【C++】Stack and Queue and Functor
本文是小编巩固自身而作,如有错误,欢迎指出!
本次我们介绍STL中的stack和queue和其相关的一些容器和仿函数
一.stack and queue
1.适配器
stack和queue其实不是真正意义上的容器,而是容器适配器,而容器适配器又是什么呢?
在C++中,容器适配器(Container Adapters)是一种特殊的容器,它们不提供独立的底层数据存储结构,而是基于其他基础容器(如 vector、deque、list)来实现特定的功能和接口。
简单来说就是之前我们学习的时要了解stack和queue的底层是什么,是数组还是队列,同理在c++就考虑他的底层是vector还是list等等
而在官方给的底层是deque
 而deque又是什么呢?
而deque又是什么呢?
2.deque
全称为“double-ended queue”,即双端队列,是 C++ 标准模板库(STL)中的一种容器。
简单来说deque就是vector和list的缝合产物
通过前面的学习我们都知道,vector的尾插时间复杂度比头插小,而list痛点在于不能随机访问,但deque就解决了这个问题
deque 是一种序列容器,它允许在容器的两端快速插入和删除元素,时间复杂度为 O(1)。与 vector 相比,deque 可以在头部和尾部高效地进行元素的插入和删除操作;与 list 相比,deque 支持随机访问元素。
deque的原理类似下图
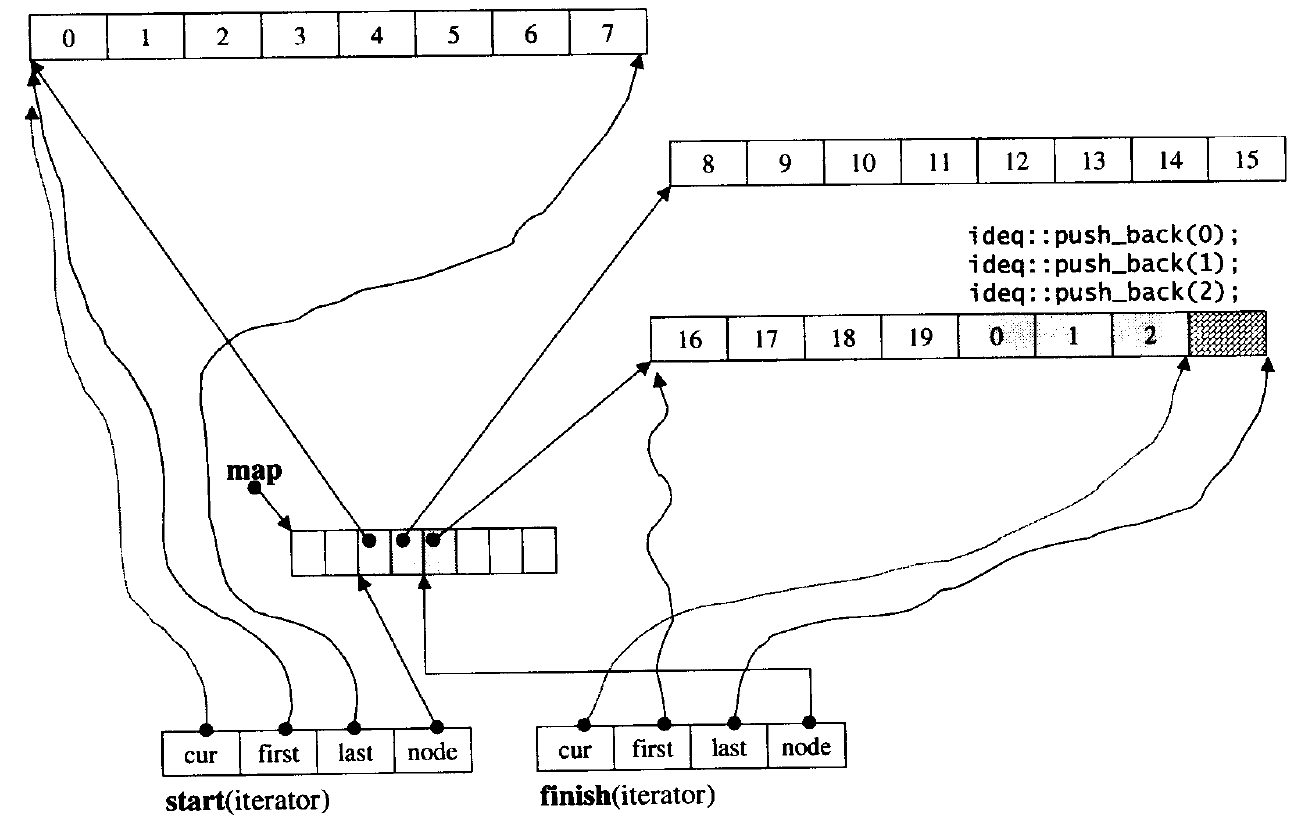
deque本质其实就是划分一个个个小数组融合成为大数组,其由一个中控数组map操作,而map中储存的就是每个小数组的地址,及其头尾指针等等。
下面是用vector实现的栈和用list实现的队列
#include<vector>
namespace bite
{template<class T>class stack{public:stack() {}void push(const T& x) {_c.push_back(x);}
void pop() {_c.pop_back();}T& top() {return _c.back();}const T& top()const {return _c.back();}size_t size()const {return _c.size();}bool empty()const {return _c.empty();}private:std::vector<T> _c;};
}
#include <list>
namespace bite
{template<class T>class queue{public:queue() {}void push(const T& x) {_c.push_back(x);}void pop() {_c.pop_front();}T& back() {return _c.back();}const T& back()const {return _c.back();}T& front() {return _c.front();}const T& front()const {return _c.front();}size_t size()const {return _c.size();}bool empty()const {return _c.empty();}private:std::list<T> _c;};
}
二.priority_queue
1.priority_queue简介
在 C++ 中,priority_queue(优先队列) 是一种特殊的容器适配器,它基于堆(Heap)数据结构实现,提供常数时间访问最大/最小元素的能力(默认最大堆)。
我们看下以下用例
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{priority_queue<int> pq;pq.push(3);pq.push(5);pq.push(6);pq.push(1);pq.push(9);while (!pq.empty()){cout << pq.top();pq.pop();}return 0;}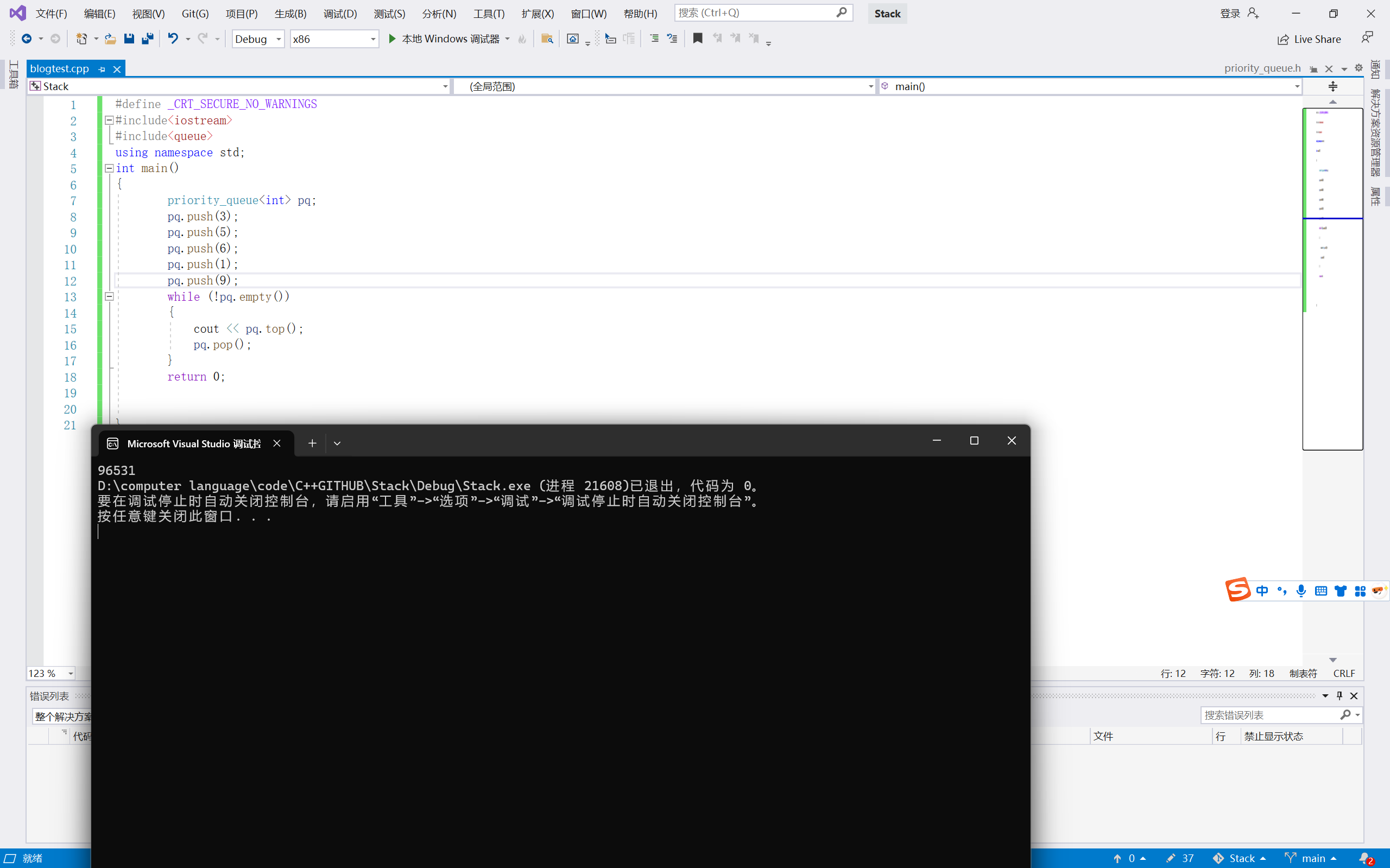
我们看出来这是系统默认的情况(最大堆),那么如果我们自己实现要自己模拟实现想要最小堆建怎么办呢?
我们先看看模拟实现是什么样的
#pragma once
#include<vector>
template<class T>
class Less
{
public:bool operator()(const T& x,const T& y){return x < y;}};
template<class T>
class Greater
{
public:bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y){return x > y;}
};
namespace yiming
{template<class T,class Container=std::vector<T>,class Compare=Less<T>>class priority_queue{public:priority_queue() = default;template <class InputIterator>priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last):con(first,last){//向下调整建堆for (int i = (con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2;i >= 0;i--){adjust_down(i);}}void push(const T& x){con.push_back(x);adjust_up(con.size() - 1);}void pop(){swap(con[0], con[con.size() - 1]);con.pop_back();adjust_down(0);}const T& top(){return con[0];}bool empty()const{return con.empty();}size_t size()const{return con.size();}private:void adjust_up(int child)//向上调整{Compare com;int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){if (com(con[parent], con[child])){swap(con[child], con[parent]);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else{break;}}}void adjust_down(int parent){Compare com;size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;while (child < con.size()){if (child + 1 < con.size() && com(con[child], con[child + 1]))//选出最大的child++child;if (com(con[parent], con[child])){swap(con[parent], con[child]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else{break;}}}private:Container con;};
}
其中我们看到了主要决定这个模拟实现的类型就行这样一个模版
template<class T,class Container=std::vector<T>,class Compare=Less<T>>我们看到通过这个模版的Compare就可以实现建大堆小堆,这里就涉及到一个概念,仿函数
2.仿函数
仿函数(Functor)是C++中一种行为类似函数的对象,通过重载
operator()实现。它可以是普通函数指针、类成员函数指针或定义了operator()的类对象。
其实简单来说就是把一个类包装成函数的样子
如上述代码中的
template<class T>
class Less
{
public:bool operator()(const T& x,const T& y){return x < y;}};
template<class T>
class Greater
{
public:bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y){return x > y;}
};这样就可以通过模版来实现改变建大堆小堆了
三.测试代码
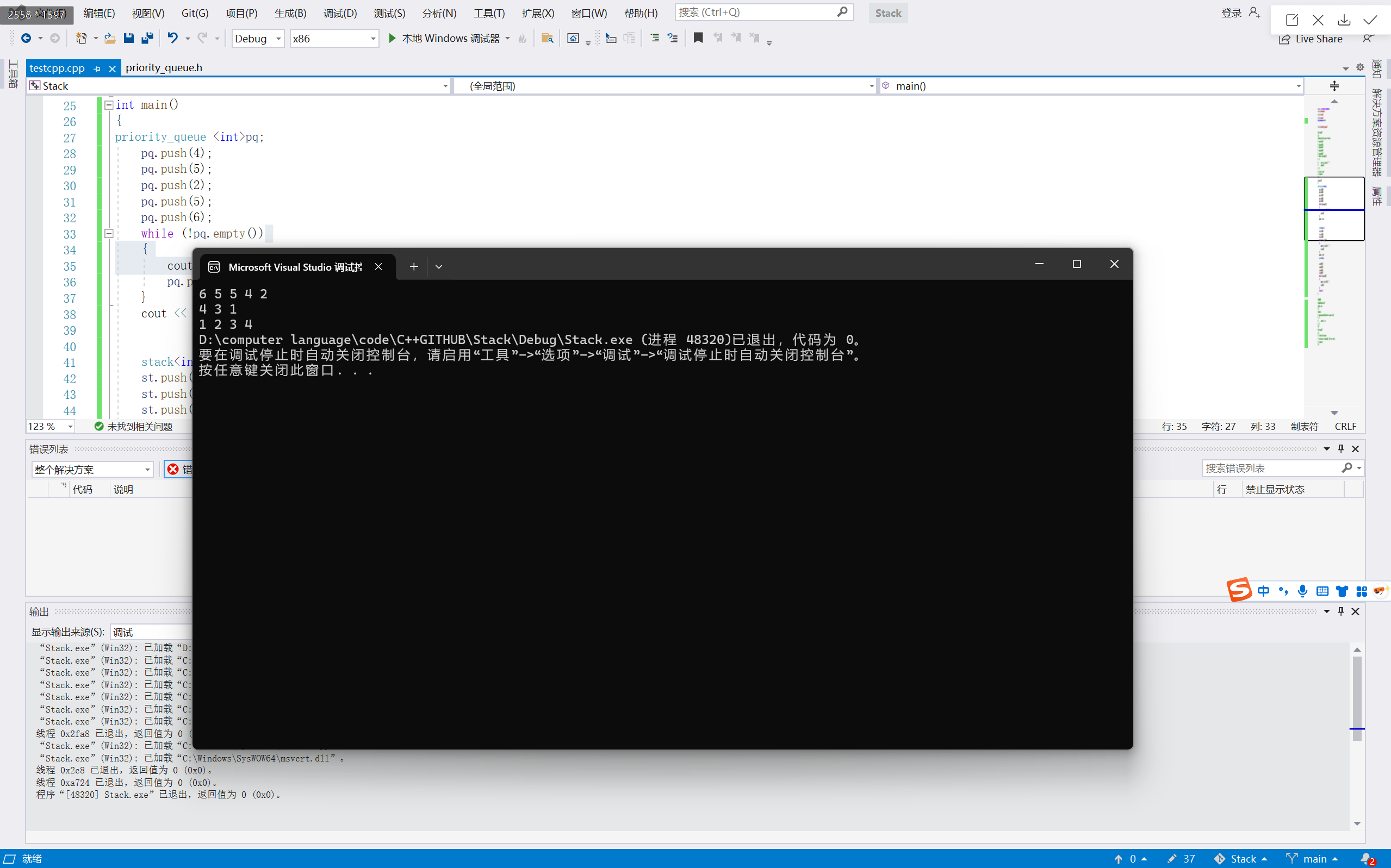
int main()
{
priority_queue <int>pq;pq.push(4);pq.push(5);pq.push(2);pq.push(5);pq.push(6);while (!pq.empty()){cout << pq.top() << " ";pq.pop();}cout << endl;stack<int> st;st.push(1);st.push(3);st.push(4);while (!st.empty()){cout << st.top() << " ";st.pop();}cout << endl;queue<int>q;q.push(1);q.push(2);q.push(3);q.push(4);while (!q.empty()){cout << q.front()<<" ";q.pop();}return 0;
}
本次分享就到这里结束了,后续会继续更新,感谢阅读!