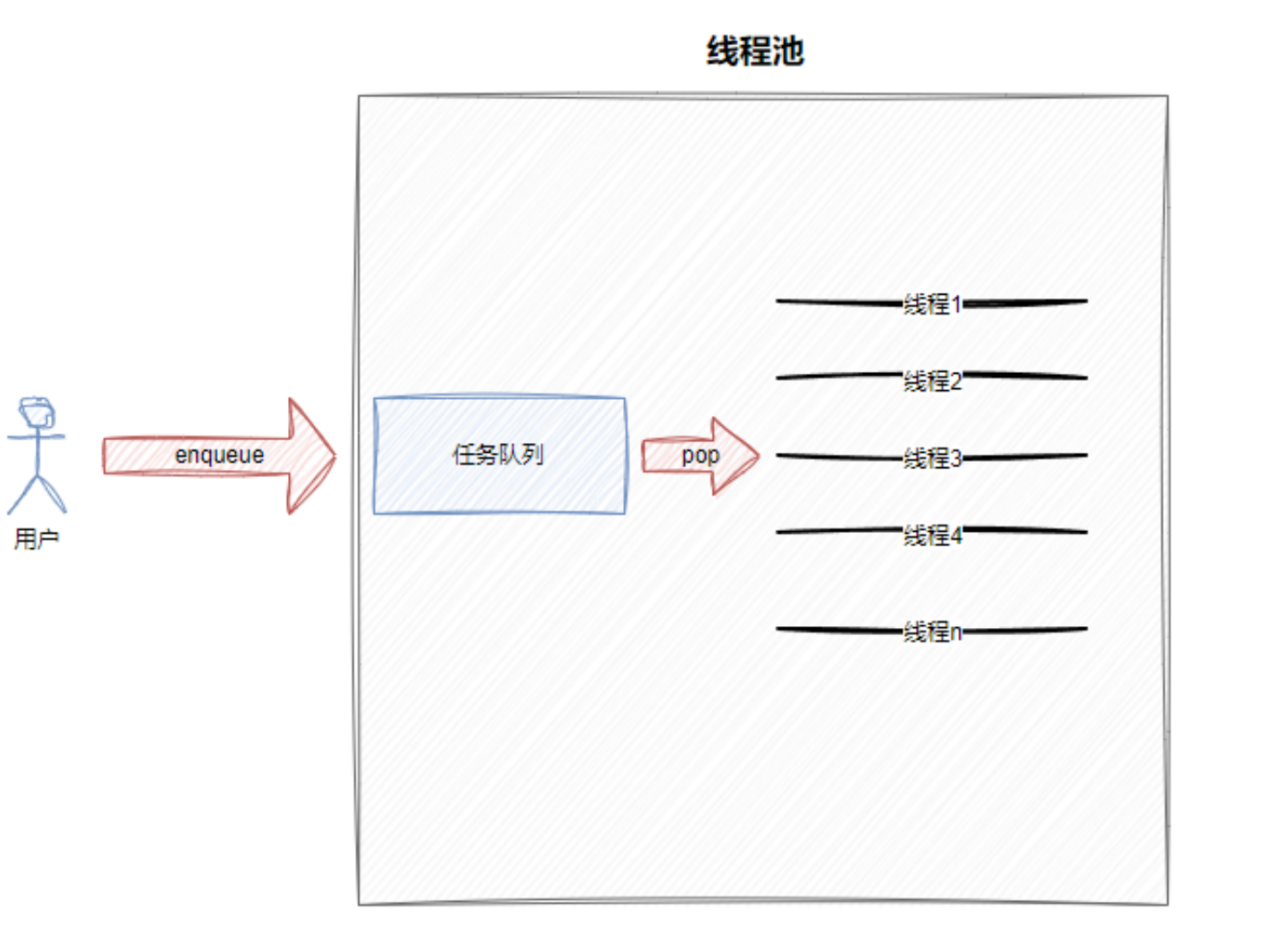
2.2 如何将任务传递给线程
首先,任务队列一定是定义在线程池内部的,我们要使线程访问到任务队列及保护任务队列的锁,就要使这些线程能访问到线程池本身。
所以,我们在线程池内部定义线程的运行函数,即不断循环访问任务队列获取任务:
void ThreadHandler()
{while (true){Task task;{LockGuard lockguard(_queue_mutex);while (_queue.empty() && _isrunning){_not_empty.wait(_queue_mutex);}if (_queue.empty() && !_isrunning)break;task = _queue.front();_queue.pop();}task();}LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "线程[" << Thread::GetMyName() << "]退出...";
}但是直接将该函数传递给线程是不行的。例如,在构造线程时,直接将该函数以及this传过去:
ThreadPool(unsigned int thread_num = default_thread_num): _isrunning(true)
{if (thread_num <= 0)throw ThreadPoolException("线程数量过少!");for (int i = 1; i <= thread_num; i++)_threads.emplace_back("thread-" + std::to_string(i), ThreadHandler, this);
}编译就会出现如下报错:
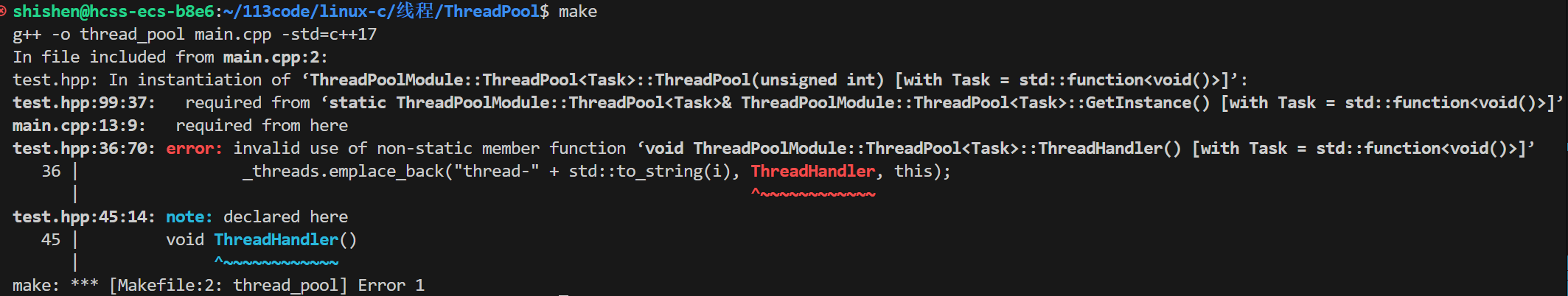
这个编译错误的核心原因是:非静态成员函数(ThreadHandler)不能直接作为函数名传递给线程构造函数。非静态成员函数的调用必须依赖于一个类的实例(this指针),而直接进行传参时,编译器无法自动关联实例,因此判定为 “无效使用非静态成员函数”。
让线程执行非静态成员函数的正确方式是使用lambda表达式捕捉this并包装该函数:
[this] { ThreadHandler();
}然后像这样传参:
_threads.emplace_back("thread-" + std::to_string(i), [this]{ ThreadHandler(); });2.3 懒汉实现1
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include "Mutex.hpp"
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include "Cond.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"using namespace MutexModule;
using namespace ThreadModule;
using namespace CondModule;
using namespace LogModule;namespace ThreadPoolModule
{class ThreadPoolException : public std::runtime_error{public:explicit ThreadPoolException(const std::string &message): std::runtime_error("ThreadPoolException: " + message) {}};static const unsigned int default_thread_num = 6;static const unsigned int default_capacity = 9;template <typename Task>class ThreadPool{private:ThreadPool(unsigned int thread_num = default_thread_num): _isrunning(true){if (thread_num <= 0)throw ThreadPoolException("线程数量过少!");for (int i = 1; i <= thread_num; i++)_threads.emplace_back("thread-" + std::to_string(i), [this]{ ThreadHandler(); });}~ThreadPool(){}ThreadPool(const ThreadPool<Task>&) = delete;ThreadPool<Task>& operator=(const ThreadPool<Task>&) = delete;void ThreadHandler(){while (true){Task task;{LockGuard lockguard(_queue_mutex);while(_queue.empty() && _isrunning){_not_empty.wait(_queue_mutex);}if(_queue.empty() && !_isrunning)break;task = _queue.front();_queue.pop();}task();}LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "线程[" << Thread::GetMyName() << "]退出...";}void Start(){for (auto &thread : _threads)thread.Start();LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "线程池已启动...";}public:void Stop(){_isrunning = false;_not_empty.broadcast();LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "线程池开始停止...";}void Wait(){if(_isrunning)throw ThreadPoolException("等待前线程池未停止!");for (auto &thread : _threads)thread.Join();LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "等待成功, 线程已全部退出...";}void PushTask(const Task &task){if(!_isrunning)throw ThreadPoolException("线程池已停止, 无法继续增加任务!");_queue.push(task);_not_empty.signal();}static ThreadPool<Task>& GetInstance(){static ThreadPool<Task> Instance;Instance.Start();return Instance;}private:bool _isrunning;std::vector<Thread> _threads;std::queue<Task> _queue;Mutex _queue_mutex;Cond _not_empty;};
}2.4 懒汉实现2
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include "Mutex.hpp"
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include "Cond.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"using namespace MutexModule;
using namespace ThreadModule;
using namespace CondModule;
using namespace LogModule;namespace ThreadPoolModule
{class ThreadPoolException : public std::runtime_error{public:explicit ThreadPoolException(const std::string &message): std::runtime_error("ThreadPoolException: " + message) {}};static const unsigned int default_thread_num = 6;static const unsigned int default_capacity = 9;template <typename Task>class ThreadPool{private:ThreadPool(unsigned int thread_num = default_thread_num): _isrunning(true){if (thread_num <= 0)throw ThreadPoolException("线程数量过少!");for (int i = 1; i <= thread_num; i++)_threads.emplace_back("thread-" + std::to_string(i), [this]{ ThreadHandler(); });}~ThreadPool(){_ins = nullptr;}ThreadPool(const ThreadPool<Task>&) = delete;ThreadPool<Task>& operator=(const ThreadPool<Task>&) = delete;void ThreadHandler(){while (true){Task task;{LockGuard lockguard(_queue_mutex);while(_queue.empty() && _isrunning){_not_empty.wait(_queue_mutex);}if(_queue.empty() && !_isrunning)break;task = _queue.front();_queue.pop();}task();}LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "线程[" << Thread::GetMyName() << "]退出...";}void Start(){for (auto &thread : _threads)thread.Start();LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "线程池已启动...";}public:void Stop(){_isrunning = false;_not_empty.broadcast();LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "线程池开始停止...";}void Wait(){if(_isrunning)throw ThreadPoolException("等待前线程池未停止!");for (auto &thread : _threads)thread.Join();delete _ins;LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "等待成功, 线程已全部退出...";}void PushTask(const Task &task){if(!_isrunning)throw ThreadPoolException("线程池已停止, 无法继续增加任务!");_queue.push(task);_not_empty.signal();}static ThreadPool<Task> *const GetInstance(){if (_ins == nullptr){LockGuard lockguard(_mutex);if (_ins == nullptr){try{_ins = new ThreadPool<Task>();}catch (const std::exception &e){std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';}_ins->Start();}}return _ins;}private:bool _isrunning;std::vector<Thread> _threads;std::queue<Task> _queue;static ThreadPool<Task> *_ins;Mutex _queue_mutex;static Mutex _mutex;Cond _not_empty;};template <typename Task>ThreadPool<Task> *ThreadPool<Task>::_ins = nullptr;template <typename Task>Mutex ThreadPool<Task>::_mutex;
}相比较于第一种,第二种可以在调用Stop以及Wait函数之后重新启动。
