Spring Boot 2.6.0+ 循环依赖问题及解决方案
Spring Boot 2.6.0+ 循环依赖问题及解决方案
目录
- 背景
- 解决方案
- 1. 配置文件开启循环依赖(侵入性最低,临时方案)
- 2. @Lazy 延迟注入(侵入性低,推荐优先尝试)
- 3. 手动从容器获取(ApplicationContextAware,侵入性中等)
- 4. 接口隔离 / 中间层解耦(侵入性高,推荐长期方案)
- 5. 事件驱动(ApplicationEvent,侵入性中等,适合通知场景)
- 总结
- 版本差异补充
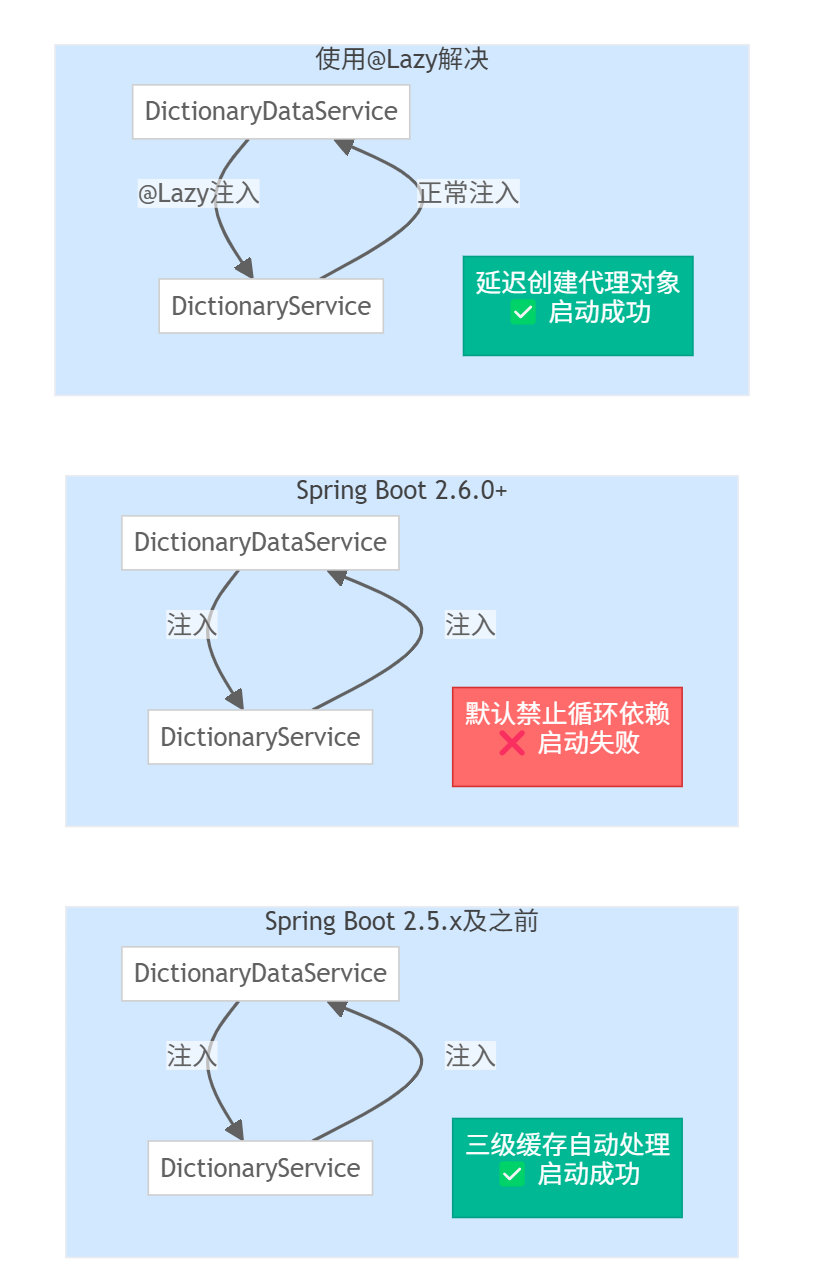
背景
从 Spring Boot 2.6.0 开始,Spring 团队默认禁止了循环依赖(circular references),这是一个重要的设计变更。主要原因包括:
- 设计原则:循环依赖通常暗示着不良的代码设计,违反了单一职责原则
- 初始化问题:循环依赖可能导致难以预测的bean初始化顺序和状态
- 调试困难:循环依赖使得问题排查变得复杂
- 性能考虑:三级缓存机制增加了额外的内存开销
配置变更:
spring:main:allow-circular-references: false # 2.6+ 默认值
常见错误信息:
The dependencies of some of the beans in the application context form a cycle:
┌─────┐
| dictionaryServiceImpl defined in file [...DictionaryServiceImpl.class]
↑ ↓
| dictionaryDataServiceImpl defined in file [...DictionaryDataServiceImpl.class]
└─────┘
解决方案
1. 配置文件开启循环依赖(侵入性最低,临时方案)
适用场景:快速解决遗留项目的启动问题,临时过渡方案
# application.yml
spring:main:allow-circular-references: true
优点:
- 零代码修改
- 立即生效
- 保持原有业务逻辑不变
缺点:
- 治标不治本
- 可能隐藏潜在的设计问题
- 不符合Spring新版本的设计理念
2. @Lazy 延迟注入(侵入性低,推荐优先尝试)
适用场景:简单的双向依赖,不需要在初始化时立即使用依赖对象
实现方式:
@Service
public class DictionaryDataServiceImpl implements DictionaryDataService {@Lazy // 延迟加载,打破循环依赖@Resourceprivate DictionaryService dictionaryService;public void someMethod() {// 只有在真正调用时才会初始化 dictionaryServiceDictionary dict = dictionaryService.getById(1);}
}@Service
public class DictionaryServiceImpl implements DictionaryService {@Resourceprivate DictionaryDataService dictionaryDataService; // 保持正常注入// 业务逻辑...
}
工作原理:
@Lazy注入的是一个代理对象,而非真实的bean- 只有在第一次调用方法时,才会触发真实bean的创建
- 从而避开了启动时的循环依赖检查
优点:
- 代码侵入性小
- 保持了依赖注入的便利性
- 符合Spring的设计理念
缺点:
- 首次调用时性能略有损失
- 需要明确哪个依赖使用@Lazy
3. 手动从容器获取(ApplicationContextAware,侵入性中等)
适用场景:需要更灵活的依赖获取方式,或者依赖关系比较复杂
实现方式一:ApplicationContextAware接口
@Service
public class DictionaryDataServiceImpl implements DictionaryDataService, ApplicationContextAware {private ApplicationContext applicationContext;private DictionaryService dictionaryService;@Overridepublic void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {this.applicationContext = applicationContext;}private DictionaryService getDictionaryService() {if (dictionaryService == null) {dictionaryService = applicationContext.getBean(DictionaryService.class);}return dictionaryService;}public void someMethod() {Dictionary dict = getDictionaryService().getById(1);}
}
实现方式二:SpringContextHolder工具类
// 工具类
@Component
public class SpringContextHolder implements ApplicationContextAware {private static ApplicationContext context;@Overridepublic void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {context = applicationContext;}public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> beanClass) {return context.getBean(beanClass);}public static <T> T getBean(String beanName, Class<T> beanClass) {return context.getBean(beanName, beanClass);}
}// 业务类使用
@Service
public class DictionaryDataServiceImpl implements DictionaryDataService {public void someMethod() {DictionaryService dictionaryService = SpringContextHolder.getBean(DictionaryService.class);Dictionary dict = dictionaryService.getById(1);}
}
优点:
- 完全避免了循环依赖
- 可以动态获取bean
- 适合复杂的依赖场景
缺点:
- 失去了依赖注入的便利性
- 代码可读性稍差
- 增加了与Spring框架的耦合
4. 接口隔离 / 中间层解耦(侵入性高,推荐长期方案)
适用场景:重构现有架构,从根本上解决循环依赖问题
方案一:提取公共服务
// 提取公共逻辑到新的服务
@Service
public class DictionaryCommonService {@Resourceprivate DictionaryMapper dictionaryMapper;@Resource private DictionaryDataMapper dictionaryDataMapper;public Dictionary findDictionaryById(Integer id) {return dictionaryMapper.selectById(id);}public List<DictionaryData> findDatasByDictId(Integer dictId) {return dictionaryDataMapper.selectByDictId(dictId);}
}// 重构后的服务
@Service
public class DictionaryServiceImpl implements DictionaryService {@Resourceprivate DictionaryCommonService dictionaryCommonService;@Overridepublic JsonResult articleTypeList() {// 使用公共服务Dictionary dict = dictionaryCommonService.findDictionaryById(1);List<DictionaryData> dataList = dictionaryCommonService.findDatasByDictId(dict.getDictId());// 处理逻辑...}
}@Service
public class DictionaryDataServiceImpl implements DictionaryDataService {@Resourceprivate DictionaryCommonService dictionaryCommonService;// 业务逻辑使用公共服务
}
方案二:接口隔离原则
// 定义最小化接口
public interface DictionaryQueryService {Dictionary getById(Integer id);
}public interface DictionaryDataQueryService {List<DictionaryData> getByDictId(Integer dictId);
}// 实现类只依赖需要的接口
@Service
public class DictionaryServiceImpl implements DictionaryService, DictionaryQueryService {@Resourceprivate DictionaryDataQueryService dictionaryDataQueryService;// 实现逻辑...
}@Service
public class DictionaryDataServiceImpl implements DictionaryDataService, DictionaryDataQueryService {@Resourceprivate DictionaryQueryService dictionaryQueryService;// 实现逻辑...
}
优点:
- 从根本上解决了设计问题
- 提高了代码的可维护性
- 符合SOLID原则
- 降低了模块间的耦合度
缺点:
- 需要大量的代码重构
- 可能涉及业务逻辑的调整
- 短期内工作量较大
5. 事件驱动(ApplicationEvent,侵入性中等,适合通知场景)
适用场景:一个服务需要通知另一个服务执行某些操作
实现方式:
// 定义事件
public class DictionaryDataChangeEvent extends ApplicationEvent {private final String dictCode;public DictionaryDataChangeEvent(Object source, String dictCode) {super(source);this.dictCode = dictCode;}public String getDictCode() {return dictCode;}
}// 事件发布者
@Service
public class DictionaryDataServiceImpl implements DictionaryDataService {@Resourceprivate ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;@Overridepublic boolean save(DictionaryData entity) {boolean success = super.save(entity);if (success) {// 发布事件而不是直接调用其他服务eventPublisher.publishEvent(new DictionaryDataChangeEvent(this, entity.getDictCode()));}return success;}
}// 事件监听者
@Service
public class DictionaryServiceImpl implements DictionaryService {@EventListenerpublic void handleDictionaryDataChange(DictionaryDataChangeEvent event) {// 处理字典数据变更后的逻辑String dictCode = event.getDictCode();// 清除缓存、更新状态等}
}
优点:
- 完全解耦了两个服务
- 支持异步处理
- 便于扩展(多个监听者)
- 符合事件驱动架构
缺点:
- 增加了系统复杂度
- 调试相对困难
- 需要理解事件驱动模式
总结
| 方案 | 侵入性 | 适用场景 | 推荐指数 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 配置开启循环依赖 | 最低 | 快速修复、临时方案 | ⭐⭐ | 治标不治本 |
| @Lazy注解 | 低 | 简单双向依赖 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 优先推荐 |
| 手动获取bean | 中等 | 复杂依赖关系 | ⭐⭐⭐ | 失去注入便利性 |
| 接口隔离/中间层 | 高 | 架构重构 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 长期最佳方案 |
| 事件驱动 | 中等 | 通知场景 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 解耦效果好 |
建议处理流程:
- 短期:使用
@Lazy快速解决启动问题 - 中期:分析业务逻辑,评估是否需要重构
- 长期:通过接口隔离或中间层彻底解决循环依赖
版本差异补充
Spring Boot 2.5.x 及之前:
- 默认
allow-circular-references: true - 三级缓存自动处理循环依赖
- 开发者通常不会意识到循环依赖问题
Spring Boot 2.6.0+:
- 默认
allow-circular-references: false - 启动时检查并报错
- 强制开发者关注和解决循环依赖
Spring Boot 3.0+:
- 继续保持对循环依赖的严格控制
- 进一步鼓励良好的设计模式
- 可能在未来版本中完全移除循环依赖支持
这个变更体现了Spring团队对代码质量和架构设计的重视,虽然短期内会带来一些迁移成本,但长期来看有利于项目的可维护性和稳定性。
