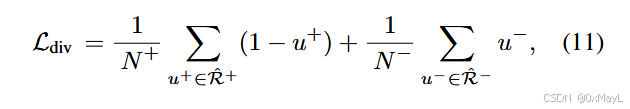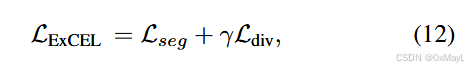深度学习·ExCEL
WSSS
ExCEL方法
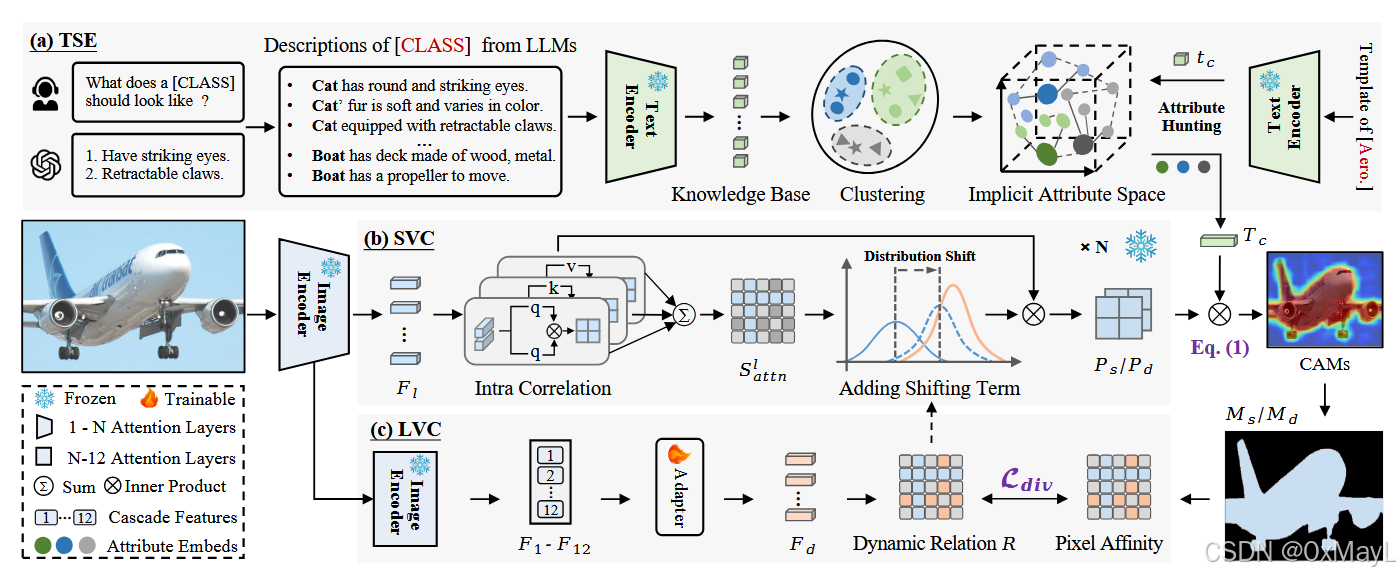
TSE
“only indicates the presence of objects while limited providing dense knowledge for” (Yang 等, 2025, p. 20225) (pdf) 🔤仅表示物体的存在,而有限地提供密集的知识🔤
- 传统的text prompt 只能表示物体存在,不能提供任何其他的信息,所以在语义分割这种密集任务中表现不佳.
- 对每一个类都查询GPT获得具体的描述信息,总共n=20个特征

“This knowledge base gathers descriptive properties for the whole dataset, building a strong foundation for the textual category representation” (Yang 等, 2025, p. 20226) (pdf) 🔤该知识库收集了整个数据集的描述性属性,为文本类别表示奠定了坚实的基础🔤
- 作者不是简单的讲所有GPT生成的额外类别属性简单的融合,而是将这些属性聚类为更加通用的属性,将其转换为一种隐式属性的搜索过程。
“The clustered attributes efficiently capture shared contextual knowledge from other categories, supplementing missing information for target class recognition” (Yang 等, 2025, p. 20226) (pdf) 🔤聚类属性有效地捕获来自其他类别的共享上下文知识,补充目标类识别的缺失信息🔤
“The use of attributes makes the knowledge more compact and representative, leading to precise text prompting.” (Yang 等, 2025, p. 20226) (pdf) 🔤属性的使用使知识更加紧凑和具有代表性,从而实现精确的文本提示。🔤
- 作者对这些知识库中的属性进行聚类,得到B个聚类中心,其中B=112或者224(Pascal VOC or COCO)
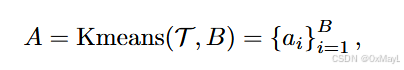
- 给定一个class token,将聚类中心与其计算相似度分数,然后根据分数选取前K个进行text embedding的融合,权重就是聚类分数,然后注意有个权重λ\lambdaλ
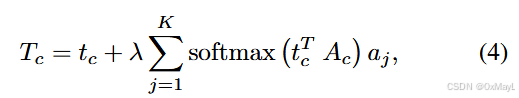
VC Visual Calibrations
- 动机:CLIP缺乏细粒度的信息,导致补丁和文本对齐不合理。
“lack fine-grained information, leading to unreasonable localization maps via patch-text alignment.” (Yang 等, 2025, p. 20226) (pdf) 🔤缺乏细粒度信息,导致通过补丁文本对齐导致不合理的本地化映射。🔤
Static Visual Calibration
However, due to the inherent image-text alignment of CLIP, the original q-k attention produces overly uniform attention maps,
“homogenizing diverse tokens from v to capture broad semantics for global image representation (see discussions in Sec. 4.4).” (Yang 等, 2025, p. 20226) (pdf) 🔤将 V 中的不同标记同质化,以捕获全局图像表示的广泛语义(参见第 4.4 节中的讨论)。🔤
- 将自注意力机制替换为Intra-correltation机制
- 只在最后几层进行计算,分别对q,k,v计算,权重相等。

Learnable Visual Calibration
- 简单来说,就是引用一个额外的适配器adptor
- 对通过刚才方式计算的注意图进行额外的修正
- R矩阵的目的是:影响特征的分布,激活相关的token,避免激活无关的token
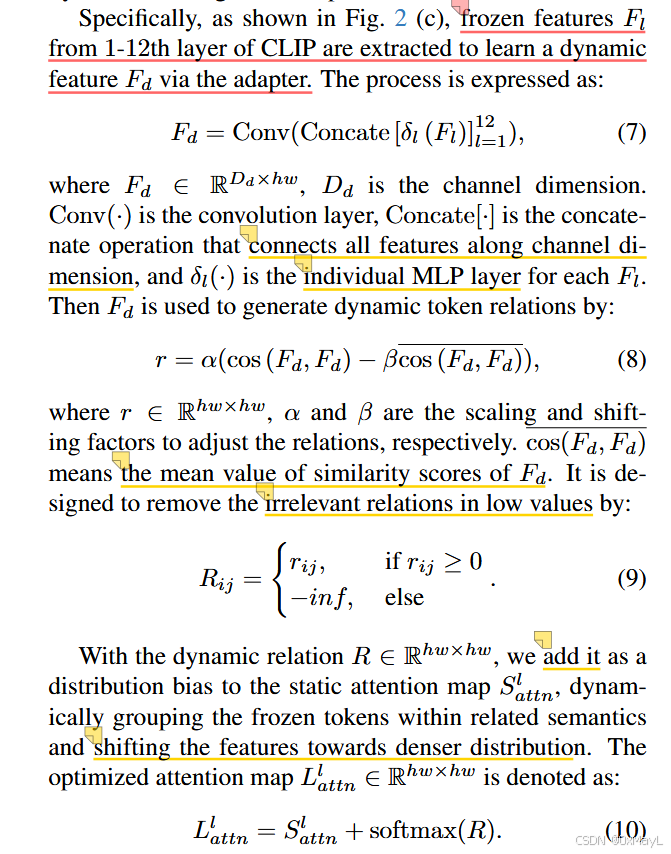
- 训练适配器的损失函数: