Spring简单的读取和存储对象
Spring简单的读取和存储对象
文章目录
- Spring简单的读取和存储对象
- 存储对象
- 添加注解存储Bean对象
- 类注解
- @Controller(控制器存储)
- @Service(服务存储)
- @Repository(仓库储存)
- @Component(组件存储)
- @Configuration(配置存储)
- 类注解的不同用途
- 方法注解
- @Bean
- 类注解需搭配方法注解使用
- 重命名@Bean
- 获取对象
- 属性注入
- 构造方法注入
- Setter方法注入
- 三种注入优缺点分析
- @Resource:另一种关键字注入
- 同一类型多个@Bean报错问题
- 解决办法
在 Spring 中想要更简单的存储和读取对象的核心是使用注解,也就是我们接下来要学习 Spring 中的相关注解,来存储和读取 Bean 对象
存储对象
添加注解存储Bean对象
- 将对象存储在Spring中,有两种注解可以实现:
- 类注解:@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component、@Configuration
- 方法注解:@Bean
下面我们来一个个讲解:
类注解
@Controller(控制器存储)
- 使用@Controller存储Bean的代码如下:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controller
public class UserController {@GetMapping("/hello")@ResponseBodypublic String sayHello() {return "Hello, Spring!";}
}
@Service(服务存储)
- 使用@Service存储Bean的代码如下:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service
public class UserService {public String getUserNameById(int id) {// 模拟从数据库获取用户姓名的业务逻辑return "User" + id;}
}
@Repository(仓库储存)
- 使用@Repository存储Bean的代码如下:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;@Repository
public class UserRepository {public boolean saveUser(String name) {// 模拟保存用户到数据库的操作System.out.println("Saving user: " + name);return true;}
}
@Component(组件存储)
- 使用@Component存储Bean的代码如下:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
public class CommonUtils {public String formatData(String data) {// 模拟数据格式化操作return data.toUpperCase();}
}
@Configuration(配置存储)
- 使用@Repository存储Bean的代码如下:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration
public class AppConfig {// 配置类中通常结合@Bean注解使用,用于定义Bean
}
类注解的不同用途
-
既然功能是一样的,为什么需要这么多的类注解呢?
-
那么为什么需要这么多的类注解也是相同的原因,就是让程序员看到类注解之后,就能直接了解当前类的用途,比如:
-
@Controller:表示的是业务逻辑层
-
@Service:服务层
-
@Repository:持久层
-
@Configuration:配置层
程序的工程分层,调用流程如下:
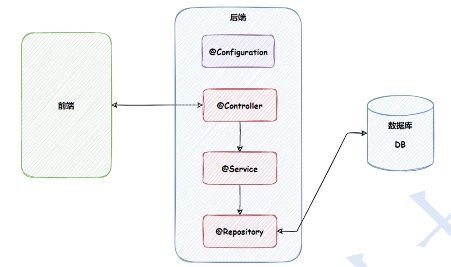
补充:
- 查看 @Controller / @Service / @Repository / @Configuration 等注解的源码发现:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Configuration {@AliasFor(annotation = Component.class)String value() default "";boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
其实这些注解里面都有一个注解 @Component,说明它们本身就是属于 @Component 的 “子类”
方法注解
@Bean
类注解是添加到某个类上的,而方法注解是放到某个方法上的,如以下代码的实现:
public class Users {@Beanpublic User user1() {User user = new User();user.setName("Java");return user;}
}
然而,当我们写完以上代码,尝试获取 bean 对象中的 user1 时却发现,根本获取不到:
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");User user = (User) context.getBean("user1");System.out.println(user.toString());}
}
以上程序的执行结果如下:(报错)
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No bean named 'user1' availableat org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanDefinition(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:876)at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(AbstractBeanFactory.java:1344)at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:309)at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:204)at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.getBean(AbstractApplicationContext.java:1116)at com.bit.Application.main(Application.java:12)
这是为什么嘞?
类注解需搭配方法注解使用
- 在Spring中,方法注解需要和类注解一起搭配使用,才能将对象正常添加到容器中
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;@Configuration
public class AppConfig {@Beanpublic RestTemplate restTemplate() {return new RestTemplate();}
}
重命名@Bean
- 可以通过设置name属性,给Bean进行重命名操作
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration
public class AppConfig {// 通过name属性将Bean重命名为"myUser"@Bean(name = "myUser")public User user() {User user = new User();user.setName("张三");return user;}
}import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);// 使用重命名后的Bean名称"myUser"来获取BeanUser user = (User) context.getBean("myUser");System.out.println(user);}
}
- 假如Bean有多个名字,name可以省略
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration
public class AppConfig {// 通过 name 属性设置多个 Bean 名称:user1、userBean、myUser@Bean({"user1", "userBean", "myUser"})public User user() {User user = new User();user.setName("示例用户");return user;}
}
获取对象
获取 bean 对象也叫做对象装配,是把对象取出来放到某个类中,有时候也叫对象注入
对象装配(对象注入)的实现方法以下 3 种:
- 属性注入
- 构造方法注入
- Setter 注入
接下来,我们分别来看
下面我们按照实际开发中的模式,将 Service 类注入到 Controller 类中
属性注入
- 直接在类的属性上使用 @Autowired 注解,Spring 会自动从容器中找到匹配类型的 Bean 并注入到该属性中
@Controller
public class UserController {// 直接在属性上添加 @Autowired,自动注入 UserService 类型的 Bean@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;public void getUserInfo() {// 直接使用注入的 userServiceuserService.getUser();}
}
构造方法注入
在类的构造方法上使用 @Autowired 注解(Spring 4.3+ 中,若类只有一个构造方法,可省略注解),Spring 会通过构造方法将依赖的 Bean 传入并赋值
@Controller
public class UserController {// 通常用 final 修饰,保证不可变性private final UserService userService;// 构造方法注入,依赖在对象创建时就确定@Autowiredpublic UserController(UserService userService) {this.userService = userService;}public void getUserInfo() {userService.getUser();}
}
Setter方法注入
- 在类的 Setter 方法上使用 @Autowired 注解,Spring 会通过调用 Setter 方法将依赖的 Bean 注入
@Controller
public class UserController {private UserService userService;// Setter 方法注入@Autowiredpublic void setUserService(UserService userService) {this.userService = userService;}public void getUserInfo() {userService.getUser();}
}
三种注入优缺点分析
- 属性注入的优点是简洁,使用方便;缺点是只能用于 IoC 容器,如果是非 IoC 容器不可用,并且只有在使用的时候才会出现 NPE(空指针异常)
- 构造方法注入是 Spring 推荐的注入方式,它的缺点是如果有多个注入会显得比较臃肿,但出现这种情况你应该考虑一下当前类是否符合程序的单一职责的设计模式了,它的优点是通用性,在使用之前一定能把保证注入的类不为空
- Setter 方式是 Spring 前期版本推荐的注入方式,但通用性不如构造方法,所有 Spring 现版本已经推荐使用构造方法注入的方式来进行类注入了
@Resource:另一种关键字注入
- 在进行类注入时,除了可以使用 @Autowired 关键字之外,我们还可以使用 @Resource 进行注入,如下代码所示:
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service
public class UserService {// 注入另一个Bean@Resourceprivate UserDao userDao; // 业务方法...
}
@Autowired 和 @Resource 的区别
- 出身不同:@Autowired 来自于 Spring,而 @Resource 来自于 JDK 的注解
- 使用时设置的参数不同:相比于 @Autowired 来说,@Resource 支持更多的参数设置,例如 name 设置,根据名称获取 Bean
同一类型多个@Bean报错问题
@Component
public class Users {@Beanpublic User user1() {User user = new User();user.setId(1);user.setName("Java");return user;}@Beanpublic User user2() {User user = new User();user.setId(2);user.setName("MySQL");return user;}
}
在另一个类中获取 User 对象,如下代码如下:
@Controller
public class UserController4 {// 注入@Resourceprivate User user;public User getUser() {return user;}
}
以上程序的执行结果如下:
NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.bit.models.User'
报错的原因是,非唯一的 Bean 对象
解决办法
解决同一个类型,多个 bean 的解决方案有以下两个:
- 使用
@Resource(name="user1")定义 - 使用
@Qualifier注解定义名称。
①使用 @Resource(name="XXX")
@Controller
class UserController4 {// 注入@Resource(name = "user1")private User user;public User getUser() {return user;}
}
②使用 @Qualifier
@Controller
public class UserController5 {// 注入@Autowired@Qualifier(value = "user2")private User user;public User getUser() {return user;}
}
总结:
- 上面两种本质上都是指定注入哪一个同一类型的Bean
- @Resource和@Qualifier,本质区别就是@Resource已经有属性注入功能,所以不再需要像@Qualifier一样,需要和@Autowired搭配使用
