C++ string类
目录
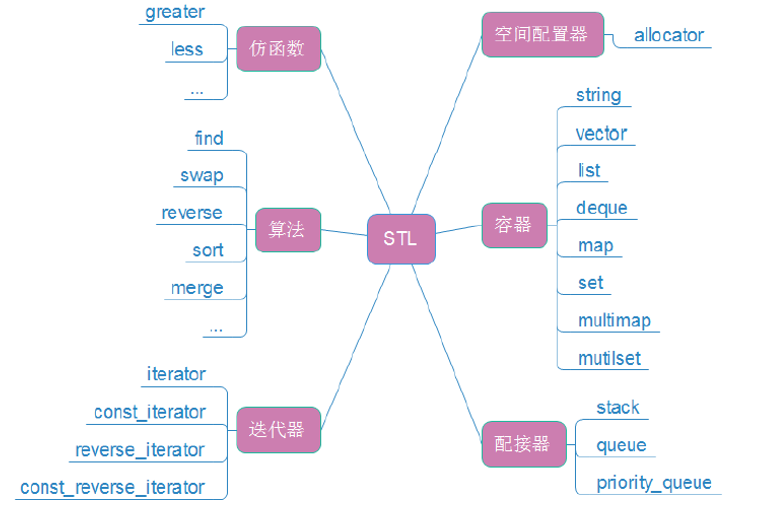
一.STL简介
1. 什么是STL
2.STL的版本(了解即可)
编辑
二.String类
1.认识string类
2.string类的常用接口说明
2.1构造函数
2.2 string类对象的容量操作
2.3string类对象的访问及遍历操作
2.5. string类非成员函数
2.6 vs和g++下string结构的说明
2.6.1 vs下string的结构
2.6.2 g++下string的结构
3.C++11的小语法(auto关键字和范围for)
3.1auto关键字(做类型推导)
3.2范围for(遍历方便)
4.string类的实现
string.h
string.cpp
test.cpp
5.浅拷贝和深拷贝问题
5.1浅拷贝
5.1深拷贝
6.string 在线OJ题目
一.STL简介
1. 什么是STL
2.STL的版本(了解即可)
1.HP STL (原始版本 - 1994年):
-
地位: 由Alexander Stepanov和Meng Lee在惠普实验室开发,是STL的原始实现和概念起源。
-
特点: 开源、模板化、包含核心组件(容器、算法、迭代器、函数对象)。奠定了STL的设计理念和基本架构。
-
现状: 是历史起点,但已不再是主流使用版本。
2.SGI STL (标准化前的重要实现 - 1990年代末):
-
地位: 由Silicon Graphics公司基于HP STL进行大幅改进和扩展的实现。
-
特点:
-
性能优化: 做了大量性能优化,效率很高。
-
扩展组件: 引入了重要的非标准但广泛使用的组件,如
hash_map,hash_set(后来成为标准的unordered_map,unordered_set)、slist(单链表)、rope(长字符串处理) 以及强大的内存分配器(如alloc)。 -
文档优秀: 提供了非常清晰、深入的在线文档,对理解STL内部机制和设计思想影响深远。
-
-
影响: 成为许多早期编译器(如GCC早期版本)STL实现的基础,其设计和扩展组件对C++标准库的发展产生了巨大影响。其文档至今仍是经典学习资料。
-
现状: 本身作为一个独立实现已较少直接使用,但其思想和组件被广泛吸收。
3.STLport (跨平台移植版本 - 1990年代末至2000年代初):
-
地位: 一个旨在提供高性能、跨平台且符合标准的STL实现的开源项目。
-
目标: 解决早期不同编译器(尤其是Windows上的VC++)自带STL实现质量、性能、可移植性和标准符合性不一致的问题。
-
特点: 基于SGI STL,注重可移植性、调试模式支持、标准符合性(努力跟进C++98/03标准)。
-
现状: 在早期VC++(如VC6)时代非常流行,作为替换编译器自带STL的方案。随着主流编译器(GCC, Clang, MSVC)自身STL实现质量的飞速提升和标准化,STLport的重要性已大大降低,项目基本停止活跃。
4.标准库STL实现 (主流编译器自带):
-
地位: 目前绝对主流的STL使用方式。C++标准(C++98/03, C++11, C++14, C++17, C++20, C++23)定义了STL(严格来说是标准库中的容器、算法、迭代器、函数对象等部分)的接口和行为规范。
-
实现者: 各大编译器厂商(或开源社区)负责根据标准规范实现自己的版本:
-
GNU (GCC):
libstdc++(通常称为GNU C++ Library) -
LLVM/Clang:
libc++ -
Microsoft (MSVC): MSVC STL (历史上曾称Dinkumware STL, 现在官方称MSVC STL)
-
其他: Embarcadero C++ Builder, Intel C++ Compiler等也有其实现或适配。
-
-
特点:
-
标准符合性: 严格遵循(或努力追赶)最新的C++标准规范。
-
与编译器深度集成: 紧密配合编译器的特性(如ABI、优化、错误信息)。
-
持续演进: 不断加入对新标准特性(C++11/14/17/20/23)的支持(如移动语义、智能指针、新容器
unordered_map/set,array,forward_list, 并行算法、范围操作等)。 -
性能优化: 各实现都在性能上进行激烈竞争和持续优化。
-
平台适配性: 针对特定操作系统和硬件架构进行优化。
-
-
现状: 是当今C++开发者直接使用的STL实现。选择哪个版本通常取决于你选择的编译器。
总结:
-
HP STL: 始祖,奠定基础。
-
SGI STL: 承前启后,性能卓越,扩展丰富,影响深远(特别是文档)。
-
STLport: 特定历史时期(跨平台/标准符合性需求强烈,编译器实现不佳时)的流行移植方案。
-
编译器自带标准库STL (
libstdc++,libc++, MSVC STL): 绝对主流,严格遵循标准,深度集成编译器,持续演进更新。开发者日常接触和使用的就是这些实现。
主要包括这些内容:
二.string类
1.认识string类
有关string类的介绍
2.string类的常用接口说明
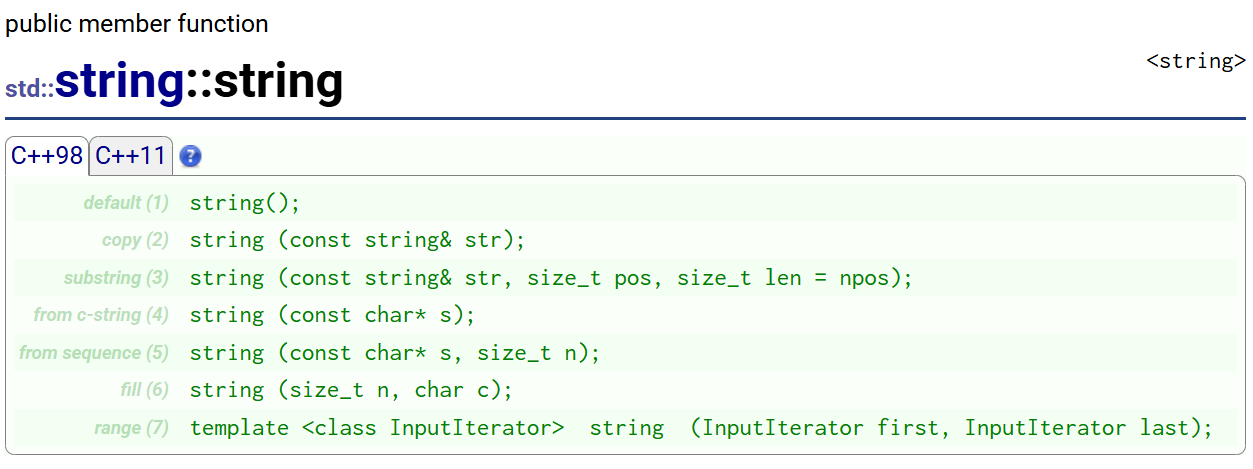
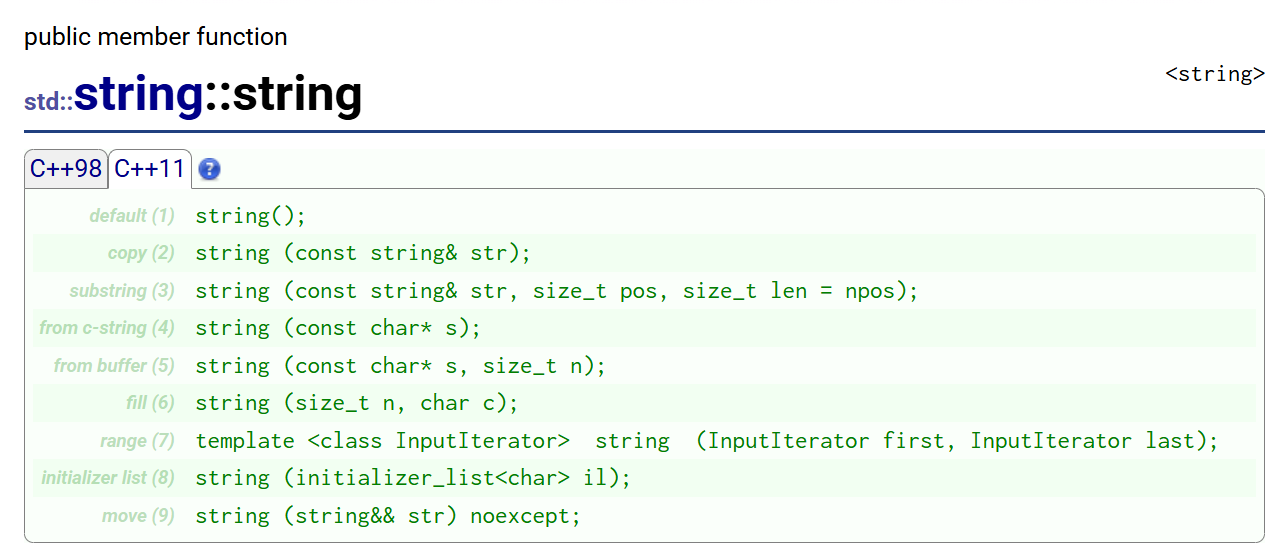
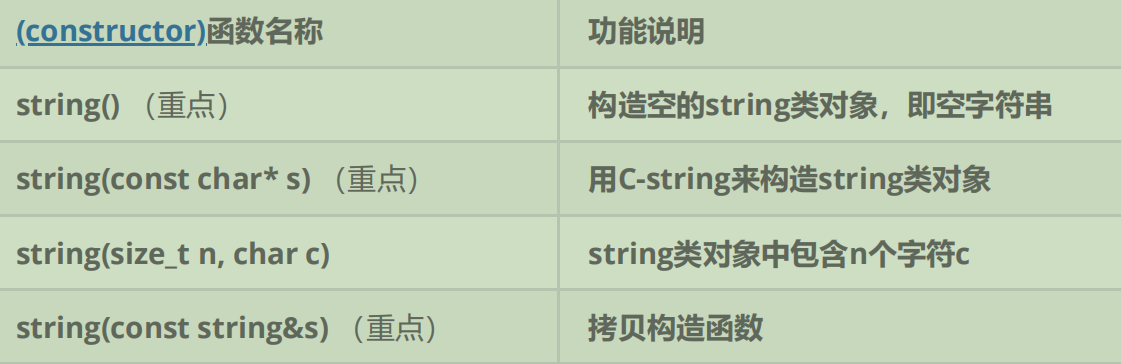
2.1构造函数
文档链接:cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/string/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1;string s2("hello world");string s3(s2);cout << s1 << endl;cout << s2 << endl;cout << s3 << endl;//cin >> s1;//cout << s1 << endl;string s4(s2, 6, 15);cout << s4 << endl;string s5(s2, 6);cout << s5 << endl;string s6("hello world", 5);cout << s6 << endl;string s7(10, 'X');cout << s7 << endl;s6[0] = 'x';cout << s6 << endl;return 0;
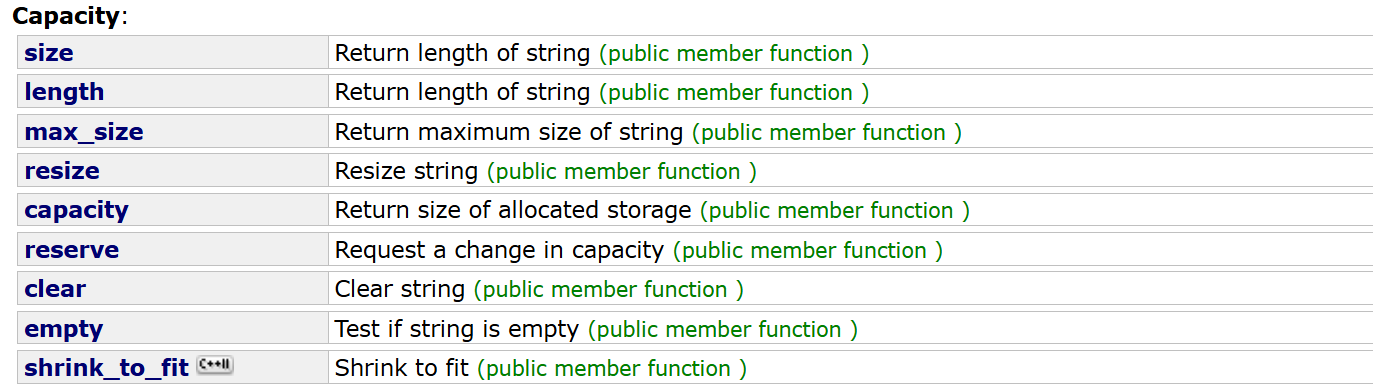
}2.2 string类对象的容量操作
文档链接:string - C++ Reference
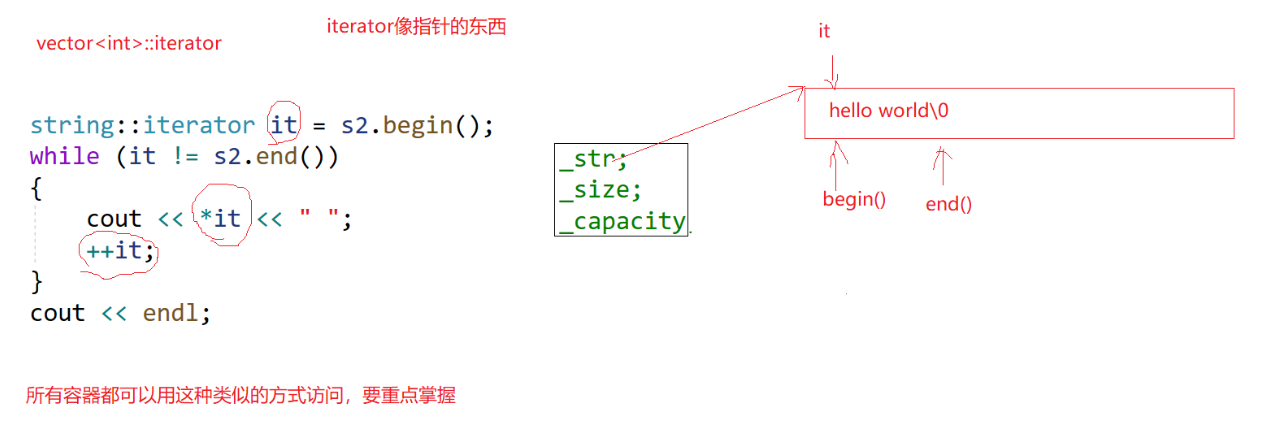
2.3string类对象的访问及遍历操作
迭代器(类似于指针):
正向迭代器:
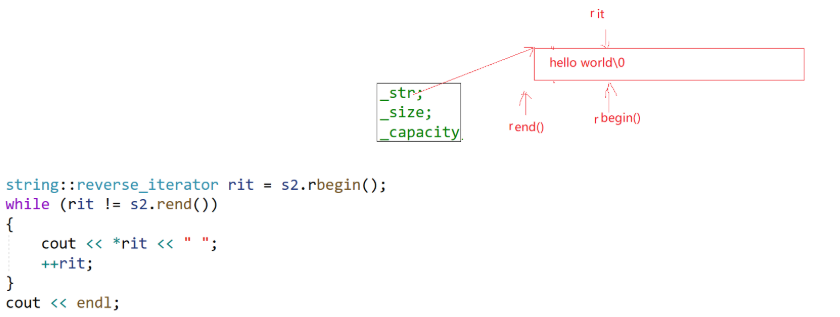
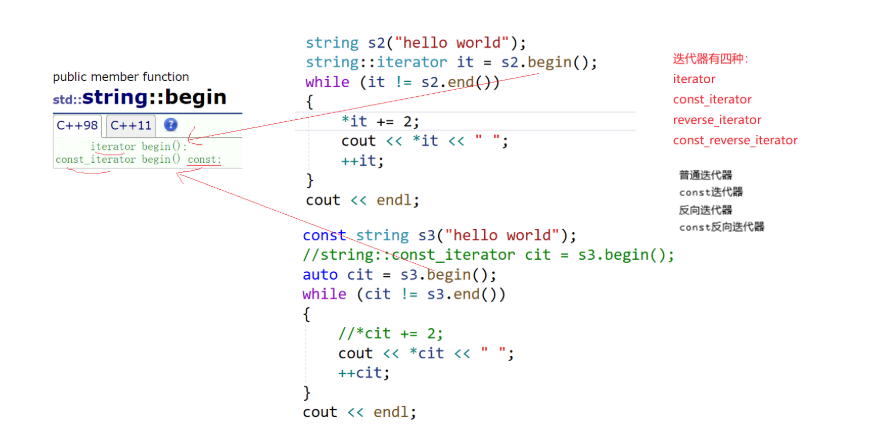
反向迭代器:


#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include<list>
using namespace std;void test_string1()
{string s1;string s2("hello world");cout << s1 << s2 << endl;s2[0] = 'x';cout << s1 << s2 << endl;// 1、下标 + []for (size_t i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++){cout << s2[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// 2、迭代器//string::iterator it = s2.begin();auto it = s2.begin();while (it != s2.end()){*it += 2;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;cout << s2 << endl;map<string, string> dict;//map<string, string>::iterator mit = dict.begin();auto mit = dict.begin();/*list<int> lt = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };list<int>::iterator lit = lt.begin();while (lit != lt.end()){cout << *lit << " ";++lit;}cout << endl;*/// 3、字符赋值,自动迭代,自动判断结束// 底层就是迭代器//for (auto ch : s2)for (auto& ch : s2){ch -= 2;cout << ch << " ";}cout << endl;cout << s2 << endl;
}void test_string2()
{string s2("hello world");string::iterator it = s2.begin();while (it != s2.end()){*it += 2;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;string::reverse_iterator rit = s2.rbegin();while (rit != s2.rend()){cout << *rit << " ";++rit;}cout << endl;const string s3("hello world");//string::const_iterator cit = s3.begin();auto cit = s3.begin();while (cit != s3.end()){//*cit += 2;cout << *cit << " ";++cit;}cout << endl;//string::const_reverse_iterator rcit = s3.rbegin();auto rcit = s3.rbegin();while (rcit != s3.rend()){// *rcit += 2;cout << *rcit << " ";++rcit;}cout << endl;
}void TestPushBack()
{// reverse 反转 逆置// reserve 保留、预留string s;// 提前开空间,避免扩容,提高效率s.reserve(100);size_t sz = s.capacity();cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';cout << "making s grow:\n";for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i){s.push_back('c');if (sz != s.capacity()){sz = s.capacity();cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';}}
}void test_string3()
{string s2("hello world");cout << s2.length() << endl;cout << s2.size() << endl;cout << s2.max_size() << endl;cout << s2.capacity() << endl;TestPushBack();string s3("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx");//cout << sizeof(s2) << endl;//cout << sizeof(s3) << endl;
}
//reserve capacity 测试 不同的编译器可能不一样
void test_string4()
{string s2("hello worldxxxxxxxxxxxxx");cout << s2.size() << endl;cout << s2.capacity() << endl << endl;s2.reserve(20);cout << s2.size() << endl;cout << s2.capacity() << endl << endl;s2.reserve(28);cout << s2.size() << endl;cout << s2.capacity() << endl << endl;s2.reserve(40);cout << s2.size() << endl;cout << s2.capacity() << endl << endl;s2.clear();cout << s2.size() << endl;cout << s2.capacity() << endl << endl;cout << typeid(string::iterator).name() << endl;cout << typeid(string::reverse_iterator).name() << endl;}int main()
{test_string4();return 0;
}2.4string类对象的修改操作

2.5. string类非成员函数

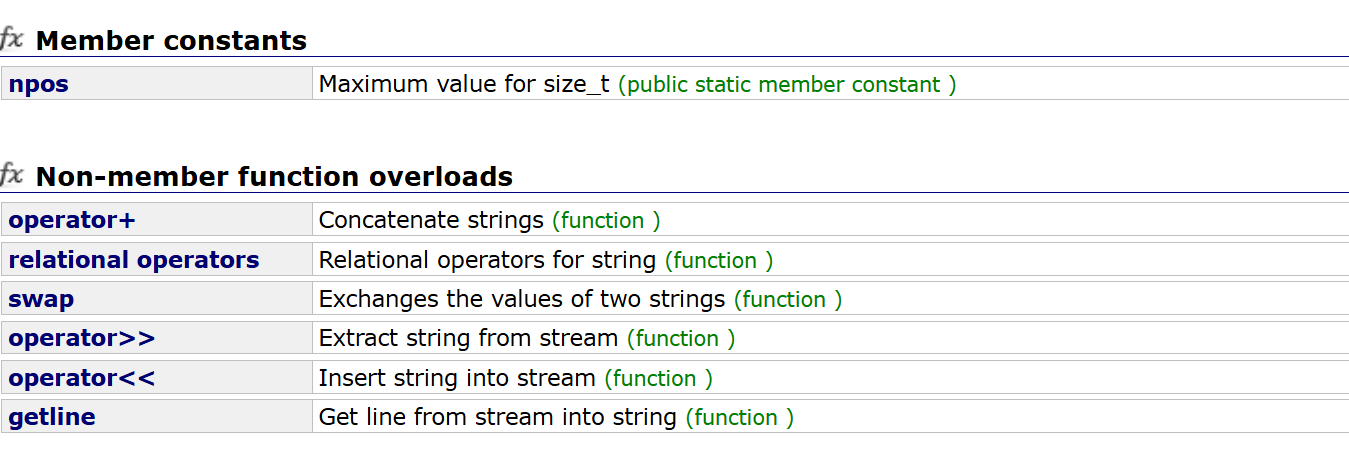
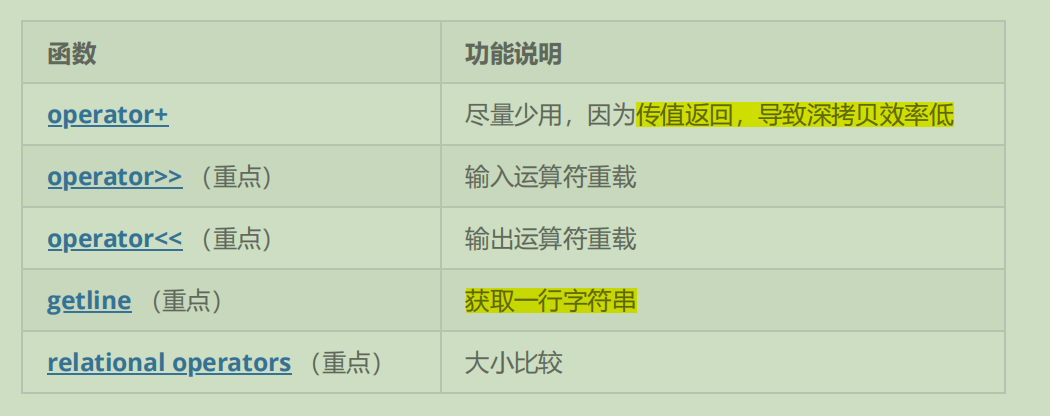 以上的接口介绍的没介绍的都可以自行查阅文档学习,不一一列举。
以上的接口介绍的没介绍的都可以自行查阅文档学习,不一一列举。
C library - C++ Reference
2.6 vs和g++下string结构的说明
2.6.1 vs下string的结构
class string
{
private:char _buff[16];char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;
};union _Bxty
{ // storage for small buffer or pointer to larger one
value_type _Buf[_BUF_SIZE];
pointer _Ptr;
char _Alias[_BUF_SIZE]; // to permit aliasing
} _Bx;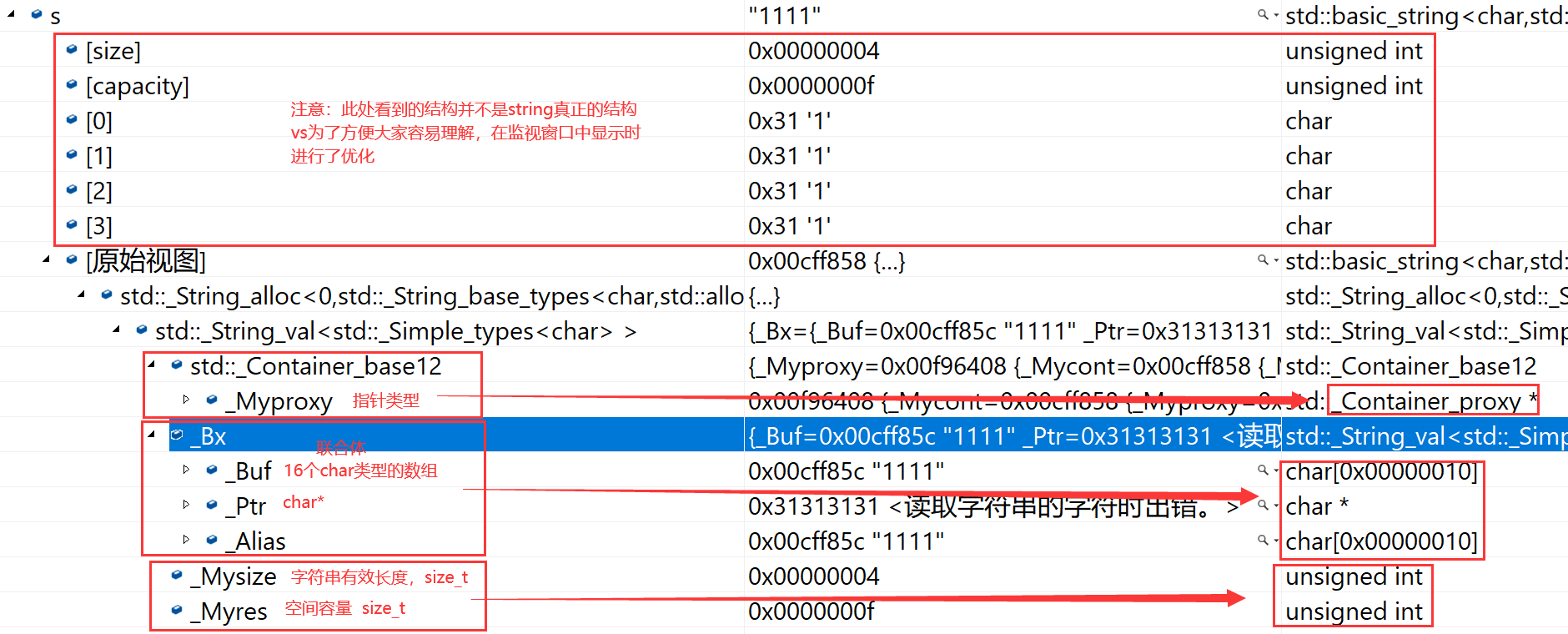
2.6.2 g++下string的结构
struct _Rep_base
{
_length;
size_type _M_capacity;
_Atomic_word _M_refcount;
};关于写时拷贝和引用计数,有兴趣的可以阅读一下这篇大佬写的文章:
C++ STL string的Copy-On-Write技术 | 酷 壳 - CoolShell
3.C++11的小语法(auto关键字和范围for)
3.1auto关键字(做类型推导)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int func1()
{return 10;
}
// 不能做参数
void func2(auto a)
{}// 可以做返回值,但是建议谨慎使用
auto func3()
{return 3;
}
int main()
{int a = 10;auto b = a;auto c = 'a';auto d = func1();// 编译报错:rror C3531: “e”: 类型包含“auto”的符号必须具有初始值设定项auto e;cout << typeid(b).name() << endl;cout << typeid(c).name() << endl;cout << typeid(d).name() << endl;int x = 10;auto y = &x;auto* z = &x;auto& m = x;cout << typeid(x).name() << endl;cout << typeid(y).name() << endl;cout << typeid(z).name() << endl;auto aa = 1, bb = 2;// 编译报错:error C3538: 在声明符列表中,“auto”必须始终推导为同一类型auto cc = 3, dd = 4.0;// 编译报错:error C3318: “auto []”: 数组不能具有其中包含“auto”的元素类型auto array[] = { 4, 5, 6 };return 0;
}#include<iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{std::map<std::string, std::string> dict = { { "apple", "苹果" },{ "orange","橙子" }, {"pear","梨"} };// auto的用武之地 简单方便快捷//std::map<std::string, std::string>::iterator it = dict.begin();auto it = dict.begin();while (it != dict.end()){cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;++it;}return 0;
}3.2范围for(遍历方便)
#include<iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };// C++98的遍历for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]); ++i){array[i] *= 2;}for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]); ++i){cout << array[i] << endl;}// C++11的遍历for (auto& e : array)e *= 2;for (auto e : array)cout << e << " " << endl;string str("hello world");for (auto ch : str){cout << ch << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}4.string类的实现
string.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma once#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;namespace sy
{class string{public:typedef char* iterator;typedef const char* const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _str;}iterator end(){return _str + _size;}const_iterator begin() const{return _str;}const_iterator end() const{return _str + _size;}/*string():_str(new char[1]{'\0'}),_size(0),_capacity(0){}*/// 短小频繁调用的函数,可以直接定义到类里面,默认是inlinestring(const char* str = ""){_size = strlen(str);// _capacity不包含\0_capacity = _size;_str = new char[_capacity + 1];strcpy(_str, str);}// 深拷贝问题// s2(s1)/*string(const string& s){_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];strcpy(_str, s._str);_size = s._size;_capacity = s._capacity;}*/void swap(string& s){std::swap(_str, s._str);std::swap(_size, s._size);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);}// s2(s1)// 现代写法string(const string& s){string tmp(s._str);swap(tmp);}// s2 = s1// s1 = s1/*string& operator=(const string& s){if (this != &s){delete[] _str;_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];strcpy(_str, s._str);_size = s._size;_capacity = s._capacity;}return *this;}*/// s1 = s3;//string& operator=(const string& s)//{// if (this != &s)// {// //string tmp(s._str);// string tmp(s);// swap(tmp);// }// return *this;//}// s1 = s3;string& operator=(string tmp){swap(tmp);return *this;}~string(){if (_str){delete[] _str;_str = nullptr;_size = _capacity = 0;}}const char* c_str() const{return _str;}void clear(){_str[0] = '\0';_size = 0;}size_t size() const{return _size;}size_t capacity() const{return _capacity;}char& operator[](size_t pos){assert(pos < _size);return _str[pos];}const char& operator[](size_t pos) const{assert(pos < _size);return _str[pos];}/*void copy_on_write(){if (count > 1){深拷贝}}*/void reserve(size_t n);void push_back(char ch);void append(const char* str);string& operator+=(char ch);string& operator+=(const char* str);void insert(size_t pos, char ch);void insert(size_t pos, const char* str);void erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos);size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0);size_t find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0);string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);private://char _buff[16];char* _str = nullptr;size_t _size = 0;size_t _capacity = 0;//static const size_t npos = -1;static const size_t npos;/*static const int N = 10;int buff[N];*/};bool operator<(const string& s1, const string& s2);bool operator<=(const string& s1, const string& s2);bool operator>(const string& s1, const string& s2);bool operator>=(const string& s1, const string& s2);bool operator==(const string& s1, const string& s2);bool operator!=(const string& s1, const string& s2);ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s);istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s);
}string.cpp
#include"string.h"namespace sy
{//静态成员变量⼀定要在类外进⾏初始化const size_t string::npos = -1;void string::reserve(size_t n){if (n > _capacity){char* tmp = new char[n + 1];strcpy(tmp, _str);delete[] _str;_str = tmp;_capacity = n;}}void string::push_back(char ch){if (_size == _capacity){reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);}_str[_size] = ch;++_size;_str[_size] = '\0';}string& string::operator+=(char ch){push_back(ch);return *this;}void string::append(const char* str){size_t len = strlen(str);if (_size + len > _capacity){// 大于2倍,需要多少开多少,小于2倍按2倍扩reserve(_size + len > 2 * _capacity ? _size + len : 2 * _capacity);}strcpy(_str + _size, str);_size += len;}string& string::operator+=(const char* str){append(str);return *this;}void string::insert(size_t pos, char ch){assert(pos <= _size);if (_size == _capacity){reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);}// 挪动数据size_t end = _size + 1;while (end > pos){_str[end] = _str[end - 1];--end;}_str[pos] = ch;++_size;}void string::insert(size_t pos, const char* s){assert(pos <= _size);size_t len = strlen(s);if (_size + len > _capacity){// 大于2倍,需要多少开多少,小于2倍按2倍扩reserve(_size + len > 2 * _capacity ? _size + len : 2 * _capacity);}size_t end = _size + len;while (end > pos + len - 1){_str[end] = _str[end - len];--end;}for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++){_str[pos + i] = s[i];}_size += len;}void string::erase(size_t pos, size_t len){assert(pos < _size);if (len >= _size - pos){_str[pos] = '\0';_size = pos;}else{for (size_t i = pos + len; i <= _size; i++){_str[i - len] = _str[i];}_size -= len;}}size_t string::find(char ch, size_t pos){assert(pos < _size);for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++){if (_str[i] == ch){return i;}}//找不到返回-1return npos;}size_t string::find(const char* str, size_t pos){assert(pos < _size);const char* ptr = strstr(_str + pos, str);if (ptr == nullptr){return npos;}else{return ptr - _str;}}string string::substr(size_t pos, size_t len){assert(pos < _size);// len大于剩余字符长度,更新一下lenif (len > _size - pos){len = _size - pos;}string sub;sub.reserve(len);for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++){sub += _str[pos + i];}return sub;}bool operator<(const string& s1, const string& s2){return strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str()) < 0;}bool operator<=(const string& s1, const string& s2){return s1 < s2 || s1 == s2;}bool operator>(const string& s1, const string& s2){return !(s1 <= s2);}bool operator>=(const string& s1, const string& s2){return !(s1 < s2);}bool operator==(const string& s1, const string& s2){return strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str()) == 0;}bool operator!=(const string& s1, const string& s2){return !(s1 == s2);}ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s){for (auto ch : s){out << ch;}return out;}istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s){s.clear();const int N = 256;char buff[N];int i = 0;char ch;//in >> ch;ch = in.get();while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n'){buff[i++] = ch;if (i == N - 1){buff[i] = '\0';s += buff;i = 0;}//in >> ch;ch = in.get();}if (i > 0){buff[i] = '\0';s += buff;}return in;}
}test.cpp
#include"string.h"namespace sy
{void test_string1(){string s1;string s2("hello world");cout << s1.c_str() << endl;cout << s2.c_str() << endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++){s2[i] += 2;}cout << s2.c_str() << endl;for (auto e : s2){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;string::iterator it = s2.begin();while (it != s2.end()){//*it += 2;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}void test_string2(){string s1("hello world");s1 += 'x';s1 += '#';cout << s1.c_str() << endl;s1 += "hello";cout << s1.c_str() << endl;s1.insert(5, '$');cout << s1.c_str() << endl;s1.insert(0, '$');cout << s1.c_str() << endl;string s2("hello world");cout << s2.c_str() << endl;s2.insert(5, "$$$");cout << s2.c_str() << endl;s2.insert(0, "$$$&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&");cout << s2.c_str() << endl;}void test_string3(){string s1("hello world");s1.erase(6, 100);cout << s1.c_str() << endl;string s2("hello world");s2.erase(6);cout << s2.c_str() << endl;string s3("hello world");s3.erase(6, 3);cout << s3.c_str() << endl;}void test_string4(){string s("test.cpp.zip");size_t pos = s.find('.');string suffix = s.substr(pos);cout << suffix.c_str() << endl;string copy(s);cout << copy.c_str() << endl;s = suffix;cout << suffix.c_str() << endl;cout << s.c_str() << endl;s = s;cout << s.c_str() << endl;}void test_string5(){string s1("hello world");string s2("hello world");cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;cout << ("hello world" < s2) << endl;cout << (s1 == "hello world") << endl;cout << ("hello world" == "hello world") << endl;cout << s1 << s2 << endl;string s0;cin >> s0;cout << s0 << endl;}void test_string6(){string s1("hello world");string s2 = s1;cout << s1 << endl;cout << s2 << endl;string s3("xxxxxxxxxxxxxx");s1 = s3;cout << s1 << endl;cout << s3 << endl;}void test_string7(){string s1("hello world");string s2("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx");std::swap(s1, s2);s1.swap(s2);}
}
int main()
{sy::test_string1();sy::test_string2();sy::test_string3();sy::test_string4();sy::test_string5();sy::test_string6();sy::test_string7();return 0;
}5.浅拷贝和深拷贝问题
5.1浅拷贝
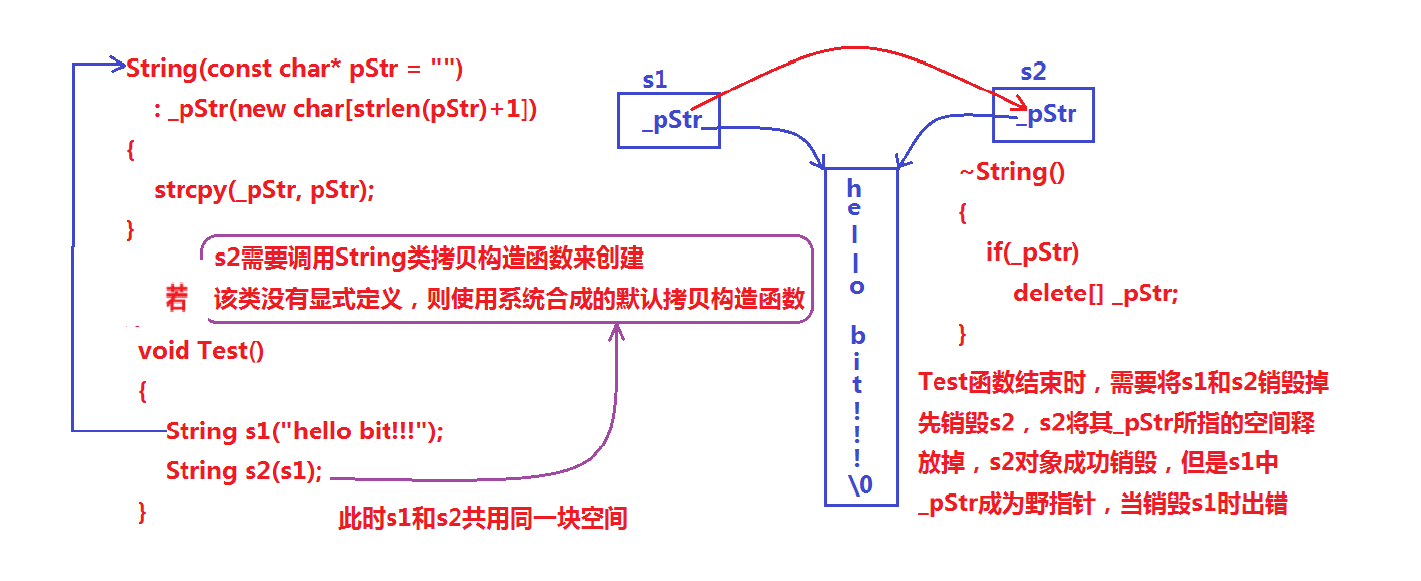
5.1深拷贝
如果一个类中涉及到资源的管理,其拷贝构造函数、赋值运算符重载以及析构函数必须要显式给出。一般情况都是按照深拷贝方式提供。

6.string 在线OJ题目
415. 字符串相加 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:string addStrings(string num1, string num2) {string str;int end1=num1.size()-1,end2=num2.size()-1;int next=0;while(end1>=0 || end2>=0){int val1 = end1 >=0 ? num1[end1--]-'0' : 0;int val2 = end2 >=0 ? num2[end2--]-'0' : 0;int ret=val1+val2+next;next=ret / 10;ret=ret % 10;str +=('0'+ret);}if(next==1)str+='1';reverse(str.begin(),str.end());return str;}
};917. 仅仅反转字母 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:bool isLetter(char ch){if(ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z')return true;if(ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')return true;return false;}string reverseOnlyLetters(string S) {if(S.empty())return S;size_t begin = 0, end = S.size()-1;while(begin < end){while(begin < end && !isLetter(S[begin]))++begin;while(begin < end && !isLetter(S[end]))--end;swap(S[begin], S[end]);++begin;--end;}return S;}
};class Solution {public://1. 分别对字符串进行正序查询和反序查询// 2. 如果所查询的字符下标相等,说明此字符只出现了一次int firstUniqChar(string s) {for(int i=0; i<s.size(); ++i){int index = s.find(s[i]);int reverse_index = s.rfind(s[i]); if(index == reverse_index)return i;}return -1;}};class Solution {
public:int firstUniqChar(string s) {int a[256]={0};for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){a[s[i]]+=1;} for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){if(1==a[s[i]]){return i;}}return -1;}
};字符串最后一个单词的长度_牛客题霸_牛客网
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;
int main()
{string str;getline(cin, str);reverse(str.begin(), str.end());string::iterator it = str.begin();int count = 0;while (it != str.end() && * it != ' '){count++;++it;}cout << count << endl;return 0;
}#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string line;// 不要使用cin>>line,因为会它遇到空格就结束了// while(cin>>line)while(getline(cin, line)){size_t pos = line.rfind(' ');cout<<line.size()-pos-1<<endl;}return 0;
}class Solution {
public:bool isletter(char ch){if((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >='A' && ch <='Z') ||(ch >='0' && ch <= '9')){return true;}return false;}bool isPalindrome(string s) {//全部转成小写字母for(auto& ch :s){if(ch >='A' && ch <='Z'){ch+=32;}}int begin=0;int end=s.size()-1;while(begin < end){while(begin < end && !isletter(s[begin])){++begin;}while(begin < end && !isletter(s[end])){--end;}if(s[begin]!=s[end]){return false;}else{++begin;--end;}}return true;}
};541. 反转字符串 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:void Reverse(string& s, int start, int end) {char tmp;end--;while (start < end){tmp = s[start];s[start] = s[end];s[end] = tmp;start++;end--;}}string reverseStr(string s, int k){int len = s.size();for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 2 * k){if (i + k < len)Reverse(s, i, i + k);elseReverse(s, i, len);}return s;}
};557. 反转字符串中的单词 III - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:string reverseWords(string s) {string::iterator it = s.begin();int count = 0;int end = 0;auto ptr = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){if(*it == ' '){std::reverse(ptr, s.begin() + count);ptr = s.begin() + count + 1;}count++;it++;}std::reverse(ptr, s.end());return s;}
};43. 字符串相乘 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
void MulItem(string& tmp, string& num1, char a){int i = 0, sign = 0;int mul = 0;while (i < num1.size()){mul = (num1[i] - '0') * (a - '0') + sign;if (mul >= 10){sign = mul / 10;mul %= 10;}elsesign = 0;tmp.push_back(mul + '0');i++;}if (sign > 0)tmp.push_back(sign + '0');}//对应位相加,sign进位采用引用传递int AddItem(int a, int b, int& sign){int add = a + b + sign;if (add >= 10){sign = 1;add -= 10;}elsesign = 0;return add;}//错位相加void MoveAdd(string& result, string& tmp, int k){int i, j;i = k;j = 0;int sign = 0;while (i < result.size() && j < tmp.size()){result[i] = AddItem(result[i] - '0', tmp[j] - '0', sign) + '0';i++;j++;}while (i < result.size() && sign){result[i] = AddItem(result[i] - '0', 0, sign) + '0';i++;}while (j < tmp.size()){int v = AddItem(0, tmp[j] - '0', sign);result.push_back(v + '0');j++;}if (sign)result.push_back(sign + '0');}string multiply(string num1, string num2){//先翻转数据,方便进位处理reverse(num1.begin(), num1.end());reverse(num2.begin(), num2.end());string tmp, result;for (int i = 0; i < num2.size(); ++i){//使用num2的每一个数据乘以num1MulItem(tmp, num1, num2[i]);//将乘得的结果进行错位相加MoveAdd(result, tmp, i);tmp.clear();}//处理前导0while (result.size() != 1 && result.back() == '0')result.pop_back();//翻转数据,恢复数据reverse(result.begin(), result.end());return result;}
};