Leetcode 深度优先搜索 (9)
111. 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
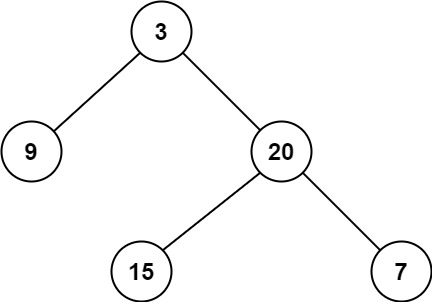
输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出: 2
广度优先搜索(BFS)思路:
- BFS利用队列进行层序遍历,从根节点开始逐层向下遍历。
- 每访问到一个节点时,判断其是否为叶子节点(即没有左右子节点)。
- 一旦遇到第一个叶子节点,当前遍历的层数即为最小深度,可以立即返回。
- 这种方法保证了最先到达的叶子节点就是距离根节点最近的。
public class Solution {public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);int depth = 1;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();// 判断是否为叶子节点if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {return depth;}if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);}depth++;}return depth;}
}
深度优先搜索(DFS)递归思路:
- 如果根节点为空,返回0。
- 如果左子树为空,递归计算右子树的最小深度并加1。
- 如果右子树为空,递归计算左子树的最小深度并加1。
- 如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树最小深度的较小值加1。
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}// 如果左子树为空,递归右子树if (root.left == null) {return minDepth(root.right) + 1;}// 如果右子树为空,递归左子树if (root.right == null) {return minDepth(root.left) + 1;}// 左右子树都不为空,取较小值return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1;}
深度优先搜索(DFS)非递归思路:
- 使用栈(Stack)来模拟递归过程。
- 每个栈元素存储一个节点和其当前深度。
- 从根节点入栈,循环弹栈处理:
- 如果当前节点是叶子节点,更新最小深度。
- 否则,将其左右子节点(如果存在)和对应深度入栈。
- 最终返回最小深度。
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;Stack<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(new Pair<>(root, 1));int minDepth = Integer.MAX_VALUE;while (!stack.isEmpty()) {Pair<TreeNode, Integer> current = stack.pop();TreeNode node = current.getKey();int depth = current.getValue();if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {minDepth = Math.min(minDepth, depth);}if (node.right != null) {stack.push(new Pair<>(node.right, depth + 1));}if (node.left != null) {stack.push(new Pair<>(node.left, depth + 1));}}return minDepth;}// 辅助类,用于存储节点和深度static class Pair<K, V> {private K key;private V value;public Pair(K key, V value) {this.key = key;this.value = value;}public K getKey() { return key; }public V getValue() { return value; }}
