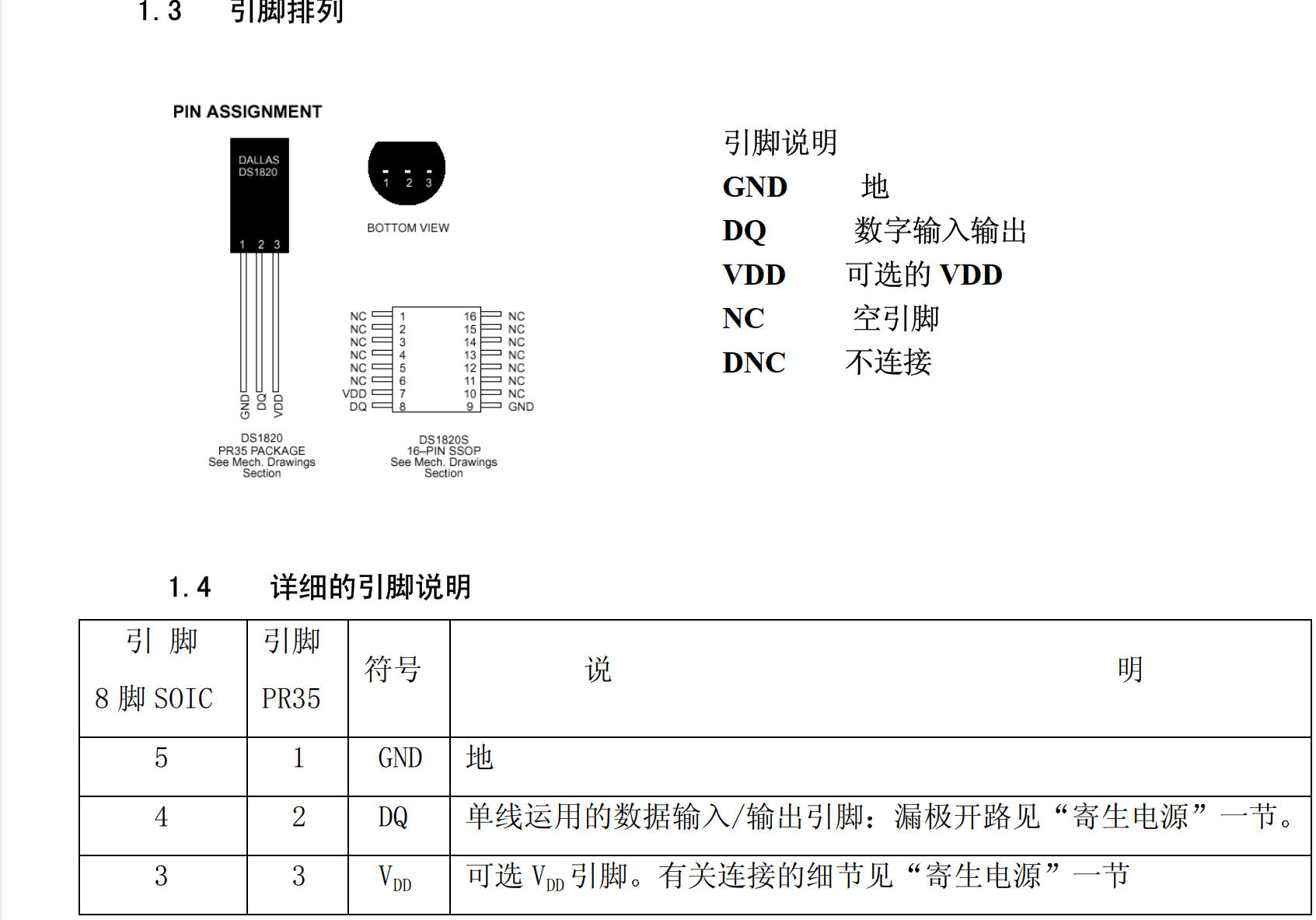
platform平台驱动、gpio单总线通信
前瞻
一、
不需要总线的:led灯控制、beep、按键
需要总线通信的:
基于gpio的单总线通信的传感器:ds18b20、dht11、超声波测距
基于i2c总线:LM75
基于spi总线:ADXL345
总线通信需要总线控制器
总线协议在软件代码的体现其实就是按照传感器时序图进行复位、读写操作。
所以单总线协议就是指按照传感器手册的复位时序图进行复位,然后用读写时序图读写,就算是单总线协议了吗
是的,单总线协议(1-Wire)的核心就是严格按照传感器手册的时序要求进行复位、读/写操作。你的理解基本正确,但需要补充一些关键细节:
1. 单总线协议的本质
单总线协议是一种 基于严格时序的串行通信协议,其核心包括:
复位脉冲(Reset):主机拉低总线 480µs~960µs,然后释放,等待从机(如 DS18B20)回应一个低电平(60µs~240µs),表示设备存在。
读写时序:
写 0:主机拉低总线 60µs~120µs。
写 1:主机拉低总线 1µs~15µs,然后释放。
读数据:主机拉低总线 1µs~15µs,然后在 15µs 内采样总线电平。
数据格式:
每个字节按 LSB(最低位优先) 传输。
需支持标准 ROM 命令(如
0xCC跳过 ROM)和功能命令(如0x44启动温度转换)。
2. 你的代码是否算单总线协议?
是的! 你的代码完全符合 DS18B20 的 1-Wire 协议要求:
复位:
ds18b20_reset()实现了复位和存在检测。写操作:
ds18b20_writebit()和ds18b20_writebyte()严格遵循写时序。读操作:
ds18b20_readbit()和ds18b20_readbyte()符合读时序。命令序列:
ds18b20_readvalue()发送了0xCC(跳过 ROM)和0x44(启动转换),最后读取数据。
3. 单总线协议的完整流程
以 DS18B20 为例,完整流程包括:
复位 → 检测设备存在。
发送 ROM 命令(如
0xCC跳过 ROM)。发送功能命令(如
0x44启动温度转换)。**
那uart、i2c、spi协议是指按照传感器时序图进行这些操作吗
是的,UART、I2C、SPI 协议的核心也是严格按照传感器或芯片手册的时序图进行通信,但它们与单总线(1-Wire)协议在实现方式、硬件支持和复杂度上有显著区别。以下是详细对比:
1. 协议的本质区别
| 特性 | 单总线 (1-Wire) | UART | I2C | SPI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 信号线数量 | 1 根(数据线 + 地线) | 2 根(TX、RX) | 2 根(SCL、SDA) | 4 根(SCK、MOSI、MISO、CS) |
| 通信方式 | 半双工(严格时序控制) | 全双工(异步) | 半双工(同步) | 全双工(同步) |
| 时序关键性 | 极高(µs 级延时) | 中等(波特率匹配) | 中等(时钟同步) | 高(时钟边沿采样) |
| 硬件支持 | 需软件模拟或专用控制器 | 多数 MCU 内置硬件 UART | 多数 MCU 内置硬件 I2C | 多数 MCU 内置硬件 SPI |
| 典型应用 | DS18B20 等简单传感器 | 调试串口、模块通信 | 传感器、EEPROM | 高速设备(Flash、屏幕) |
2. 如何理解“按时序图操作”?
(1) 单总线(1-Wire)
完全依赖软件模拟时序(如你的
ds18b20_reset()、ds18b20_writebit())。例:DS18B20 的复位时序:
c
复制
下载
// 主机拉低 480µs~960µs gpio_set_value(gpio, 0); udelay(480); // 释放总线,等待从机响应 gpio_set_value(gpio, 1);
(2) UART
依赖波特率(Baud Rate),时序体现在字节格式(起始位、数据位、停止位)。
例:发送字节
0x55(二进制01010101):text
复制
下载
时序图:起始位(0) + 8位数据(LSB优先) + 停止位(1)
(3) I2C
依赖时钟(SCL)同步,时序包括:
起始条件(SCL 高时 SDA 下降沿)。
数据位在 SCL 低电平时变化,高电平时采样。
停止条件(SCL 高时 SDA 上升沿)。
例:读取 I2C 设备(地址
0x50)的寄存器0x00:text
复制
下载
时序图:START → 写地址(0x50) → 写寄存器(0x00) → RESTART → 读数据 → STOP
(4) SPI
依赖时钟边沿(SCK)采样,时序包括:
模式(CPOL/CPHA)决定时钟极性和采样边沿。
数据在 SCK 的上升沿或下降沿传输。
例:SPI 模式 0(CPOL=0, CPHA=0):
text
复制
下载
时序图:SCK 低电平时数据变化,上升沿采样。
3. 关键结论
单总线:
最底层,需完全手动控制 GPIO 时序(如你的代码)。
适用于简单、低速设备(如 DS18B20)。
UART/I2C/SPI:
通常由硬件控制器实现,开发者只需配置寄存器(如波特率、时钟频率)。
若没有硬件支持,也可软件模拟(如用 GPIO 模拟 I2C),但复杂度和稳定性较低。
共同点:
无论哪种协议,都必须严格遵循芯片手册的时序图!
差异在于时序的复杂性和硬件支持程度。
4. 实际开发建议
优先使用硬件控制器(如 MCU 的 I2C/SPI 外设),避免软件模拟。
单总线设备:
若需驱动多个 DS18B20,建议改用 Linux 内核的w1-gpio驱动(已内置 1-Wire 协议栈)。调试工具:
用逻辑分析仪抓取时序,对比手册检查是否合规。
LED不需要专用控制器的原因
简单的工作机制:
LED是简单的单向导通器件,只需提供适当的电压和电流即可工作
本质上是一个二极管,具有非线性I-V特性
控制方式简单:
可以直接通过开关控制通断
亮度调节可通过PWM(脉宽调制)或改变电流实现
不需要复杂的通信协议
应用场景:
指示用途:简单的开/关状态
照明用途:可能需要恒流驱动,但仍属简单控制
传感器需要总线控制器的原因
复杂的数据交互:
传感器需要发送采集的数据
可能需要接收配置参数或控制指令
双向通信需求
标准化接口需求:
总线控制器实现标准通信协议(I2C, SPI, CAN, RS485等)
解决不同设备间的互操作性问题
处理电气特性匹配(电平转换、阻抗匹配等)
数据处理功能:
数据打包/解包
错误检测与校正
协议转换(如将传感器数据转换为网络协议)
二、总线
之前以及把驱动中设备相关信息从驱动独立出来,放到设备树了,现在由于传感器等的使用需要用到总线,所以直接把总线独立出来。
platform_device platform_bus platform_driver
自己注册 内核写好了 自己编写
platform_device_register
注册过时,直接设备树转化
但是要手动配置设备树后转化
一、platform平台虚拟总线(把led、蜂鸣器、emmc、网卡、adc等不需要总线的设备也用总线来简化管理)
(1)、match设备与驱动的匹配方法
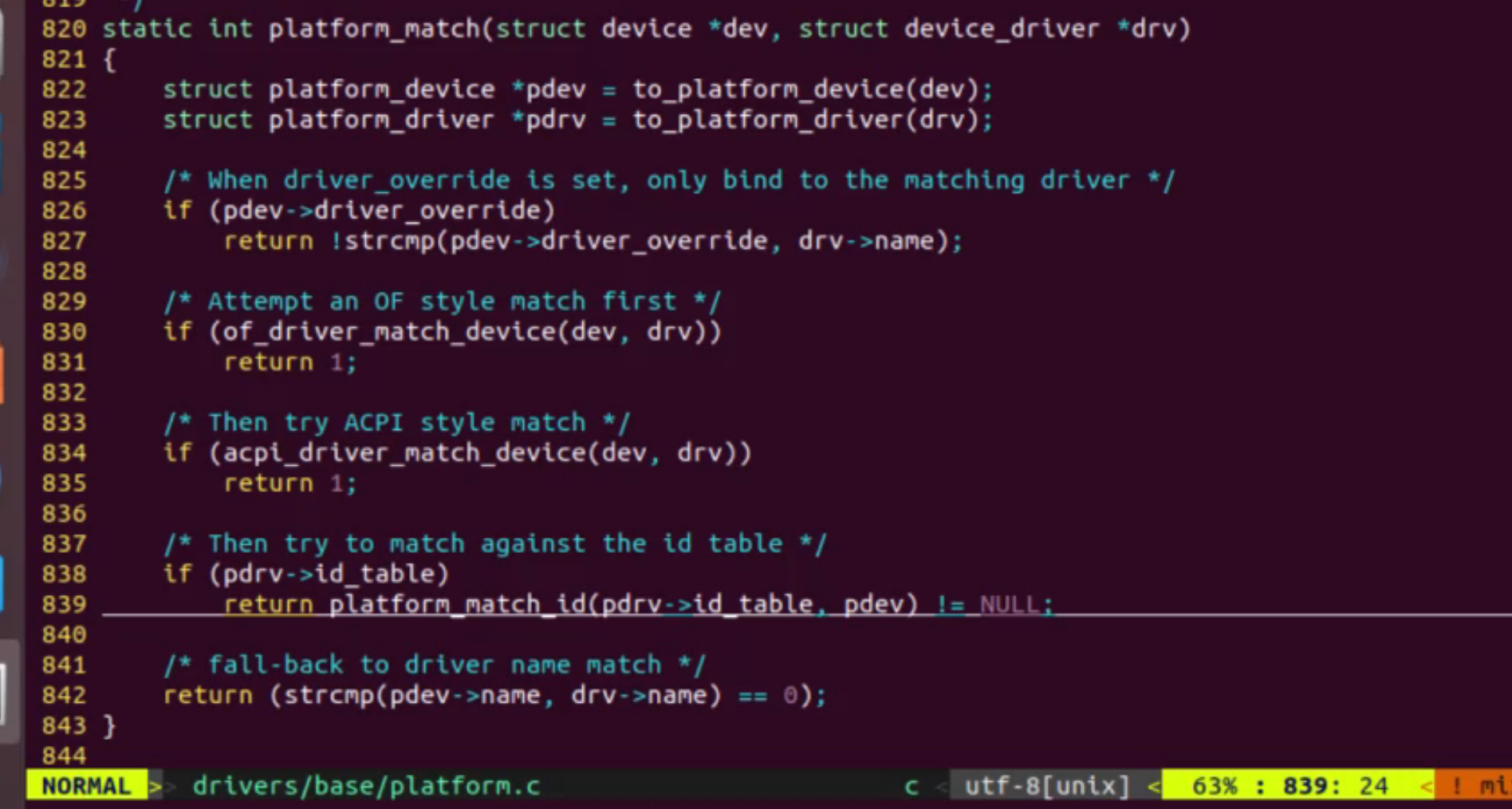
1、设备指定驱动的名字(第一优先级)
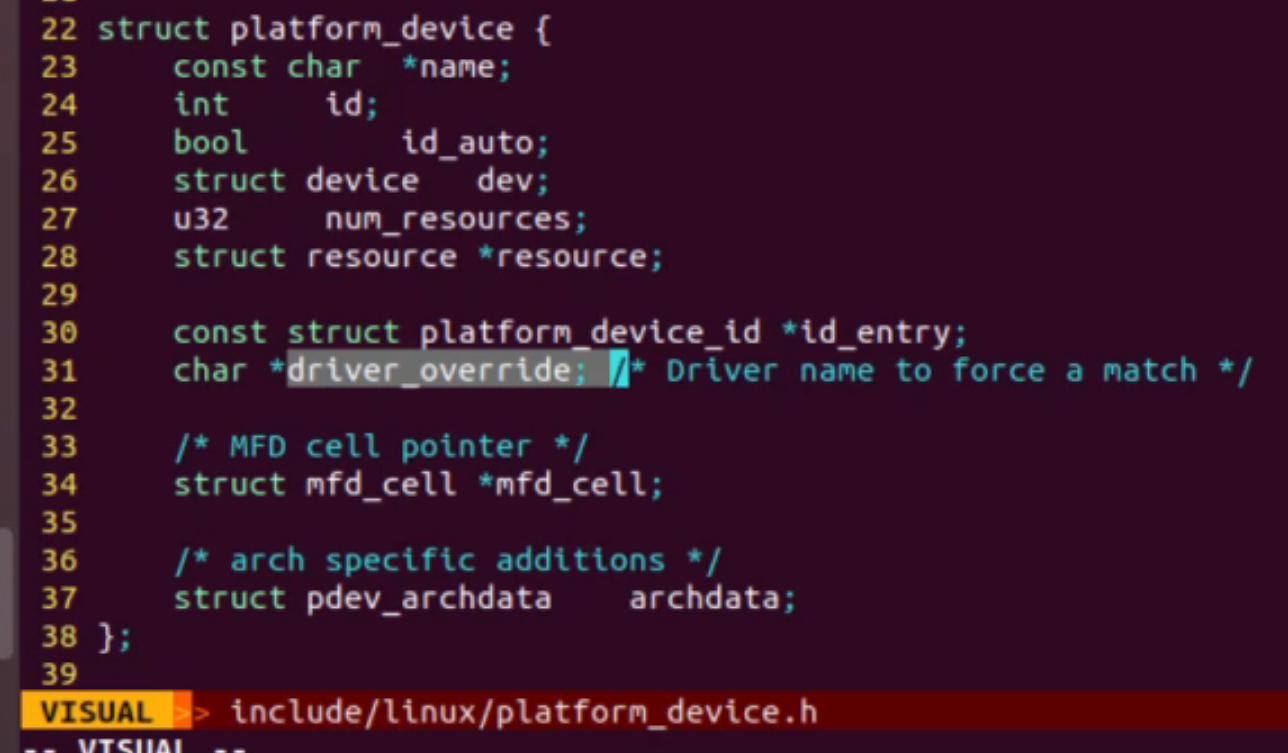
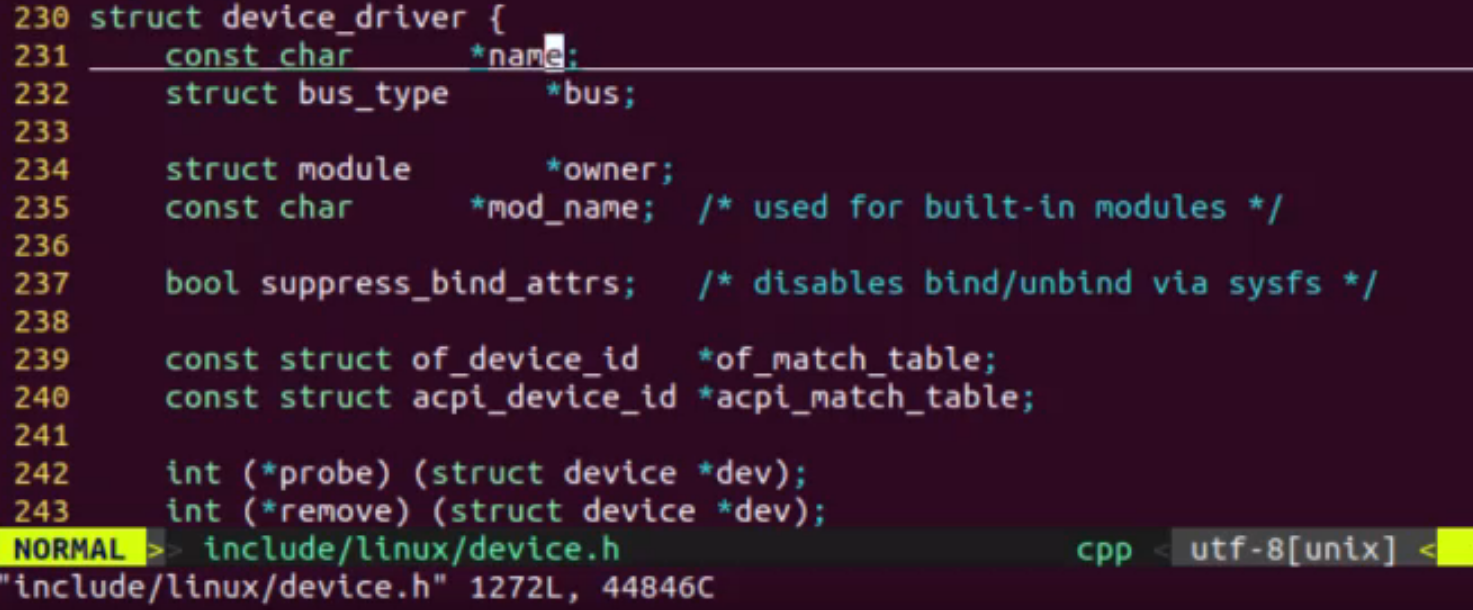
2、驱动中的of_match_table与设备名相同
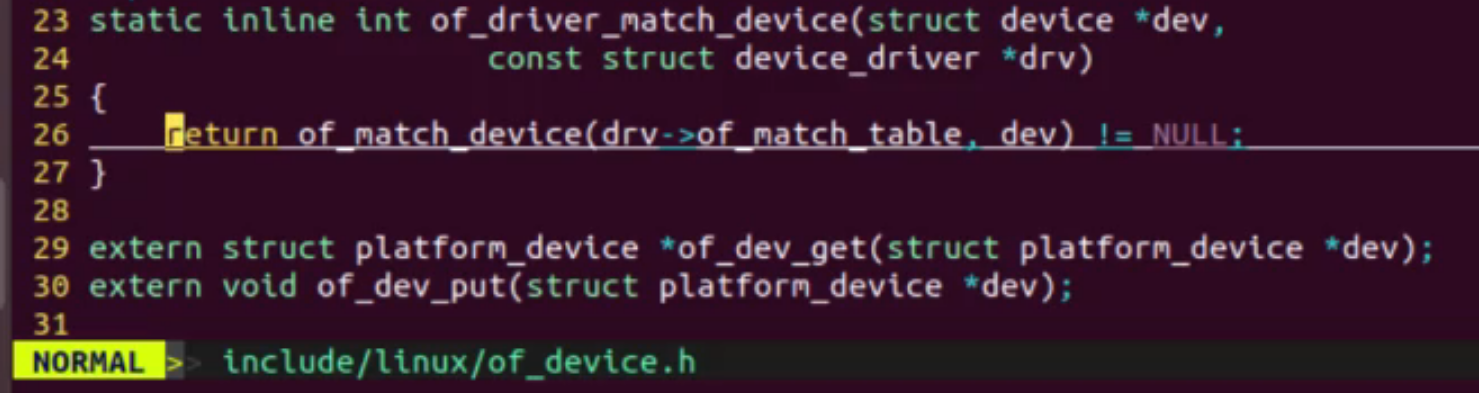
3、x86架构下的api匹配模式(适用pc端)
4、驱动中的ip_table与设备名相同
5、驱动名与设备名相同
自己写的平台驱动里面有个probe函数,设备跟驱动匹配成功就会执行该函数
remove注销设备
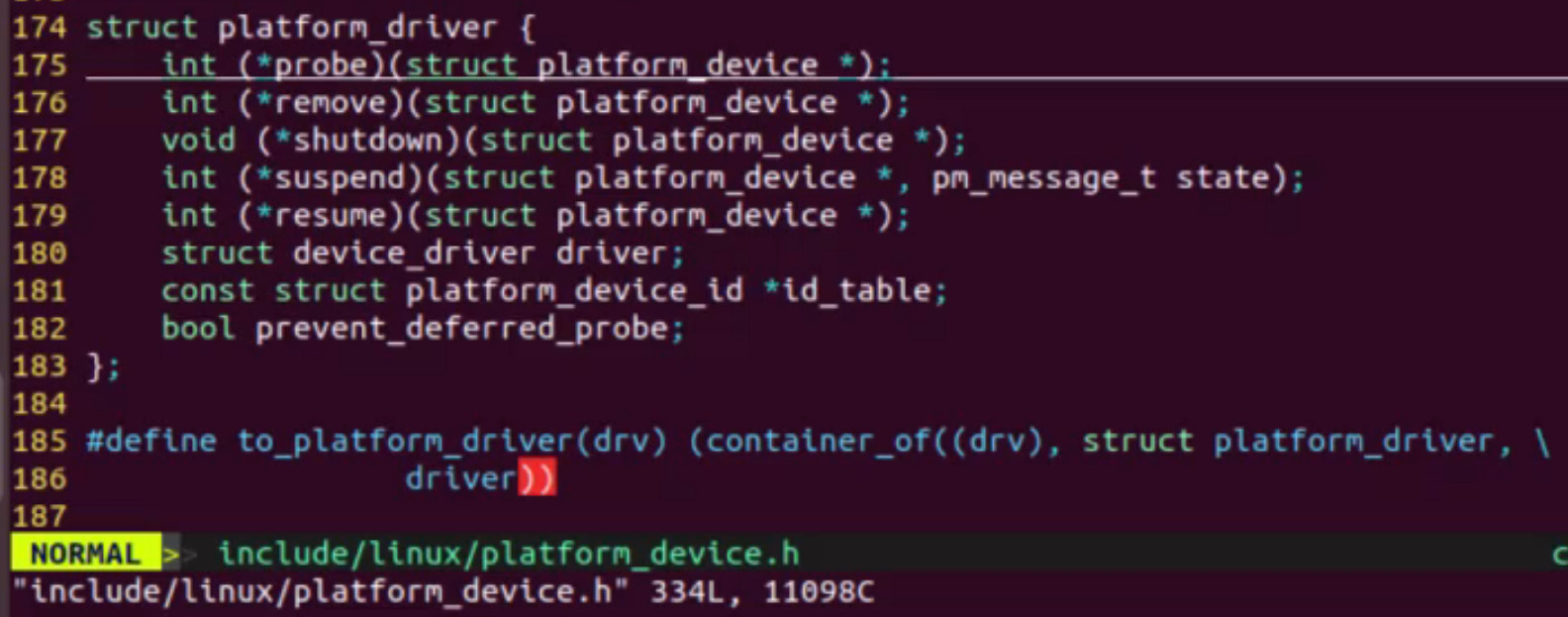
(2)驱动编写
注册设备、重写文件操作结构体、创建设备节点,应用层通过文件操作操作寄存器控制设备
寄存器信息来自跟驱动匹配成功的设备
设备树
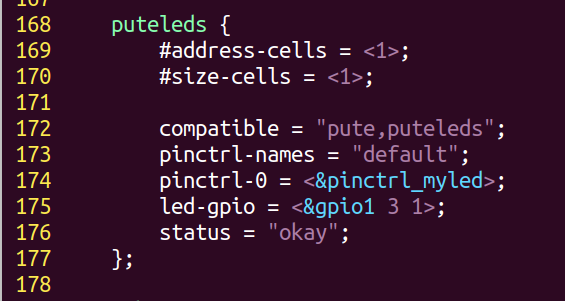
驱动
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include<linux/device.h>
#include<asm/io.h>
#include<asm-generic/io.h>
#include<asm/uaccess.h>
#include<linux/string.h>
#include<linux/io.h>
#include<linux/of.h>
#include <linux/of_address.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include<linux/miscdevice.h>
#include<linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
static int ledstat;//自定义的led灯状态变量
static int ledgpio = 0;
static struct mutex led_lock;
//文件操作函数
static ssize_t led_read(struct file *fp, char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off)
{int ret;//当用户调用read时,把ledstat的值给用户ret = copy_to_user(puser,&ledstat,sizeof(ledstat));pr_info("read success\n");return sizeof(ledstat);
}
static ssize_t led_write(struct file *fp, const char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off)
{int ret;//拷贝用户调用write写入的数据到ledstatret = copy_from_user(&ledstat,puser,sizeof(ledstat));mutex_lock(&led_lock);//写入1开灯if(ledstat == 1){//置0开灯gpio_set_value(ledgpio,0);}//写入0关灯if(ledstat == 0){//置1关灯gpio_set_value(ledgpio,1);}mutex_unlock(&led_lock);pr_info("write success\n");return ret;
}
static int led_open(struct inode *node, struct file *fp)
{pr_info("open success\n");return 0;
}
static int led_release(struct inode *node, struct file *fp)
{pr_info("release success\n");return 0;
}
//文件操作函数结构体
static struct file_operations fops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE, //计数,表示有几个模块调用文件操作.open = led_open,.release = led_release, .read = led_read,.write = led_write
};static struct miscdevice misc_device = {.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,//次设备号申请.name = "misc_led",//设备节点名.fops = &fops,//绑定文件操作函数结构体
};static int led_probe(struct platform_device *pdevice)
{struct device_node *dtslednode = NULL;//初始化锁mutex_init(&led_lock);//注册混杂设备misc_register(&misc_device);//获取设备树节点dtslednode = pdevice->dev.of_node;//获取引脚编号ledgpio = of_get_named_gpio(dtslednode,"led-gpio",0);//GPIO方向设为输出gpio_direction_output(ledgpio,1);//设备树已初始化为高电平ledstat = 0;pr_info("led_probe success\n");return 0;
}
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *pdevice)
{//释放引脚编号gpio_free(ledgpio);//销毁混杂设备misc_deregister(&misc_device);pr_info("led_remove success\n");return 0;
}//平台设备驱动匹配
static struct of_device_id led_of_match_table[] = {{.compatible = "pute,puteleds"},{},
};
static struct platform_device_id led_id_table[] = {{.name = "puteleds"},{},
};
static struct platform_driver led_platform_drv = {.driver = {.name = "puteleds",.of_match_table = led_of_match_table,},.id_table = led_id_table,.probe = led_probe,.remove = led_remove,
};//驱动入口内调函数
static int __init led_init(void)
{//向内核注册一个平台驱动,将其绑定到platform虚拟总线上,并触发匹配设备的功能platform_driver_register(&led_platform_drv);pr_info("beep init success\n");return 0;
}//驱动出口内调函数
static void __exit led_exit(void)
{//销毁平台驱动platform_driver_unregister(&led_platform_drv);pr_info("beep exit success\n");return;
}//驱动入口
module_init(led_init);
//驱动出口
module_exit(led_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");二、利用gpio单总线通信采集ds18b20传感器

线与特性:只有当都为高电平时表示没有收发数据,只要有一方想要收发数据,就要先拉低电平。
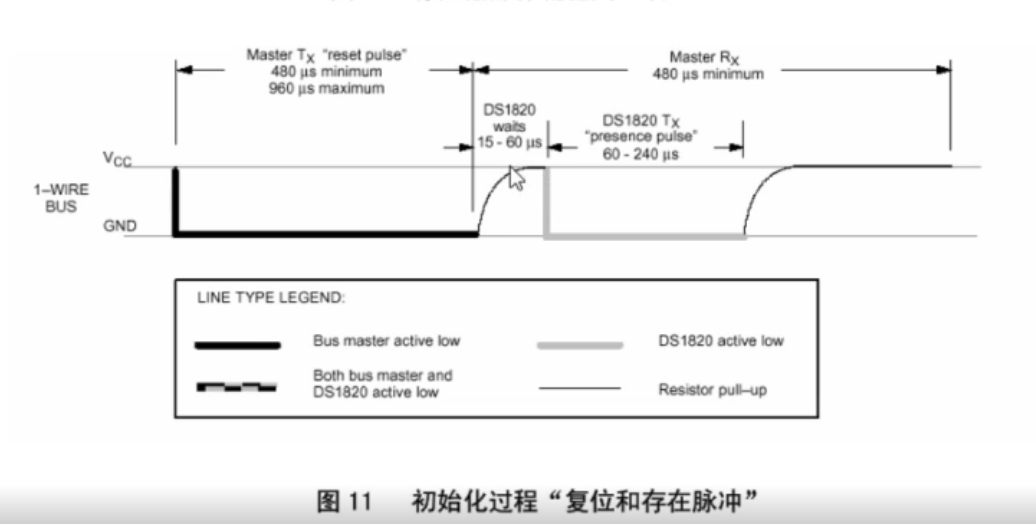
1、初始化:

2、rom操作 0xcc跳过rom
3、存储器操作 0x44 启动温度转换
4、等待转化完成
5、初始化
6、rom操作 0xcc
7、存储器操作 0xbe读前两个字节返回数据,*0.0625即温度
发送0xcc:即发送一个字节,先看看怎么发送一位
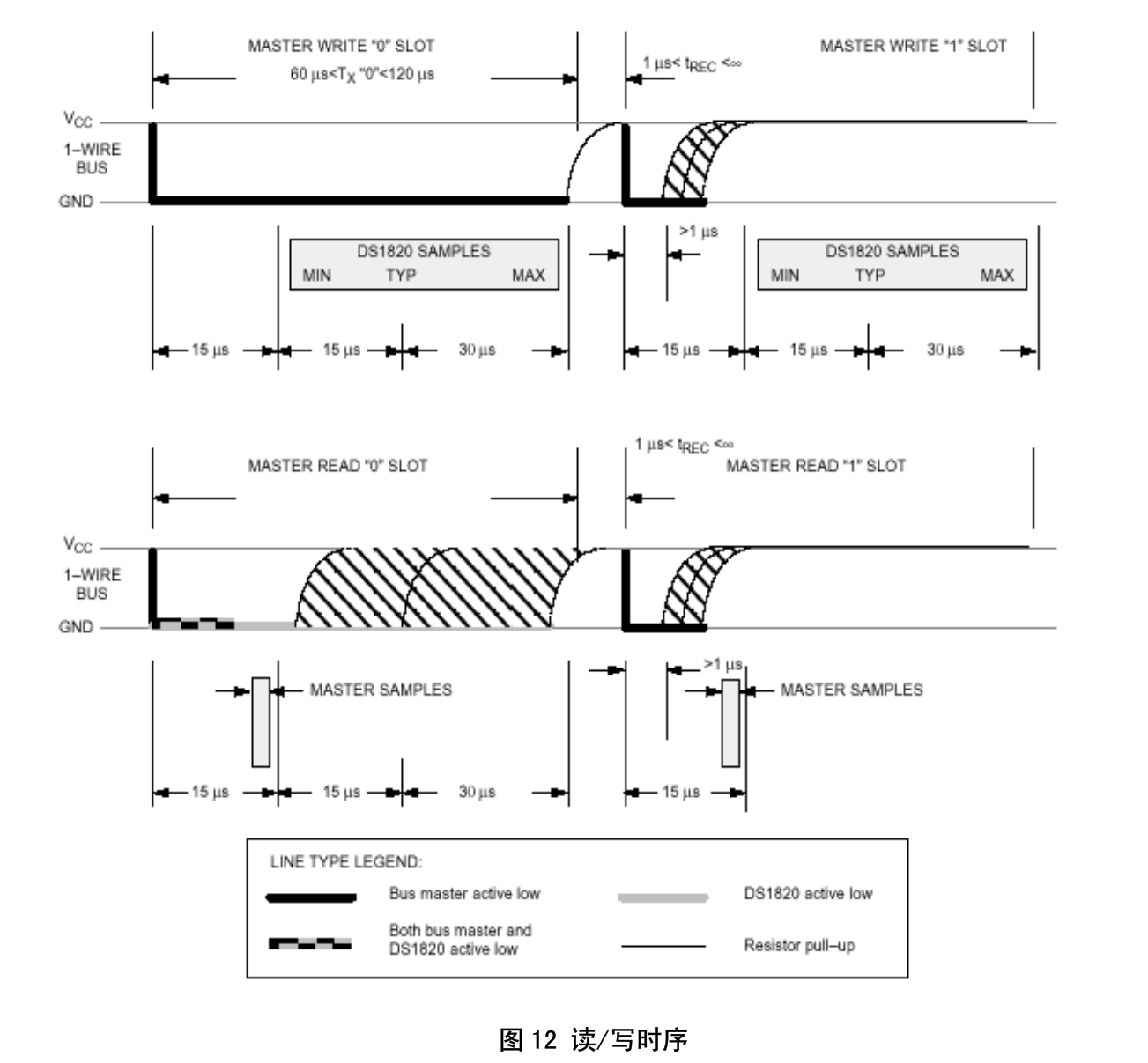
write:
 12位默认,即等待750毫秒
12位默认,即等待750毫秒
read:

延时用delay实现
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/of.h>
#include <linux/of_address.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
static int ds18b20state; //自定义的led灯状态变量
static int ds18b20gpio = 0;
static struct mutex ds18b20_lock;static int ds18b20_reset(void)
{int timeout = 20;//拉低480-960usgpio_set_value(ds18b20gpio, 0);udelay(960);gpio_set_value(ds18b20gpio, 1);udelay(60);//等待低电平到来gpio_direction_input(ds18b20gpio);timeout = 20;while (gpio_get_value(ds18b20gpio) && timeout--);if (gpio_get_value(ds18b20gpio))return -1;//等待高电平到来while (!gpio_get_value(ds18b20gpio));udelay(410);gpio_direction_output(ds18b20gpio, 1);return 0;
}static void ds18b20_writebit(unsigned char data)
{//拉低 > 1usgpio_set_value(ds18b20gpio, 0);udelay(5);if (data)gpio_set_value(ds18b20gpio, 1);udelay(115);gpio_set_value(ds18b20gpio, 1);udelay(3);return;
}static void ds18b20_writebyte(unsigned char byte)
{int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 8; i++){ds18b20_writebit(byte & 0x01);byte >>= 1;}return;
}static unsigned char ds18b20_readbit(void)
{unsigned char data = 0;//拉低 > 1usgpio_set_value(ds18b20gpio, 0);udelay(5);gpio_set_value(ds18b20gpio, 1);gpio_direction_input(ds18b20gpio);udelay(7);data = gpio_get_value(ds18b20gpio);gpio_direction_output(ds18b20gpio, 1);udelay(50);return data;
}static unsigned char ds18b20_readbyte(void)
{unsigned char byte = 0;int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 8; i++){if (ds18b20_readbit())byte |= 0x1 << i;}return byte;
}static int ds18b20_readvalue(unsigned long *pvalue)
{int ret = 0;unsigned short th = 0;unsigned short tl = 0;//初始化设备ret = ds18b20_reset();if (-1 == ret)return -1;//跳过ROM(0xcc)ds18b20_writebyte(0xcc);//操作存储器(0x44)ds18b20_writebyte(0x44);//等待转换完成msleep(750);//初始化设备ret = ds18b20_reset();if (-1 == ret)return -1;//跳过ROM(0xcc)ds18b20_writebyte(0xcc);//操作存储器(0xBE)ds18b20_writebyte(0xbe);//读取数据(前2个字节)tl = ds18b20_readbyte();th = ds18b20_readbyte();*pvalue = ((th << 8) | tl); return 0;
}static ssize_t ds18b20_read(struct file *fp, char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off)
{unsigned long ret = 0;unsigned long value = 0;ret = ds18b20_readvalue(&value);if (ret != 0)return -1;ret = copy_to_user(puser, &value, sizeof(value));if (ret)pr_info("copy_to_user failed\n");return sizeof(value);
}static ssize_t ds18b20_write(struct file *fp, const char __user *puser, size_t n,loff_t *off)
{int ret;//拷贝用户调用write写入的数据到ds18b20stateret = copy_from_user(&ds18b20state, puser, sizeof(ds18b20state));mutex_lock(&ds18b20_lock);//写入1开灯if (ds18b20state == 1){//置0开灯gpio_set_value(ds18b20gpio, 0);}//写入0关灯if (ds18b20state == 0){//置1关灯gpio_set_value(ds18b20gpio, 1);}mutex_unlock(&ds18b20_lock);pr_info("write success\n");return ret;
}
static int ds18b20_open(struct inode *node, struct file *fp)
{pr_info("open success\n");return 0;
}
static int ds18b20_release(struct inode *node, struct file *fp)
{pr_info("release success\n");return 0;
}
//文件操作函数结构体
static struct file_operations fops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE, //计数,表示有几个模块调用文件操作.open = ds18b20_open,.release = ds18b20_release,.read = ds18b20_read,.write = ds18b20_write};static struct miscdevice misc_device = {.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, //次设备号申请.name = "misc_ds18b20", //设备节点名.fops = &fops, //绑定文件操作函数结构体
};static int ds18b20_probe(struct platform_device *pdevice)
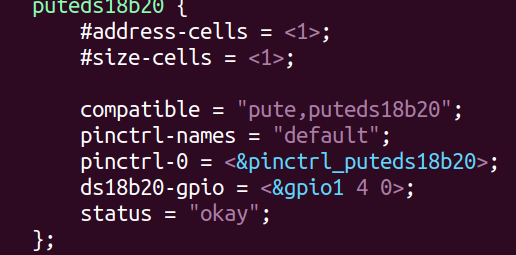
{struct device_node *dtslednode = NULL;//初始化锁mutex_init(&ds18b20_lock);//注册混杂设备misc_register(&misc_device);//获取设备树节点dtslednode = pdevice->dev.of_node;//获取引脚编号ds18b20gpio = of_get_named_gpio(dtslednode, "ds18b20-gpio", 0);// GPIO方向设为输出gpio_direction_output(ds18b20gpio, 1);//设备树已初始化为高电平ds18b20state = 0;pr_info("ds18b20_probe success\n");return 0;
}
static int ds18b20_remove(struct platform_device *pdevice)
{//释放引脚编号gpio_free(ds18b20gpio);//销毁混杂设备misc_deregister(&misc_device);pr_info("ds18b20_remove success\n");return 0;
}//平台设备驱动匹配
static struct of_device_id ds18b20_of_match_table[] = {{.compatible = "pute,puteds18b20"},{},
};
static struct platform_device_id ds18b20_id_table[] = {{.name = "puteds18b20"},{},
};
static struct platform_driver ds18b20_platform_drv = {.driver ={.name = "puteds18b20",.of_match_table = ds18b20_of_match_table,},.id_table = ds18b20_id_table,.probe = ds18b20_probe,.remove = ds18b20_remove,
};//驱动入口内调函数
static int __init ds18b20_init(void)
{//向内核注册一个平台驱动,将其绑定到platform虚拟总线上,并触发匹配设备的功能platform_driver_register(&ds18b20_platform_drv);pr_info("ds18b20 init success\n");return 0;
}//驱动出口内调函数
static void __exit ds18b20_exit(void)
{//销毁平台驱动platform_driver_unregister(&ds18b20_platform_drv);pr_info("ds18b20 exit success\n");return;
}//驱动入口
module_init(ds18b20_init);
//驱动出口
module_exit(ds18b20_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(void)
{int fd = 0;unsigned long value = 0;fd = open("/dev/misc_ds18b20", O_RDWR);if (-1 == fd){perror("fail to open");return -1;}while (1){read(fd, &value, sizeof(value));printf("value = %.2lf\n", value * 0.0625);sleep(1);}close(fd);return 0;
}dht11
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/of.h>
#include <linux/of_address.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
extern void msleep(unsigned int msecs);
static int dht11state; //自定义的led灯状态变量
static int dht11gpio = 0;
static struct mutex dht11_lock;static void dht11_send_start(void)
{ int ret = 0;//拉低 > 18msret = gpio_direction_output(dht11gpio, 1);if (ret)pr_info("gpio_direction_output failed\n");gpio_set_value(dht11gpio, 0);msleep(20);//拉高gpio_set_value(dht11gpio, 1);return;
}static int dht11_recv_reply(void)
{int ret = 0;int timeout = 0;ret = gpio_direction_input(dht11gpio);if (ret)pr_info("gpio_direction_input failed\n");while (gpio_get_value(dht11gpio) && timeout < 200) {udelay(5);timeout++;}if (timeout >= 200)return -1;while (!gpio_get_value(dht11gpio));while (gpio_get_value(dht11gpio));return 0;
}static unsigned char dht11_recv_byte(void)
{unsigned char data = 0;int ret = 0;int cnt = 0;int i = 0;ret = gpio_direction_input(dht11gpio);if (ret)pr_info("gpio_direction_input failed\n");for (i = 7; i >= 0; i--) {cnt = 0;while (!gpio_get_value(dht11gpio));while (gpio_get_value(dht11gpio)) {udelay(5);cnt++; }if (cnt > 8)data |= 0x1 << i; }return data;
}static ssize_t dht11_read(struct file *fp, char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off)
{int ret = 0;long nret = 0;unsigned char data[5] = {0};dht11_send_start();ret = dht11_recv_reply();if (-1 == ret)return -1;data[0] = dht11_recv_byte();data[1] = dht11_recv_byte();data[2] = dht11_recv_byte();data[3] = dht11_recv_byte();data[4] = dht11_recv_byte();ret = gpio_direction_output(dht11gpio, 1);if (ret)pr_info("gpio_direction_output failed\n");if (data[0] + data[1] + data[2] + data[3] != data[4])return -2;nret = copy_to_user(puser, data, 4);if (nret)pr_info("copy_to_user failed\n");return 4;
}////////////////////////////////////////////////static ssize_t dht11_write(struct file *fp, const char __user *puser, size_t n,loff_t *off)
{int ret;//拷贝用户调用write写入的数据到dht11stateret = copy_from_user(&dht11state, puser, sizeof(dht11state));mutex_lock(&dht11_lock);//写入1开灯if (dht11state == 1){//置0开灯gpio_set_value(dht11gpio, 0);}//写入0关灯if (dht11state == 0){//置1关灯gpio_set_value(dht11gpio, 1);}mutex_unlock(&dht11_lock);pr_info("write success\n");return ret;
}
static int dht11_open(struct inode *node, struct file *fp)
{pr_info("open success\n");return 0;
}
static int dht11_release(struct inode *node, struct file *fp)
{pr_info("release success\n");return 0;
}
//文件操作函数结构体
static struct file_operations fops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE, //计数,表示有几个模块调用文件操作.open = dht11_open,.release = dht11_release,.read = dht11_read,.write = dht11_write};static struct miscdevice misc_device = {.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, //次设备号申请.name = "misc_dht11", //设备节点名.fops = &fops, //绑定文件操作函数结构体
};static int dht11_probe(struct platform_device *pdevice)
{struct device_node *dtslednode = NULL;//初始化锁mutex_init(&dht11_lock);//注册混杂设备misc_register(&misc_device);//获取设备树节点dtslednode = pdevice->dev.of_node;//获取引脚编号dht11gpio = of_get_named_gpio(dtslednode, "ds18b20-gpio", 0);// GPIO方向设为输出gpio_direction_output(dht11gpio, 1);//设备树已初始化为高电平dht11state = 0;pr_info("dht11_probe success\n");return 0;
}
static int dht11_remove(struct platform_device *pdevice)
{//释放引脚编号gpio_free(dht11gpio);//销毁混杂设备misc_deregister(&misc_device);pr_info("dht11_remove success\n");return 0;
}//平台设备驱动匹配
static struct of_device_id dht11_of_match_table[] = {{.compatible = "pute,puteds18b20"},{},};
static struct platform_device_id dht11_id_table[] = {{.name = "puteds18b20"},{},
};
static struct platform_driver dht11_platform_drv = {.driver ={.name = "puteds18b20",.of_match_table = dht11_of_match_table,},.id_table = dht11_id_table,.probe = dht11_probe,.remove = dht11_remove,
};//驱动入口内调函数
static int __init dht11_init(void)
{//向内核注册一个平台驱动,将其绑定到platform虚拟总线上,并触发匹配设备的功能platform_driver_register(&dht11_platform_drv);pr_info("dht11 init success\n");return 0;
}//驱动出口内调函数
static void __exit dht11_exit(void)
{//销毁平台驱动platform_driver_unregister(&dht11_platform_drv);pr_info("dht11 exit success\n");return;
}//驱动入口
module_init(dht11_init);
//驱动出口
module_exit(dht11_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main(void)
{int fd = 0;unsigned char data[4] = {0};char hum[32] = {0};char temp[32] = {0};fd = open("/dev/misc_dht11", O_RDWR);if (-1 == fd){perror("fail to open");return -1;}while (1){read(fd, data, sizeof(data));sprintf(hum, "%d.%d", data[0], data[1]);sprintf(temp, "%d.%d", data[2], data[3]);printf("hum = %.2lf, temp = %.2lf\n", atof(hum), atof(temp));sleep(2);}close(fd);return 0;
}前瞻结束
19.platform驱动框架
1.概念
Linux设备驱动非常重视软件的可重用性和跨平台能力。如果我们多个平台需要设备A,而A在不同板子上的硬件信息不同,所以驱动中就需要写很多if else 来区分不同的硬件平台,来做不同的硬件操作。

这种操作非常麻烦,所以我们想将设备信息从驱动中剥离开来,让驱动拿到硬件平台信息。所以逐渐衍生出来了如下模型。
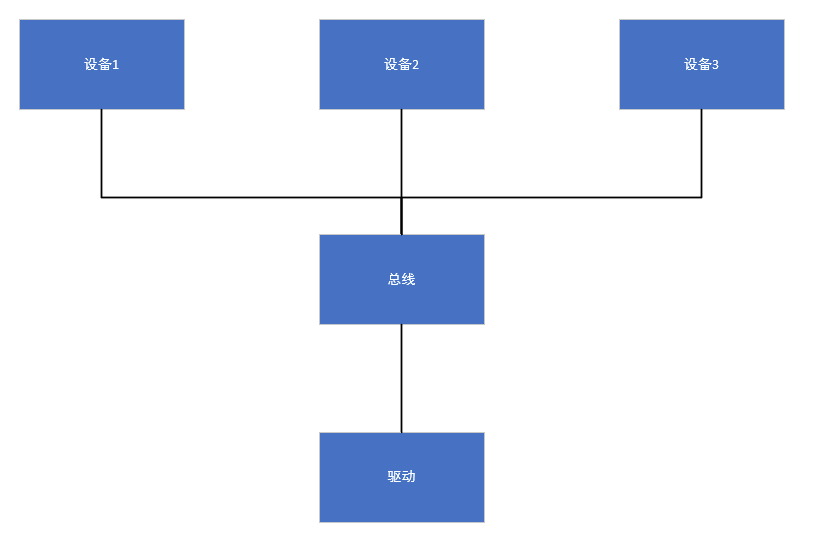
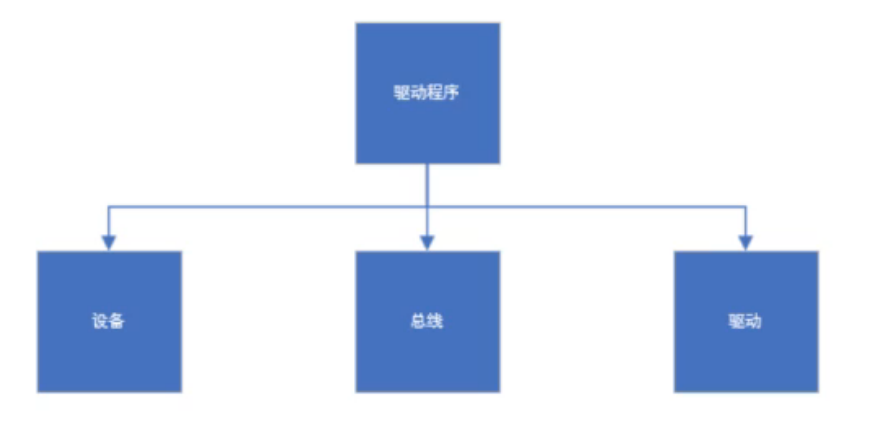
设备:存放硬件平台的寄存器信息及地址信息(后来衍生出了设备树概念)
总线:负责对设备与驱动进行管理及匹配
驱动:通过总线与设备按照规则匹配成功后,拿到设备信息,并进行对设备的操作。
相比如I2c、 SPI这些有实际物理总线的硬件,芯片上面有一些外设之间没有通过总线连接,比如ADC、网卡,如果我们想将这些硬件驱动也通过这种模型设计完成,内核设计者们为我们设计了platform总线架构,也称为虚拟平台总线。

结构中:
设备类型为 platform_device 类型
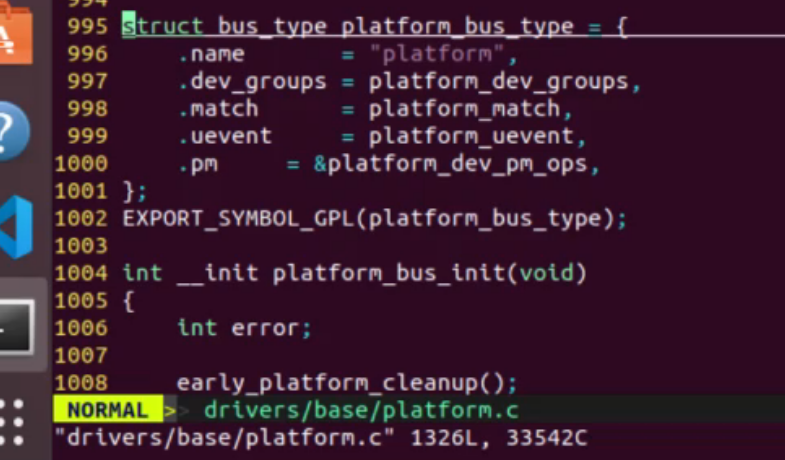
总线类型为 platform_bus_type 类型
驱动类型为 platform_driver 类型
设备端包含了物理平台寄存器信息及中断信息,这部分信息目前位于设备树中,内核自动将其转换为platform_device类型,总线负责将设备与驱动进行匹配,匹配成功执行驱动中的probe函数指针指向的接口来加载驱动。
相比如之前驱动通过设备树手动获得节点数据,这种总线形式能够自动匹配并获得节点数据。两者的区别:
| 特性 | Platform 架构 | 直接解析设备树 |
| 标准化程度 | 符合内核驱动模型 | 依赖自定义实现 |
| 热插拔支持 | 自动响应设备动态变化 | 仅支持静态设备 |
| 资源管理安全性 | 自动分配/释放,防冲突 | 手动管理,易泄漏或冲突 |
| 代码可维护性 | 硬件变动仅需修改设备树 | 硬件变动需修改驱动代码 |
| 适用场景 | 通用设备、需热插拔的设备 | 固定基础设施(如中断控制器) |
函数接口:
| platform_driver_register | 向内核注册一个平台驱动,将其绑定到platform虚拟总线上,并触发匹配设备的功能 |
| platform_driver_unregister | 从内核注销平台驱动,解除与所有绑定设备的关联,并触发驱动的remove回调释放资源 |
| module_platform_driver | 用于自动生成驱动注册/注销的模版代码,简化平台驱动模块化加载 |
| platform_get_resource | 从平台设备中提取硬件资源信息 |
| platform_get_irq | 从平台设备中获取中断资源 |
| platform_set_drvdata | 存储驱动私有数据 |
| platform_get_drvdata | 读取驱动私有数据 |
platform_driver_register(drv);
void platform_driver_unregister(struct platform_driver *drv);
module_platform_driver(__platform_driver);
struct resource *platform_get_resource(struct platform_device *dev, unsigned int
type, unsigned int num);
int platform_get_irq(struct platform_device *dev, unsigned int num);
static inline void platform_set_drvdata(struct platform_device *pdev, void
*data);
static inline void *platform_get_drvdata(const struct platform_device *pdev);20.I2C设备驱动
采用传统的字符设备驱动编写方式在处理总线编程时非常复杂,假设有M个控制器,每个控制器上可能接不同的N个外设,那么我们需要编写的驱动将是M*N个,如下图所示:
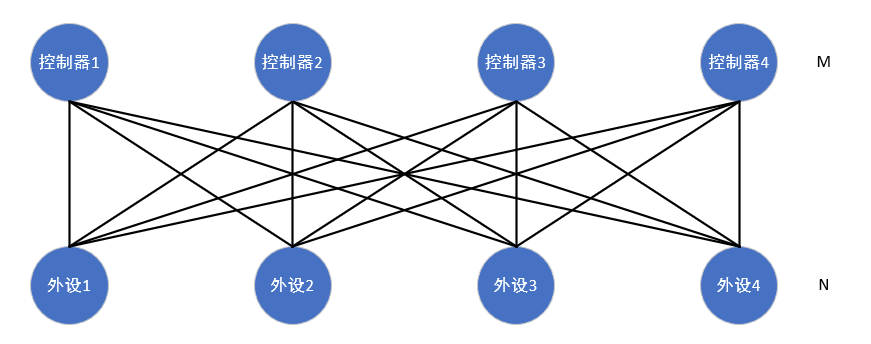
这样显然是不能被接受的, M*N是一种强耦合的设计方式,所以我们提炼出一个中间层,让M与中间层耦合, N也与中间层耦合,所以就有了如下模型:
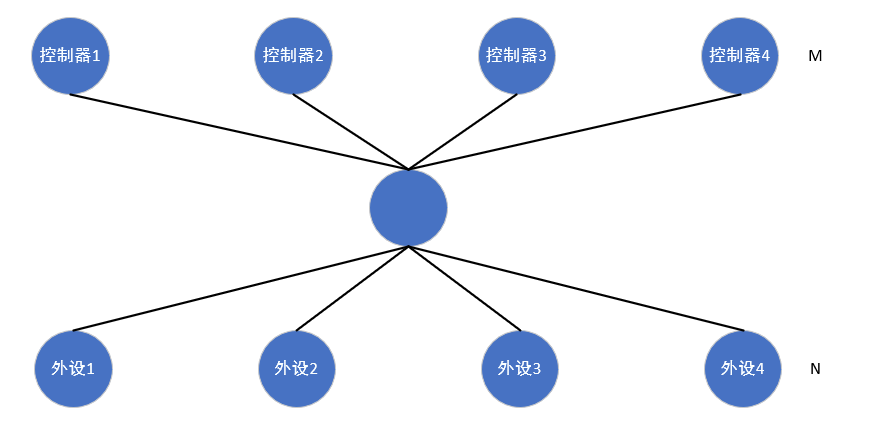
那么我们逐渐将主机控制器驱动与外设传感器驱动进行分离,这样主机控制器驱动与外设控制器驱动互不关心,外设可以通过访问核心层的通用API进行数据传输,主机和外设之间可以进行任意组合。
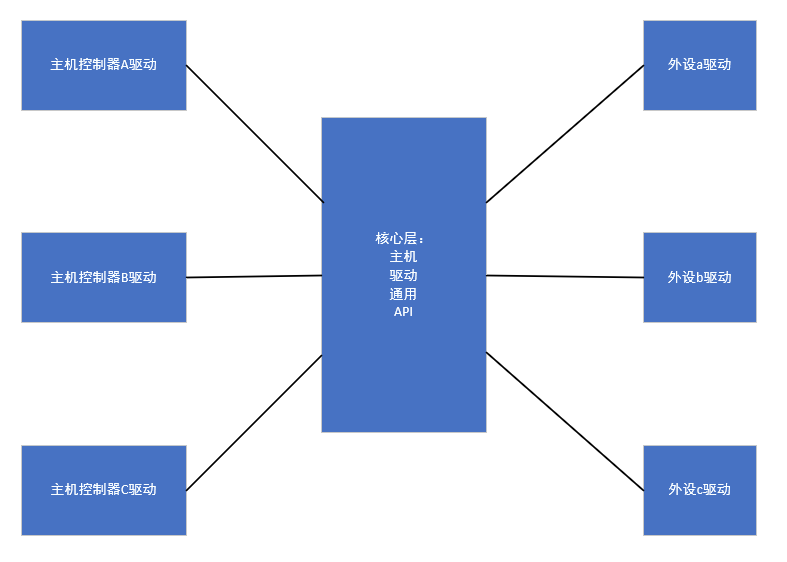
所以后续的I2c子系统框架、 SPI子系统框架、 USB子系统框架等总线驱动都是这种模型。
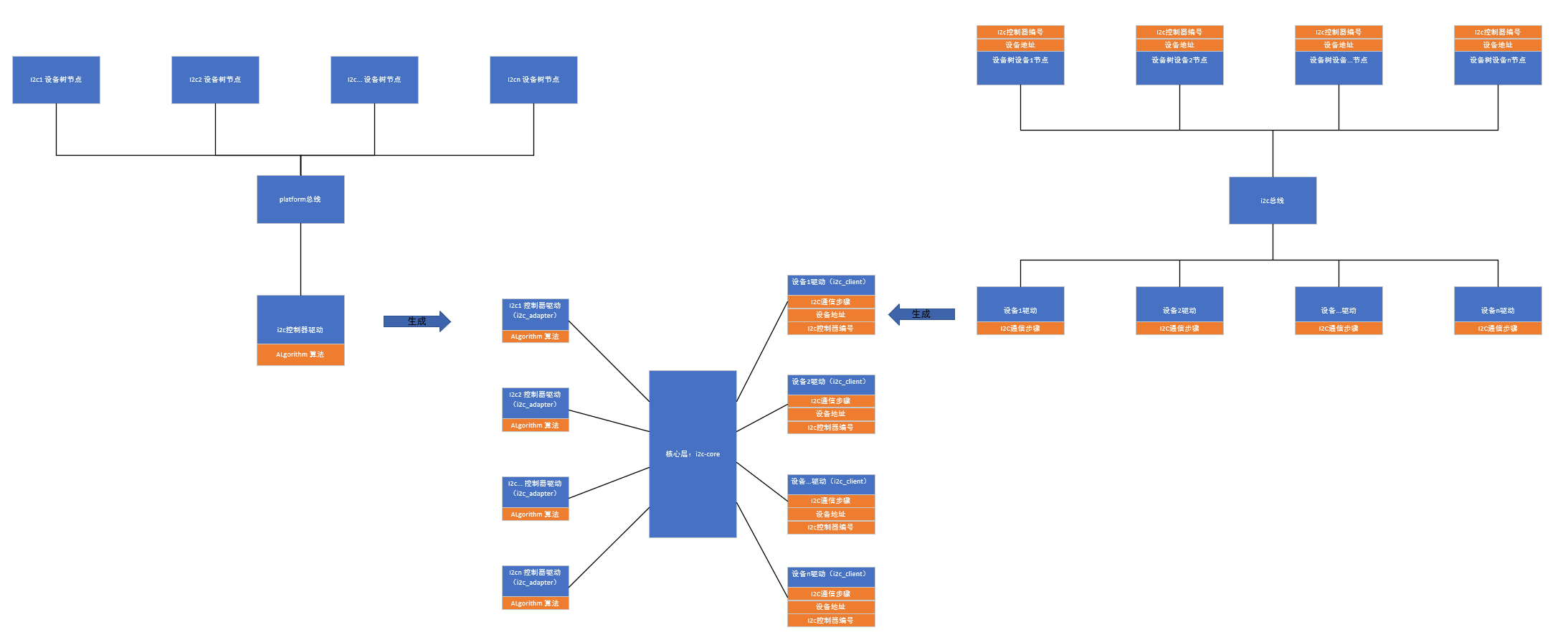
| 函数名 | 功能 |
| i2c_add_driver | 向I2c子系统注册驱动,并触发设备匹配流程 |
| i2c_del_driver | 注销I2c驱动,释放资源并解除设备绑定 |
i2c_add_driver(driver);
void i2c_del_driver(struct i2c_driver *driver)21.SPI设备驱动
SPI驱动和I2c驱动是类似的,具体实现如下图所示:
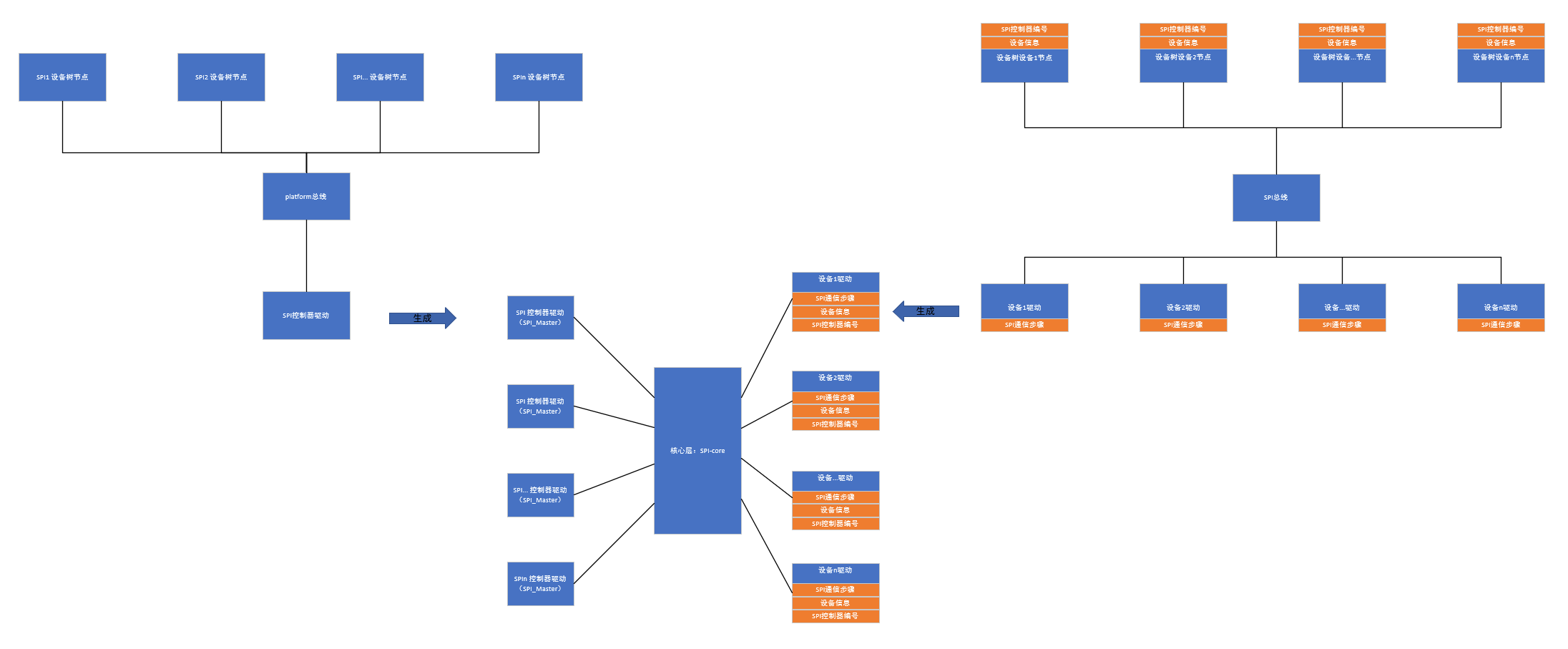
| 函数名 | 功能 |
| spi_register_driver | 向SPI子系统注册驱动,实现设备匹配 |
| spi_unregister_driver | 注销SPI驱动,清理资源 |
int spi_register_driver(struct spi_driver *sdrv);
static inline void spi_unregister_driver(struct spi_driver *sdrv)