string类
一. STL
STL(Standard Template Library,标准模板库)是 C++ 编程语言的一个重要组成部分,主要用于提供通用的数据结构和算法,以提高代码的复用性和开发效率。而且是一个包罗数据结构与算法的软件框架。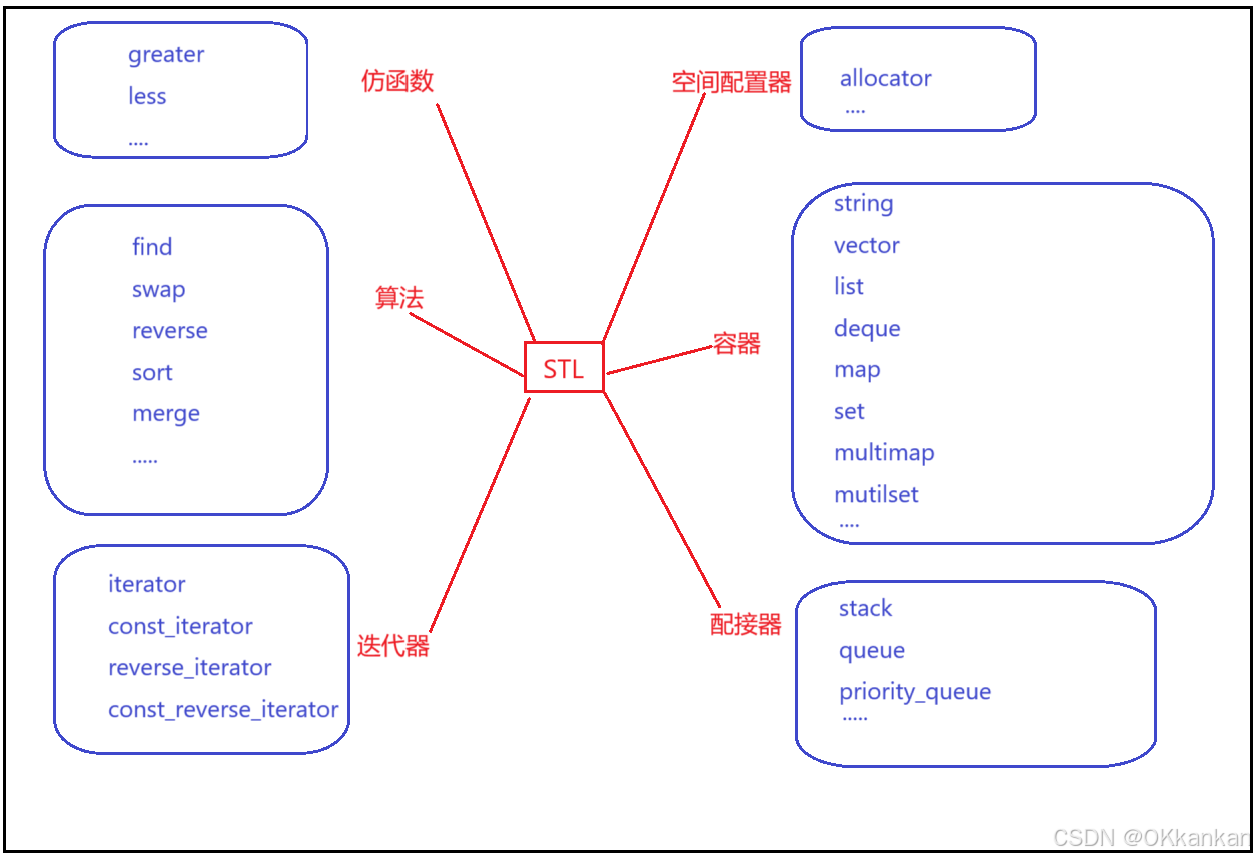
上面是STL的六大组件,STL为C++提供了大量的数据结构算法以及众多的库函数,在实现很多程序的时候提供了非常便捷的方法,提高了开发效率并且保证了代码的质量,也增强了代码的可读性,今天我们主要来认识一下STL中非常重要的一部分string类,string类主要是管理字符串的,为什么要学习string呢?在C语言中当我们要实现字符串的增删查减时其实是比较复杂的,我们需要自己开辟空间以及调用大量的库函数来帮助我们实现,但是在学习了string类之后你就会发现很多关于字符串的算法会变的方便很多。
二. 标准库中的string类
2.1 string类的初步了解及使用
在使用string类的时候必须包含#include头文件以及using namespace std;
在string类中包含了大量的库函数以及算法,我们要学会使用一些文档来帮助我们记忆学习,比如在C++刚开始学习的时候我推荐大家使用的一个网站,就是可以查询C++库函数的使用方法以及它所包含的结构算法,我把链接放在这里:https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/。
下面就是string一些基本的用法,我们要先学会使用一些基本的语法,后面再一步步数量掌握:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//字符串的初始化
int main()
{string s1;string s2 = "hello world";string s3(s2);//指定字符重复多次初始化string s4(5, 'a');cout << s1 << endl;cout << s2 << endl;cout << s3 << endl;cout << s4 << endl;return 0;
}
//字符串的拼接、删除、查找、替换等
int main()
{string s1 = "hello ";string s2 = "world";//使用 + 拼接string s3 = s1 + s2;//使用append拼接s1.append(s2);cout << s3 << endl;cout << s1 << endl;//查找字符串string s4 = "hello China";size_t pos = s4.find("China");if (pos != string::npos) {cout << "Found 'China' at position: " << pos << endl;}else {cout << "Did not find 'China'" <<endl;}//替换字符串string s5 = "Hello World";size_t pos1 = s5.find("World");if (pos1 !=string::npos) {// 替换子字符串s5.replace(pos1, 5, "Universe");}cout << "Replaced string: " << s5 << endl;//遍历字符串string s6 = "Hello";// 使用范围 for 循环遍历for (char c : s6) //这里相当于把s6依次赋给c{cout << c << " ";}cout << endl;// 使用迭代器遍历for (string::iterator it = s6.begin(); it != s6.end(); ++it) {cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;//字符串长度string s7 = "zheng";// 获取字符串长度size_t length = s7.length();//这里使用size也可以cout << "Length of str: " << length << endl;return 0;
}
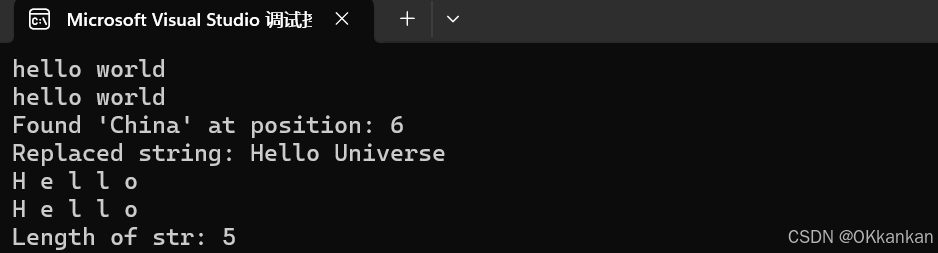 上面就是string类中的一些基本的使用,我们先要掌握好这些基础的使用才会在后面的学习更加如鱼得水,当然这只是string中的一小部分,我们要学会去查看文档得到我们需要的函数。
上面就是string类中的一些基本的使用,我们先要掌握好这些基础的使用才会在后面的学习更加如鱼得水,当然这只是string中的一小部分,我们要学会去查看文档得到我们需要的函数。
2.2 auto和范围for
auto:
1.在早期C/C++中auto的含义是:使用auto修饰的变量,是具有自动存储器的局部变量,后来这个不重要了。C++11中,标准委员会变废为宝赋予了auto全新的含义即:auto不再是一个存储类型指示符,而是作为一个新的类型指示符来指示编译器,auto声明的变量必须由编译器在编译时期推导而得。2.用auto声明指针类型时,用auto和auto*没有任何区别,但用auto声明引用类型时则必须加&,当在同一行声明多个变量时,这些变量必须是相同的类型,否则编译器将会报错,因为编译器实际只对第一个类型进行推导,然后用推导出来的类型定义其他变量。3.auto不能作为函数的参数,可以做返回值,但是建议谨慎使用。4.auto不能直接用来声明数组。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int func1()
{return 10;
}
// 不能做参数
//void func2(auto a)
//{}// 可以做返回值,但是建议谨慎使用
auto func3()
{return 3;
}
int main()
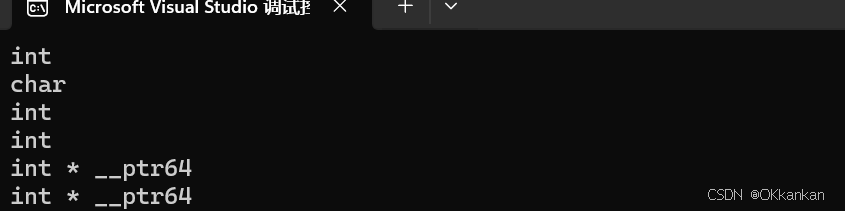
{int a = 10;auto b = a;//b的类型就和a的类型一样,intauto c = 'a';auto d = func1();// 编译报错:rror C3531: “e”: 类型包含“auto”的符号必须具有初始值设定项//auto e;cout << typeid(b).name() << endl;cout << typeid(c).name() << endl;cout << typeid(d).name() << endl;int x = 10;auto y = &x;//此时y就是一个指针类型auto* z = &x;auto& m = x;cout << typeid(x).name() << endl;cout << typeid(y).name() << endl;cout << typeid(z).name() << endl;//auto aa = 1, bb = 2;// 编译报错:error C3538: 在声明符列表中,“auto”必须始终推导为同一类型//auto cc = 3, dd = 4.0;// 编译报错:error C3318: “auto []”: 数组不能具有其中包含“auto”的元素类型//auto array[] = { 4, 5, 6 };return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>//这里是关于红黑树的,我们后面会详细讲解
using namespace std;
int main()
{std::map<std::string, std::string> dict = { { "apple", "苹果" },{ "orange","橙子" }, {"pear","梨"} };// auto的用武之地//std::map<std::string, std::string>::iterator it = dict.begin();auto it = dict.begin();//省略了很多代码while (it != dict.end()){cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;++it;}return 0;
}范围for:
1.对于一个有范围的集合而言,由程序员来说明循环的范围是多余的,有时候还会容易犯错误。因此C++11中引入了基于范围的for循环。for循环后的括号由冒号“ :”分为两部分:第一部分是范围内用于迭代的变量,第二部分则表示被迭代的范围,自动迭代,自动取数据,自动判断结束。2.范围for可以作用到数组和容器对象上进行遍历。3.范围for的底层很简单,容器遍历实际就是替换为迭代器,这个从汇编层也可以看到。
//范围for
#include<iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
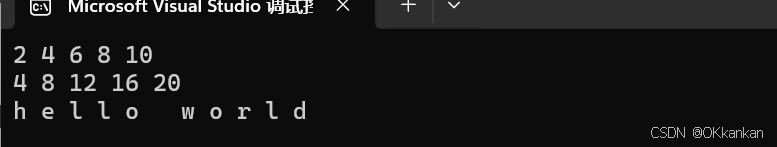
{int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };// C++98的遍历for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]); ++i){array[i] *= 2;}for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]); ++i){cout << array[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// C++11的遍历for (auto& e : array)e *= 2;for (auto e : array){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;string str("hello world");for (auto ch : str){cout << ch << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
 2.3 string类的常用接口说明
2.3 string类的常用接口说明
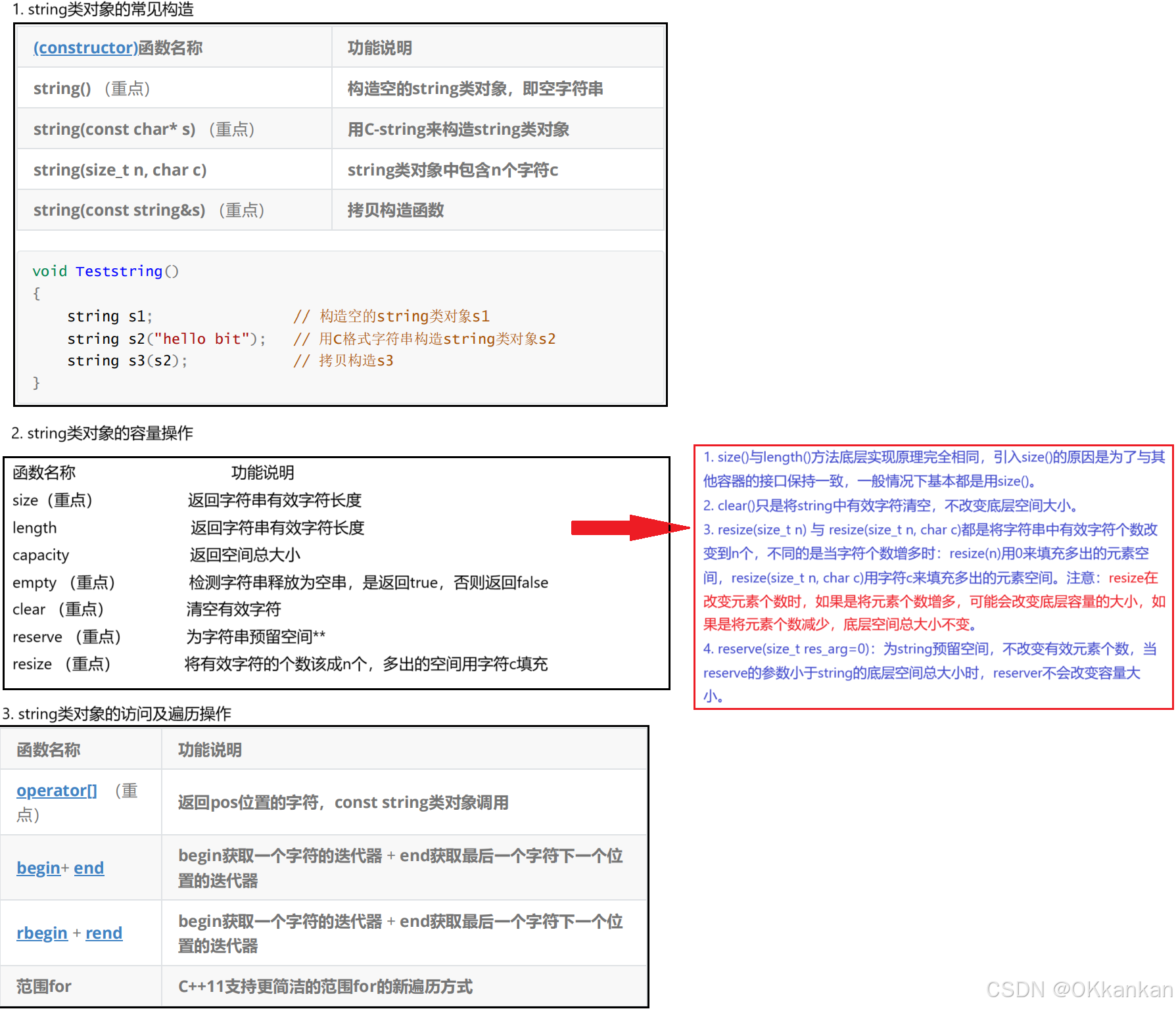
其实在string容器中还有大量的函数使用,大家可以参考C++文档去熟悉熟悉,并且有一半的函数必须要求我们熟练使用牢记。
2.3.1 string类对象的访问及遍历操作
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string str1 = "hello world";for (size_t i = 0; i < str1.size(); i++){cout << str1[i] <<"";}cout << endl;const string constStr = str1;char ch = constStr[0];cout << "const string 使用 operator[] 获取首字符:" << ch << endl;//for (size_t i = 0; i < str1.size(); i++)//{// constStr[i] = a; //不允许修改数据//}//begin和end的使用for (auto it = str1.begin(); it != str1.end(); ++it){cout << *it;}cout << endl;//rbegin和rend的使用for (auto it = str1.rbegin(); it != str1.rend(); ++it) {cout << *it;}cout << endl;return 0;
}2.3.2 string类对象的修改操作
int main()
{string str1="hello ";str1.push_back('w');str1.push_back('o');str1.push_back('r');cout << str1 << endl;str1.append("ld"); //在一个字符串的后面追加一个字符串cout << str1 << endl;//定义一个新的字符串string str2 = "good";str1 += str2; //使用operator+=在字符串后面加上str2cout << str1 << endl;return 0;
}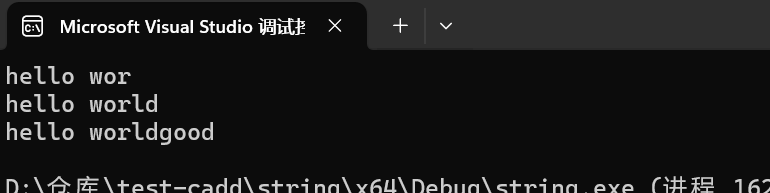 1.在string尾部追加字符时,s.push_back(c) / s.append(1, c) / s += 'c'三种的实现方式差不多,一般情况下string类的+=操作用的比较多,+=操作不仅可以连接单个字符,还可以连接字符串。 2. 对string操作时,如果能够大概预估到放多少字符,可以先通过reserve把空间预留好。
1.在string尾部追加字符时,s.push_back(c) / s.append(1, c) / s += 'c'三种的实现方式差不多,一般情况下string类的+=操作用的比较多,+=操作不仅可以连接单个字符,还可以连接字符串。 2. 对string操作时,如果能够大概预估到放多少字符,可以先通过reserve把空间预留好。
下面是string类中其他函数的一些用法:
int main()
{string str = "hello world";//c_strconst char* cStyleStr = str.c_str();cout << "c_str 返回的C格式字符串:" << cStyleStr << endl;//find + npos:从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置// 找字符 'W',从位置0开始找size_t findPos = str.find('w', 0);if (findPos != string::npos) {cout << "find 找到 'w' 的位置:" << findPos << endl; // 输出: 6}else {cout << "未找到目标字符" << endl;}// 找不存在的字符 'Z'size_t notFindPos = str.find('Z', 0);if (notFindPos != string::npos) {cout << "找到 'Z' 的位置:" << notFindPos << endl;}else {cout << "find 未找到 'Z',返回 npos" << endl;}// 6. rfind:从字符串pos位置开始往前找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置// 从位置 str.size() - 1(最后一个字符位置)往前找 'e'size_t rfindPos = str.rfind('e', str.size() - 1);if (rfindPos != string::npos) {cout << "rfind 找到 'e' 的位置:" << rfindPos << endl; // 输出 1}else {cout << "rfind 未找到目标字符" << endl;}// 7. substr:在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回// 从位置6开始,截取5个字符(World)string sub = str.substr(6, 5);cout << "substr 截取结果:" << sub << endl; // 输出: Worldreturn 0;
}以上就是string类的一些基本的使用方法,后面我会接着写一篇string类的模拟实现,帮助大家更好的了解底层逻辑。
