第1记 cutlass examples 00 的认真调试分析
0. 目标
这一篇似乎是 第0记 的重复,目标不太一样。上一篇是破冰,这篇主要是抓各种 cuda 的细节。为后边讨论更高阶的 cutlass 的原理与应用做好要点铺垫。编译catlass 在上一篇中有详述,这里略过。
再贴一遍 basic_gemm.cu 源码:
// Standard Library includes
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>// Helper methods to check for errors
#include "helper.h"//
// CUTLASS includes needed for single-precision GEMM kernel
//// Defines cutlass::gemm::device::Gemm, the generic Gemm computation template class.
#include "cutlass/gemm/device/gemm.h"///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// This function defines a CUTLASS GEMM kernel instantiation, constructs its parameters object,
// and launches it on the CUDA device.
//
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Define a CUTLASS GEMM template and launch a GEMM kernel.
cudaError_t CutlassSgemmNN(int M,int N,int K,float alpha,float const *A,int lda,float const *B,int ldb,float beta,float *C,int ldc) {// Define type definition for single-precision CUTLASS GEMM with column-major// input matrices and 128x128x8 threadblock tile size (chosen by default).//// To keep the interface manageable, several helpers are defined for plausible compositions// including the following example for single-precision GEMM. Typical values are used as// default template arguments. See `cutlass/gemm/device/default_gemm_configuration.h` for more details.//// To view the full gemm device API interface, see `cutlass/gemm/device/gemm.h`using ColumnMajor = cutlass::layout::ColumnMajor;using CutlassGemm = cutlass::gemm::device::Gemm<float, // Data-type of A matrixColumnMajor, // Layout of A matrixfloat, // Data-type of B matrixColumnMajor, // Layout of B matrixfloat, // Data-type of C matrixColumnMajor>; // Layout of C matrix// Define a CUTLASS GEMM typeCutlassGemm gemm_operator;// Construct the CUTLASS GEMM arguments object.//// One of CUTLASS's design patterns is to define gemm argument objects that are constructible// in host code and passed to kernels by value. These may include pointers, strides, scalars,// and other arguments needed by Gemm and its components.//// The benefits of this pattern are (1.) a structured, composable strategy for passing host-constructible// arguments to kernels and (2.) minimized initialization overhead on kernel entry.//CutlassGemm::Arguments args({M , N, K}, // Gemm Problem dimensions{A, lda}, // Tensor-ref for source matrix A{B, ldb}, // Tensor-ref for source matrix B{C, ldc}, // Tensor-ref for source matrix C{C, ldc}, // Tensor-ref for destination matrix D (may be different memory than source C matrix){alpha, beta}); // Scalars used in the Epilogue//// Launch the CUTLASS GEMM kernel.//cutlass::Status status = gemm_operator(args);//// Return a cudaError_t if the CUTLASS GEMM operator returned an error code.//if (status != cutlass::Status::kSuccess) {return cudaErrorUnknown;}// Return success, if no errors were encountered.return cudaSuccess;
}///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// The source code after this point in the file is generic CUDA using the CUDA Runtime API
// and simple CUDA kernels to initialize matrices and compute the general matrix product.
//
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Kernel to initialize a matrix with small integers.
__global__ void InitializeMatrix_kernel(float *matrix,int rows,int columns,int seed = 0) {int i = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;int j = threadIdx.y + blockIdx.y * blockDim.y;if (i < rows && j < columns) {int offset = i + j * rows;// Generate arbitrary elements.int const k = 16807;int const m = 16;float value = float(((offset + seed) * k % m) - m / 2);matrix[offset] = value;}
}/// Simple function to initialize a matrix to arbitrary small integers.
cudaError_t InitializeMatrix(float *matrix, int rows, int columns, int seed = 0) {dim3 block(16, 16);dim3 grid((rows + block.x - 1) / block.x,(columns + block.y - 1) / block.y);InitializeMatrix_kernel<<< grid, block >>>(matrix, rows, columns, seed);return cudaGetLastError();
}////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Allocates device memory for a matrix then fills with arbitrary small integers.
cudaError_t AllocateMatrix(float **matrix, int rows, int columns, int seed = 0) {cudaError_t result;size_t sizeof_matrix = sizeof(float) * rows * columns;// Allocate device memory.result = cudaMalloc(reinterpret_cast<void **>(matrix), sizeof_matrix);if (result != cudaSuccess) {std::cerr << "Failed to allocate matrix: "<< cudaGetErrorString(result) << std::endl;return result;}// Clear the allocation.result = cudaMemset(*matrix, 0, sizeof_matrix);if (result != cudaSuccess) {std::cerr << "Failed to clear matrix device memory: "<< cudaGetErrorString(result) << std::endl;return result;}// Initialize matrix elements to arbitrary small integers.result = InitializeMatrix(*matrix, rows, columns, seed);if (result != cudaSuccess) {std::cerr << "Failed to initialize matrix: "<< cudaGetErrorString(result) << std::endl;return result;}return result;
}////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Naive reference GEMM computation.
__global__ void ReferenceGemm_kernel(int M,int N,int K,float alpha,float const *A,int lda,float const *B,int ldb,float beta,float *C,int ldc) {int i = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;int j = threadIdx.y + blockIdx.y * blockDim.y;if (i < M && j < N) {float accumulator = 0;for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k) {accumulator += A[i + k * lda] * B[k + j * ldb];}C[i + j * ldc] = alpha * accumulator + beta * C[i + j * ldc];}
}/// Reference GEMM computation.
cudaError_t ReferenceGemm(int M,int N,int K,float alpha,float const *A,int lda,float const *B,int ldb,float beta,float *C,int ldc) {dim3 block(16, 16);dim3 grid((M + block.x - 1) / block.x,(N + block.y - 1) / block.y);ReferenceGemm_kernel<<< grid, block >>>(M, N, K, alpha, A, lda, B, ldb, beta, C, ldc);return cudaGetLastError();
}////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Allocate several matrices in GPU device memory and call a single-precision
/// CUTLASS GEMM kernel.
cudaError_t TestCutlassGemm(int M, int N, int K, float alpha, float beta) {cudaError_t result;//// Define several matrices to be used as operands to GEMM kernels.//// Compute leading dimensions for each matrix.int lda = M;int ldb = K;int ldc = M;// Compute size in bytes of the C matrix.size_t sizeof_C = sizeof(float) * ldc * N;// Define pointers to matrices in GPU device memory.float *A;float *B;float *C_cutlass;float *C_reference;//// Allocate matrices in GPU device memory with arbitrary seeds.//result = AllocateMatrix(&A, M, K, 0);if (result != cudaSuccess) {return result;}result = AllocateMatrix(&B, K, N, 17);if (result != cudaSuccess) {cudaFree(A);return result;}result = AllocateMatrix(&C_cutlass, M, N, 101);if (result != cudaSuccess) {cudaFree(A);cudaFree(B);return result;}result = AllocateMatrix(&C_reference, M, N, 101);if (result != cudaSuccess) {cudaFree(A);cudaFree(B);cudaFree(C_cutlass);return result;}result = cudaMemcpy(C_reference, C_cutlass, sizeof_C, cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice);if (result != cudaSuccess) {std::cerr << "Failed to copy C_cutlass matrix to C_reference: "<< cudaGetErrorString(result) << std::endl;cudaFree(C_reference);cudaFree(C_cutlass);cudaFree(B);cudaFree(A);return result;}//// Launch CUTLASS GEMM.//result = CutlassSgemmNN(M, N, K, alpha, A, lda, B, ldb, beta, C_cutlass, ldc);if (result != cudaSuccess) {std::cerr << "CUTLASS GEMM kernel failed: "<< cudaGetErrorString(result) << std::endl;cudaFree(C_reference);cudaFree(C_cutlass);cudaFree(B);cudaFree(A);return result;}//// Verify.//// Launch reference GEMMresult = ReferenceGemm(M, N, K, alpha, A, lda, B, ldb, beta, C_reference, ldc);if (result != cudaSuccess) {std::cerr << "Reference GEMM kernel failed: "<< cudaGetErrorString(result) << std::endl;cudaFree(C_reference);cudaFree(C_cutlass);cudaFree(B);cudaFree(A);return result;}// Copy to host and verify equivalence.std::vector<float> host_cutlass(ldc * N, 0);std::vector<float> host_reference(ldc * N, 0);result = cudaMemcpy(host_cutlass.data(), C_cutlass, sizeof_C, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);if (result != cudaSuccess) {std::cerr << "Failed to copy CUTLASS GEMM results: "<< cudaGetErrorString(result) << std::endl;cudaFree(C_reference);cudaFree(C_cutlass);cudaFree(B);cudaFree(A);return result;}result = cudaMemcpy(host_reference.data(), C_reference, sizeof_C, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);if (result != cudaSuccess) {std::cerr << "Failed to copy Reference GEMM results: "<< cudaGetErrorString(result) << std::endl;cudaFree(C_reference);cudaFree(C_cutlass);cudaFree(B);cudaFree(A);return result;}//// Free device memory allocations.//cudaFree(C_reference);cudaFree(C_cutlass);cudaFree(B);cudaFree(A);//// Test for bit equivalence of results.//if (host_cutlass != host_reference) {std::cerr << "CUTLASS results incorrect." << std::endl;return cudaErrorUnknown;}return cudaSuccess;
}////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Entry point to basic_gemm example.
//
// usage:
//
// 00_basic_gemm <M> <N> <K> <alpha> <beta>
//
int main(int argc, const char *arg[]) {//// Parse the command line to obtain GEMM dimensions and scalar values.//// GEMM problem dimensions.int problem[3] = { 128, 128, 128 };for (int i = 1; i < argc && i < 4; ++i) {std::stringstream ss(arg[i]);ss >> problem[i - 1];}// Scalars used for linear scaling the result of the matrix product.float scalars[2] = { 1, 0 };for (int i = 4; i < argc && i < 6; ++i) {std::stringstream ss(arg[i]);ss >> scalars[i - 4];}//// Run the CUTLASS GEMM test.//cudaError_t result = TestCutlassGemm(problem[0], // GEMM M dimensionproblem[1], // GEMM N dimensionproblem[2], // GEMM K dimensionscalars[0], // alphascalars[1] // beta);if (result == cudaSuccess) {std::cout << "Passed." << std::endl;}// Exit.return result == cudaSuccess ? 0 : -1;
}///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
1. 通过调试找到全部源代码
找源代码很难么?一般是不难的,cutlass 中还是不容易找到。这里先将这个前置环节搞定,通过调试,把函数都找出来,特别是 实现计算 GEMM 的 cuda kernel 的源代码。
调试开始:
$ cd build/examples/00_basic_gemm/
$ cuda-gdb ./00_basic_gemm启动运行调试:
(cuda-gdb) start在 main 函数中,481 行,我们可以看到一个明显是计算 gemm 的函数,
cudaError_t result = TestCutlassGemm(...)
于是给它打个断点:
(cuda-gdb) b 481进入函数 TestCutlassGemm( ... ) 后,发现 360行的函数是计算 gemm 的,打个断电:
result = CutlassSgemmNN(M, N, K, alpha, A, lda, B, ldb, beta, C_cutlass, ldc);
(cuda-gdb) b 360进入函数 CutlassSgemmNN( ... ) 后,发现 133 行的 cutlass::Status status = gemm_operator(args); 是计算 gemm 的函数,打个断点,c 到此处后step in :
(cuda-gdb) b 133
(cuda-gdb) continue
(cuda-gdb) s发现代码走到了 文件 include/cutlass/gemm/device/gemm.h 的 751 行,operator() 的函数体中存在两个函数:initialize() ; run();
看上去,run 是执行 gemm的的函数:打断点后step in 后,走到了同一个文件的742行 的return underlying_operator_.run(stream); 函数体中。
再 step进函数体中,走到了同一个文件的 473行,这里像是一个真正的业务函数:
/// Runs the kernel using initialized state.Status run(cudaStream_t stream = nullptr) {ThreadblockSwizzle threadblock_swizzle;dim3 grid = threadblock_swizzle.get_grid_shape(params_.grid_tiled_shape);dim3 block(GemmKernel::kThreadCount, 1, 1);cudaError_t result;int smem_size = int(sizeof(typename GemmKernel::SharedStorage));if (smem_size >= (48 << 10)) {result = cudaFuncSetAttribute(Kernel<GemmKernel>,cudaFuncAttributeMaxDynamicSharedMemorySize,smem_size);if (result != cudaSuccess) {return Status::kErrorInternal;}}cutlass::arch::synclog_setup();cutlass::Kernel<GemmKernel><<<grid, block, smem_size, stream>>>(params_);result = cudaGetLastError();return result == cudaSuccess ? Status::kSuccess : Status::kErrorInternal;}
其中cutlass::Kernel<GemmKernel><<<grid, block, smem_size, stream>>>(params_);
使用 cuda 语法启动一个 cuda kernel 函数。
这个函数依然可以 step in 到函数体:
(cuda-gdb) s代码逻辑走进了 文件 include/cutlass/device_kernel.h 的 75 行:
/// Generic CUTLASS kernel template.
template <typename Operator>
CUTLASS_GLOBAL
void Kernel(typename Operator::Params params) {// Dynamic shared memory base pointerextern __shared__ int SharedStorageBase[];// Declare pointer to dynamic shared memory.typename Operator::SharedStorage *shared_storage =reinterpret_cast<typename Operator::SharedStorage *>(SharedStorageBase);Operator op;op(params, *shared_storage);cutlass::arch::synclog_print();
}其中,Operator 的 op 是真正的 gemm 计算的 cuda kernel,但应该是 __device__ 修饰的。
这里我们用 ptype 来查看 Opertor 是什么:
(cuda-gdb) ptype显示如下:
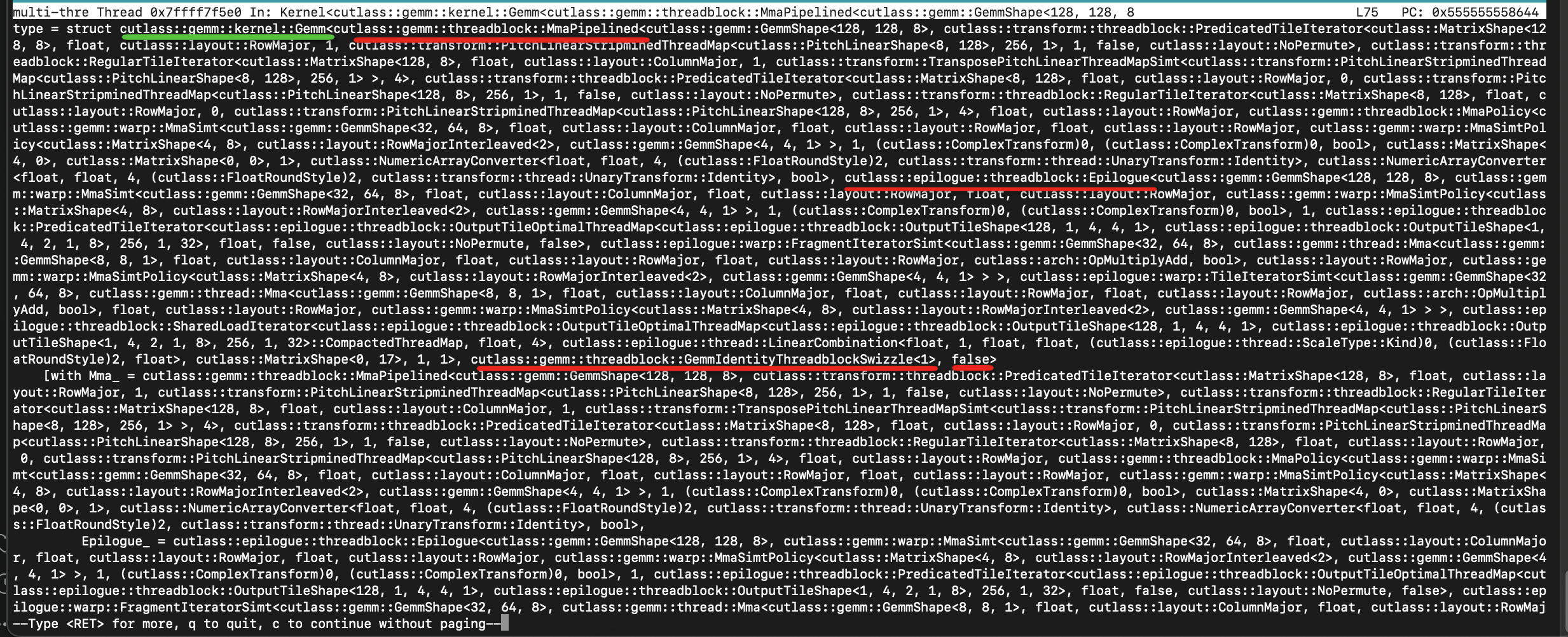
这里只知道 Operator 的类型是 cutlass::gemm::kernel::Gemm<...>,走到这里,并没有帮我们真正找到 cuda kernel 的实现,仅仅知道其名字。
回到 文件 include/cutlass/gemm/device/gemm.h 的 473 行:
cutlass::Kernel<GemmKernel><<<grid, block, smem_size, stream>>>(params_);我们找一下 GemmKernel 的定义:
在相同文件的264 行:
using GemmKernel = typename kernel::DefaultGemm<对 DefaultGemm 右击,在vscode 中,定位到了 文件:include/cutlass/gemm/kernel/default_gemm.h 的 271 行。
struct DefaultGemm<ElementA, LayoutA, kAlignmentA, ElementB, LayoutB, kAlignmentB, ElementC,layout::RowMajor, ElementAccumulator, arch::OpClassTensorOp,arch::Sm89, ThreadblockShape, WarpShape, InstructionShape,EpilogueOutputOp, ThreadblockSwizzle, Stages, SplitKSerial,Operator, SharedMemoryClear, GatherA, GatherB, ScatterD, PermuteDLayout, PermuteALayout, PermuteBLayout> {/// Define the threadblock-scoped matrix multiply-accumulateusing Mma = typename cutlass::gemm::threadblock::DefaultMma<ElementA, LayoutA, kAlignmentA, ElementB, LayoutB, kAlignmentB,ElementAccumulator, layout::RowMajor, arch::OpClassTensorOp, arch::Sm89,ThreadblockShape, WarpShape, InstructionShape, Stages,Operator, false, SharedMemoryClear, GatherA, GatherB,PermuteALayout, PermuteBLayout>::ThreadblockMma;static const int kPartitionsK = ThreadblockShape::kK / WarpShape::kK;/// Define the epilogueusing Epilogue =typename cutlass::epilogue::threadblock::DefaultEpilogueTensorOp<ThreadblockShape, typename Mma::Operator, kPartitionsK, EpilogueOutputOp,EpilogueOutputOp::kCount, ScatterD, PermuteDLayout>::Epilogue;/// Define the kernel-level GEMM operator.using GemmKernel = kernel::Gemm<Mma, Epilogue, ThreadblockSwizzle, SplitKSerial>;
};再对第294行的 Gemm 使用 go to defination,就到了Gemm 的定义,在文件 include/cutlass/gemm/kernel/gemm.h 第59行开始,其中 第 203 行 包含一个 operator()算符,是真正的 cuda kernel的实现:
/// Executes one GEMMCUTLASS_DEVICEvoid operator()(Params const ¶ms, SharedStorage &shared_storage) {// Compute threadblock locationThreadblockSwizzle threadblock_swizzle;cutlass::gemm::GemmCoord threadblock_tile_offset =threadblock_swizzle.get_tile_offset(params.swizzle_log_tile);// Early exit if CTA is out of rangeif (params.grid_tiled_shape.m() <= threadblock_tile_offset.m() ||params.grid_tiled_shape.n() <= threadblock_tile_offset.n()) {return;}// Compute initial location in logical coordinatescutlass::MatrixCoord tb_offset_A{threadblock_tile_offset.m() * Mma::Shape::kM,threadblock_tile_offset.k() * params.gemm_k_size,};cutlass::MatrixCoord tb_offset_B{threadblock_tile_offset.k() * params.gemm_k_size,threadblock_tile_offset.n() * Mma::Shape::kN};// Problem size is a function of threadblock index in the K dimensionint problem_size_k = min(params.problem_size.k(), (threadblock_tile_offset.k() + 1) * params.gemm_k_size);// Compute threadblock-scoped matrix multiply-addint gemm_k_iterations = (problem_size_k - tb_offset_A.column() + Mma::Shape::kK - 1) / Mma::Shape::kK;// Compute position within threadblockint thread_idx = threadIdx.x;// Construct iterators to A and B operandstypename Mma::IteratorA iterator_A(params.params_A,params.ref_A.data(),{params.problem_size.m(), problem_size_k},thread_idx,tb_offset_A,params.gather_A_indices);typename Mma::IteratorB iterator_B(params.params_B,params.ref_B.data(),{problem_size_k, params.problem_size.n()},thread_idx,tb_offset_B,params.gather_B_indices);// Broadcast the warp_id computed by lane 0 to ensure dependent code// is compiled as warp-uniform.int warp_idx = canonical_warp_idx_sync();int lane_idx = threadIdx.x % 32;//// Main loop//// Construct thread-scoped matrix multiplyMma mma(shared_storage.main_loop, thread_idx, warp_idx, lane_idx);typename Mma::FragmentC accumulators;accumulators.clear();if (!kSplitKSerial || gemm_k_iterations > 0) {// Compute threadblock-scoped matrix multiply-addmma(gemm_k_iterations, accumulators, iterator_A, iterator_B, accumulators);}//// Epilogue//OutputOp output_op(params.output_op);//// Masked tile iterators constructed from members//threadblock_tile_offset =threadblock_swizzle.get_tile_offset(params.swizzle_log_tile);//assume identity swizzleMatrixCoord threadblock_offset(threadblock_tile_offset.m() * Mma::Shape::kM,threadblock_tile_offset.n() * Mma::Shape::kN);int block_idx = threadblock_tile_offset.m() + threadblock_tile_offset.n() * params.grid_tiled_shape.m();// Construct the semaphore.Semaphore semaphore(params.semaphore + block_idx, thread_idx);// If performing a reduction via split-K, fetch the initial synchronizationif (kSplitKSerial && params.grid_tiled_shape.k() > 1) {// Fetch the synchronization lock initially but do not block.semaphore.fetch();// Indicate which position in a serial reduction the output operator is currently updatingoutput_op.set_k_partition(threadblock_tile_offset.k(), params.grid_tiled_shape.k());}// Tile iterator loading from source tensor.typename Epilogue::OutputTileIterator iterator_C(params.params_C,params.ref_C.data(),params.problem_size.mn(),thread_idx,threadblock_offset,params.scatter_D_indices);// Tile iterator writing to destination tensor.typename Epilogue::OutputTileIterator iterator_D(params.params_D,params.ref_D.data(),params.problem_size.mn(),thread_idx,threadblock_offset,params.scatter_D_indices);Epilogue epilogue(shared_storage.epilogue, thread_idx, warp_idx, lane_idx);// Wait on the semaphore - this latency may have been covered by iterator constructionif (kSplitKSerial && params.grid_tiled_shape.k() > 1) {// For subsequent threadblocks, the source matrix is held in the 'D' tensor.if (threadblock_tile_offset.k()) {iterator_C = iterator_D;}semaphore.wait(threadblock_tile_offset.k());}// Execute the epilogue operator to update the destination tensor.epilogue(output_op, iterator_D, accumulators, iterator_C); //// Release the semaphore//if (kSplitKSerial && params.grid_tiled_shape.k() > 1) {int lock = 0;if (params.grid_tiled_shape.k() == threadblock_tile_offset.k() + 1) {// The final threadblock resets the semaphore for subsequent grids.lock = 0;}else {// Otherwise, the semaphore is incrementedlock = threadblock_tile_offset.k() + 1;}semaphore.release(lock);}}调试部分先到此为止,接下来我们分析这个 operator () 的主题逻辑。
2. operator() 逻辑路线
2.1. 一般的gemm 逻辑思路
写个gemm:
2.2. operator() 的逻辑思路
未完待续
。。。。
