JAVA 锁—— synchronized
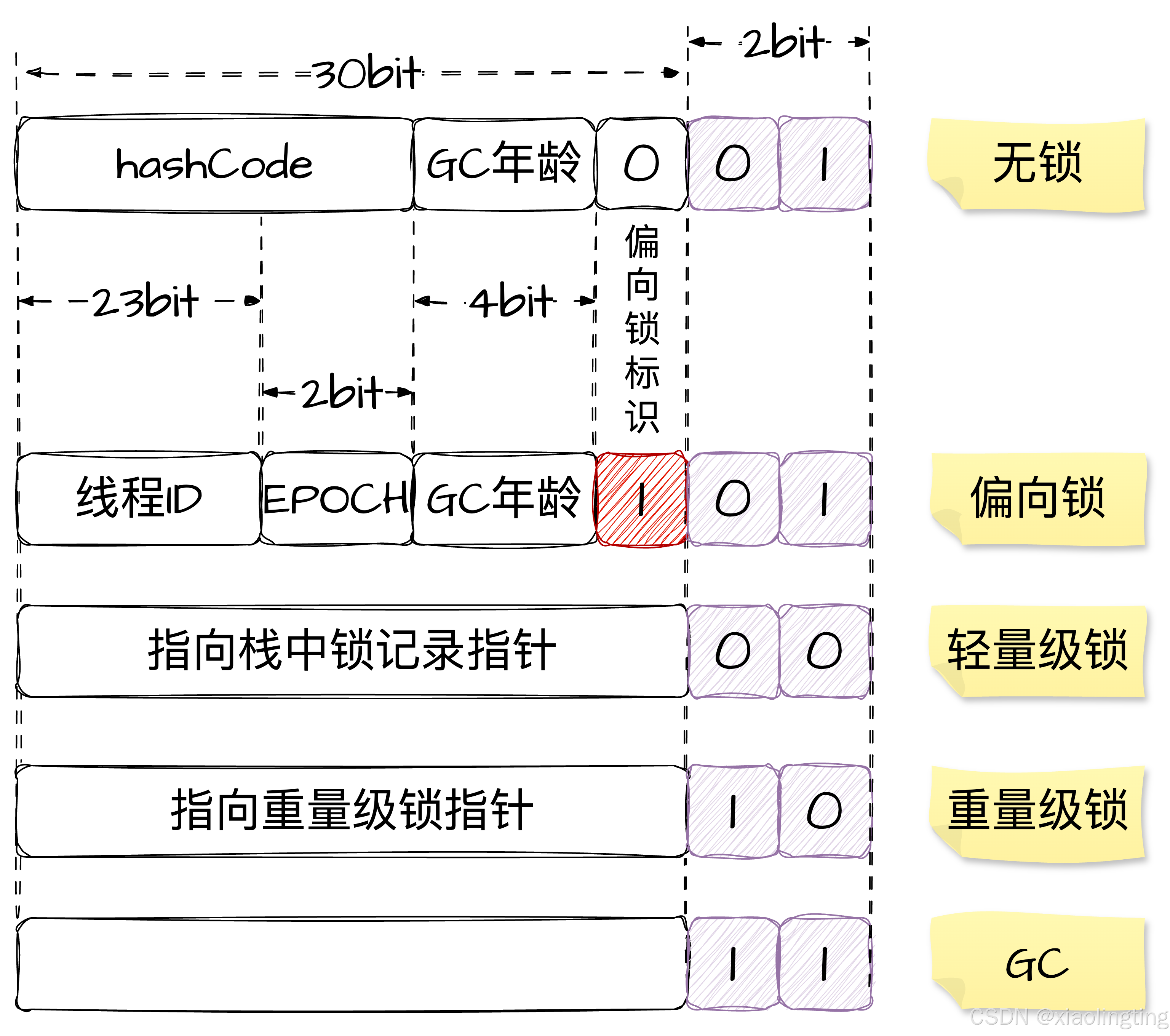
32 位机器上java对象头中,
markWord示意图如上所示,64 位机器扩展前面标识位数,如 hashcode(25 -> 31),线程ID(23 -> 54)
如果启用了偏向锁:
synchronized添加偏向锁:只有1个线程加锁的情况下,此时一定没有竞争!synchronized添加轻量级锁:超过1个线程,且交替加锁,此时没有竞争。synchronized添加重量级锁:超过1个线程,同时加锁,或加锁时,其它线程没释放锁,此时发生了竞争。
一、基本概念
注:下面代码大部分基于 JDK 8 分析,后续有 JDK23 的分析。
1、偏向锁
为方便观察 Java 内存对象,我们使用JOL工具,详见Java对象的内存分布(一)。
1.1、代码
/*** 程序运行前最好等待5秒,开启偏向锁。* 因为 jvm 启动也有加锁需求,防止 jvm 启动时受偏向锁影响,比如锁升级带来消耗,* 故而 jvm 完全启动后(大约4s,通过参数 -XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0 进行调整),才会应用偏向锁。*/public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{Thread.sleep(5000l); Object lock = new Object();System.out.println("---第一次----");System.out.println("加锁前:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("加锁中:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}System.out.println("加锁后:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());System.out.println("---第二次----");System.out.println("加锁前:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("加锁中:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}System.out.println("加锁后:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}
1.2 运行结果

- 大端模式:高位字节存放于内存的低地址端,低位字节存放于内存的高地址端,便于人类阅读。
- 小端模式:低位字节存放于内存的低地址端,高位字节存放于内存的高地址端,便于机器处理。
| 存储模式 | 示例(0x12345678) |
|---|---|
| 大端(Big-Endian) | 0x12 0x34 0x56 0x78 |
| 小端(Little-Endian) | 0x78 0x56 0x34 0x12 |
1.3、注意事项
Object.hashCode()方法和System.identityHashCode()会让对象不能使用偏向锁,所以如果想使用偏向锁,那就最好重写hashCode方法。
- 无锁和偏向锁占用相同位置,不像轻量级锁和重量级锁可以将原位置信息拷贝到其它地方进行备份,所以当对象已经存储了
hashcode之后,加锁时会跳过偏向锁。- 偏向锁不会释放,即解锁后,锁对象头MarkWord不变。
- JDK [6, 15),偏向锁默认开启,从 JDK 15 开始,默认关闭,可以通过
-XX:+UseBiasedLocking开启,从JDK 18 开始彻底移除偏向锁。
2、轻量级锁
2.1、代码
/*** 开启偏向锁后,2个线程交替加锁,偏向锁升级为轻量级锁。*/public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{Thread.sleep(5000l); // 等待5秒,开启偏向锁Object lock = new Object();System.out.println("---第一次----");System.out.println("加锁前:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("加锁中:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}System.out.println("加锁后:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());System.out.println("---第二次----");Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("线程2:");System.out.println("加锁中:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}System.out.println("线程2:");System.out.println("加锁后:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());});thread.start();}
2.2、运行结果

2.3、锁细节
轻量级锁加锁时,markWord中会存储指向栈中锁记录的指针,栈中锁记录存储的就是未加锁时原来的markWord,解锁时方便还原回去。
假如
markWord中存储了hashcode,使用时先访问markWord发现加了轻量级锁,顺着栈指针找到栈中锁记录,即可找到hashcode。
3、重量级锁
3.1、代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{Thread.sleep(5000l); // 等待5秒,开启偏向锁Object lock = new Object();System.out.println("---第一次----");System.out.println("加锁前:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("加锁中:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}System.out.println("解锁后:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());System.out.println("---第二次----");Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("线程2:[" + Thread.currentThread() + "] 加锁中:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());try {Thread.sleep(5000L); // 这里持锁5s,确保线程3加锁发生竞争;} catch (java.lang.Exception e) {}}});Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("线程3:[" + Thread.currentThread() + "] 加锁中:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}});thread2.start();thread3.start();Thread.sleep(8000L); // 等待8s,确保线程锁释放;System.out.println("解锁后:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}
3.2、运行结果

3.3、Monitor
-
偏向锁、轻量级锁只要发生竞争,就会升级为重量级锁,注意,这里一步到位,不会自旋。
-
升级为重量级锁后,其它线程自旋多次失败后,会进入 cxq 列表(相当于栈)中自旋,自旋达到阈值后,仍未获取锁,则进入阻塞状态。
-
重量级锁加锁时,
markWord中会存储指向 Monitor 的指针,Monitor 会存储未加锁时原来的markWord,解锁后还原回去。【JDK8实验如此,JDK23实验不一样】假如
markWord中存储了hashcode,使用时先访问markWord发现加了重量级锁,顺着重量级锁指针找到Monitor,即可找到hashcode。
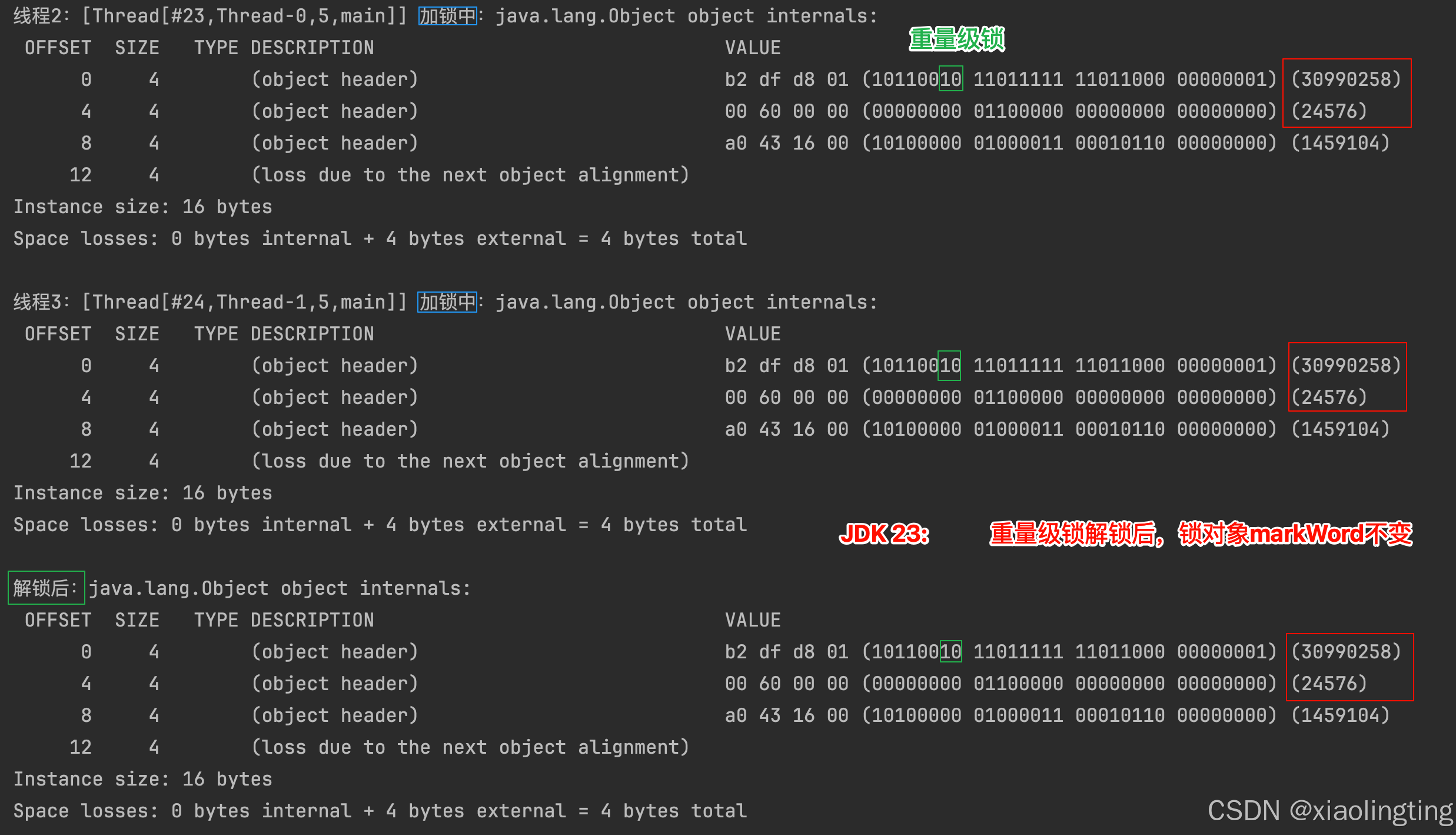
截止目前为止,上述代码均在 JDK 8上讨论;下面讨论 JDK23:
- 重量级锁加锁时,
markWord中会存储指向 Monitor 的指针,Monitor 会存储未加锁时原来的markWord,解锁时markWord不变。【JDK23实验,代码不变,运行结果如下图所示】
ObjectMonitor细节如下:

由上图可知,
wait()、notify()、notifyAll()只能在重量级锁中调用,换言之,在偏向锁和轻量级锁中调用这3个方法时,会升级为重量级锁。
CAS详见CAS基础概念。
3.4、重量级锁会降级为轻量级锁吗?
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{Thread.sleep(5000l); // 等待5秒,开启偏向锁Object lock = new Object();System.out.println("---第一次----");System.out.println("加锁前:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("加锁中:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}System.out.println("解锁后:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());System.out.println("---第二次----");Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("线程2:[" + Thread.currentThread() + "] 加锁中:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());try {Thread.sleep(5000L); // 这里持锁5s,确保线程3加锁发生竞争;} catch (java.lang.Exception e) {}}});Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("线程3:[" + Thread.currentThread() + "] 加锁中:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}});thread2.start();thread3.start();Thread.sleep(8000L); // 等待8s,确保线程锁释放;System.out.println("解锁后:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());Thread thread4 = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("线程4:[" + Thread.currentThread() + "] 加锁中:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}});thread4.start();
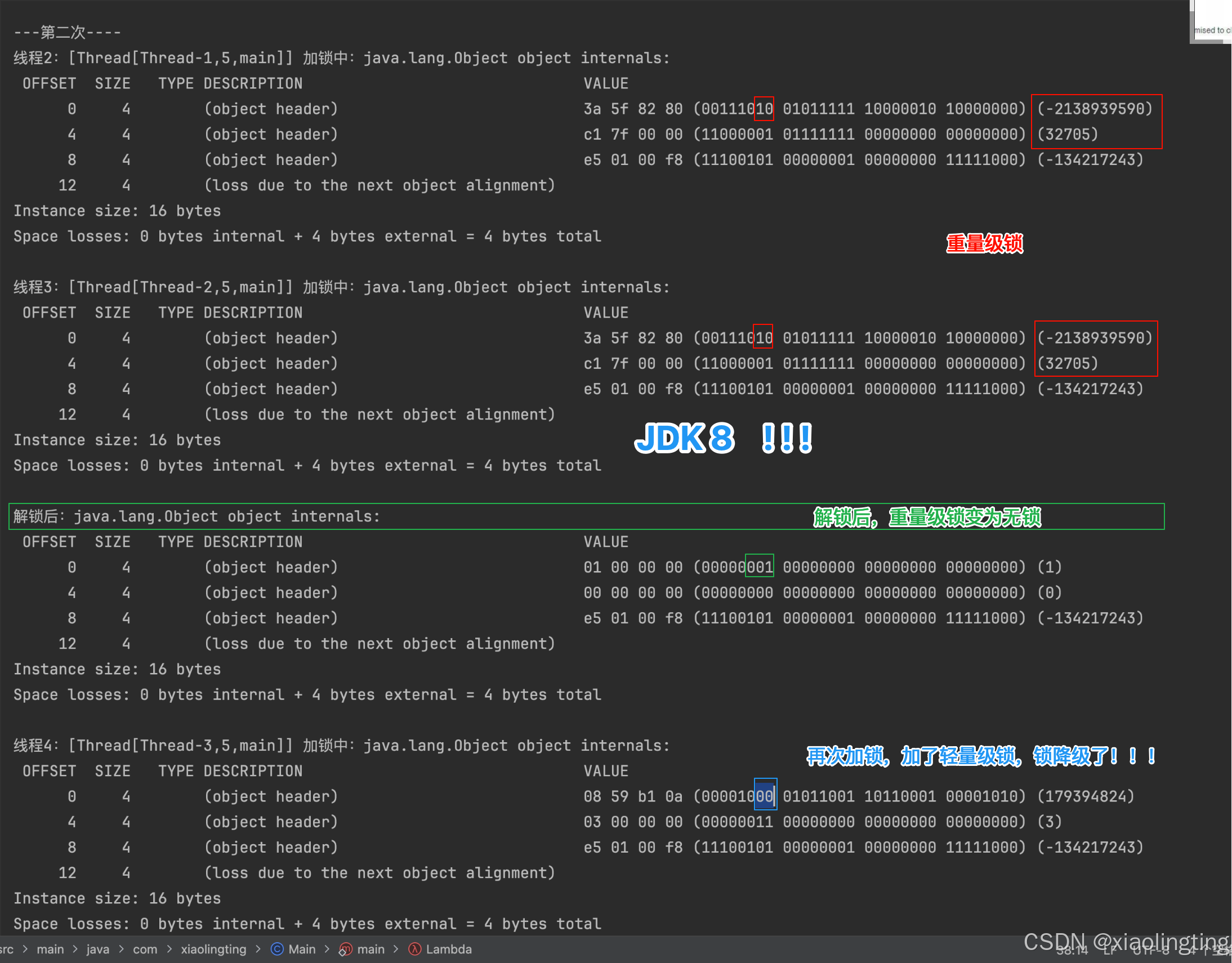
【JDK 8 重量级锁会降级为轻量级锁】
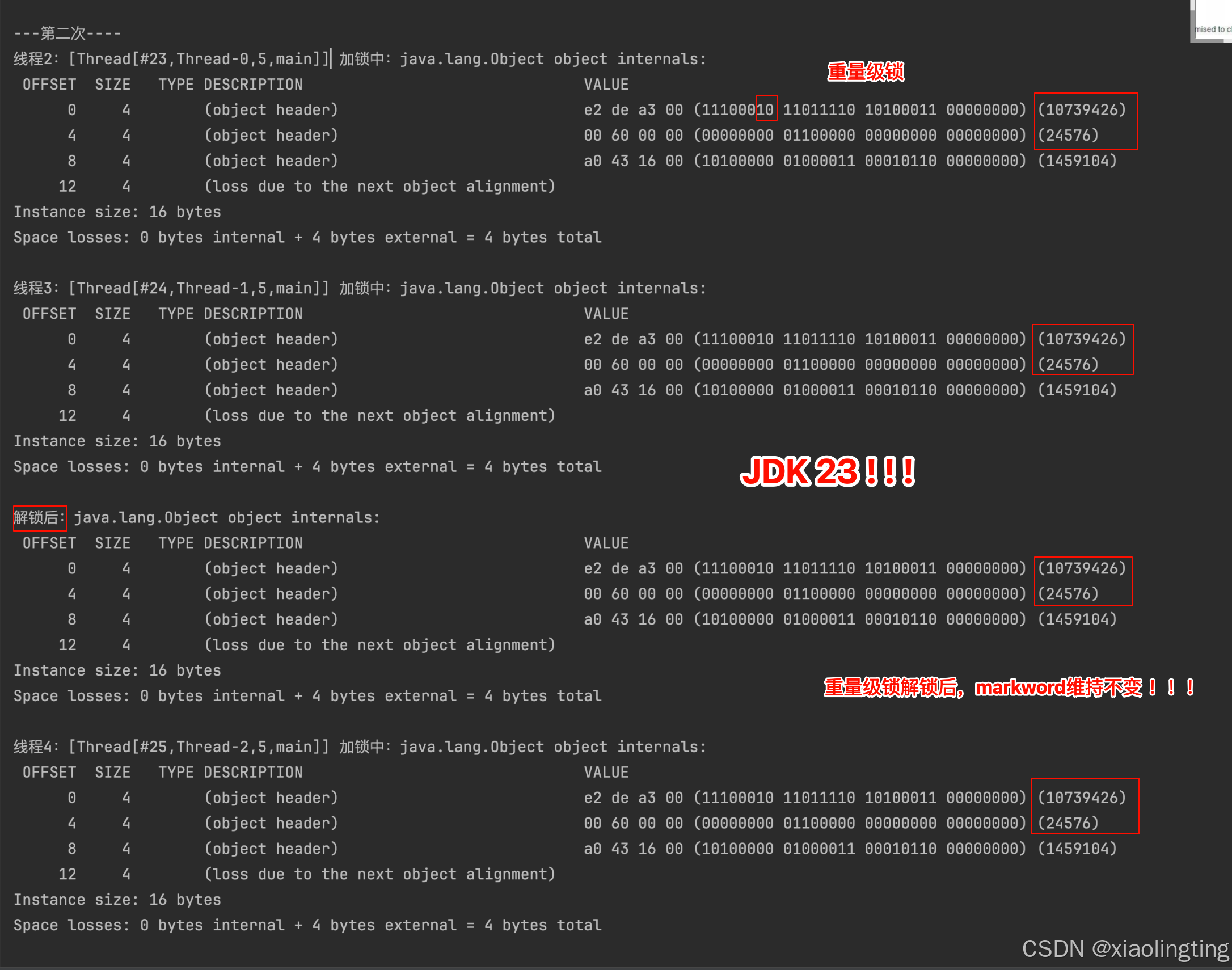
【JDK 23 重量级锁不会降级为轻量级锁】
二、补充知识
1、hashcode对锁的影响
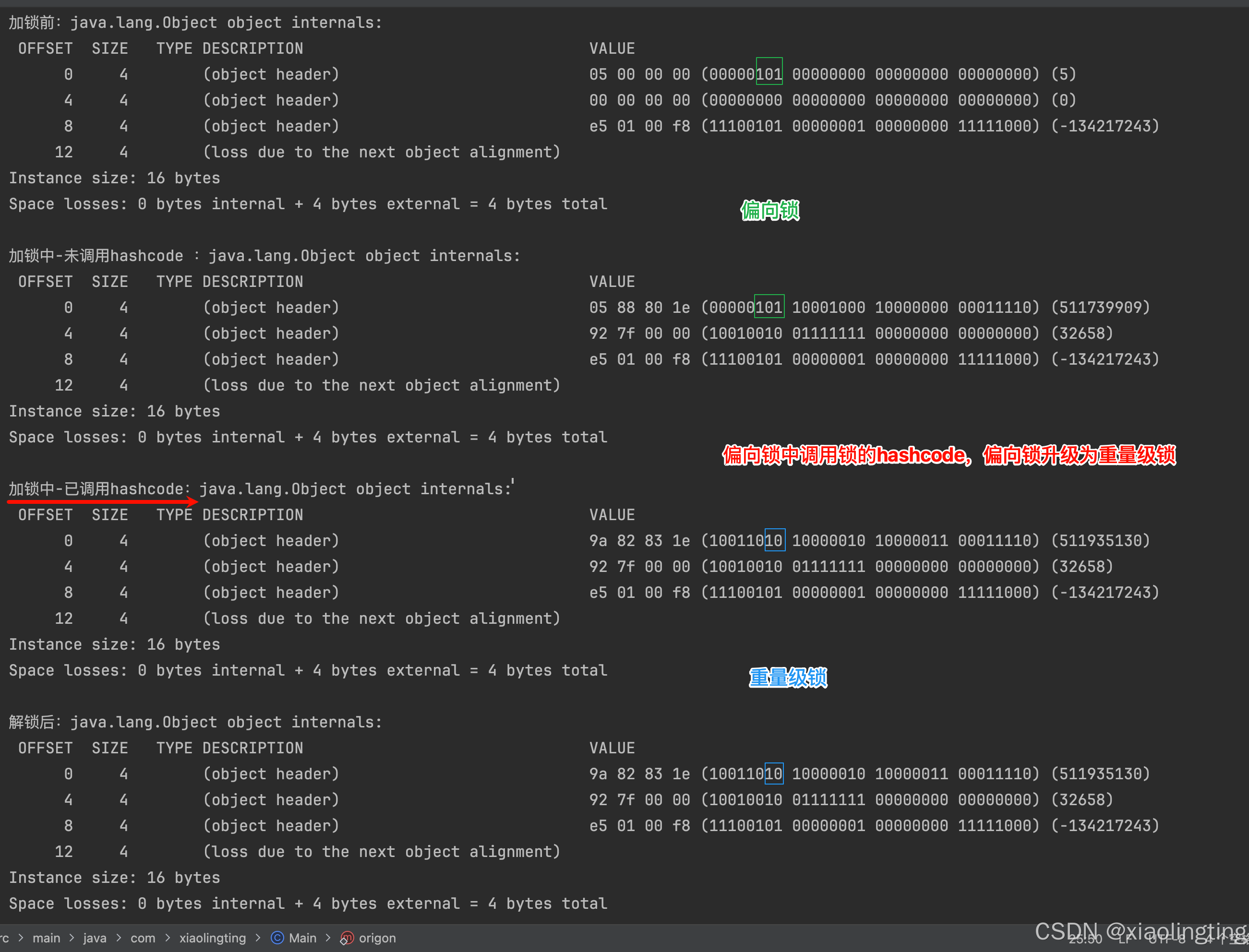
1.1、偏向锁状态中,首次调用锁的hashcode后,偏向锁会直接升级为重量级锁。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{Thread.sleep(5000l); // 等待5秒,开启偏向锁Object lock = new Object();System.out.println("---第一次----");System.out.println("加锁前:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("加锁中-未调用hashcode :" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());lock.hashCode();System.out.println("加锁中-已调用hashcode:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}System.out.println("解锁后:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}
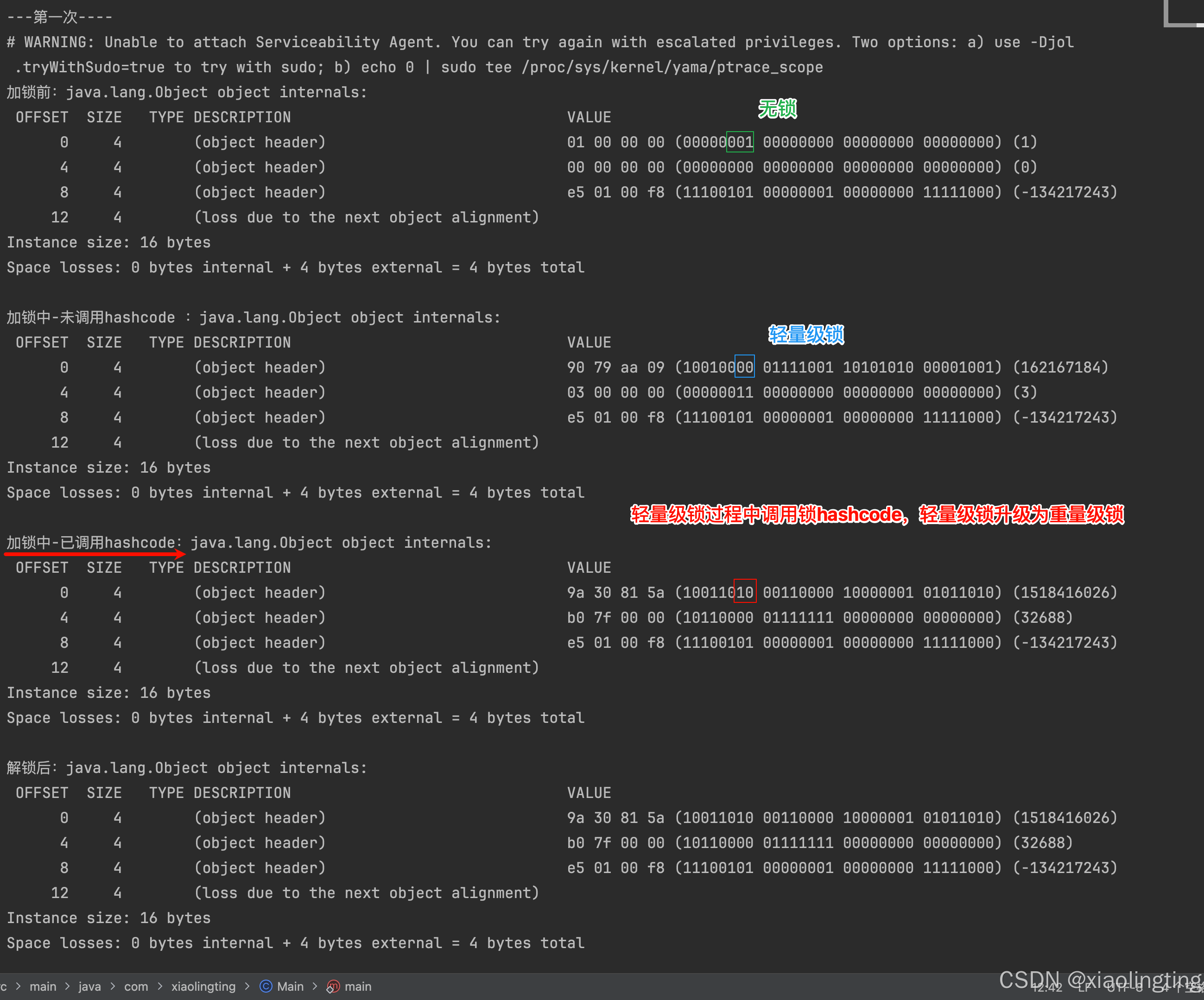
1.2、轻量级锁状态中,首次调用锁的hashcode后,锁升级为重量级锁?
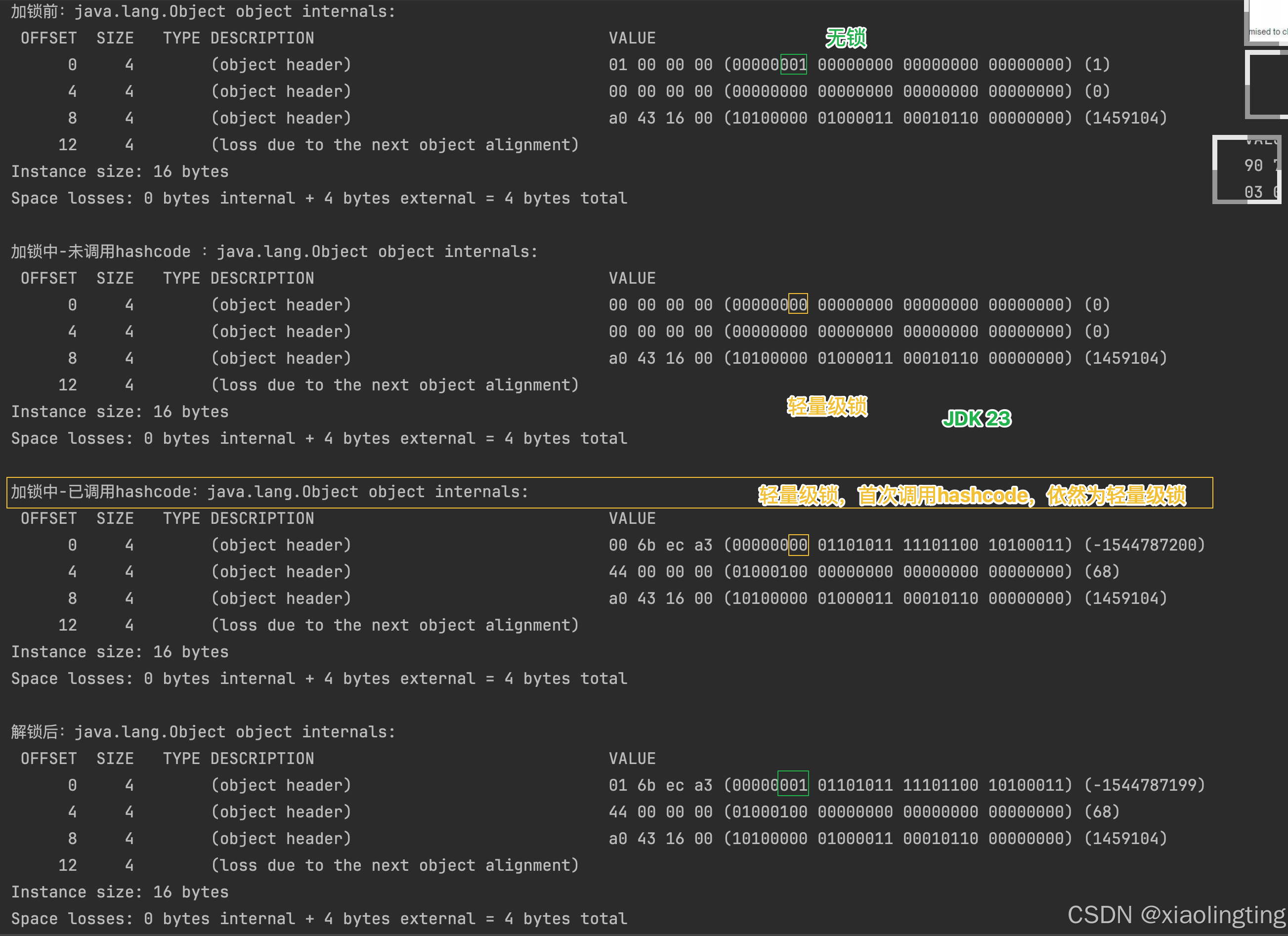
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{Object lock = new Object();System.out.println("---第一次----");System.out.println("加锁前:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("加锁中-未调用hashcode :" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());lock.hashCode();System.out.println("加锁中-已调用hashcode:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}System.out.println("解锁后:" + ClassLayout.parseInstance(lock).toPrintable());}
【JDK 8 升级重量级锁】
【JDK 23 维持轻量级锁】
唯一不变就是变化,JDK也在不断的演进,昨天还正确的观点,今天就错误了;今天错误的观点也可能明天就正确了。
所以看到任何观点,都要保持怀疑态度啊,每个人都有自己的观点,切忌坐井观天,故步自封,一定要跳出去,用发展的视角看问题。
