Elasticsearch(高性能分布式搜索引擎)01
一、初识Elasticsearch
1、认识和安装
(1)Elasticsearch是由elastic公司开发的一套搜索引擎技术,它是elastic技术栈中的一部分。完整的技术栈包括:
Elasticsearch:用于数据存储、计算和搜索
Logstash/Beats:用于数据收集
Kibana:用于数据可视化
整套技术栈被称为ELK,经常用来做日志收集、系统监控和状态分析等等。
(2)我们要安装的内容包含2部分:
elasticsearch:存储、搜索和运算
kibana:图形化展示
kibana安装是为了方便操作elasticsearch。
使用docker安装:
先上传资料中的tar包就省的下载了,
之后加载为镜像:
docker load -i es.tar
docker load -i kibana.tar再执行:
docker run -d \--name es \-e "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m" \-e "discovery.type=single-node" \-v es-data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data \-v es-plugins:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins \--privileged \--network hm-net \-p 9200:9200 \-p 9300:9300 \elasticsearch:7.12.1
docker run -d \
--name kibana \
-e ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=http://es:9200 \
--network=hm-net \
-p 5601:5601 \
kibana:7.12.12、倒排索引
正向索引是最传统的,根据id索引的方式。但根据词条查询时,必须先逐条获取每个文档,然后判断文档中是否包含所需要的词条,是根据文档找词条的过程。
而倒排索引则相反,是先找到用户要搜索的词条,根据词条得到保护词条的文档的id,然后根据id获取文档。是根据词条找文档的过程。
倒排索引中有两个非常重要的概念:
文档(
Document):用来搜索的数据,其中的每一条数据就是一个文档。例如一个网页、一个商品信息词条(
Term):对文档数据或用户搜索数据,利用某种算法分词,得到的具备含义的词语就是词条。例如:我是中国人,就可以分为:我、是、中国人、中国、国人这样的几个词条
倒排索引流程:
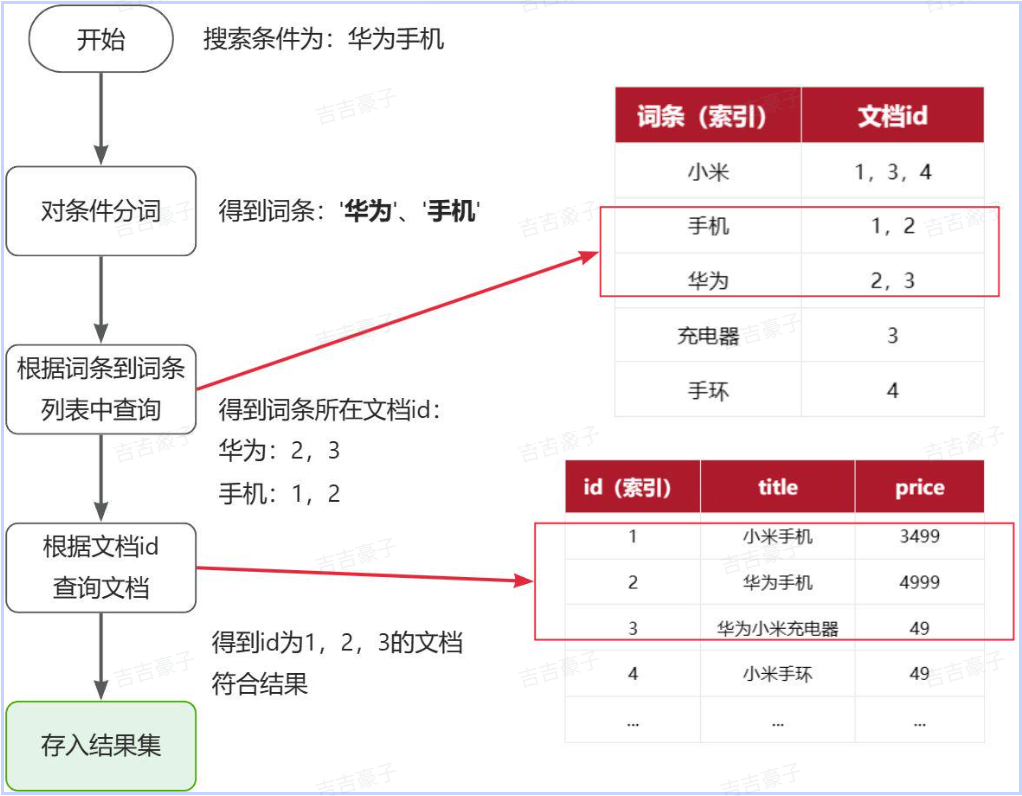
流程描述:
1)用户输入条件"华为手机"进行搜索。
2)对用户输入条件分词,得到词条:华为、手机。
3)拿着词条在倒排索引中查找(由于词条有索引,查询效率很高),即可得到包含词条的文档id:1、2、3。
4)拿着文档id到正向索引中查找具体文档即可(由于id也有索引,查询效率也很高)。
虽然要先查询倒排索引,再查询倒排索引,但是无论是词条、还是文档id都建立了索引,查询速度非常快!无需全表扫描。
3、IK分词器
1、安装
中文分词汪汪需要根据语义分析,比较复杂,这就需要用到中文分词器,例如IK分词器。
其安装方式只需将材料中提供好的分词器放入elasticsearch的插件目录中即可:
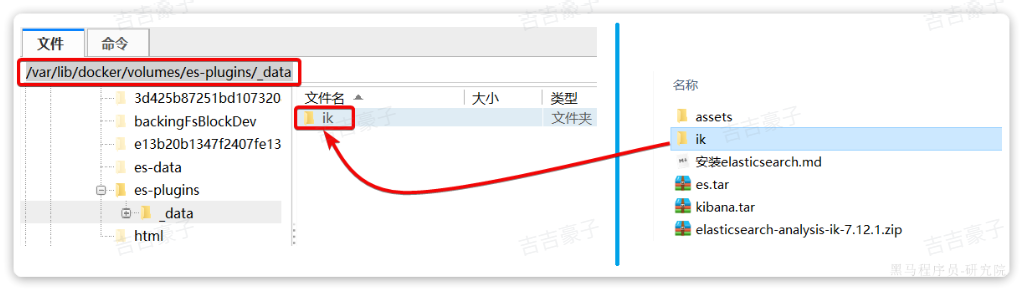
然后重启es:
docker restart es2、使用
我们在Kibana的DevTools上来测试分词器,首先测试Elasticsearch官方提供的标准分词器:
POST /_analyze
{"analyzer": "standard","text": "黑马程序员学习java太棒了"
}
结果:
{"tokens" : [{"token" : "黑","start_offset" : 0,"end_offset" : 1,"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>","position" : 0},{"token" : "马","start_offset" : 1,"end_offset" : 2,"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>","position" : 1},{"token" : "程","start_offset" : 2,"end_offset" : 3,"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>","position" : 2},{"token" : "序","start_offset" : 3,"end_offset" : 4,"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>","position" : 3},{"token" : "员","start_offset" : 4,"end_offset" : 5,"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>","position" : 4},{"token" : "学","start_offset" : 5,"end_offset" : 6,"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>","position" : 5},{"token" : "习","start_offset" : 6,"end_offset" : 7,"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>","position" : 6},{"token" : "java","start_offset" : 7,"end_offset" : 11,"type" : "<ALPHANUM>","position" : 7},{"token" : "太","start_offset" : 11,"end_offset" : 12,"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>","position" : 8},{"token" : "棒","start_offset" : 12,"end_offset" : 13,"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>","position" : 9},{"token" : "了","start_offset" : 13,"end_offset" : 14,"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>","position" : 10}]
}
测试IK分词器:
POST /_analyze
{"analyzer": "ik_smart", //或者"ik_max_word"这个分的更细"text": "黑马程序员学习java太棒了"
}结果:
{"tokens" : [{"token" : "黑马","start_offset" : 0,"end_offset" : 2,"type" : "CN_WORD","position" : 0},{"token" : "程序员","start_offset" : 2,"end_offset" : 5,"type" : "CN_WORD","position" : 1},{"token" : "学习","start_offset" : 5,"end_offset" : 7,"type" : "CN_WORD","position" : 2},{"token" : "java","start_offset" : 7,"end_offset" : 11,"type" : "ENGLISH","position" : 3},{"token" : "太棒了","start_offset" : 11,"end_offset" : 14,"type" : "CN_WORD","position" : 4}]
}
3、拓展词典
随着互联网的发展,“造词运动”也越发的频繁。出现了很多新的词语,在原有的词汇列表中并不存在。比如:“泰裤辣”,“传智播客” 等。
IK分词器无法对这些词汇分词。
所以要想正确分词,IK分词器的词库也需要不断的更新,IK分词器提供了扩展词汇的功能。
1)打开IK分词器config目录:
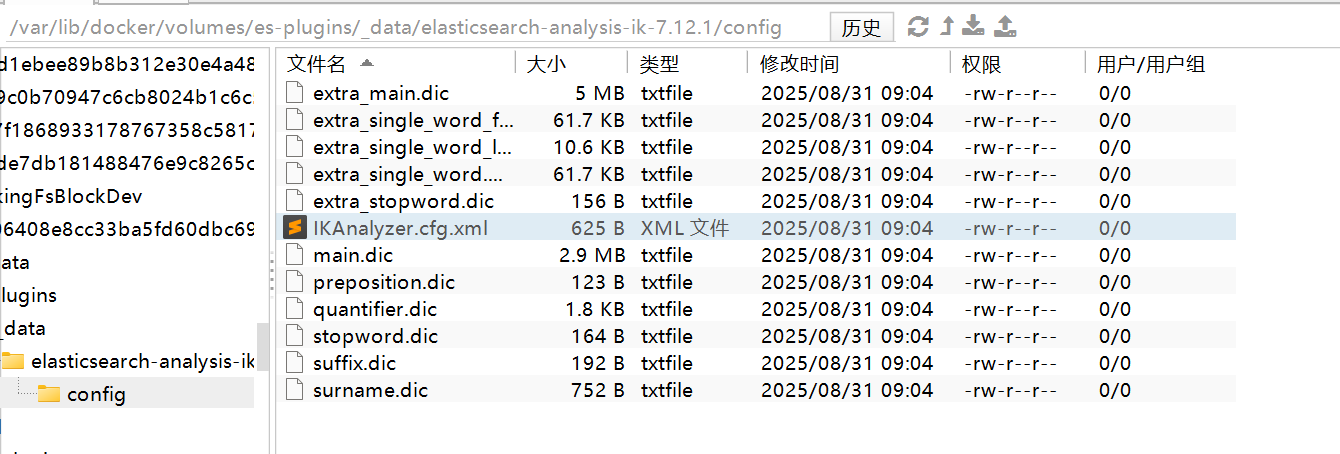
2)在IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml配置文件内容添加:即添加词典ext.dic
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd">
<properties><comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment><!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展字典 即写的ext.dic --><entry key="ext_dict">ext.dic</entry><!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展停止词字典--><entry key="ext_stopwords">stopword.dic</entry><!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展字典 --><!-- <entry key="remote_ext_dict">words_location</entry> --><!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展停止词字典--><!-- <entry key="remote_ext_stopwords">words_location</entry> -->
</properties>
3)在IK分词器的config目录新建一个 ext.dic,可以参考config目录下复制一个配置文件进行修改,在里面直接填写词即可:
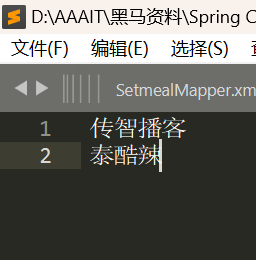
4)重启elasticsearch
4、基础概念
索引:相同类型的文档的集合
映射:索引中文档的字段约束信息,类似表的结构约束

二、索引库操作
1、Mapping映射属性
Mapping是对索引库中文档的约束,常见的Mapping属性包括:
type:字段数据类型,常见的简单类型有:字符串:
text(可分词的文本)、keyword(精确值,例如:品牌、国家、ip地址)数值:
long、integer、short、byte、double、float、布尔:
boolean日期:
date对象:
object
index:是否创建索引,默认为trueanalyzer:使用哪种分词器properties:该字段的子字段
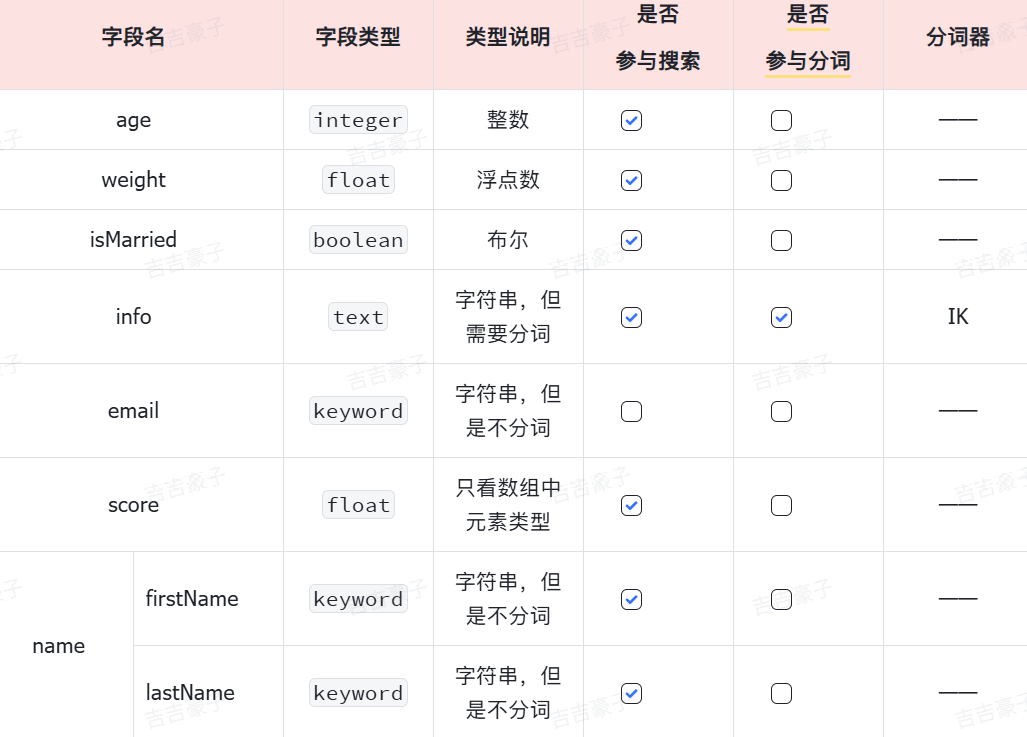
例如下面的json文档:
{"age": 21,"weight": 52.1,"isMarried": false,"info": "黑马程序员Java讲师","email": "zy@itcast.cn","score": [99.1, 99.5, 98.9],"name": {"firstName": "云","lastName": "赵"}
}对应的每个字段映射(Mapping):
2、索引库操作
由于Elasticsearch采用的是Restful风格的API,因此其请求方式和路径相对都比较规范,而且请求参数也都采用JSON风格。
我们直接基于Kibana的DevTools来编写请求做测试,由于有语法提示,会非常方便。
基本语法:
请求方式:
PUT请求路径:
/索引库名,可以自定义请求参数:
mapping映射
(1)创建索引库
PUT /索引库名称
{"mappings": {"properties": {"字段名":{"type": "text","analyzer": "ik_smart"},"字段名2":{"type": "keyword","index": "false"},"字段名3":{"properties": {"子字段": {"type": "keyword"}}},// ...略}}
}
# PUT /heima
{"mappings": {"properties": {"info":{"type": "text","analyzer": "ik_smart"},"email":{"type": "keyword","index": "false"},"name":{"properties": {"firstName": {"type": "keyword"}}}}}
}(2)查询,删除索引库
#查询索引库
GET /heima#删除索引库
DELETE /heima(3)修改索引库
倒排索引结构虽然不复杂,但是一旦数据结构改变(比如改变了分词器),就需要重新创建倒排索引,这简直是灾难。因此索引库一旦创建,无法修改mapping。
虽然无法修改mapping中已有的字段,但是却允许添加新的字段到mapping中,因为不会对倒排索引产生影响。因此修改索引库能做的就是向索引库中添加新字段,或者更新索引库的基础属性。
语法说明:
PUT /索引库名/_mapping
{"properties": {"新字段名":{"type": "integer"}}
}示例:
PUT /heima/_mapping
{"properties": {"age":{"type": "integer"}}
}三、文档操作
1、文档CRUD
(1)新增文档
请求格式如下:
POST /索引库名/_doc/文档id
{"字段1": "值1","字段2": "值2","字段3": {"子属性1": "值3","子属性2": "值4"},
}示例:
POST /heima/_doc/1
{"info": "黑马程序员Java讲师","email": "zy@itcast.cn","name": {"firstName": "云","lastName": "赵"}
}(2)查询,删除文档
#查询文档
GET /heima/_doc/1
#删除文档
DELETE /heima/_doc/1(3)修改文档
方式一:全量修改,会删除旧文档,添加新文档
全量修改是覆盖原来的文档,其本质是两步操作:
根据指定的id删除文档
新增一个相同id的文档
PUT /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
{"字段1": "值1","字段2": "值2",// ... 略
}示例:
PUT /heima/_doc/1
{"info": "黑马程序员高级Java讲师","email": "zy@itcast.cn","name": {"firstName": "云","lastName": "赵"}
}注意:如果id写错了,并且写的id不存在,就是执行了删除但什么都没删,然后执行了新增,也就是修改变成了新增操作了。
方式二:增量修改,修改指定字段值
POST /{索引库名}/_update/文档id
{"doc": {"字段名": "新的值",}
}示例:
POST /heima/_update/1
{"doc": {"email": "ZhaoYun@itcast.cn"}
}2、批量处理
Elasticsearch中允许通过一次请求中携带多次文档操作,也就是批量处理,语法格式如下:

直接写 POST /_bulk,
新增的话:第一行指定操作的类型,索引库名,id,第二行是请求参数。
删除:直接指定就可以。
更新:第一行指定操作的类型,索引库名,id,第二行是请求参数。
示例:
#批量新增
POST /_bulk
{"index":{"_index":"heima","_id":3}}
{"info":"黑马程序员Java讲师","age":"18","email":"132552@12123.com","name":{"firstName":"嘉豪","lastName":"耿"}}
{"index":{"_index":"heima","_id":"4"}}
{"info":"黑马程序员前端讲师","age":"18","email":"zhangsan@itcast.cn","name":{"firstName":"三","lastName":"张"}}#批量删除
POST /_bulk
{"delete":{"_index":"heima","_id":"3"}}
{"delete":{"_index":"heima","_id":"4"}}四、JavaRestClient
1、客户端初始化
1)引入es的RestHighLevelClient依赖:
<dependency><groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId><artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
</dependency>2)因为SpringBoot默认的ES版本是7.17.10,所以我们需要覆盖默认的ES版本:
<properties><elasticsearch.version>7.12.1</elasticsearch.version></properties>3)初始化RestHighLevelClient:
初始化的代码如下:
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));示例:
package com.hmall.item.es;import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.io.IOException;public class ElasticTest {private RestHighLevelClient client;@Testvoid testConnection(){System.out.println("client = " + client);}@BeforeEachvoid setUp(){client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(HttpHost.create("http://192.168.100.128:9200")));}@AfterEachvoid teartDown() throws IOException {if(client != null){client.close();}}
}
2、商品表Mapping映射
结合数据库表结构,以上字段对应的mapping映射属性如下:
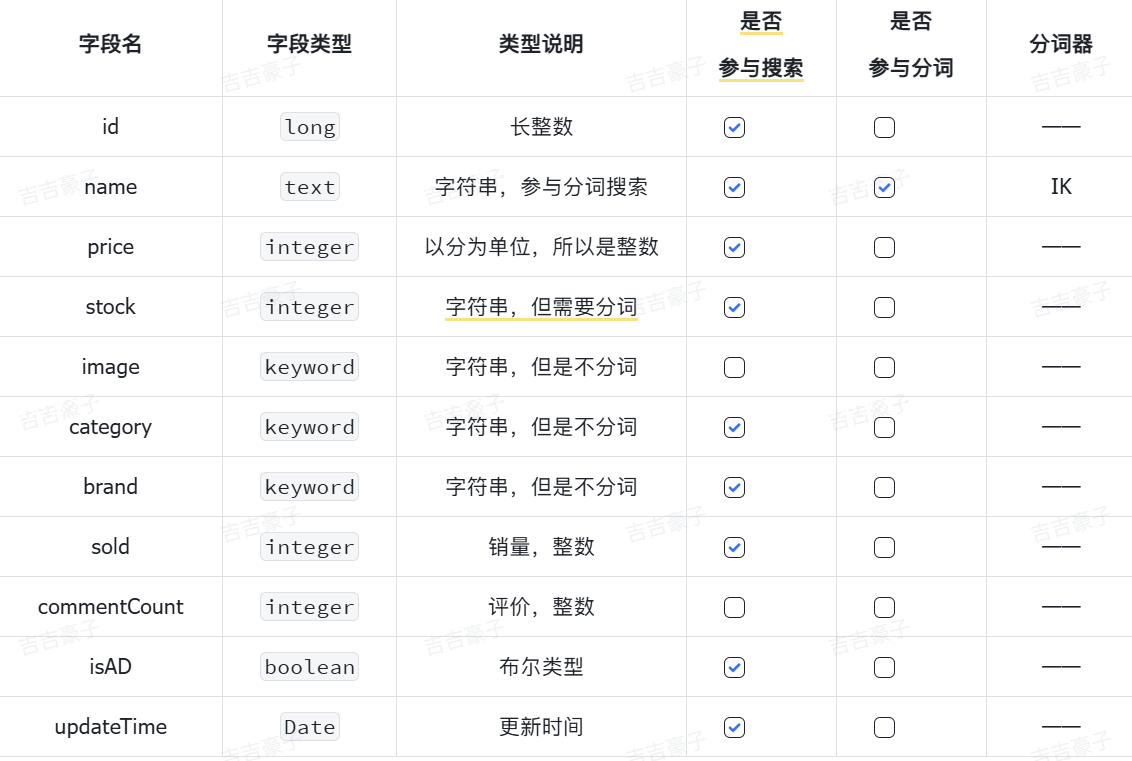
因此,最终我们的索引库文档结构应该是这样:
PUT /items
{"mappings": {"properties": {"id": {"type": "keyword"},"name":{"type": "text","analyzer": "ik_max_word"},"price":{"type": "integer"},"stock":{"type": "integer"},"image":{"type": "keyword","index": false},"category":{"type": "keyword"},"brand":{"type": "keyword"},"sold":{"type": "integer"},"commentCount":{"type": "integer","index": false},"isAD":{"type": "boolean"},"updateTime":{"type": "date"}}}
}3、索引库操作
创建索引库
创建索引库的JavaAPI与Restful接口API对比:


RequestOptions.DEFAULT: 这是 RequestOptions 类的一个常量实例,代表了一组默认的请求选项。这些选项可以包括认证信息、超时设置等。使用 RequestOptions.DEFAULT 意味着你接受所有默认的配置来发送请求。
创建索引库:
@Testvoid testCreateIndex() throws IOException {// 1、准备Request对象CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("items");// 2、准备请求参数request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON);// 3、发送请求client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}private static final String MAPPING_TEMPLATE = "{\n" +" \"mappings\": {\n" +" \"properties\": {\n" +" \"id\": {\n" +" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +" },\n" +" \"name\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" +" },\n" +" \"price\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +" },\n" +" \"stock\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +" },\n" +" \"image\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +" \"index\": false\n" +" },\n" +" \"category\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +" },\n" +" \"brand\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +" },\n" +" \"sold\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +" },\n" +" \"commentCount\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"integer\",\n" +" \"index\": false\n" +" },\n" +" \"isAD\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"boolean\"\n" +" },\n" +" \"updateTime\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"date\"\n" +" }\n" +" }\n" +" }\n" +"}";查询,删除索引库
查看、删除索引库:
@Testvoid testGetIndex() throws IOException {// 1、准备Request对象GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("items");// 3、发送请求//client.indices().get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);//这个可以判断是否存在boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println("exits=" + exists);}@Testvoid testDeleteIndex() throws IOException {// 1、准备Request对象DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("items");// 3、发送请求client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}4、文档操作
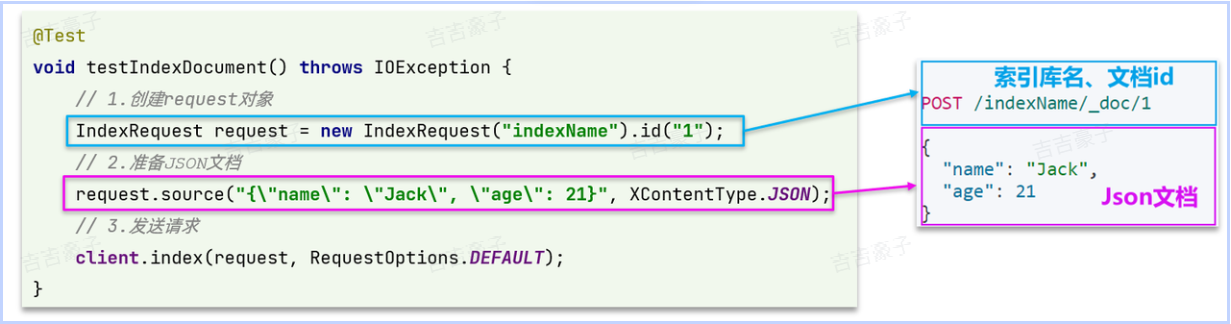
新增文档
新增文档的JavaAPI如下:
索引库结构与数据库结构还存在一些差异,因此我们要定义一个索引库结构对应的实体。
在hm-service模块的com.hmall.item.domain.dto包中定义一个新的DTO:
package com.hmall.item.domain.po;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import lombok.Data;import java.time.LocalDateTime;@Data
@ApiModel(description = "索引库实体")
public class ItemDoc{@ApiModelProperty("商品id")private String id;@ApiModelProperty("商品名称")private String name;@ApiModelProperty("价格(分)")private Integer price;@ApiModelProperty("商品图片")private String image;@ApiModelProperty("类目名称")private String category;@ApiModelProperty("品牌名称")private String brand;@ApiModelProperty("销量")private Integer sold;@ApiModelProperty("评论数")private Integer commentCount;@ApiModelProperty("是否是推广广告,true/false")private Boolean isAD;@ApiModelProperty("更新时间")private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}示例:
@Testvoid testIndexDoc() throws IOException {// 0、准备文档数据Item item = itemService.getById(5001211L);//将数据库数据转为文档数据ItemDoc itemDoc = BeanUtil.copyProperties(item, ItemDoc.class);// 1、准备RequestIndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("item").id(item.getId().toString());//类型不同,需要转为字符串// 2、准备请求参数request.source(JSONUtil.toJsonStr(itemDoc), XContentType.JSON); //hutool工具包转为json// 3、发送请求client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}查询文档
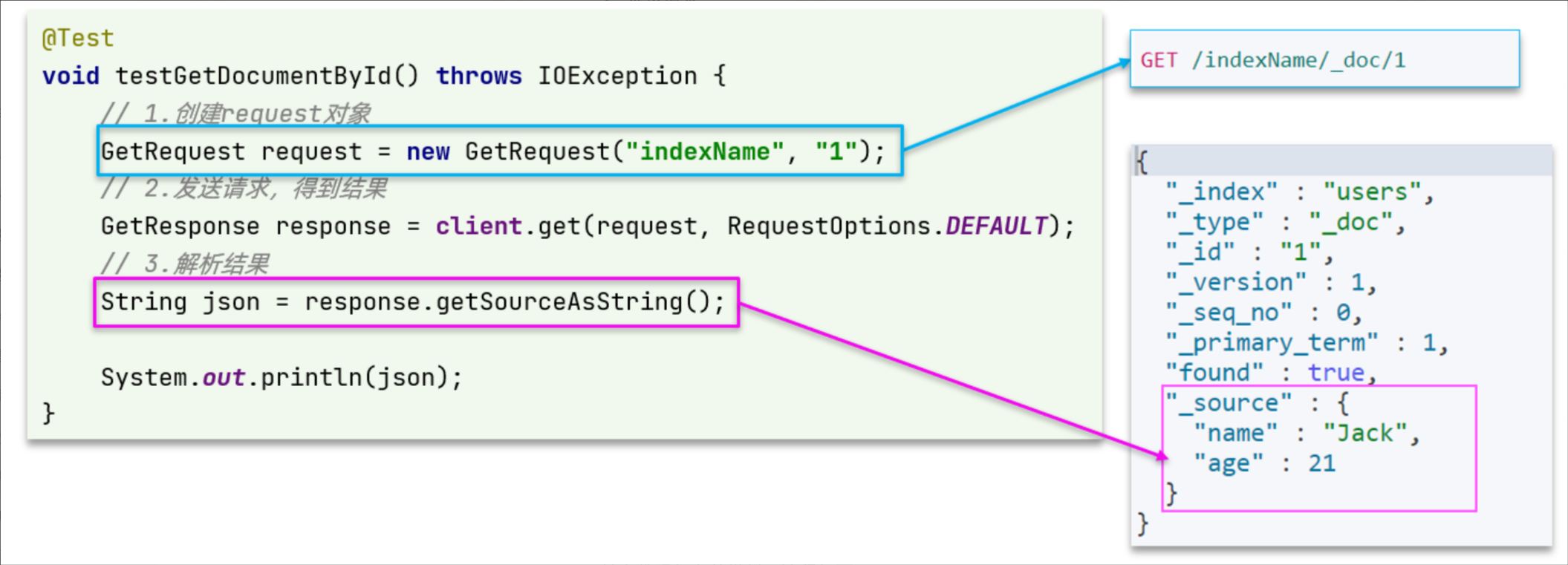
查询文档JavaAPI:
获取到的response会得到所有信息(完整的json的结果),所以需要解析结果来获取里面的source
示例:
/*** 查询文档* @throws IOException*/@Testvoid testGetDoc() throws IOException {// 1、准备RequestGetRequest request = new GetRequest("item", "5001211");// 2、发送请求GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);//3、 解析响应结果String json = response.getSourceAsString();//使用hutool工具包将字符串转化为想要的java对象JSONUtil.toBean(json,ItemDoc.class);}删除文档
删除文档JavaAPI:

示例:
@Testvoid testDeleteDoc() throws IOException {// 1、准备RequestDeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest("item", "5001211");// 2、发送请求client.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}修改文档
修改文档数据有两种方式:
- 方式一:全量更新。再次写入id一样的文档,就会删除旧文档,添加新文档。其实就是新增的javaAPI。
- 方式二:局部更新。只更新指定部分字段。
局部更新文档API:
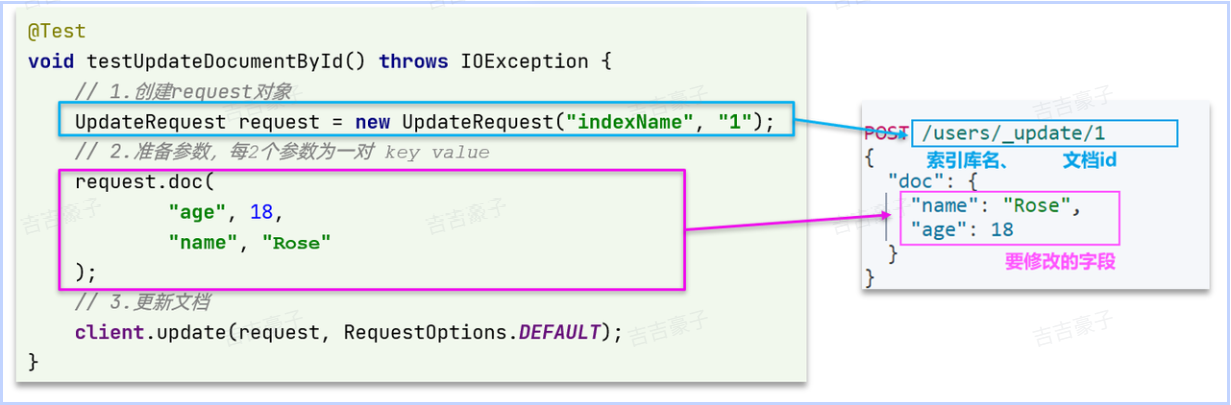
示例:
/*** 修改文档* @throws IOException*/@Testvoid testUpdateDoc() throws IOException{// 1、准备RequestUpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest("item", "5001211");// 2、准备请求参数request.doc("price","25600");// 3、发送请求client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}5、批处理
批量新增操作
/*** 批量操作** @throws IOException*/@Testvoid testBulkDoc() throws IOException {int pageNo = 1, pageSize = 500;while (true) {// 0、准备文档数据Page<Item> page = itemService.lambdaQuery().eq(Item::getStatus, 1).page(Page.of(pageNo, pageSize));List<Item> records = page.getRecords();if (records == null || records.isEmpty()) {return;}// 1、准备RequestBulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();// 2、准备请求参数/* 基本的批量操作request.add(new IndexRequest("items").id("1").source("json",XContentType.JSON));request.add(new IndexRequest("items").id("2").source("json",XContentType.JSON));request.add(new IndexRequest("items").id("3").source("json",XContentType.JSON));request.add(new DeleteRequest("items").id("1"));request.add(new DeleteRequest("items").id("2"));request.add(new DeleteRequest("items").id("3"));*/for (Item item : records) {request.add(new IndexRequest("items").id(item.getId().toString()).source(JSONUtil.toJsonStr(BeanUtil.copyProperties(item, ItemDoc.class)), XContentType.JSON));}// 3、发送请求client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);// 4、翻页pageNo++;}}