【C++组件】Elasticsearch 安装及使用

🌈 个人主页:Zfox_
🔥 系列专栏:C++框架/库

目录
- 🔥 介绍
- 🔥 ES 安装
- 🦋 安装 kibana
- 🦋 ES 客户端的安装
- 🔥 ES 核心概念
- 🦋 索引(Index)
- 🦋 类型(Type)
- 🦋 字段(Field)
- 🦋 映射(mapping)
- 🦋 文档 (document)
- 🔥 Kibana 访问 es 进行测试
- 通过网页访问 kibana
- 🔥 ES 客户端接口介绍
- 🔥 入门案例
- 🔥 ES 客户端 API 二次封装思想
- 🔥 共勉
🔥 介绍
Elasticsearch, 简称 ES,它是个开源分布式搜索引擎,它的特点有:分布式,零配置,自动发现,索引自动分片,索引副本机制, restful 风格接口,多数据源,自动搜索负载等。它可以近乎实时的存储、检索数据;本身扩展性很好,可以扩展到上百台服务器,处理 PB 级别的数据。 es 也使用 Java 开发并使用 Lucene 作为其核心来实现所有索引和搜索的功能,但是它的目的是通过简单的 RESTful API 来隐藏 Lucene 的复杂性,从而让全文搜索变得简单。
Elasticsearch 是面向文档 (document oriented) 的,这意味着它可以存储整个对象或文档(document)。然而它不仅仅是存储,还会索引 (index) 每个文档的内容使之可以被搜索。在 Elasticsearch 中,你可以对文档(而非成行成列的数据)进行索引、搜索、排序、过滤。
🔥 ES 安装
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
# 上边的添加方式会导致一个 apt-key 的警告,如果不想报警告使用下边这个
curl -s https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring gnupgring:/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/icsearch.gpg --import# 添加镜像源仓库
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elasticsearch.list
# 更新软件包列表
sudo apt update
# 安装 es
sudo apt-get install elasticsearch=7.17.21
# 启动 es
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch
# 安装 ik 分词器插件
sudo /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-plugin install https://get.infini.cloud/elasticsearch/analysis-ik/7.17.21
# 重启
sudo systemctl restart elasticsearch
# 开机自启动
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch
# 查看 es 服务的状态
sudo systemctl status elasticsearch.service
# 验证 es 是否安装成功
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/"
设置外网访问:如果新配置完成的话,默认只能在本机进行访问。
vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml# 新增配置
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
浏览器访问 http://xxx.xxx.xx.xx:9200/
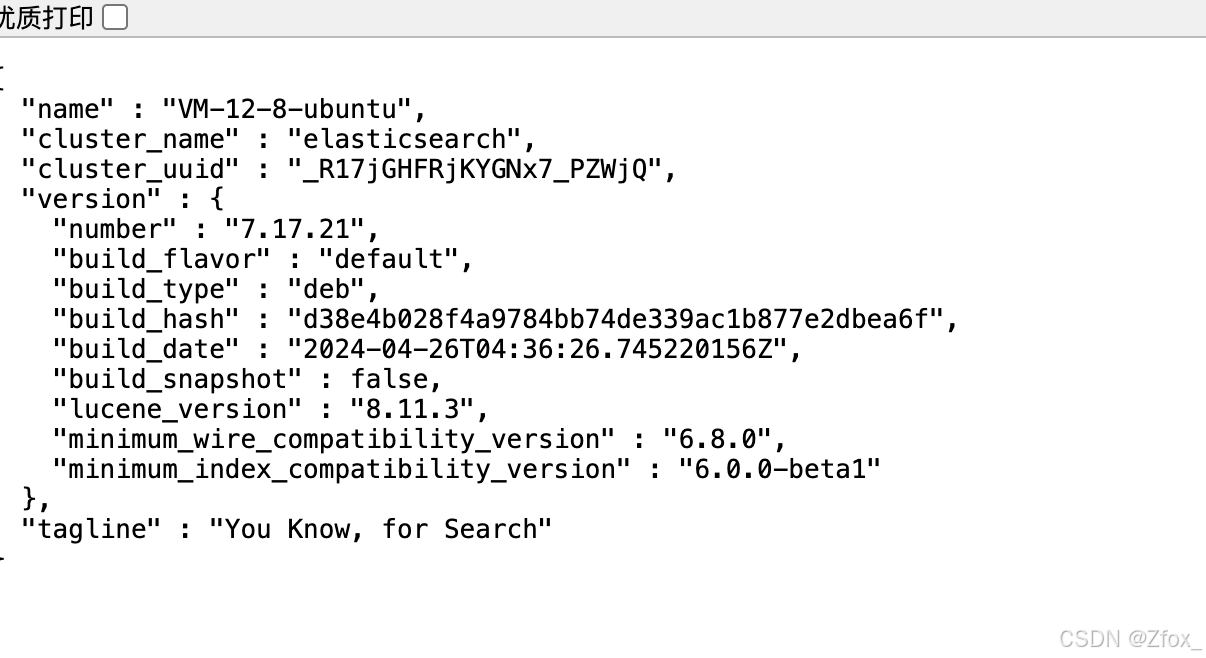
🦋 安装 kibana
使用 apt 命令安装 Kibana。
sudo apt install kibana配置 Kibana(可选):
根据需要配置 Kibana。配置文件通常位于 /etc/kibana/kibana.yml。可能需要设置如服务器地址、端口、 Elasticsearch URL 等。
sudo vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
例如,你可能需要设置 Elasticsearch 服务的 URL: 大概 32 行左右
elasticsearch.host: "http://localhost:9200"启动 Kibana 服务:
安装完成后,启动 Kibana 服务
sudo systemctl start kibana设置开机自启(可选):
如果你希望 Kibana 在系统启动时自动启动,可以使用以下命令来启用自启动
sudo systemctl enable kibana验证安装:
使用以下命令检查 Kibana 服务的状态
sudo systemctl status kibana访问 Kibana:
在浏览器中访问 Kibana,通常是 http://<your-ip>:5601
🦋 ES 客户端的安装
需要先安装 MicroHTTPD 库
不然 make 的时候编译出错:这是子模块 googletest 没有编译安装
sudo apt-get install libmicrohttpd-dev
# 克隆代码
git clone https://github.com/seznam/elasticlient
# 切换目录
cd elasticlient
# 更新子模块
git submodule update --init --recursive
# 编译代码
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr ..
make
# 安装
make install
🔥 ES 核心概念
🦋 索引(Index)
一个索引就是一个拥有几分相似特征的文档的集合。比如说,你可以有一个客户数据的索引,一个产品目录的索引,还有一个订单数据的索引。一个索引由一个名字来标识(必须全部是小写字母的),并且当我们要对应于这个索引中的文档进行索引、搜索、更新和删除的时候,都要使用到这个名字。在一个集群中,可以定义任意多的索引。
🦋 类型(Type)
在一个索引中,你可以定义一种或多种类型。一个类型是你的索引的一个逻辑上的分类/分区,其语义完全由你来定。通常,会为具有一组共同字段的文档定义一个类型。比如说,我们假设你运营一个博客平台并且将你所有的数据存储到一个索引中。在这个索引中,你可以为用户数据定义一个类型,为博客数据定义另一个类型,为评论数据定义另一个类型…
🦋 字段(Field)
字段相当于是数据表的字段,对文档数据根据不同属性进行的分类标识。

🦋 映射(mapping)
映射是在处理数据的方式和规则方面做一些限制,如某个字段的数据类型、默认值、分析器、是否被索引等等,这些都是映射里面可以设置的,其它就是处理 es 里面数据的一些使用规则设置也叫做映射,按着最优规则处理数据对性能提高很大,因此才需要建立映射,并且需要思考如何建立映射才能对性能更好。
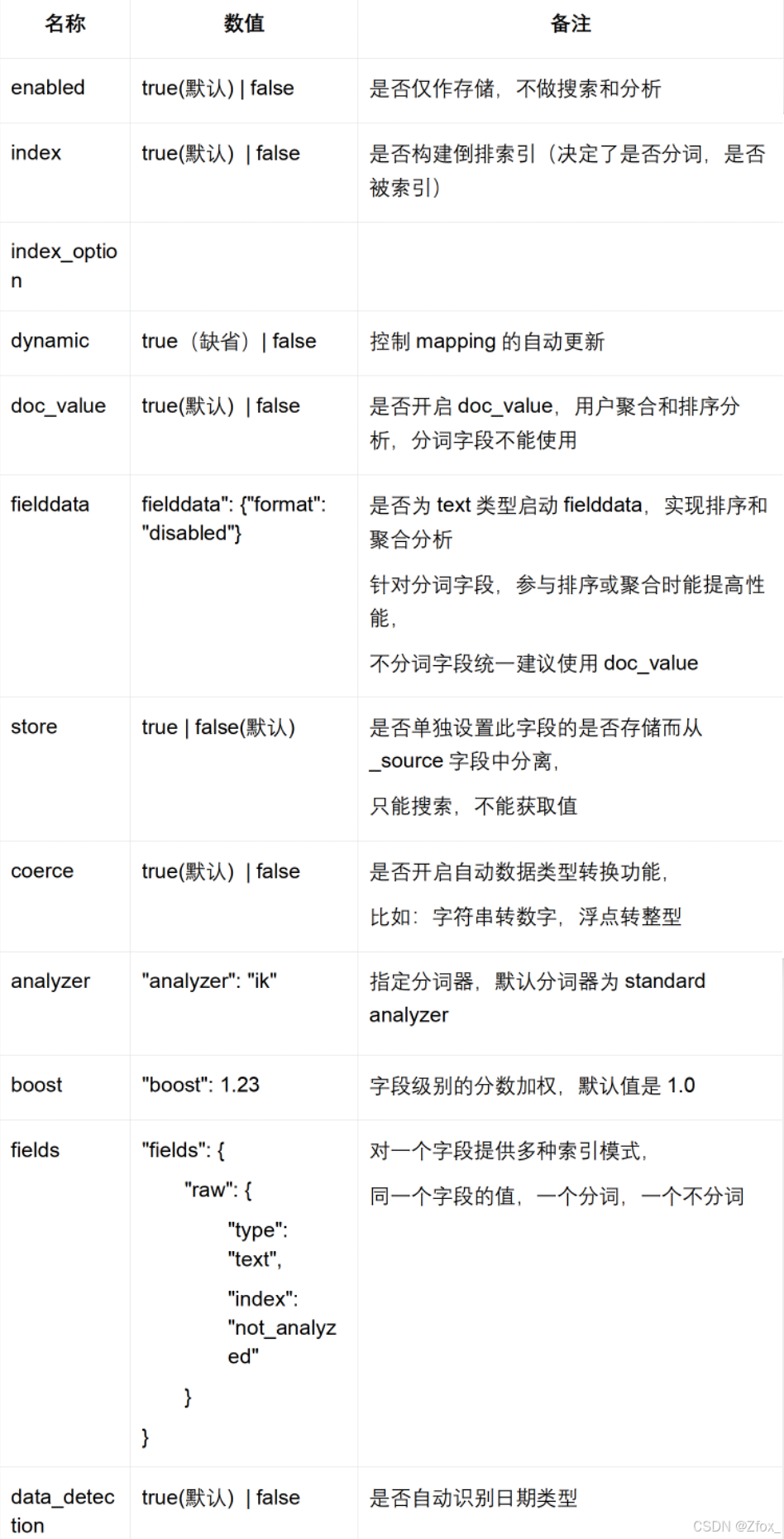
🦋 文档 (document)
一个文档是一个可被索引的基础信息单元。比如,你可以拥有某一个客户的文档,某一个产品的一个文档或者某个订单的一个文档。文档以 JSON(Javascript ObjectNotation)格式来表示,而 JSON 是一个到处存在的互联网数据交互格式。在一个 index/type 里面,你可以存储任意多的文档。一个文档必须被索引或者赋予一个索引的 type。
Elasticsearch 与传统关系型数据库相比如下:
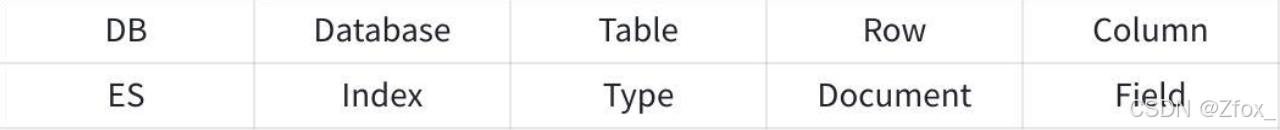
🔥 Kibana 访问 es 进行测试
通过网页访问 kibana
创建索引库
POST /user/_doc
{"settings" : {"analysis" : {"analyzer" : {"ik" : {"tokenizer" : "ik_max_word" // 最大粒度分词 - 你好 你 好 你好}}}},"mappings" : {"dynamic" : true, // 自动更新"properties" : {"nickname" : {"type" : "text", // 字段是文本类型"analyzer" : "ik_max_word" // 使用中文分词器},"user_id" : {"type" : "keyword", // 是一个文本类型,但是是关键字,不进行分词"analyzer" : "standard" // 使用默认标准分词器},"phone" : {"type" : "keyword","analyzer" : "standard"},"description" : {"type" : "text","enabled" : false // 仅做存储,不做搜索},"avatar_id" : {"type" : "keyword","enabled" : false}}}
}
新增数据:
POST /user/_doc/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":"1"}}
{"user_id" : "USER4b862aaa-2df8654a-7eb4bb65-e3507f66","nickname" : "昵称 1","phone" : "手机号 1","description" : "签名 1","avatar_id" : "头像 1"}
{"index":{"_id":"2"}}
{"user_id" : "USER14eeeaa5-442771b9-0262e455-e4663d1d","nickname" : "昵称 2","phone" : "手机号 2","description" : "签名 2","avatar_id" : "头像 2"}
{"index":{"_id":"3"}}
{"user_id" : "USER484a6734-03a124f0-996c169dd05c1869","nickname" : "昵称 3","phone" : "手机号 3","description" : "签名 3","avatar_id" : "头像 3"}
{"index":{"_id":"4"}}
{"user_id" : "USER186ade83-4460d4a6-8c08068f-83127b5d","nickname" : "昵称 4","phone" : "手机号 4","description" : "签名 4","avatar_id" : "头像 4"}
{"index":{"_id":"5"}}
{"user_id" : "USER6f19d074-c33891cf-23bf5a83-57189a19","nickname" : "昵称 5","phone" : "手机号 5","description" : "签名 5","avatar_id" : "头像 5"}
{"index":{"_id":"6"}}
{"user_id" : "USER97605c64-9833ebb7-d0455353-35a59195","nickname" : "昵称 6","phone" : "手机号 6","description" : "签名 6","avatar_id" : "头像 6"}
查看并搜索数据
GET /user/_doc/_search?pretty
{"query" : {"bool" : {"must_not" : [ // 必须不遵循的条件{"terms" : {"user_id.keyword" : ["USER4b862aaa-2df8654a-7eb4bb65-e3507f66","USER14eeeaa5-442771b9-0262e455-e4663d1d","USER484a6734-03a124f0-996c169dd05c1869"]}}],"should" : [ // 应该遵循的条件 有任意一个成功就ok{"match" : {"user_id" : "昵称"}},{"match" : {"nickname" : "昵称"}},{"match" : {"phone" : "昵称"}}]}}
}
terms: 完全匹配
match:分词匹配
过滤条件,是我的好友就过滤掉,在搜索好友进行添加的时候,就可以过滤掉
"user_id.keyword" keyword 不进行分词
"USER4b862aaa-2df8654a-7eb4bb65-e3507f66",
"USER14eeeaa5-442771b9-0262e455-e4663d1d",
"USER484a6734-03a124f0-996c169dd05c1869"
删除索引:
DELETE /user
POST /user/_doc/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}}
}
🔥 ES 客户端接口介绍
/*** Perform search on nodes until it is successful. Throws exception if all nodes* has failed to respond.* \param indexName specification of an Elasticsearch index.* \param docType specification of an Elasticsearch document type.* \param body Elasticsearch request body.* \param routing Elasticsearch routing. If empty, no routing has been used.** \return cpr::Response if any of node responds to request.* \throws ConnectionException if all hosts in cluster failed to respond.*/cpr::Response search(const std::string &indexName, 索引名称 userconst std::string &docType, 索引类型 docconst std::string &body, 请求正文,json字符串const std::string &routing = std::string());/*** Get document with specified id from cluster. Throws exception if all nodes* has failed to respond.* \param indexName specification of an Elasticsearch index.* \param docType specification of an Elasticsearch document type.* \param id Id of document which should be retrieved.* \param routing Elasticsearch routing. If empty, no routing has been used.** \return cpr::Response if any of node responds to request.* \throws ConnectionException if all hosts in cluster failed to respond.*/cpr::Response get(const std::string &indexName,const std::string &docType,const std::string &id = std::string(),const std::string &routing = std::string());/*** Index new document to cluster. Throws exception if all nodes has failed to respond.* \param indexName specification of an Elasticsearch index.* \param docType specification of an Elasticsearch document type.* \param body Elasticsearch request body.* \param id Id of document which should be indexed. If empty, id will be generated* automatically by Elasticsearch cluster.* \param routing Elasticsearch routing. If empty, no routing has been used.** \return cpr::Response if any of node responds to request.* \throws ConnectionException if all hosts in cluster failed to respond.*/ 创建索引 新增数据cpr::Response index(const std::string &indexName, 索引名称const std::string &docType, 类型const std::string &id, 自己制定或者es生成数据idconst std::string &body, 请求正文const std::string &routing = std::string());/*** Delete document with specified id from cluster. Throws exception if all nodes* has failed to respond.* \param indexName specification of an Elasticsearch index.* \param docType specification of an Elasticsearch document type.* \param id Id of document which should be deleted.* \param routing Elasticsearch routing. If empty, no routing has been used.** \return cpr::Response if any of node responds to request.* \throws ConnectionException if all hosts in cluster failed to respond.*/cpr::Response remove(const std::string &indexName,const std::string &docType,const std::string &id,const std::string &routing = std::string());/*** Initialize the Client.* \param hostUrlList Vector of URLs of Elasticsearch nodes in one Elasticsearch cluster.* Each URL in vector should ends by "/".* \param timeout Elastic node connection timeout.*/explicit Client(const std::vector<std::string> &hostUrlList,std::int32_t timeout = 6000);
🔥 入门案例
针对上边通过 kibana 添加的数据通过客户端 api 进行一次数据获取。
#include <elasticlient/client.h>
#include <cpr/cpr.h>
#include <iostream>int main()
{// 1. 构造 ES 客户端elasticlient::Client client({"http://127.0.0.1:9200/"});// 2. 发起搜索请求try {cpr::Response resp = client.search("user", "_doc", "{\"query\": { \"match_all\": {} }}");// 3. 打印响应状态码和响应正文std::cout << resp.status_code << std::endl;std::cout << resp.text << std::endl;} catch (std::exception &e) {std::cout << "请求失败: " << e.what() << std::endl;return -1;}return 0;
}
🔥 ES 客户端 API 二次封装思想
封装客户端 api 主要是因为,客户端只提供了基础的数据存储获取调用功能,无法根据我们的思想完成索引的构建,以及查询正文的构建,需要使用者自己组织好 json 进行序列化后才能作为正文进行接口的调用。
而封装的目的就是简化用户的操作,将索引的 json 正文构造,以及查询搜索的正文构造操作给封装起来,使用者调用接口添加字段就行,不用关心具体的 json 数据格式。
封装内容:
- 索引构造过程的封装
- 索引正文构造过程,大部分正文都是固定的,唯一不同的地方是各个字段不同的名称以及是否只存储不索引这些选项,因此重点关注以下几个点即可:
- 字段类型: type : text / keyword (目前只用到这两个类型)
- 是否索引: enable : true/false
- 索引的话分词器类型: analyzer : ik_max_word / standard
- 新增文档构造过程的封装
- 新增文档其实在常规下都是单条新增,并非批量新增,因此直接添加字段和值就行
- 文档搜索构造过程的封装
- 搜索正文构造过程,我们默认使用条件搜索,我们主要关注的两个点:
- 应该遵循的条件是什么: should 中有什么
- 条件的匹配方式是什么: match 还是 term/terms,还是 wildcard
- 过滤的条件字段是什么: must_not 中有什么
- 过滤的条件字段匹配方式是什么: match 还是 wildcard,还是 term/terms
整个封装的过程其实就是对 Json::Value 对象的一个组织的过程,并无太大的难点。
elasticsearch.hpp
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <elasticlient/client.h>
#include <json/json.h>
#include <cpr/cpr.h>
#include "logger.hpp"// 实现字符串的序列化
bool Serialize(const Json::Value &val, std::string &body)
{std::stringstream ss;// 先实例化一个工厂类对象Json::StreamWriterBuilder swb;// 再使用工厂类对象来生产派生类std::unique_ptr<Json::StreamWriter> sw(swb.newStreamWriter());int ret = sw->write(val, &ss);if(ret != 0){std::cout << "Json Serialize failed!" << std::endl;return false;}body = ss.str();return true;
}// 实现json字符串的反序列化
bool UnSerialize(const std::string &body, Json::Value &val)
{// 实例化工厂类对象Json::CharReaderBuilder crb;std::unique_ptr<Json::CharReader> cr(crb.newCharReader());std::string errs;bool ret = cr->parse(body.c_str(), body.c_str() + body.size(), &val, &errs);if(ret == false){std::cout << "Json UnSerialize failed! " << errs << std::endl;return false;}return true;
}// 构造索引
class ESIndex {
public:ESIndex(std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> &client, const std::string &index_name, const std::string &type) : _name(index_name), _type(type), _client(client){Json::Value analysis;Json::Value analyzer;Json::Value ik;Json::Value tokenizer;tokenizer["tokenizer"] = "ik_max_word";ik["ik"] = tokenizer;analyzer["analyzer"] = ik;analysis["analysis"] = analyzer;_index["settings"] = analysis;}ESIndex& append(const std::string &key, const std::string &type = "text", const std::string &analyzer = "ik_max_word", bool enabled = true) {Json::Value fields;fields["type"] = type;fields["analyzer"] = analyzer;if (enabled == false) fields["enabled"] = enabled;_propertis[key] = fields;return *this;}bool create(const std::string &index_id = "default_index_id") {Json::Value mappings;mappings["dynamic"] = true;mappings["properties"] = _propertis;_index["mappings"] = mappings;std::string body;bool ret = Serialize(_index, body);if (ret == false) {LOG_ERROR("索引序列化失败!");return false;}// 发起搜索请求try {cpr::Response resp = _client->index(_name, _type, index_id, body);if (resp.status_code < 200 || resp.status_code >= 300) {LOG_ERROR("创建ES索引 {} 失败, 响应状态码异常: {}", _name, resp.status_code);return false;}} catch (std::exception &e) {LOG_ERROR("创建ES索引 {} 失败: {}", _name, e.what());return false;}return true;}private:std::string _name;std::string _type;Json::Value _propertis;Json::Value _index;std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> _client;
};// 添加数据
class ESInsert {
public:ESInsert(std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> &client, const std::string &index_name, const std::string &type) : _name(index_name), _type(type), _client(client){}ESInsert& append(const std::string &key, const std::string &val) {_item[key] = val;return *this;}bool insert(const std::string &id = "") {std::string body;bool ret = Serialize(_item, body);if (ret == false) {LOG_ERROR("索引序列化失败!");return false;}// 发起搜索请求try {cpr::Response resp = _client->index(_name, _type, id, body);if (resp.status_code < 200 || resp.status_code >= 300) {LOG_ERROR("新增数据 {} 失败, 响应状态码异常: {}", body, resp.status_code);return false;}} catch (std::exception &e) {LOG_ERROR("新增数据 {} 失败: {}", body, e.what());return false;}return true;}private:std::string _name;std::string _type;Json::Value _item;std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> _client;
};// 删除数据
class ESRemove {public:ESRemove(std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> &client, const std::string &index_name, const std::string &type) : _name(index_name), _type(type), _client(client){}bool remove(const std::string &id) {// 发起请求try {cpr::Response resp = _client->remove(_name, _type, id);if (resp.status_code < 200 || resp.status_code >= 300) {LOG_ERROR("删除数据 {} 失败, 响应状态码异常: {}", id, resp.status_code);return false;}} catch (std::exception &e) {LOG_ERROR("删除数据 {} 失败: {}", id, e.what());return false;}return true;}private:std::string _name;std::string _type;std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> _client;
};// 搜索数据
class ESSearch {
public:ESSearch(std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> &client, const std::string &index_name, const std::string &type) : _name(index_name), _type(type), _client(client){}// 必须不遵循的条件ESSearch& append_must_not_terms(const std::string &key, const std::vector<std::string> &vals) {Json::Value fields;for (const auto &val : vals) {fields[key].append(val);}Json::Value terms;terms["terms"] = fields;_must_not.append(terms);return *this;}ESSearch& append_should_match(const std::string &key, const std::string &val) {Json::Value field;field[key] = val;Json::Value match;match["match"] = field;_should.append(match);return *this;}Json::Value search() {Json::Value cond;if (!_must_not.empty()) cond["must_not"] = _must_not; if (!_should.empty()) cond["should"] = _should; Json::Value query;query["bool"] = cond;Json::Value root;root["query"] = query;std::string body;bool ret = Serialize(root, body);if (ret == false) {LOG_ERROR("索引序列化失败!");return Json::Value();}cpr::Response resp;// 发起搜索请求try {resp = _client->search(_name, _type, body);if (resp.status_code < 200 || resp.status_code >= 300) {LOG_ERROR("检索数据 {} 失败, 响应状态码异常: {}", body, resp.status_code);return Json::Value();}} catch (std::exception &e) {LOG_ERROR("检索数据 {} 失败: {}", body, e.what());return Json::Value();}// 反序列化响应正文Json::Value json_res;ret = UnSerialize(resp.text, json_res);if (ret == false) {LOG_ERROR("检索数据 {} 结果反序列化失败", resp.text);return Json::Value();}return json_res["hits"]["hits"];}private:std::string _name;std::string _type;Json::Value _must_not; // 必须不遵循的条件Json::Value _should; // 应该遵循的条件std::shared_ptr<elasticlient::Client> _client;
};
🔥 共勉
😋 以上就是我对 【C++组件】Elasticsearch 安装及使用 的理解, 觉得这篇博客对你有帮助的,可以点赞收藏关注支持一波~ 😉

