五分钟聊一聊AQS源码
系列文章目录
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 一、AQS是一个构建锁和同步器的框架
- 二、AQS重要的组成部分
- 1、volatile int state
- 2、Node节点
- 3、多线程如何抢锁
- 4、加入等待后,线程如何变化
- 5、如何释放锁
一、AQS是一个构建锁和同步器的框架
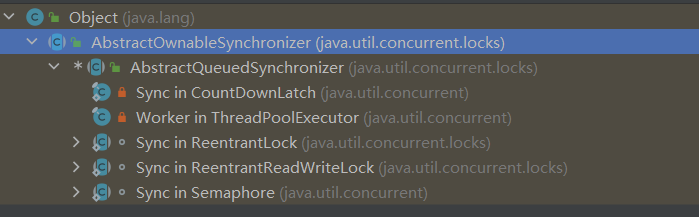
全称是AbstractQueuedSynchronizer, java里面的抽象类,用来构建锁和同步器(ReentranLock, Semaphore, CountDownLatch等)
核心思想:通过一个FIFO队列管理线程的阻塞和唤醒
以下这些 Java 并发工具类都是基于 AQS 实现的:
| 组件 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ReentrantLock | 可重入锁 |
| ReentrantReadWriteLock | 读写锁 |
| Semaphore | 信号量,控制并发数 |
| CountDownLatch | 倒计时门闩 |
| CyclicBarrier | 循环屏障 |
| FutureTask | 异步任务 |
二、AQS重要的组成部分
1、volatile int state
state 的作用管理同步变量的状态,state等于多少代表加锁,解锁,在不同的子类中有不同的实现,以ReentranLock为例:state=0, 共享资源没有被加锁,state=1代表共享资源已经被线程加锁,state>1代表加了多把锁, 修改state的一个方法是CAS.
2、Node节点
没有抢到锁的线程加入链表
abstract static class Node {volatile Node prev; // initially attached via casTailvolatile Node next; // visibly nonnull when signallableThread waiter; // visibly nonnull when enqueuedvolatile int status; // written by owner, atomic bit ops by others
status表示的含义
CANCELLED 1, 代表该线程已取消
SIGNAL -1, 表示后继节点需要被唤醒
CONDIYION -2
PROPAGATE -3
3、多线程如何抢锁
假设有三个线程A,B,C此时都在抢锁,假设A抢到了
A进行CAS将state改成1, 改成功,返回true, 执行 setExclusiveOwnerThread
B这个时候也在抢锁,进行CAS的时候,将0改成1,失败,因为state已经是1了,返回失败,调用acquire
C这个时候也在抢锁,进行CAS的时候,将0改成1,失败,因为state已经是1了,返回失败,调用acquireB抢锁失败,执行acquire(1)--》往后追溯就是执行final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires){},
final void lock(){if(compareAndSetState(0,1)){setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());}else{acquire(1)}}final void acquire(int arg) {if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE),arg))selfInterrupt();}final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires){
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}/*
如果A执行完毕(将state set to 0),那么int c=getState();c=0, 因为state=0, 没有线程在占用锁,所以B可以通过CAS的方式获得锁如果A还在执行,没有释放锁,那么int c=getState();c=1, 因为current=B, getExclusiveOwnerThread()是A,所以返回falsegetExclusiveOwnerThread()获取当前线程, 假设A还没有释放锁,但是A现在需要竞争第二把锁,A也会执行到final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires){}里面,current=A=getExclusiveOwnerThread(),执行else if语句块,nextc=1+1=2;state=2, 这就是可重入锁的实现,允许同一个线程抢到多把锁,state值也会发生变化再回到之前假设A占用锁,B线程返回false,回到最开始的方法,if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE),arg)), 前部分取反返回true, 再看acquireQueued方法,先看addWaiter方法B执行到addWaiter, AQS中的等待队列是空的,此时head=null, tail=null,先获取当前线程,将当前线程打包成node节点,执行方法enq(node), 这个方法是在构建链表, 最后在调用外层acquireQueued方法,请看第四小节解释*/final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires){
final Thread current=Thread.currentThread();
int c=getState();
if(c==0){if(compareAndSetState(0,1)){setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}
}else if(current==getExclusiveOwnerThread()){int nextc=c+acquires;if(nextc <0) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded")setState(nextc);return true;
}return false;
}private Node addWaiter(Node node){Node node=new Node(Thread.currentThread(),mode) ;Node pred=tailif(pred!=null){node.prev=predif(compareAndSetTail(pred, node)){pred.next=nodereturn node}}enq(node)return node
}Node enq(final Node node){for(;;){Node t=tail;if(t==null){if(compareAndSetHead(new Node())){tail=head}else{node.prev=tif(compareAndSetTail(t,node)){t.next=nodereturn t}}}}
}4、加入等待后,线程如何变化
final void acquire(int arg) {if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE),arg))selfInterrupt();
}/*
线程B的前驱节点是head, if(p==head && tryAcquired(arg)),线程B尝试加锁
线程C前驱节点是线程B, 所以if不满足,C执行if(shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p,node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())C执行shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire, ws初始值=0, 进入else{},通过CAS的方式,将线程B的节点status 0->-1, acquireQueued是一个死循环,所以线程C一直在执行这个方法再次执行,ws=-1=Node.SIGNAL, 返回true, 执行parkAndCheckInterrupt, 将线程C阻塞,返回true到这里也能看出来,线程B不断尝试获取锁,B后驱节点此时都是被阻塞的**/final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg){boolean failed=true;try{bolean interrupted=false;for(;;){final Node p=node.predecessor();if(p==head && tryAcquired(arg)){setHead(node);p.next=null;failed=false;return interrupted;}if(shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p,node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())interrupted=true;}}finally{if(failed)cancelAcquire(node);}
}
}
static Boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node){int ws=pred.waitStatusif(ws==Node.SIGNAL) return trueif(ws>0){do{node.prev=pred=pred.prev}while(pred.waitStatue>0);pred.next=node}else{compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred,ws,Node.SIGNAL)}return false
}
final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt(){LockSupport.park(this);return Thread.interrrupted();
}
