Prim算法
一,prim算法逻辑
1.理解:克鲁斯卡尔算法关注的是边,普里姆算法关注的是点
把图中每个顶点比作孤岛,点亮一座孤岛就可以解锁附近的孤岛
每次解锁的点都是离自身最近的点
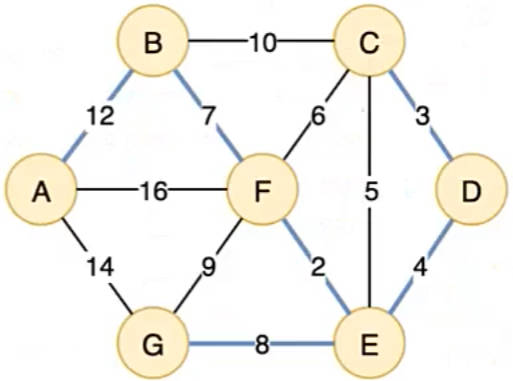
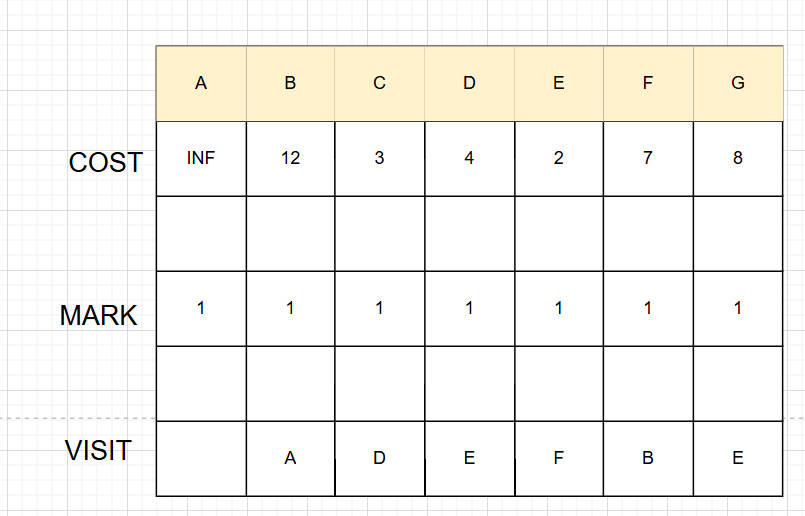
2.普里姆算法流程
a.采用邻接矩阵表示,考虑要查找最小值,初始化不存在的边的值为INF
b.准备工作
cost边的权值数组,保存到该条边的权值
mark标记已访问的点
visit从哪个顶点访问过来的
c.执行操作
任意找到一个激活点,更新三个数组
从cost数组找到权值最小的顶点,激活该顶点
在边集数组中保存visit和当前节点的编号,以及权值
重复c操作
二,代码实现
1.头文件中的接口
//
// Created by 27893 on 2025/8/1.
//#ifndef PRIM_H
#define PRIM_H
#include "common.h"
#include "../MatrixGraph/MatrixGraph.h"int primMGraph(MGraph*graph,int startV,EdgeSet*result);
#endif //PRIM_H
//
// Created by 27893 on 2025/8/1.
//#ifndef COMON_H
#define COMON_H
typedef struct {int begin;int end;int weight;
}EdgeSet;
#endif //COMON_H
2.将头文件中的接口一一实现
//
// Created by 27893 on 2025/8/1.
//#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Prim.h"int primMGraph(MGraph *graph, int startV, EdgeSet *result) {int*cost=malloc(sizeof(int)*graph->nodeNum);int*mark=malloc(sizeof(int)*graph->nodeNum);int*visit=malloc(sizeof(int)*graph->nodeNum);if (cost==NULL||mark==NULL||visit==NULL) {return 0;}int sum=0;//初始化激活startvfor (int i=0;i<graph->nodeNum;i++) {cost[i]=graph->edges[startV][i];mark[i]=0;if (graph->edges[startV][i]<INF) {visit[i]=startV;}else {visit[i]=i;}}mark[startV]=1;for (int i=0;i<graph->nodeNum-1;i++) {//1.在cost找到最小值int k=0,mini=INF;for (int j=0;j<graph->nodeNum;j++) {if (mark[j]==0&&cost[j]<mini) {mini=cost[j];k=j;}}//2.更新边集数组result[i].begin=visit[k];result[i].end=k;result[i].weight=mini;mark[k]=1;sum+=mini;//3.更新cost数组for (int j=0;j<graph->nodeNum;j++) {if (mark[j]==0&&graph->edges[k][j]<cost[j]) {cost[j]=graph->edges[k][j];visit[j]=k;}}}free(cost);free(mark);free(visit);return sum;
}
3,测试是否有bug
//
// Created by 27893 on 2025/7/31.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>#include "Kruskal.h"
#include "Prim.h"void setupMGraph01(MGraph *graph, int edgeValue) {const char *names[] = {"A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G"};initMGraph(graph, names, 7, 0, edgeValue);addMGraph(graph, 0, 1, 12);addMGraph(graph, 0, 5, 16);addMGraph(graph, 0, 6, 14);addMGraph(graph, 1, 2, 10);addMGraph(graph, 1, 5, 7);addMGraph(graph, 2, 3, 3);addMGraph(graph, 2, 4, 5);addMGraph(graph, 2, 5, 6);addMGraph(graph, 3, 4, 4);addMGraph(graph, 4, 5, 2);addMGraph(graph, 4, 6, 8);addMGraph(graph, 5, 6, 9);
}
void test01() {MGraph graph;EdgeSet*edges;int num;EdgeSet*result;int sumweight;setupMGraph01(&graph,0);edges=malloc(sizeof(EdgeSet)*graph.edgeNum);num=initEdgeSet(&graph,edges);printf("edges num:%d\n",num);sortEdgeSet(edges,num);result=malloc(sizeof(EdgeSet)*graph.nodeNum-1);sumweight=kruskalMGraph(&graph,edges,num,result);printf("sumweight:%d\n",sumweight);for (int i=0;i<graph.nodeNum-1;i++) {printf("edges[%d]:%s----%d----%s\n",i+1,graph.vex[result[i].begin].show,result[i].weight,graph.vex[result[i].end].show);}
}
void test02() {MGraph graph;setupMGraph01(&graph,INF);EdgeSet*result;result=malloc(sizeof(EdgeSet)*(graph.nodeNum-1));int sum=primMGraph(&graph,0,result);printf("sumWeight:%d\n",sum);for (int i=0;i<graph.nodeNum-1;i++) {printf("edges[%d]:%s----%d----%s\n",i+1,graph.vex[result[i].begin].show,result[i].weight,graph.vex[result[i].end].show);}
}
int main() {test01();test02();return 0;
}