Linux Ansible的安装与基本使用
Ansible 自动化介绍
Ansible 自动化介绍
手动执行任务和自动化执行任务
手动执行任务缺点:
- 很容易遗漏某个步骤或错误地执行某个步骤。 步骤是否正确执行或产生预期的结果的验证通常有限。
- 管理大量服务器很容易会出现差异,加大维护的难度,并给IT环境带来错误或不稳定性。
自动化执行任务优点:
- 通过标准化,确保快速、正确地部署和配置所有系统。
- 自动执行日常计划重复性任务,从而空出时间并专注于更重要的事情。
- 更快速的交付应用。
基础架构即代码
-
良好的自动化系统允许实施基础架构即代码方法。**基础架构即代码意味着可以使用机器可读的自动化语言来定义和描述IT基础架构所处的状态。**理想情况下,这种自动化语言也应该非常便于人类阅读,因为这样就可以轻松了解所处的状态并对其进行更改。
-
如果自动化语言使用简单文本文件表示,还可以使用版本控制系统管理。 这样做的好处是每个更改都可以嵌入到版本控制系统中,可以获得随时间所做更改的历史记录,可以将系统恢复到更早的配置。这样就奠定了一个遵循DevOps的基础。开发人员可以在自动化语言中定义所需的配置。操作员可以更轻松地查看这些更改以提供反馈,并使用该自动化可重复地确保系统处于开发人员期望的状态。
Ansible 与 DevOps
百度百科:DevOps(Development 和 Operations 的组合词)是一组过程、方法与系统的统称,用于促进开发(应用程序/软件工程)、技术运营和质量保障(QA)部门之间的沟通、协作与整合。它是一种重视“软件开发人员(Dev)”和“IT运维技术人员(Ops)”之间沟通合作的文化、运动或惯例。透过自动化“软件交付”和“架构变更”的流程,来使得构建、测试、发布软件能够更加地快捷、频繁和可靠。
DevOps的关键在于 communication(沟通和交流)。
Ansible是第一款可以在整个IT范围读取和编写的自动化语言,也是唯一能够从头至尾自动化应用生命周期和持续交付管道的自动化引擎。
什么是 ANSIBLE?
Ansible is a simple automation language,通过Playbooks描述和配置IT基础架构。
Ansible可以管理强大的自动化任务,适用于不同的生产环境。同时,Ansible对于新用户来说,也可以很快的上手运用到生产环境。
使用案例:
- OpenStack 搭建和维护
- OpenShift 搭建和维护
- ceph 搭建和维护
Ansible 特点
-
简单:Ansible Playbooks 是一个人们非常容易查阅,理解和更改的文本文件,用户不需要具备特定的代码编写技能。
-
功能强大:可以使用Ansible部署应用,例如配置管理,工作流自动化,网络自动化。还可用于编排整个应用生命周期。
-
无代理:Ansible 是一个无代理的架构,通过OpenSSH或者WinRM连接到hosts,并执行任务,推送小的程序(Ansible modules)到这些主机上。这些程序用于设置系统到预期状态。在Ansible执行完成后,任何之前推送的模块,都会被删除。Ansible可以随时使用,因为被管理主机上不需要配置特定代理。正是因为这点,Ansible 才更加高效和安全。
-
跨平台支持:可以管理Linux、UNIX、windows 和网络设备。
-
非常准确地描述应用:Ansible Playbook使用YAML格式描述生产环境。
-
可以通过版本控制管理:Ansible Playbooks和projects是纯文本格式,可以当作源码存放在版本控制系统中。
-
非常容易与其他系统集成: HP SA,Puppet,Jenkins,红帽卫星服务器等。
Ansible 概念和架构
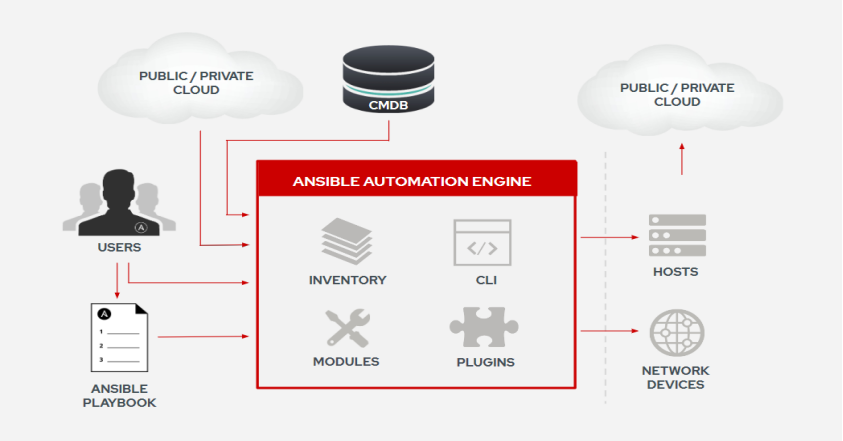
- NODES:Ansible架构中有两种计算机类型:
- 控制节点,安装有ansible软件的节点。
- 受管节点,被ansible管理的Linux系统、Windows系统、网络设备等。
- INVENTORY:受管主机清单。
- PLAYBOOK:Ansible用户只需要编写playbook,确保主机是预期状态。
- 每个playbook可以包含多个play。
- 每个play会在一组hosts上按顺序执行一系列tasks。
- 每个task都执行一个模块,模块是一个小的代码段(Python,PowerShell,或者其他语言)。Ansible自带几百个模块,执行不同类型自动化任务,例如操作系统文件,安装软件,API调用。Tasks,plays和Playbooks是 idempotent(幂等的),在相同的主机上多次安全地执行Playbooks,让主机是正确的状态。如果主机已经是预期状态,则Playbook不会做任何改变。
- PLUGINS,添加到Ansible中的代码段,用于扩展Ansible平台。
Ansible Way
- Complexity Kills Productivity(复杂性会破坏效率),越简单越好。Ansible的设计宗旨是工具易用,自动化易写易读,所以在创建自动化时尽可能地追求简单化。
- Optimize For Readability(专为易读性优化),Ansible自动化语言围绕简单易读的声明性文本文件来构建。正确编写的Ansible Playbook可以清楚地记录您的工作流自动化。
- Think Declaratively(声明式思维),Ansible是一种要求状态引擎。它通过表达您希望系统处于何种状态来解决如何自动化IT部署的问题。Ansible的目标是通过仅执行必要的更改,使您的系统处于所需的状态。
Ansible 用例
- 配置管理:集中化配置文件管理和部署是Ansible的常见用例,很多高级用户也是通过这种方式了解Ansible自动化平台。
- 应用部署:通过Ansible定义应用,以及使用红帽Ansible Tower管理部署时,各团队可以更加有效地管理从开发到生产的整个应用生命周期。
- 工作流管理:Ansible 和红帽Ansible Tower有助于简化调配系统的流程,不论您是要PXE引导和kickstart安装裸机恢复服务器或虚拟机,还是从模板创建虚拟机或云实例。
- 持续交付:创建CI/CD管道需要多个团队的协调和参与。如果没有组织内人人可用的简单自动化平台,就无法实现这个目标。Ansible Playbook让您的应用可以在整个生命周期内得到正确部署(和管理)
- 安全性和合规性:当您在Ansible Playbook中定义安全策略时,也可以将扫描和修复整站安全策略集成到其他自动化流程中。确保安全应该是您所有部署中不可或缺的组成部分,而不是事后才去考虑的部分。
- 编排:仅配置本身不足以定义您的环境,您还需定义多个配置间就应如何交互,并确保以整体的方式管理各类分散资源。
Ansible 部署
准备实验环境
实验环境 /etc/hosts
10.1.8.10 controller.wsh.cloud controller
10.1.8.11 node1.wsh.cloud node1
10.1.8.12 node2.wsh.cloud node2
10.1.8.13 node3.wsh.cloud node3
10.1.8.14 node4.wsh.cloud node4
配置控制节点 wsh 用户使用wsh用户免密登录所有节点,并免提sudo提权执行任何命令。
# 所有节点配置/etc/hosts
[root@all-node ~]# cat >> /etc/hosts <<EOF################# ansible #################
10.1.8.10 controller.wsh.cloud controller
10.1.8.11 node1.wsh.cloud node1
10.1.8.12 node2.wsh.cloud node2
10.1.8.13 node3.wsh.cloud node3
10.1.8.14 node4.wsh.cloud node4
EOF# 所有节点添加用户
[root@all-node ~]# useradd wsh
[root@all-node ~]# echo redhat | passwd --stdin wsh# 所有节点,配置免密提权
[root@all-node ~]# echo 'wsh ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL' > /etc/sudoers.d/wsh# 创建密钥对
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ [ -d ~/.ssh ] || mkdir -m 700 .ssh
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -f .ssh/id_rsa -N ''# 推送公钥到目标主机
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ sudo yum install -y sshpass
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ for host in controller node{1..4}
do sshpass -p redhat ssh-copy-id wsh@$host
done# 验证免密登录
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ for host in controller node{1..4}
do ssh wsh@$host hostname
done
controller.wsh.cloud
node1.wsh.cloud
node2.wsh.cloud
node3.wsh.cloud
node4.wsh.cloud
控制节点
控制节点即用来安装 Ansible 软件的主机节点。控制节点可以是一个或多个,由 ansible 管理的主机不用安装 Ansible。
提示:控制节点是Linux或UNIX系统,不支持 Windows 作为控制节点。
安装 ansible
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ sudo yum install -y ansible
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --version
ansible 2.9.27config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfgconfigured module search path = [u'/home/wsh/.ansible/plugins/modules', u'/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansibleexecutable location = /usr/bin/ansiblepython version = 2.7.5 (default, Jun 28 2022, 15:30:04) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44)]
受管节点
Linux
受管节点满足的要求取决于控制节点连接它们的方式以及它们要运行的模块:
- Python 版本:Linux和UNIX受管节点需要安装Python才能运行大部分的模块。
- 一些模块不需要Python。例如,raw模块的参数直接通过配置的远程shell运行,在没有Python环境的设备上使用。不过,raw模块难以通过安全的幂等方式使用。
Windows
Ansible随附了多个专门为Microsoft Windows系统设计的模块。这些模块列在Ansible模块索引的Windows Modules 部分。
大部分专门为Microsoft Windows受管节点设计的模块需要在受管节点上:
- 安装 Power Shell 3.0或更高版本。
- 配置 Power Shell 远程连接。
- 安装.NET Framework 4.0或更高版本。
本课程的示例中使用基于Linux的受管节点,不会深入阐述管理基于Microsoft Windows的受管节点时的具体差别和必要调整。可以在Ansible网站上查看更多信息。
网络设备
还可以使用Ansible自动化来配置受管网络设备,例如路由器和交换机。Ansible包含大量专门为此目的而设计的模块。其中包括对Cisco IOS、IOSXR和NX-OS的支持;Juniper Junos;AristaEOS;以及基于VyOS的网络设备等。
由于大多数网络设备无法运行Python,因此Ansible在控制节点上运行网络模块,而不是在受管节点上运行。特殊连接方法也用于与网络设备通信,通常使用SSH上的CLI、SSH上的XML或HTTP(S)上的API。
由器和交换机。Ansible包含大量专门为此目的而设计的模块。其中包括对Cisco IOS、IOSXR和NX-OS的支持;Juniper Junos;AristaEOS;以及基于VyOS的网络设备等。
由于大多数网络设备无法运行Python,因此Ansible在控制节点上运行网络模块,而不是在受管节点上运行。特殊连接方法也用于与网络设备通信,通常使用SSH上的CLI、SSH上的XML或HTTP(S)上的API。
Ansible 基本使用
Ansible 清单
Ansible 软件包中文件
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ rpm -ql ansible
- 配置文件目录 /etc/ansible
- 执行文件目录 /usr/bin
- lib依赖库目录 /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible
- 插件 /usr/share/ansible/plugins
- Help文档目录 /usr/share/doc/ansible
- Man文档目录 /usr/share/man/man1/
主机清单
Inventory 定义Ansible将要管理的一批主机。这些主机也可以分配到组中,以进行集中管理 组可以包含子组,主机也可以是多个组的成员。清单还可以设置应用到它所定义的主机和组的变量。
通过以下方式定义主机清单:
- 静态主机清单: 以文本文件的方式来定义。
- 动态主机清单: 使用外部信息提供程序通过脚本或其他程序来自动生成。目的是从启动环境中获取主机清单,例如openstack、kubernetes、zabbix等。
静态主机清单
主机清单支持多种格式,例如ini、yaml、脚本等。
本次课程使用 ini 格式。
最简单的静态清单
受管节点的主机名或IP地址的列表,每行一个。
示例:
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ vim inventory
web1.example.com
web2.example.com
db1.example.com
db2.example.com
192.0.2.42
验证主机是否在inventory中
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory web1.example.comhosts (1):web1.example.com
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory 192.0.2.42hosts (1):192.0.2.42
ansible命令通过–inventory PATHNAME或-i PATHNAME选项在命令行中指定清单文件的位置,其中PATHNAME是所需清单文件的路径。
主机组
还可以将受管节点组织为主机组。通过主机组,更加有效地对一系列系统运行Ansible。
格式:
[groupname]
hostname
hostip
示例:
app1.example.com[webservers]
web1.example.com
web2.example.com[dbservers]
db1.example.com
db2.example.com
192.0.2.42192.0.2.43
验证:
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory webservershosts (2):web1.example.comweb2.example.com# 注意:192.0.2.43属于dbservers组
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory dbservershosts (4):db1.example.comdb2.example.com192.0.2.42192.0.2.43
有两个组总是存在的:
- all:包含inventory中所有主机。
- ungrouped:inventory中列出的,但不属于任何组的主机。
验证:
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory allhosts (7):app1.example.comweb1.example.comweb2.example.comdb1.example.comdb2.example.com192.0.2.42192.0.2.43
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory ungroupedhosts (1):app1.example.com
根据需要,将主机分配在多个组中,例如根据主机的角色、其物理位置以及是否在生产环境中等因素。
[webservers]
web1.example.com
web2.example.com
192.168.3.7[dbservers]
db1.example.com
db2.example.com
192.0.2.42[eastdc]
web1.example.com
db1.example.com[westdc]
web2.example.com
db2.example.com
验证:
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory webservershosts (3):web1.example.comweb2.example.com192.168.3.7
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory eastdchosts (2):web1.example.comdb1.example.com
主机组嵌套
一个主机组还可以属于另外一个主机组。
示例:
[eastdc]
web1.example.com
db1.example.com[westdc]
web2.example.com
db2.example.com[dc:children]
eastdc
westdc
验证:
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory dchosts (4):web1.example.comdb1.example.comweb2.example.comdb2.example.com
子组中的主机组必须定义,否则会出现语法上的报错。
示例:
[eastdc]
web1.example.com
db1.example.com[westdc]
web2.example.com
db2.example.com[dc:children]
eastdc
westdc
node1
验证:
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory dc[WARNING]: * Failed to parse /home/laoma/inventory with yaml plugin: Syntax
Error while loading YAML. did not find expected <document start> The error
appears to be in '/home/laoma/inventory': line 2, column 1, but may be elsewhere
in the file depending on the exact syntax problem. The offending line appears to
be: [eastdc] web1.example.com ^ here[WARNING]: * Failed to parse /home/laoma/inventory with ini plugin:
/home/laoma/inventory:12: Section [dc:children] includes undefined group:
node1[WARNING]: Unable to parse /home/laoma/inventory as an inventory source[WARNING]: No inventory was parsed, only implicit localhost is available[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note that
the implicit localhost does not match 'all'hosts (4):web1.example.comdb1.example.comweb2.example.comdb2.example.com
范围简写
通过指定主机名称或IP地址的范围来简化Ansible主机清单。您可以指定数字或字母范围。
语法:[start:end]
示例:
# 代表192.168.4.0-192.168.7.255
[priv]
192.168.[4:7].[0:255]#代表01,02...20
[hosts]
host[01:20].example.com# 代表a b c
[servers]
server[a:c].example.com
验证:
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory hostshosts (20):host01.example.comhost02.example.com
......host19.example.comhost20.example.com[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory privhosts (1024):192.168.4.0192.168.4.1192.168.4.2
......192.168.7.253192.168.7.254192.168.7.255[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory servershosts (3):node1.example.comnode2.example.comserverc.example.com
以下是错误的范围示例:
[servers]
server[0a:2c].example.com
验证:
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible --list-hosts -i inventory all[WARNING]: * Failed to parse /home/laoma/inventory with yaml plugin: Syntax
Error while loading YAML. did not find expected <document start> The error
appears to be in '/home/laoma/inventory': line 2, column 1, but may be elsewhere
in the file depending on the exact syntax problem. The offending line appears to
be: [servers] server[0a:2c].example.com ^ here[WARNING]: * Failed to parse /home/laoma/inventory with ini plugin: invalid
literal for int() with base 10: '0a'[WARNING]: Unable to parse /home/laoma/inventory as an inventory source[WARNING]: No inventory was parsed, only implicit localhost is available[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note that
the implicit localhost does not match 'all'hosts (0):
动态主机清单
使用外部数据提供的信息动态生成Ansible清单信息。
本课程内容不做进一步讨论。
ansible-inventory 命令
通过不同的格式查看清单文件。
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible-inventory --help
Usage: ansible-inventory [options] [host|group]Options:--ask-vault-pass ask for vault password--export When doing an --list, represent in a way that isoptimized for export,not as an accurate representationof how Ansible has processed it-h, --help show this help message and exit-i INVENTORY, --inventory=INVENTORY, --inventory-file=INVENTORYspecify inventory host path or comma separated hostlist. --inventory-file is deprecated--output=OUTPUT_FILE When doing an --list, send the inventory to a fileinstead of of to screen--playbook-dir=BASEDIRSince this tool does not use playbooks, use this as asubstitute playbook directory.This sets the relativepath for many features including roles/ group_vars/etc.--toml Use TOML format instead of default JSON, ignored for--graph--vars Add vars to graph display, ignored unless used with--graph--vault-id=VAULT_IDS the vault identity to use--vault-password-file=VAULT_PASSWORD_FILESvault password file-v, --verbose verbose mode (-vvv for more, -vvvv to enableconnection debugging)--version show program's version number, config file location,configured module search path, module location,executable location and exit-y, --yaml Use YAML format instead of default JSON, ignored for--graphActions:One of following must be used on invocation, ONLY ONE!--list Output all hosts info, works as inventory script--host=HOST Output specific host info, works as inventory script--graph create inventory graph, if supplying pattern it mustbe a valid group nameShow Ansible inventory information, by default it uses the inventory script
JSON format
示例清单:
app1.example.com[webservers]
web1.example.com
web2.example.com
192.168.3.7[dbservers]
db1.example.com
db2.example.com
192.0.2.42[eastdc]
web1.example.com
db1.example.com[westdc]
web2.example.com
db2.example.com[dc:children]
eastdc
westdc
验证:
# 树形结构显示
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible-inventory -i inventory --graph
@all:|--@dbservers:| |--192.0.2.42| |--db1.example.com| |--db2.example.com|--@dc:| |--@eastdc:| | |--db1.example.com| | |--web1.example.com| |--@westdc:| | |--db2.example.com| | |--web2.example.com|--@ungrouped:| |--app1.example.com|--@webservers:| |--192.168.3.7| |--web1.example.com| |--web2.example.com# yaml格式显示
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ ansible-inventory -i inventory --list -y
all:children:dbservers:hosts:192.0.2.42: {}db1.example.com: {}db2.example.com: {}dc:children:eastdc:hosts:db1.example.com: {}web1.example.com: {}westdc:hosts:db2.example.com: {}web2.example.com: {}ungrouped:hosts:app1.example.com: {}webservers:hosts:192.168.3.7: {}web1.example.com: {}web2.example.com: {}
管理 ANSIBLE 配置文件
配置文件位置和优先级
- 环境变量 ANSIBLE_CONFIG
- ./ansible.cfg,当前位置中的 ansible.cfg,当前位置一般是项目目录。
- ~/.ansible.cfg
- /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
从上到下,优先级越来越低。
建议:在当前目录下定义ansible.cfg文件。
验证优先级:
# 环境准备
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ mkdir web && cd web# 查看ansible命令当前使用的配置文件
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible --version
ansible 2.9.27config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfgconfigured module search path = [u'/home/wsh/.ansible/plugins/modules', u'/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansibleexecutable location = /usr/bin/ansiblepython version = 2.7.5 (default, Jun 28 2022, 15:30:04) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44)]
# 或者
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible --version | grep 'config file'config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg[wsh@controller web ✔]$ touch ~/.ansible.cfg
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible --version | grep 'config file'config file = /home/wsh/.ansible.cfg[wsh@controller web ✔]$ touch ansible.cfg
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible --version | grep 'config file'config file = /home/wsh/web/ansible.cfg[wsh@controller web ✔]$ export ANSIBLE_CONFIG=/opt/ansible.cfg
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ sudo touch /opt/ansible.cfg
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible --version | grep 'config file'config file = /opt/ansible.cfg
配置文件解析
ansible 默认配置文件 /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg。
Ansible 配置文件包括以下部分:
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ grep "^\[" /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
[defaults]
[inventory]
[privilege_escalation]
[paramiko_connection]
[ssh_connection]
[persistent_connection]
[accelerate]
[selinux]
[colors]
[diff]
常用参数解析如下:
[defaults]
# inventory 指定清单文件路径
inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts# 并发执行同一个任务的主机数量
forks = 5# ansible检查任务是否执行完成的时间间隔
poll_interval = 15# 连接登录到受管主机时是否提示输入密码
ask_pass = True# 控制facts如何收集
# smart - 如果facts已经收集过了,就不收集了。
# implicit - facts收集,剧本中使用gather_facts: False关闭facts收集。
# explicit - facts不收集,剧本中使用gather_facts: True关闭facts收集。
gathering = implicit# 收集facts范围
# all - gather all subsets
# network - gather min and network facts
# hardware - gather hardware facts (longest facts to retrieve)
# virtual - gather min and virtual facts
# facter - import facts from facter
# ohai - import facts from ohai
# You can combine them using comma (ex: network,virtual)
# You can negate them using ! (ex: !hardware,!facter,!ohai)
# A minimal set of facts is always gathered.
gather_subset = all# 收集facts超时时间
gather_timeout = 10# 变量注入,通过ansible_facts引用
inject_facts_as_vars = True# 定义角色路径,以冒号分隔
roles_path = /etc/ansible/roles# SSH是否检验 host key
host_key_checking = False# 连接登录到受管主机时使用的用户身份
remote_user = root# ansible 命令和ansible-playbook 命令输出内容存放位置
log_path = /var/log/ansible.log# ansible 命令默认模块
module_name = command# ssh 私钥文件位置
private_key_file = /path/to/file# 默认ansible-vault命令的密码文件
vault_password_file = /path/to/vault_password_file# 定义ansible_managed变量值
ansible_managed = Ansible managed# 剧本执行过程中,遇到未定义的变量不报错
error_on_undefined_vars = False# 系统告警启用
system_warnings = True# 下架告警启用
deprecation_warnings = True# 使用command和shell模块时,是否提示告警
command_warnings = False# facts保存在哪里,例如redis
fact_caching = memory[inventory]
# 启用的清单插件, 默认为: 'host_list', 'script', 'auto', 'yaml', 'ini', 'toml'
#enable_plugins = host_list, virtualbox, yaml, constructed# 当清单源是一个目录的时候,忽略这些后缀的清单文件
#ignore_extensions = .pyc, .pyo, .swp, .bak, ~, .rpm, .md, .txt, ~, .orig, .ini, .cfg, .retry[privilege_escalation]
# 连接到受管主机后是否需要进行权限提升或切换用户
become=True# 使用何种方式进行用户切换或提权
become_method=sudo# 用户切换或提权后的对应用户
become_user=root# 进行用户切换或提权时是否提示输入密码
become_ask_pass=False
说明:“#” 和 ";"开头的行,作为注释。
配置文件示例
对于基本操作, 使用 [defaults] 和 [privilege_escalation] 即可。
配置文件示例
[defaults]
inventory = ./inventory
#ask_pass = True
remote_user = wsh
#module_name = command[privilege_escalation]
become=True
become_method=sudo
become_user=root
become_ask_pass=False
最终效果:
[[wsh@controller web ✔]app]$ ansible all -a id
node3 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
node2 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
node1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
node4 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
ansible-config 命令
用于分析ansible命令的配置。
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible-config -h
usage: ansible-config [-h] [--version] [-v] {list,dump,view} ...View ansible configuration.positional arguments:{list,dump,view}list Print all config optionsdump Dump configurationview View configuration fileoptional arguments:--version show program's version number, config file location,configured module search path, module location, executablelocation and exit-h, --help show this help message and exit-v, --verbose verbose mode (-vvv for more, -vvvv to enable connectiondebugging)
ansible-config view
查看当前ansible配合文件内容。
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible --version | grep 'config file'config file = /home/wsh/web/ansible.cfg[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible-config view
[defaults]
inventory = ./inventory
#ask_pass = True
remote_user = wsh
#module_name = command[privilege_escalation]
become=True
become_method=sudo
become_user=root
become_ask_pass=False
ansible-config dump
当前ansible生效的所有配置,包括所有默认值。
[[wsh@controller web ✔]]$ ansible-config dump
ACTION_WARNINGS(default) = True
AGNOSTIC_BECOME_PROMPT(default) = True
ALLOW_WORLD_READABLE_TMPFILES(default) = False
......
DEFAULT_HOST_LIST(/home/wsh/web/ansible.cfg) = [u'/home/wsh/web/inventory']
......
DEFAULT_REMOTE_USER(/home/wsh/web/ansible.cfg) = wsh
......
ansible-config list
查看所有配置参数用途,配置位置等。
ACTION_WARNINGS:default: truedescription: [By default Ansible will issue a warning when received from a taskaction (module or action plugin), These warnings can be silenced by adjustingthis setting to False.]env:- {name: ANSIBLE_ACTION_WARNINGS}ini:- {key: action_warnings, section: defaults}name: Toggle action warningstype: booleanversion_added: '2.5'
AGNOSTIC_BECOME_PROMPT:default: truedescription: Display an agnostic become prompt instead of displaying a prompt containingthe command line supplied become methodenv:- {name: ANSIBLE_AGNOSTIC_BECOME_PROMPT}
localhost 连接
默认Ansible连接到受管主机的协议为 smart (通常采用最有效的方式 - SSH)。如本地清单中并未指定localhost,Ansible会隐式设置localhost,并使用local连接类型连接localhost。
- local连接类型会忽略remote_user的设置,并且直接在本地系统上运行命令。
- 如果使用了特权提升,此时ansible将会在运行sudo时使用运行Ansible命令的账户的身份进行提权,而非remote_user所指定的账户。
更改 localhost 连接方式:清单中包涵 localhost。
运行 AD HOC 命令
实验环境
[wsh@controller ~ ✔]$ mkdir web && cd web[[wsh@controller web ✔]]$ cat > ansible.cfg <<'EOF'
[defaults]
remote_user = laoma
inventory = ./inventory[privilege_escalation]
become = True
become_user = root
become_method = sudo
become_ask_pass = False
EOF[[wsh@controller web ✔]]$ cat > inventory <<'EOF'
[controllers]
controller[nodes]
node[1:4]
EOF
ansible AD HOC 命令
命令作用:
-
快速执行单个Ansible任务,而不需要将它保存下来供以后再次运行。它们是简单的在线操作,无需编写playbook即可运行。
-
快速测试和更改很有用。 例如,您可以使用临时命令确保一组服务器上的/ etc/hosts文件中存在某一特定的行。您可以使用另一个临时命令在许多不同的计算机上高效重启一项服务,或者确保特定的软件包为最新版本。
命令语法:
ansible host-pattern -m module [-a 'module arguments'] [-i inventory]
- host-pattern,是inventory中定义的主机或主机组,可以为ip、hostname、inventory中的group组名、具有“,”或“*”或“:”等特殊字符的匹配型字符串,是必选项。
- -m module,module是一个小程序,用于实现具体任务。
- -a ‘module arguments’,是模块的参数。
- -i inventory,指定inventory文件。
命令执行结果颜色说明:
Ansible的返回结果都非常友好,用3种颜色来表示执行结果:
- 红色:表示执行过程有异常,一般会中止剩余所有的任务。
- 绿色:表示目标主机已经是预期状态,不需要更改 。
- 黄色:表示命令执行结束后目标有状态变化,并设置为预期状态,所有任务均正常执行。
Ansible 部分模块
Ansible 模块存放位置:/usr/lib/python*/site-packages/ansible
官网:模块清单。
- 文件模块
- copy: 将控制主机上的文件复制到受管节点,类似于scp
- file: 设置文件的权限和其他属性
- lineinfile: 确保特定行是否在文件中
- synchronize: 使用 rsync 将控制主机上的文件同步到受管节点
- 软件包模块
- package: 自动检测操作系统软件包管理器
- yum: 使用 YUM 软件包管理器管理软件包
- apt: 使用 APT 软件包管理器管理软件包
- gem: 管理 Rubygem
- pip: 从 PyPI 管理 Python 软件包
- 系统模块
- ansible.posix.firewalld : 使用firewalld管理任意端口和服务
- reboot: 重新启动计算机
- service: 管理服务
- user、group: 管理用户和组帐户
- NetTools模块
- get_url: 通过HTTP、HTTPS或FTP下载文件
- nmcli: 管理网络
- uri: 与 Web 服务交互
ansible-doc 命令
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible-doc -h
usage: ansible-doc [-h] [--version] [-v] [-M MODULE_PATH][--playbook-dir BASEDIR][-t {become,cache,callback,cliconf,connection,httpapi,inventory,lookup,netconf,shell,module,strategy,vars}][-j] [-F | -l | -s | --metadata-dump][plugin [plugin ...]]plugin documentation toolpositional arguments:plugin Pluginoptional arguments:--metadata-dump **For internal testing only** Dump json metadata forall plugins.--playbook-dir BASEDIRSince this tool does not use playbooks, use this as asubstitute playbook directory.This sets the relativepath for many features including roles/ group_vars/etc.--version show program's version number, config file location,configured module search path, module location,executable location and exit-F, --list_files Show plugin names and their source files withoutsummaries (implies --list)-M MODULE_PATH, --module-path MODULE_PATHprepend colon-separated path(s) to module library (default=~/.ansible/plugins/modules:/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules)-h, --help show this help message and exit-j, --json Change output into json format.-l, --list List available plugins-s, --snippet Show playbook snippet for specified plugin(s)-t {become,cache,callback,cliconf,connection,httpapi,inventory,lookup,netconf,shell,module,strategy,vars}, --type {become,cache,callback,cliconf,connection,httpapi,inventory,lookup,netconf,shell,module,strategy,vars}Choose which plugin type (defaults to "module").Available plugin types are : ('become', 'cache','callback', 'cliconf', 'connection', 'httpapi','inventory', 'lookup', 'netconf', 'shell', 'module','strategy', 'vars')-v, --verbose verbose mode (-vvv for more, -vvvv to enableconnection debugging)See man pages for Ansible CLI options or website for tutorials
https://docs.ansible.com
示例:
# 查看模块清单及说明
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible-doc -l
fortios_router_community_list Configure community lists i...
azure_rm_devtestlab_info Get Azure DevTest Lab facts
ecs_taskdefinition register a task definition ...
......# 查看模块清单及位置
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible-doc -F
fortios_router_community_list /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages
azure_rm_devtestlab_info /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages
ecs_taskdefinition /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages
......# 查看特定模块说明文档
[wsh@controller web ✔]$ ansible-doc user
> USER (/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible/modules/system/user.py)Manage user accounts and user attributes. For Windows targets, usethe [win_user] module instead.* This module is maintained by The Ansible Core Team# 模块选项,=开头是必选选项
OPTIONS (= is mandatory):- appendIf `yes', add the user to the groups specified in `groups'.If `no', user will only be added to the groups specified in `groups',removing them from all other groups.[Default: False]type: bool
... ...# 提示信息
NOTES:* There are specific requirements per platform on user managementutilities. However they generally come pre-installed with thesystem and Ansible will require they are present at runtime. Ifthey are not, a descriptive error message will be shown.
... ...# 参考信息
SEE ALSO:* Module authorized_keyThe official documentation on the authorized_key module.https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/modules/authorized_key_module.html
... ...# 作者
AUTHOR: Stephen Fromm (@sfromm)# METADATA描述了谁在维护该模块。
# status记录了模块开发状态。
# stableinterface: 模块的关键字稳定,将尽力确保不删除关键字或更改其含义。
# preview: 模块处于技术预览阶段,可能不稳定,其关键字可能会更改,或者它可能需要本身会受到不兼容更改的库或Web服务。
# deprecated: 未来某一发行版中将不再提供。
# removed: 模块已从发行版中移除,但因文档需要存在存根,以帮助之前的用户迁移到新的模块。METADATA:status:- stableinterface# supported_by记录了哪些社区在维护该模块:
# core:Ansible核心开发人员维护,始终随Ansible提供。
# curated:模块由社区中的合作伙伴或公司提交并维护。这些模块的维护者必须留意报告的任何问题,或者调取针对该模块提出的请求。在社区维护人员批准了更改后,上游 “core” 开发人员审核对策划模块提出的更改。核心提交者也确保因为Ansible引擎中的变化而对这些模块造成的任何问题得到修正。这些模块目前随Ansible提供,但是可能会在未来某个时候另外打包。
# community:模块不受到core上游开发人员、合作伙伴或公司的支持,完全由一般开源社区维护。此类别中的模块仍然完全可用,但对问题的响应速度完全取决于社区。这些模块目前也随Ansible提供,但是可能会在未来某个时候另外打包。supported_by: core
... ...# 模块使用示例
EXAMPLES:- name: Add the user 'johnd' with a specific uid and a primary group of 'admin'user:name: johndcomment: John Doeuid: 1040group: admin
... ...# 模块返回值说明
RETURN VALUES:append:description: Whether or not to append the user to groupsreturned: When state is 'present' and the user existstype: boolsample: True
... ...
如果现有的模块无法实现现有需求,用户也可以自行编写模块:
- Ansible会从变量ANSIBLE_LIBRARY中查找模块
- 如果该变量未设置,将会从ansible.cfg配置文件library设置的位置查找模块
command 模块
command 模块允许管理员在受管节点的命令行中运行任意命令。要运行的命令通过-a选项指定为该模块的参数。
[[wsh@controller web ✔]]$ ansible node1 -m command -a 'hostname'
node1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
node1.laoma.cloud[[wsh@controller web ✔]]$ ansible node1 -m command -a 'hostname' -o
node1 | CHANGED | rc=0 | (stdout) node1.laoma.cloud
说明:
- command 模块执行的远程命令不受受管节点上的shell处理,无法访问shell环境变量,也不能执行重定向和传送等shell操作。
- 如果临时命令没有指定模块,Ansible默认使用command模块。
shell 模块
shell模块允许您将要执行的命令作为参数传递给该模块。 Ansible随后对受管节点远程执行该命令。与command模块不同的是, 这些命令将通过受管节点上的shell进行处理。因此,可以访问shell环境变量,也可使用重定向和管道等shell操作。
[[wsh@controller web ✔]]$ ansible node1 -m command -a set
node1 | FAILED | rc=2 >>
[Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'set': 'set'[[wsh@controller web ✔]]$ ansible node1 -m shell -a set
node1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
BASH=/bin/sh
BASHOPTS=cmdhist:complete_fullquote:extquote:force_fignore:hostcomplete:interactive_comments:progcomp:promptvars:sourcepath
BASH_ALIASES=()
BASH_ARGC=()
BASH_ARGV=()
......
注意: command和shell模块要求被管理主机安装Python。
ansible AD HOC 命令选项
临时命令选项优先级高于配置文件中配置。
| 配置文件指令 | 命令行选项 |
|---|---|
| inventory | -i |
| remote_user | -u |
| ask_pass | -k, --ask-pass |
| become | –become, -b |
| become_method | –become_method |
| become_user | –become-user |
| become_ask_pass | –ask-become-pass, -K |
