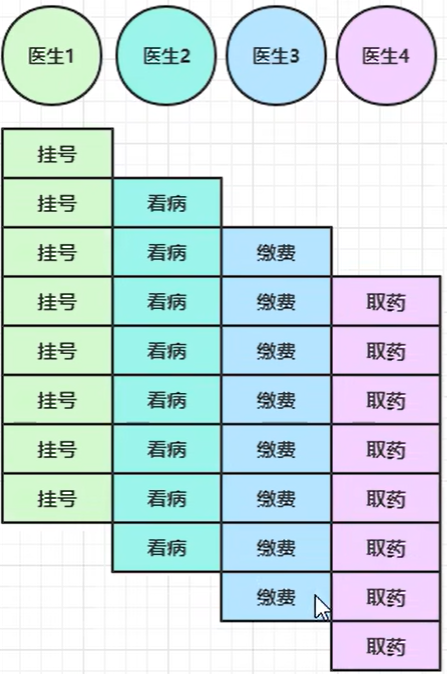
【Netty】- 入门1
Netty是一个异步的(调用时的异步)、基于事件驱动的网络应用框架。
Netty底层是基于NIO
Netty的优势
Netty vs NIO:
- 需要自己构建协议
- 解决TCP传输问题(粘包、半包)
- epoll空轮询导致CPU100%
- 对API进行增强,使之更易用
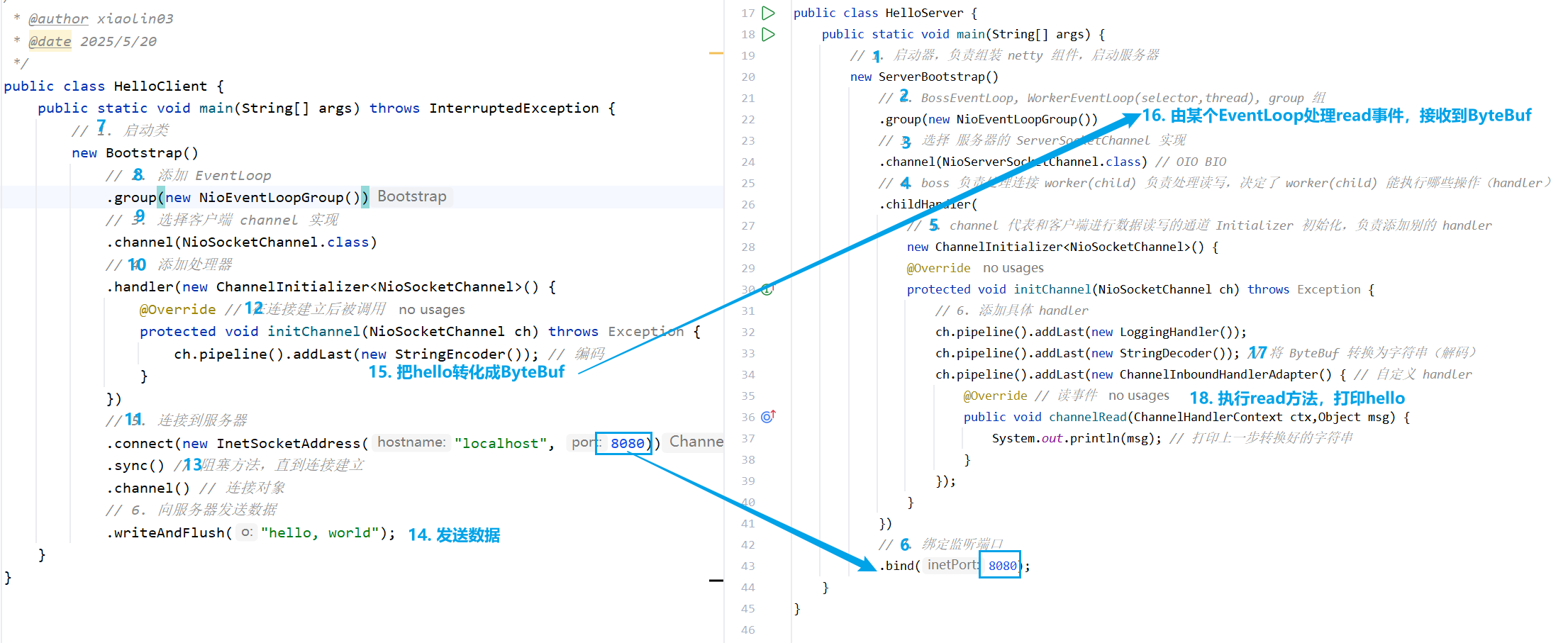
HelloWorld
服务器
public class HelloServer {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 启动器,负责组装 netty 组件,启动服务器new ServerBootstrap()// 2. BossEventLoop, WorkerEventLoop(selector,thread), group 组.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())// 3. 选择 服务器的 ServerSocketChannel 实现.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // OIO BIO// 4. boss 负责处理连接 worker(child) 负责处理读写,决定了 worker(child) 能执行哪些操作(handler).childHandler(// 5. channel 代表和客户端进行数据读写的通道 Initializer 初始化,负责添加别的 handlernew ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {// 6. 添加具体 handlerch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler());ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder()); // 将 ByteBuf 转换为字符串(解码)ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { // 自定义 handler@Override // 读事件public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,Object msg) throws Exception {System.out.println(msg); // 打印上一步转换好的字符串}});}})// 7. 绑定监听端口.bind(8080);}
}
客户端
public class HelloClient {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 1. 启动类new Bootstrap()// 2. 添加 EventLoop.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())// 3. 选择客户端 channel 实现.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)// 4. 添加处理器.handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {@Override // 在连接建立后被调用protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder()); // 编码}})// 5. 连接到服务器.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)).sync() // 阻塞方法,直到连接建立.channel() // 连接对象// 6. 向服务器发送数据.writeAndFlush("hello, world");}
}
运行顺序
channel:数据的传输通道
message:在channel中流动的数据(最开始输入的是ByteBuf,经过pipeline的加工,会变成其它类型的对象)
handler:数据的处理工序
- 工序有多道,合在一起就是pipeline
- handler分为Inbound和Outbound两类
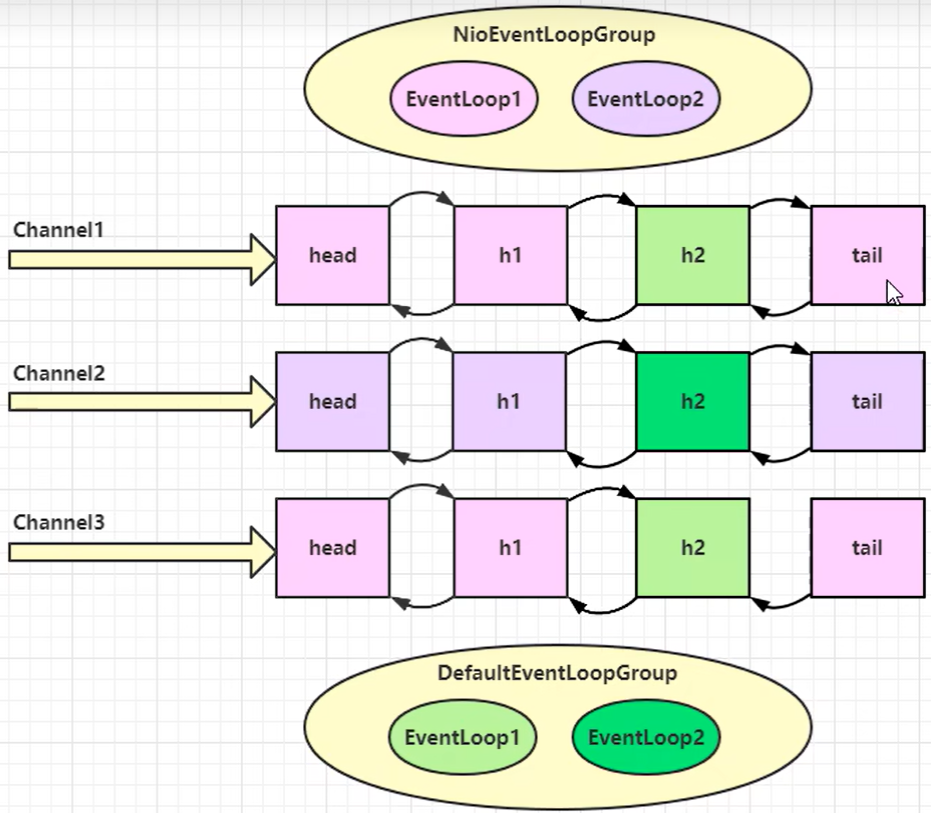
eventLoop:处理数据的工人
- 一个eventLoop可以管理多个channel的io操作;一旦eventLoop负责了某个channel,这个channel以后就都归这个eventLoop管理(绑定)
- eventLoop既可以执行io操作,还可以提交普通任务;每个eventLoop都有任务队列,队列里可以放多个channel的待处理任务
- eventLoop可以按照pipeline顺序,依次按照handler的代码处理数据,可以为每道工序指定不同的eventLoop
EventLoop
EventLoop:事件循环对象,是一个单线程执行器,里面有run方法处理Channel上源源不断的io事件
【继承】:
- j.u.c.ScheduledExecutorService:包含了线程池中的所有方法
- netty自己的OrderedEventExecutor
- 提供了boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread)方法判断一个线程是否属于EventLoop
- 提供了parent方法来看自己属于哪个EventLoopGroup
【继承】:
- 继承自netty自己的EventExecutorGroup
- 实现了Iterable接口提供便利EventLoop的能力
- 另有next方法获取集合下一个EventLoop
EventLoopGroup:事件循环组
创建事件循环组
@Test
public void testCreate() {// 创建事件循环组EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(2); // io事件、普通任务、定时任务(指定两个线程)EventLoopGroup group1 = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // io事件、普通任务、定时任务DefaultEventLoopGroup group2 = new DefaultEventLoopGroup();// 普通任务,定时任务
}
获取事件循环对象
@Test
public void testGet() {// 1. 创建事件循环组EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(2); // io事件、普通任务、定时任务// 2. 获取下一个事件循环对象(循环获取)System.out.println(group.next()); // io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@763d9750System.out.println(group.next()); // io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@5c0369c4System.out.println(group.next()); // io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@763d9750System.out.println(group.next()); // io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@5c0369c4
}
创建普通任务
@Test
public void testpuTongTask() throws InterruptedException {// 1. 创建事件循环组EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(2); // io事件、普通任务、定时任务// 2. 执行普通任务group.next().submit(()->{try {Thread.sleep(1000);}catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}log.debug("ok"); // 把这个任务交给事件循环组中某个对象处理});log.debug("main");Thread.sleep(2000); // 等待异步任务完成group.shutdownGracefully(); // 清理资源
}
创建定时任务
public void testDingShiTask() {// 1. 创建事件循环组EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(2); // io事件、普通任务、定时任务// 2. 执行定时任务group.next().scheduleAtFixedRate(()->{log.debug("ok");}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 参数:定时任务, 初始延迟时间, 间隔时间, 时间单位
}
IO任务
服务器:
@Slf4j
public class Test02EventLoopServer {public static void main(String[] args) {/*如果某个handler的执行时间耗时很长,可以独立出来一个group,让这个group来单独处理这个handler中的代码,这样就不会去影响io线程划分职责2:创建一个独立的EventLoopGroup,让这个group来单独处理handler中的代码*/EventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup();new ServerBootstrap()/*划分职责1:(boss、worker)第一个参数:boss 只负责ServerSocketChannel上accept事件第二个参数:worker 只负责socketChannel上的读写*/.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(), new NioEventLoopGroup(2)).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception { // 连接建立后被调用ch.pipeline().addLast("handler1", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { // msg是ByteBuf类型ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;log.debug(buf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); // 让消息传递给下一个handler}}).addLast(group, "handler2", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;log.debug(buf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));}});};}).bind(8080);}
}
上边涉及到了两个分工细化:
- 划分bossGroup和workerGroup,使用bossGroup负责处理客户端的连接请求(三次握手,创建SocketChannel);workerGroup负责业务处理
- 创建一个独立的EventLoopGroup,让这个group来单独处理handler中的代码
客户端:
public class Test03EventLoopClient {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 1. 启动类Channel channel = new Bootstrap()// 2. 添加 EventLoop.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())// 3. 选择客户端 channel 实现.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)// 4. 添加处理器.handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {@Override // 在连接建立后被调用protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder()); // 编码}})// 5. 连接到服务器.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)).sync() // 阻塞方法,直到连接建立.channel();// 连接对象System.out.println(channel);System.out.println("");}
}
channel只要和服务器建立连接后,服务器就会始终使用一个eventLoop来处理这个客户端的请求。如果eventLoop不够用了,就会一个eventLoop负责多个channel
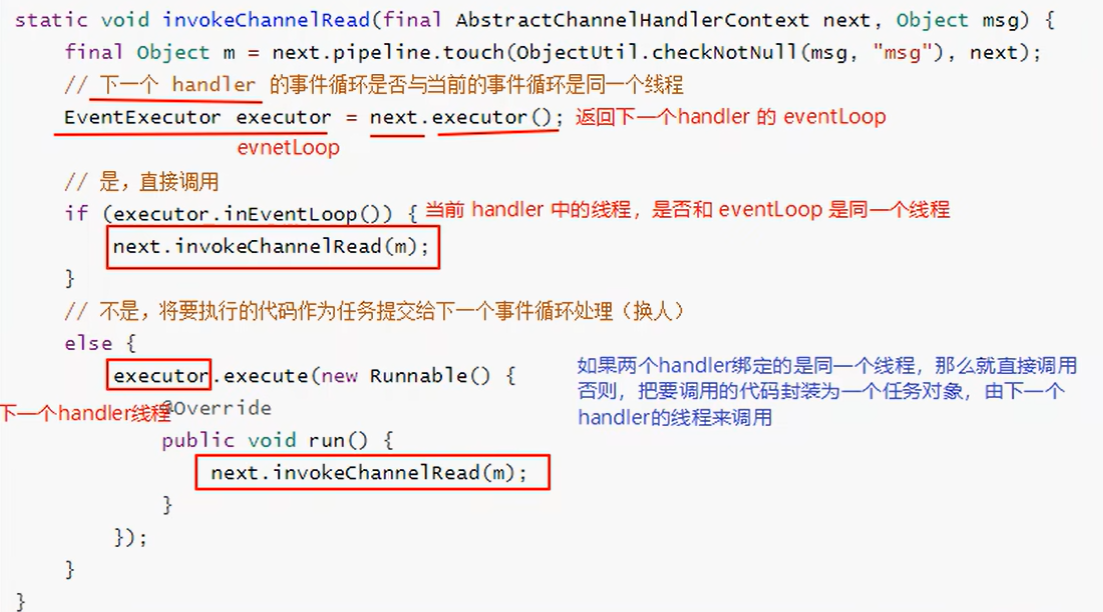
handler之间的切换源码分析
Channel
作用:
- close():关闭channel
- closeFuture():处理channel的关闭
- sync:同步等待channel关闭
- addListener:异步等待channel关闭
- pipeline():添加处理器
- write():向缓冲区写入(只有缓冲区满了才会发,没满的时候是不会发出的)
- writeAndFlush():将数据写入并刷出
ChannelFuture
问题1:连接问题
带有Future、Promise的类型都是和异步方法配合使用,用来正确处理结果。
【现象说明】:下边代码并不会正确发送数据
【分析】:connect方法是一个异步非阻塞方法:
- 异步(调用connect的方法的main线程,不关心结果)
- 非阻塞(做连接操作的是另一个nio线程,发起调用后不需要等结果)
【
原因】nio线程去建立连接可能需要1s之后,但是在这1s内,main线程并没有阻塞,还会向下运行(此时还没建立连接)
public class Test04ChannelFutureClient {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap().group(new NioEventLoopGroup()).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder()); // 编码}})/*1. 连接到服务器connect:异步(调用connect的方法的main线程,不关心结果)非阻塞(做连接操作的是另一个nio线程,发起调用后不需要等结果)nio线程去建立连接可能需要1s之后,但是在这1s内,main线程并没有阻塞,还会向下运行(此时还没建立连接)*/.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));// channelFuture.sync();// 阻塞等待nio建立连接Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();// 2. 向服务器发送数据channel.writeAndFlush("hello, world");}
}
方法1. 使用sync方法同步处理结果
public class Test04ChannelFutureClient {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap().group(new NioEventLoopGroup()).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder()); // 编码}})// 1. 连接到服务器.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));// 【方法1. 】阻塞等待nio建立连接channelFuture.sync(); // 阻塞住当前线程,直到nio线程连接建立完毕Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();// 2. 向服务器发送数据channel.writeAndFlush("hello, world");}
}
相当于:谁发起的(main线程)调用,就让谁来处理结果
方法2. 使用addListener方法异步处理结果
public class Test05ChannelFutureClient {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap().group(new NioEventLoopGroup()).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder()); // 编码}})// 1. 连接到服务器.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));// 2. 使用addListener(回调对象)方法异步处理结果channelFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {@Override // 在nio线程连接建立好后,会调用operationCompletepublic void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {Channel channel = future.channel();channel.writeAndFlush("hello world");}});}
}
让等结果、处理结果的事都给另一个线程处理
问题2:关闭问题1
假设客户端调用了close()方法后,还想要执行一些操作,但是如果按照下边的代码这样写会存在问题。
【现象】:还没有关闭,但是却先执行关闭后的操作
【分析】:由于关闭的这个线程是新开辟的线程,并不是主线程。主线程仍然是正常执行。
@Slf4j
public class Test06CloseFutureClient {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap().group(new NioEventLoopGroup()).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder()); // 编码}}).connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));Channel channel = channelFuture.sync().channel();log.debug("连接建立{}", channel);new Thread(()-> {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);while(true) {String line = scanner.nextLine();if("q".equals(line)) {channel.close(); // 异步操作(1s之后)break;}channel.writeAndFlush(line);}}, "input").start();log.debug("处理关闭之后的操作");}
}
方法1. 同步方式处理关闭
@Slf4j
public class Test06CloseFutureClient {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap().group(new NioEventLoopGroup()).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder()); // 编码}}).connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));Channel channel = channelFuture.sync().channel();log.debug("连接建立{}", channel);new Thread(()-> {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);while(true) {String line = scanner.nextLine();if("q".equals(line)) {channel.close(); // 异步操作(1s之后)break;}channel.writeAndFlush(line);}}, "input").start();// 获取CloseFuture对象(在关闭发生后处理)// 同步关闭处理ChannelFuture closeFuture = channel.closeFuture();System.out.println("waiting close...");closeFuture.sync();log.debug("处理关闭之后的操作");}
}
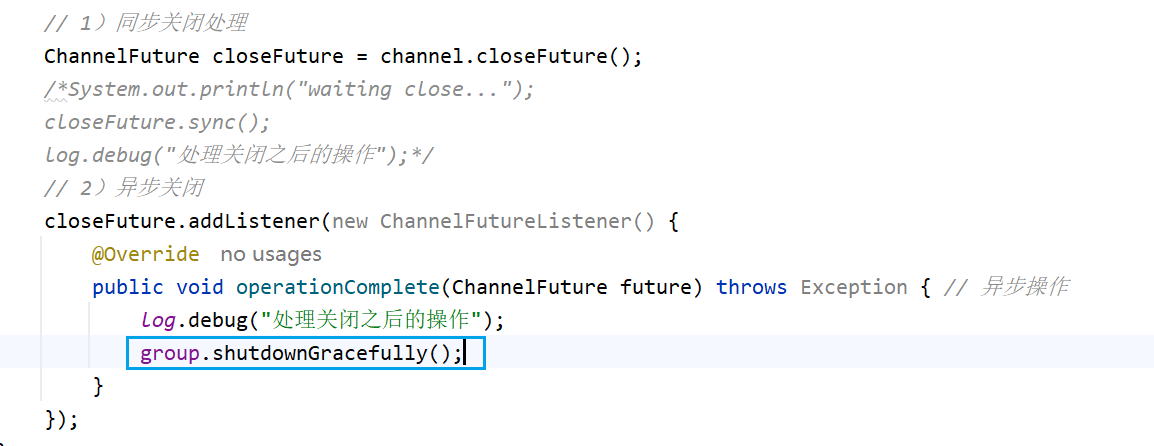
方法2. 异步方式处理关闭
ChannelFuture closeFuture = channel.closeFuture();
closeFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {@Overridepublic void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { // 异步操作log.debug("处理关闭之后的操作");}});
问题2:关闭问题2
【现象】:虽然已经调用了close方法,但是调用后客户端仍然在运行。
【原因】:因为NioEventLoopGroup()这里还有一部分线程,这些线程仍然在运行
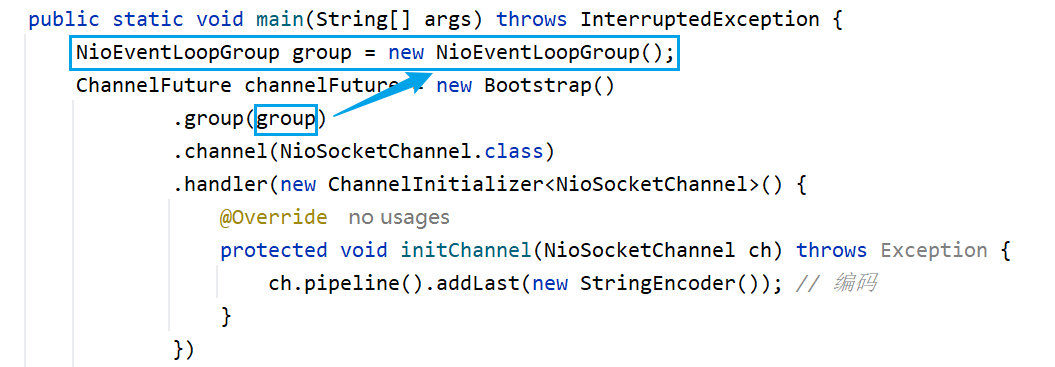
方法
将new NioEventLoopGroup()放在外边(不使用匿名对象的方式),这样就可以手动关闭(group.shutdownGracefully();)
总结
Netty里很多方法都是异步的(有点类似于CPU的流水线),如果碰到需要异步处理时,可以考虑以上几种方式
netty异步:
- 单线程没法提高效率,必须配合多线程、多核CPU才能发挥异步的优势
- 异步并没有缩短响应时间,反而有所增加
- 合理进行任务拆分也是异步的关键