Linux内核进程管理子系统有什么第四十回 —— 进程主结构详解(36)
接前一篇文章:Linux内核进程管理子系统有什么第三十九回 —— 进程主结构详解(35)
本文内容参考:
Linux内核进程管理专题报告_linux rseq-CSDN博客
《趣谈Linux操作系统 核心原理篇:第三部分 进程管理》—— 刘超
《图解Linux内核 基于6.x》 —— 姜亚华 机械工业出版社
特此致谢!
进程管理核心结构 —— task_struct
8. 进程权限相关成员
进程权限相关成员包括以下几个:
/* Process credentials: *//* Tracer's credentials at attach: */const struct cred __rcu *ptracer_cred;/* Objective and real subjective task credentials (COW): */const struct cred __rcu *real_cred;/* Effective (overridable) subjective task credentials (COW): */const struct cred __rcu *cred;这几个字段的描述如下:
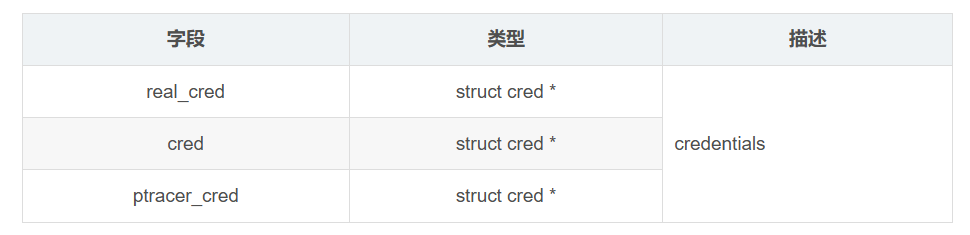
上一回开始对于struct cred进行解析,本回继续。为了便于理解和回顾,再次贴出struct cred的定义,在include/linux/cred.h中,如下:
/** The security context of a task** The parts of the context break down into two categories:** (1) The objective context of a task. These parts are used when some other* task is attempting to affect this one.** (2) The subjective context. These details are used when the task is acting* upon another object, be that a file, a task, a key or whatever.** Note that some members of this structure belong to both categories - the* LSM security pointer for instance.** A task has two security pointers. task->real_cred points to the objective* context that defines that task's actual details. The objective part of this* context is used whenever that task is acted upon.** task->cred points to the subjective context that defines the details of how* that task is going to act upon another object. This may be overridden* temporarily to point to another security context, but normally points to the* same context as task->real_cred.*/
struct cred {atomic_t usage;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_CREDENTIALSatomic_t subscribers; /* number of processes subscribed */void *put_addr;unsigned magic;
#define CRED_MAGIC 0x43736564
#define CRED_MAGIC_DEAD 0x44656144
#endifkuid_t uid; /* real UID of the task */kgid_t gid; /* real GID of the task */kuid_t suid; /* saved UID of the task */kgid_t sgid; /* saved GID of the task */kuid_t euid; /* effective UID of the task */kgid_t egid; /* effective GID of the task */kuid_t fsuid; /* UID for VFS ops */kgid_t fsgid; /* GID for VFS ops */unsigned securebits; /* SUID-less security management */kernel_cap_t cap_inheritable; /* caps our children can inherit */kernel_cap_t cap_permitted; /* caps we're permitted */kernel_cap_t cap_effective; /* caps we can actually use */kernel_cap_t cap_bset; /* capability bounding set */kernel_cap_t cap_ambient; /* Ambient capability set */
#ifdef CONFIG_KEYSunsigned char jit_keyring; /* default keyring to attach requested* keys to */struct key *session_keyring; /* keyring inherited over fork */struct key *process_keyring; /* keyring private to this process */struct key *thread_keyring; /* keyring private to this thread */struct key *request_key_auth; /* assumed request_key authority */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITYvoid *security; /* LSM security */
#endifstruct user_struct *user; /* real user ID subscription */struct user_namespace *user_ns; /* user_ns the caps and keyrings are relative to. */struct ucounts *ucounts;struct group_info *group_info; /* supplementary groups for euid/fsgid *//* RCU deletion */union {int non_rcu; /* Can we skip RCU deletion? */struct rcu_head rcu; /* RCU deletion hook */};
} __randomize_layout;上一回讲到struct cred中的3组字段:

一般来说,fsuid、euid与uid是一样的;fsgid、egid与gid也是一样的。因为谁启动的进程,就应该审核启动者有没有相关权限。但是也存在特殊情况。例如:
用户张三(zhangsan)想运行一个用户李四(lisi)安装的应用程序(比如游戏、视频播放器等)。由于是李四安装的,当然该应用程序文件的权限是rwxr--r--。也就是说文件属主(即文件所有者李四)权限为可读、可写、可执行;而属组(同组用户)权限为只可读;组外(其他用户)权限也是只可读。
那么问题来了,张三想运行该程序,但没有可执行权限,该怎么办呢?需要向用户李四要授权。李四并无意见,于是将应用程序文件的权限由rwxr--r--改为rwxr-xr-x。也就是分别给属组和组外权限加入了可执行。这样,张三就可以正常运行程序了。
接下来问题又来了,张三看着看着视频觉得不错,想把这个视频存下来;或者玩游戏过了几关,想保存进度。一点下载或保存按钮,坏了,提示无权限。为什么会这样?因为下载视频需要有保存路径的写入权限,游戏玩家数据是保存在某个文件中的,也需要写入权限。由于该文件只给所有者李四开了写入权限,而进程的euid和fsuid都是张三,那当然写不了了。
又该怎么解决这个问题呢?可以通过chmod u+s xxx命令,给这个应用程序设置set-user-id,将它的权限变为rwsr-xr-x。此时,张三再启动这个应用的时候,创建的进程uid还是张三(zhangsan),但是euid和fsuid就不是张三了,而是李四(lisi)。也就是说,因为看到了set-user-id标识,euid和fsuid就改为文件所有者即李四了。
关于chmod u+s命令,详情参考以下文章:
Linux命令 chmod 例:chmod u+s-CSDN博客

更多内容请看下回。
