深度研究——OpenAI Researcher Agent(使用OpenAI Agents SDK)
项目地址:
https://github.com/Shubhamsaboo/awesome-llm-apps.git
环境:
openai-agents
openai
streamlit
uuid
pydantic
python-dotenv
asyncio这个Web 应用程序利用了 Streamlit 框架来构建用户界面,并集成了 OpenAI 的 Agents SDK 来创建一个多智能体(Multi-Agent)系统,用于自动研究特定主题并生成报告。
可以把这个应用想象成一个自动化的研究团队,团队里有不同角色的成员(智能体),他们协同工作来完成一个研究任务。
总体概述
这个程序的核心功能是:
-
接收用户输入:用户在网页上输入一个研究主题。
-
多智能体协作:
-
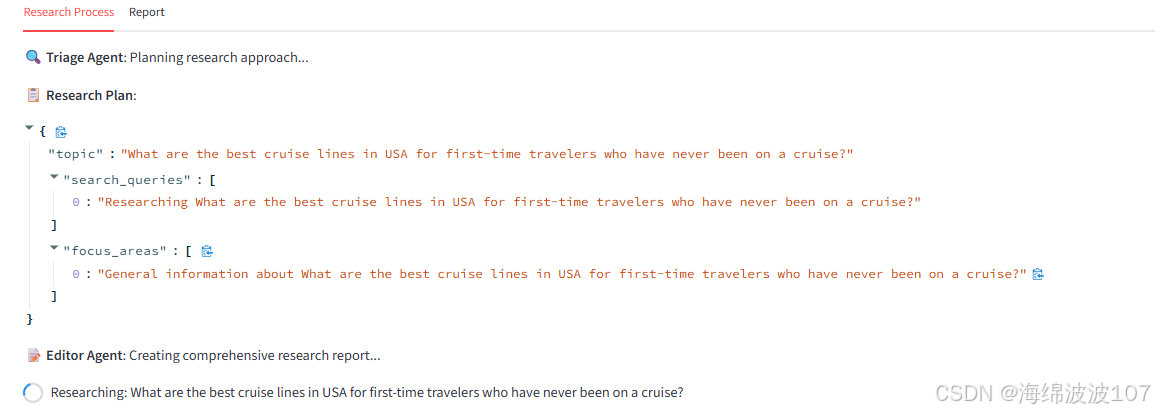
一个策划智能体 (Triage Agent) 首先分析主题,制定研究计划。
-
一个研究智能体 (Research Agent) 根据计划上网搜索信息,并记录关键事实。
-
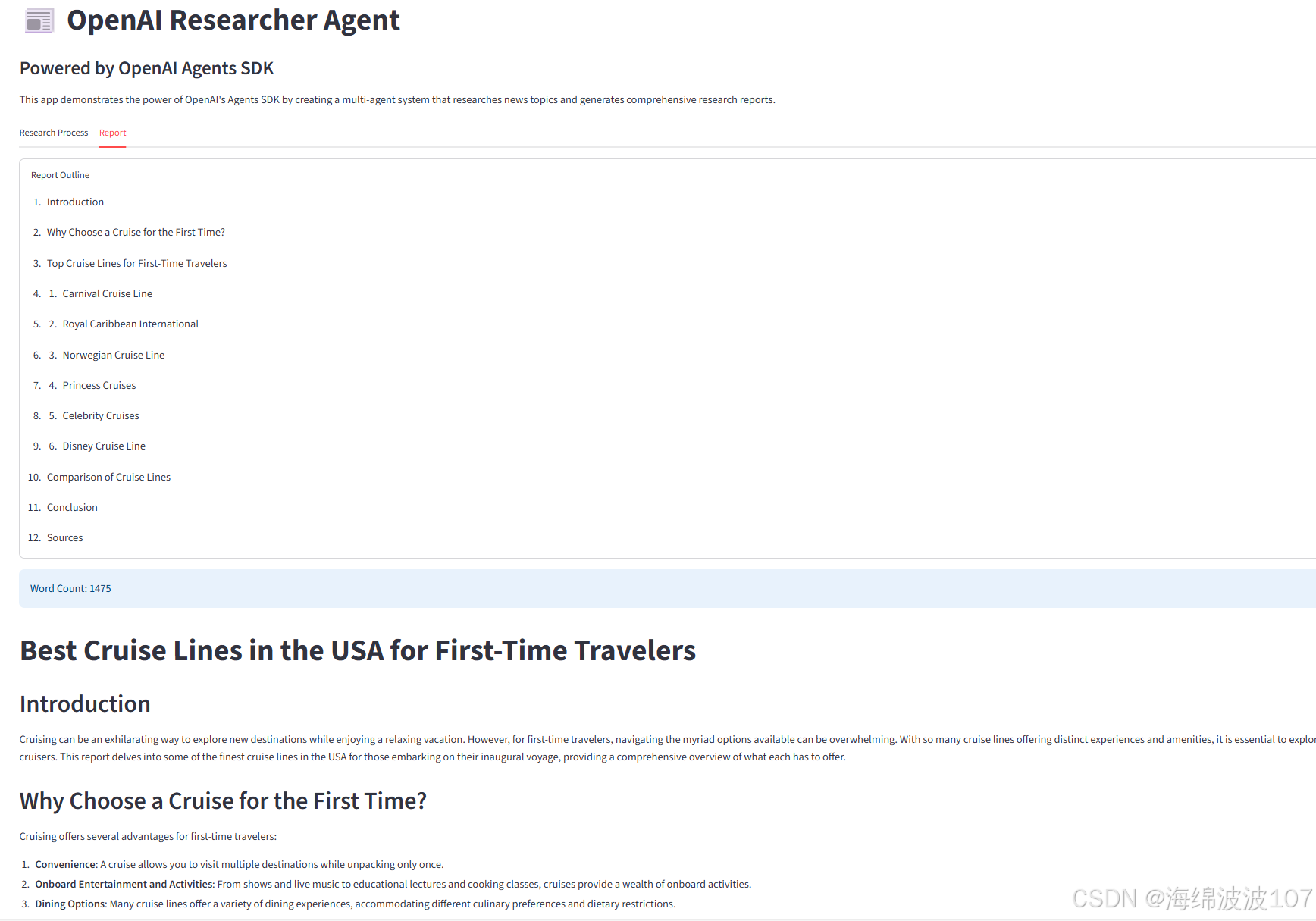
一个编辑智能体 (Editor Agent) 整合所有收集到的信息,撰写一份结构完整、内容详细的最终报告。
-
-
实时展示过程:在网页上实时显示研究的进展,比如制定的计划、收集到的事实等。
-
生成并展示报告:研究完成后,在专门的标签页中展示最终生成的报告,并提供下载功能。
代码分步详解
我们将代码分成几个部分来理解:
1. 导入库和环境设置 (import & load_dotenv)
import os
import uuid
import asyncio
import streamlit as st
from datetime import datetime
from dotenv import load_dotenvfrom agents import (Agent, Runner, WebSearchTool, function_tool, handoff, trace,
)from pydantic import BaseModel# 加载环境变量
load_dotenv()# 设置 OpenAI API Key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-proj-..."-
streamlit as st: 导入 Streamlit 库,这是构建网页界面的核心。
-
openai, agents: 导入 OpenAI Agents SDK 的相关组件。这是驱动 AI 智能体的核心。
-
Agent: 用于定义一个智能体。
-
Runner: 用于执行一个智能体或智能体流程。
-
WebSearchTool: 一个预置的工具,允许智能体访问和搜索网页。
-
function_tool: 一个装饰器,可以把普通的 Python 函数转换成能被智能体使用的工具。
-
handoff: 定义智能体之间的工作交接流程。
-
-
pydantic.BaseModel: 用于定义数据结构。这非常重要,因为它可以强制 AI 的输出遵循我们想要的格式(例如,报告必须包含标题、大纲和正文)。
-
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = ...: 这里硬编码了 OpenAI 的 API 密钥。在实际应用中,通常会使用 load_dotenv() 从一个 .env 文件中加载,这样更安全。
2. 数据模型定义 (Pydantic Models)
class ResearchPlan(BaseModel):topic: strsearch_queries: list[str]focus_areas: list[str]class ResearchReport(BaseModel):title: stroutline: list[str]report: strsources: list[str]word_count: int-
这里定义了两个数据模型,用于规范 AI 的输入和输出。
-
ResearchPlan: 要求“策划智能体”的输出必须包含 topic (主题)、search_queries (搜索关键词列表) 和 focus_areas (重点研究领域列表)。

-
ResearchReport: 要求“编辑智能体”的最终报告必须包含 title (标题)、outline (大纲)、report (报告正文) 等字段。这确保了输出的结构化和一致性。
3. 自定义工具 (Custom Tool)
@function_tool
def save_important_fact(fact: str, source: str = None) -> str:# ... 代码 ...-
@function_tool 装饰器把 save_important_fact 函数变成了一个 AI 工具。
-
这个工具的作用是,当“研究智能体”在网上找到重要信息时,可以调用这个函数来保存它。
-
st.session_state: 这是 Streamlit 的一个关键特性,它是一个字典,用于在用户与应用的多次交互之间保存状态。这里用它来存储收集到的所有事实 (collected_facts)。
4. 智能体 (Agent) 定义
这是整个应用最核心的部分,定义了三个不同角色的智能体。
-
research_agent (研究智能体)
-
角色: 研究助理。
-
任务: 根据给定的搜索词进行网络搜索,并生成一个简明扼要的摘要(2-3段,少于300词)。
-
工具: WebSearchTool (用于上网) 和 save_important_fact (用于记录发现)。
-
模型: gpt-4o-mini。
-
-
editor_agent (编辑智能体)
-
角色: 资深研究员。
-
任务: 基于原始问题和研究助理收集的资料,撰写一份全面、详细、结构化的研究报告。报告要求篇幅较长(目标1000词以上),并以 Markdown 格式输出。
-
输出类型: output_type=ResearchReport,强制它的最终输出符合我们定义的 ResearchReport 数据模型。
-
-
triage_agent (策划智能体/总管)
-
角色: 研究行动的协调员。
-
任务:
-
理解用户的主题。
-
创建一个包含主题、搜索词和重点领域的 ResearchPlan。
-
将任务交接 (handoff) 给 research_agent 去执行研究。
-
研究完成后,再将任务交接 (handoff) 给 editor_agent 去撰写报告。
-
-
handoffs: 这个参数定义了工作流。它告诉 triage_agent 它的下游是 research_agent 和 editor_agent。
-
输出类型: output_type=ResearchPlan,强制它的输出符合 ResearchPlan 数据模型。
-
5. Streamlit 界面布局和交互
# 设置页面配置
st.set_page_config(...)
st.title(...)# 侧边栏
with st.sidebar:user_topic = st.text_input(...)start_button = st.button("Start Research", ...)# 主内容区
tab1, tab2 = st.tabs(["Research Process", "Report"])-
这部分代码负责创建用户能看到的网页界面。
-
st.set_page_config: 设置网页的标题、图标等。
-
st.sidebar: 创建一个侧边栏,用于放置输入框和控制按钮。
-
st.text_input: 创建一个文本输入框,让用户输入研究主题。
-
st.button: 创建一个按钮,当用户点击时,start_button 变量会变为 True,从而触发研究流程。
-
st.tabs: 创建了两个标签页,“Research Process” (研究过程) 和 “Report” (报告),用于分开展示过程和结果。
6. 核心研究流程 (run_research 函数)
async def run_research(topic):# ...这是一个异步 (async) 函数,是整个研究工作的执行者。
-
启动: 当用户点击 "Start Research" 按钮后,这个函数被调用。
-
重置状态: 清空之前研究留下的事实和报告结果。
-
运行 Triage Agent:
-
await Runner.run(triage_agent, ...): 异步运行“策划智能体”,让它根据用户主题生成研究计划。
-
在界面上显示 "Planning research approach..." 并展示生成的计划。
-
-
运行 Research Agent & 收集事实 (隐式运行):
-
代码中虽然没有直接 Runner.run(research_agent),但 triage_agent 的结果会通过 handoff 机制传递给下游智能体。当 editor_agent 被调用时,它会接收到 triage_agent 和 research_agent 的所有工作历史和产出。
-
代码通过一个循环 await asyncio.sleep(1) 来模拟等待和实时更新。它会周期性地检查 st.session_state.collected_facts 是否有新内容,如果有,就在界面上更新“收集到的事实”列表。这给用户一种研究正在实时进行的观感。
-
-
运行 Editor Agent:
-
await Runner.run(editor_agent, triage_result.to_input_list()): 运行“编辑智能体”。triage_result.to_input_list() 会把前面所有智能体的对话历史和产出打包成一个列表,作为输入传递给编辑。
-
在界面上显示 "Creating comprehensive research report..."。
-
-
保存和展示结果:
-
将 editor_agent 生成的报告存入 st.session_state.report_result。
-
在“研究过程”标签页中显示一个报告预览。
-
7. 结果展示
with tab2:if st.session_state.research_done and st.session_state.report_result:# ...-
这部分代码在 "Report" 标签页中。
-
它会检查研究是否已完成 (research_done) 并且有报告结果 (report_result)。
-
如果结果是结构化的 ResearchReport 对象,它会分别提取标题、大纲、正文和来源进行格式化展示。
-
如果结果只是一个普通的字符串(例如出错时的备用方案),它就直接展示这个字符串。
-
st.download_button: 创建一个下载按钮,让用户可以将生成的 Markdown 报告保存到本地。
源代码:
import os
import uuid
import asyncio
import streamlit as st
from datetime import datetime
from dotenv import load_dotenvfrom agents import (Agent, Runner, WebSearchTool, function_tool, handoff, trace,
)from pydantic import BaseModel# Load environment variables
load_dotenv()# 设置 OpenAI API Key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-xxx"# Set up page configuration
st.set_page_config(page_title="OpenAI Researcher Agent",page_icon="📰",layout="wide",initial_sidebar_state="expanded"
)# Make sure API key is set
if not os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY"):st.error("Please set your OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable")st.stop()# App title and description
st.title("📰 OpenAI Researcher Agent")
st.subheader("Powered by OpenAI Agents SDK")
st.markdown("""
This app demonstrates the power of OpenAI's Agents SDK by creating a multi-agent system
that researches news topics and generates comprehensive research reports.
""")# Define data models
class ResearchPlan(BaseModel):topic: strsearch_queries: list[str]focus_areas: list[str]class ResearchReport(BaseModel):title: stroutline: list[str]report: strsources: list[str]word_count: int# Custom tool for saving facts found during research
@function_tool
def save_important_fact(fact: str, source: str = None) -> str:"""Save an important fact discovered during research.Args:fact: The important fact to savesource: Optional source of the factReturns:Confirmation message"""if "collected_facts" not in st.session_state:st.session_state.collected_facts = []st.session_state.collected_facts.append({"fact": fact,"source": source or "Not specified","timestamp": datetime.now().strftime("%H:%M:%S")})return f"Fact saved: {fact}"# Define the agents
research_agent = Agent(name="Research Agent",instructions="You are a research assistant. Given a search term, you search the web for that term and""produce a concise summary of the results. The summary must 2-3 paragraphs and less than 300""words. Capture the main points. Write succintly, no need to have complete sentences or good""grammar. This will be consumed by someone synthesizing a report, so its vital you capture the""essence and ignore any fluff. Do not include any additional commentary other than the summary""itself.",model="gpt-4o-mini",tools=[WebSearchTool(),save_important_fact],
)editor_agent = Agent(name="Editor Agent",handoff_description="A senior researcher who writes comprehensive research reports",instructions="You are a senior researcher tasked with writing a cohesive report for a research query. ""You will be provided with the original query, and some initial research done by a research ""assistant.\n""You should first come up with an outline for the report that describes the structure and ""flow of the report. Then, generate the report and return that as your final output.\n""The final output should be in markdown format, and it should be lengthy and detailed. Aim ""for 5-10 pages of content, at least 1000 words.",model="gpt-4o-mini",output_type=ResearchReport,
)triage_agent = Agent(name="Triage Agent",instructions="""You are the coordinator of this research operation. Your job is to:1. Understand the user's research topic2. Create a research plan with the following elements:- topic: A clear statement of the research topic- search_queries: A list of 3-5 specific search queries that will help gather information- focus_areas: A list of 3-5 key aspects of the topic to investigate3. Hand off to the Research Agent to collect information4. After research is complete, hand off to the Editor Agent who will write a comprehensive reportMake sure to return your plan in the expected structured format with topic, search_queries, and focus_areas.""",handoffs=[handoff(research_agent),handoff(editor_agent)],model="gpt-4o-mini",output_type=ResearchPlan,
)# Create sidebar for input and controls
with st.sidebar:st.header("Research Topic")user_topic = st.text_input("Enter a topic to research:",)start_button = st.button("Start Research", type="primary", disabled=not user_topic)st.divider()st.subheader("Example Topics")example_topics = ["What are the best cruise lines in USA for first-time travelers who have never been on a cruise?","What are the best affordable espresso machines for someone upgrading from a French press?","What are the best off-the-beaten-path destinations in India for a first-time solo traveler?"]for topic in example_topics:if st.button(topic):user_topic = topicstart_button = True# Main content area with two tabs
tab1, tab2 = st.tabs(["Research Process", "Report"])# Initialize session state for storing results
if "conversation_id" not in st.session_state:st.session_state.conversation_id = str(uuid.uuid4().hex[:16])
if "collected_facts" not in st.session_state:st.session_state.collected_facts = []
if "research_done" not in st.session_state:st.session_state.research_done = False
if "report_result" not in st.session_state:st.session_state.report_result = None# Main research function
async def run_research(topic):# Reset state for new researchst.session_state.collected_facts = []st.session_state.research_done = Falsest.session_state.report_result = Nonewith tab1:message_container = st.container()# Create error handling containererror_container = st.empty()# Create a trace for the entire workflowwith trace("News Research", group_id=st.session_state.conversation_id):# Start with the triage agentwith message_container:st.write("🔍 **Triage Agent**: Planning research approach...")triage_result = await Runner.run(triage_agent,f"Research this topic thoroughly: {topic}. This research will be used to create a comprehensive research report.")# Check if the result is a ResearchPlan object or a stringif hasattr(triage_result.final_output, 'topic'):research_plan = triage_result.final_outputplan_display = {"topic": research_plan.topic,"search_queries": research_plan.search_queries,"focus_areas": research_plan.focus_areas}else:# Fallback if we don't get the expected output typeresearch_plan = {"topic": topic,"search_queries": ["Researching " + topic],"focus_areas": ["General information about " + topic]}plan_display = research_planwith message_container:st.write("📋 **Research Plan**:")st.json(plan_display)# Display facts as they're collectedfact_placeholder = message_container.empty()# Check for new facts periodicallyprevious_fact_count = 0for i in range(15): # Check more times to allow for more comprehensive researchcurrent_facts = len(st.session_state.collected_facts)if current_facts > previous_fact_count:with fact_placeholder.container():st.write("📚 **Collected Facts**:")for fact in st.session_state.collected_facts:st.info(f"**Fact**: {fact['fact']}\n\n**Source**: {fact['source']}")previous_fact_count = current_factsawait asyncio.sleep(1)# Editor Agent phasewith message_container:st.write("📝 **Editor Agent**: Creating comprehensive research report...")try:report_result = await Runner.run(editor_agent,triage_result.to_input_list())st.session_state.report_result = report_result.final_outputwith message_container:st.write("✅ **Research Complete! Report Generated.**")# Preview a snippet of the reportif hasattr(report_result.final_output, 'report'):report_preview = report_result.final_output.report[:300] + "..."else:report_preview = str(report_result.final_output)[:300] + "..."st.write("📄 **Report Preview**:")st.markdown(report_preview)st.write("*See the Report tab for the full document.*")except Exception as e:st.error(f"Error generating report: {str(e)}")# Fallback to display raw agent responseif hasattr(triage_result, 'new_items'):messages = [item for item in triage_result.new_items if hasattr(item, 'content')]if messages:raw_content = "\n\n".join([str(m.content) for m in messages if m.content])st.session_state.report_result = raw_contentwith message_container:st.write("⚠️ **Research completed but there was an issue generating the structured report.**")st.write("Raw research results are available in the Report tab.")st.session_state.research_done = True# Run the research when the button is clicked
if start_button:with st.spinner(f"Researching: {user_topic}"):try:asyncio.run(run_research(user_topic))except Exception as e:st.error(f"An error occurred during research: {str(e)}")# Set a basic report result so the user gets somethingst.session_state.report_result = f"# Research on {user_topic}\n\nUnfortunately, an error occurred during the research process. Please try again later or with a different topic.\n\nError details: {str(e)}"st.session_state.research_done = True# Display results in the Report tab
with tab2:if st.session_state.research_done and st.session_state.report_result:report = st.session_state.report_result# Handle different possible types of report resultsif hasattr(report, 'title'):# We have a properly structured ResearchReport objecttitle = report.title# Display outline if availableif hasattr(report, 'outline') and report.outline:with st.expander("Report Outline", expanded=True):for i, section in enumerate(report.outline):st.markdown(f"{i+1}. {section}")# Display word count if availableif hasattr(report, 'word_count'):st.info(f"Word Count: {report.word_count}")# Display the full report in markdownif hasattr(report, 'report'):report_content = report.reportst.markdown(report_content)else:report_content = str(report)st.markdown(report_content)# Display sources if availableif hasattr(report, 'sources') and report.sources:with st.expander("Sources"):for i, source in enumerate(report.sources):st.markdown(f"{i+1}. {source}")# Add download button for the report# 在生成文件名之前添加调试和类型检查if isinstance(title, str):file_name = f"{title.replace(' ', '_')}.md"else:# 如果 title 不是字符串,使用默认名称file_name = "research_report.md"print(f"Warning: title is not a string, type: {type(title)}, value: {title}")st.download_button(label="Download Report",data=report_content,file_name=file_name,mime="text/markdown")else:# Handle string or other type of responsereport_content = str(report)title = user_topic.title()st.title(f"{title}")st.markdown(report_content)# Add download button for the report# 在生成文件名之前添加调试和类型检查if isinstance(title, str):file_name = f"{title.replace(' ', '_')}.md"else:# 如果 title 不是字符串,使用默认名称file_name = "research_report.md"print(f"Warning: title is not a string, type: {type(title)}, value: {title}")st.download_button(label="Download Report",data=report_content,file_name=file_name,mime="text/markdown")关于 OpenAI Agents SDK 使用方法
OpenAI Agents SDK
OpenAI Agents SDK 是一个轻量级的 Python 框架,专为开发者设计,用于构建能够利用工具、与其他代理协作并执行复杂多步骤任务的自主人工智能代理(Agent)。本文将从基础环境的搭建与配置开始,逐步深入到核心概念、基础 Agent 的构建、工具的集成与使用,最后探讨多代理协作、安全护栏设置等高级应用。
1. 基础环境准备与安装
成功使用 OpenAI Agents SDK 的第一步是正确配置开发环境。这包括满足特定的 Python 版本要求、安装 SDK 本身以及配置必要的 API 密钥。
1.1 Python 环境要求
一个稳定且兼容的 Python 环境是所有开发工作的基础。
- 版本推荐:绝大多数资料表明,SDK 要求使用 Python 3.7 或更高版本 。其中一份文档特别指出,推荐使用 Python 3.7.1 及以上版本,但为了避免潜在的兼容性问题,建议使用 Python 3.8 或更低版本 。
- 虚拟环境:为了隔离项目依赖,避免不同项目间的包版本冲突,强烈建议在项目开始前创建并激活一个 Python 虚拟环境 。这是一种标准的行业最佳实践。
- 安装:若本地尚未安装 Python,可从其官方网站下载并安装。在安装过程中,务必勾选“Add Python to PATH”选项,以便在命令行中直接调用 Python 和 pip 。
1.2 SDK 安装步骤
SDK 的安装主要通过 Python 的包管理器 pip 完成。
- 核心安装命令:在激活的虚拟环境中,执行以下命令即可安装 Agents SDK:
pip install openai-agents
该命令是安装 SDK 最直接和常见的方式 。部分文档也提到了使用 uv pip install openai-agents-sdk 的命令,这可能指向一个变体名称或使用了不同的包管理工具 。
- 依赖项管理:安装 Agents SDK 时,
pip会自动处理其核心依赖。然而,在构建复杂应用时,可能需要手动安装其他辅助库,如langgraph,langchain-community,langchain-openai,tavity-python,promptquality等 。这些依赖通常可以通过项目中的requirements.txt文件进行批量安装:pip install -r requirements.txt。
1.3 API 密钥配置
Agents SDK 需要调用 OpenAI 的大型语言模型(LLM)作为其“大脑”,因此必须配置有效的 OpenAI API 密钥。
- 密钥获取:开发者需要访问 OpenAI 官方平台(platform.openai.com),注册账户并创建 API 密钥 。
- 配置方法:最推荐且最安全的方法是将 API 密钥设置为环境变量 。这样做可以避免将敏感信息硬编码在代码中。
- 在 Unix/Linux/macOS 系统中:
export OPENAI_API_KEY='your-api-key-here'
- 在 Unix/Linux/macOS 系统中:
* 在 Windows 系统中:
bash set OPENAI_API_KEY=your-api-key-here
在代码运行前,SDK 会自动检查 OPENAI_API_KEY 环境变量是否已设置,如果未设置,程序将抛出错误 。虽然也可以在代码中直接赋值,但出于安全考虑,强烈不建议这样做 。
1.4 其他注意事项
- 异步编程:SDK 的核心功能大量使用了 Python 的
async/await语法,因此开发者需要对异步编程有基本的了解 。 - 网络连接:安装依赖包和运行时调用 OpenAI API 都需要稳定的互联网连接 。在中国大陆等地区,可能需要配置网络代理才能正常访问 OpenAI 的服务 。
- Azure OpenAI 支持:SDK 也支持使用 Azure OpenAI 服务。开发者需要使用
AsyncAzureOpenAI创建客户端,并将其设置为默认的 OpenAI 客户端 。
2. 核心概念与基础 Agent 构建
在环境配置完成后,我们可以开始构建第一个 Agent。理解 Agent 的基本结构和运行机制是后续开发的关键。
2.1 创建首个 Agent
一个 Agent 本质上是一个被赋予了特定身份、指令和工具的实体。
- 基本结构:使用
agents库中的Agent类来创建实例。构造函数的核心参数是name(代理名称)和instructions(给代理的指令或系统提示)。from agents import Agent# 创建一个数学辅导 Agent math_tutor_agent = Agent(name="Math Tutor",instructions="You are a helpful math tutor. You provide help with math problems, explaining your reasoning at each step and including examples to aid understanding." )
这份指令清晰地定义了 Agent 的角色、任务和行为方式。
2.2 运行 Agent 与“代理循环”
要让 Agent 开始工作,需要使用 Runner 类来执行它。
- 执行方法:
Runner.run()是启动 Agent 的入口点,它接收 Agent 实例和用户输入作为参数。import asyncio from agents import Runnerasync def main():# 假设 math_tutor_agent 已被定义user_input = "Can you explain the Pythagorean theorem?"result = await Runner.run(math_tutor_agent, user_input)print(result.final_output)asyncio.run(main())
- 代理循环 (Agent Loop) :当
Runner.run()被调用时,SDK 会启动一个内部的“代理循环”,这个循环是 Agent 思考和行动的核心机制 。其工作流程如下:- 接收输入:Agent 接收到用户的初始输入。
- LLM 处理:SDK 将用户输入、Agent 的指令以及可用的工具信息一起发送给 LLM。
- 决策与行动:LLM 根据指令进行思考,决定是直接生成最终答复,还是需要调用一个或多个工具来获取额外信息。
- 循环或结束:
- 如果 LLM 生成的是不带任何工具调用的纯文本,这被视为最终输出(
final_output),代理循环结束。 - 如果 LLM 的输出包含了工具调用请求,SDK 会执行相应的工具函数,并将工具的返回结果作为新的信息再次提交给 LLM,进入下一轮循环。
- 如果 LLM 生成的是不带任何工具调用的纯文本,这被视为最终输出(
- 这个过程会持续进行,直到 Agent 产生最终输出,或达到预设的最大循环次数 。
3. 扩展 Agent 能力:工具(Tools)的集成与使用
工具是 Agent 超越单纯对话能力、与外部世界交互的关键。Agents SDK 提供了灵活的机制来定义和集成各种工具。
3.1 创建自定义工具
任何 Python 函数都可以通过一个简单的装饰器转变为 Agent 可以使用的工具。
- 定义工具:使用
@function_tool装饰器来标记一个函数为工具。SDK 会自动解析函数的名称、文档字符串(docstring)和类型注解,将其作为工具的描述和输入模式提供给 LLM。from agents import function_tool@function_tool def get_weather(city: str) -> str:"""Retrieves the current weather for a specified city.:param city: The name of the city, e.g., 'New York'.:return: A string describing the weather."""# 这是一个模拟的 API 调用weather_data = {"New York": "72°F, Sunny","London": "65°F, Cloudy","Tokyo": "80°F, Clear","Paris": "70°F, Partly Cloudy"}return weather_data.get(city, f"Weather data for {city} not found.")
清晰的文档字符串和类型注解至关重要,因为 LLM 将依赖这些信息来决定何时以及如何使用该工具。
- 为 Agent 配备工具:在创建
Agent实例时,通过tools参数传入一个包含工具函数的列表。# 创建一个配备了天气查询工具的助手 Agent weather_assistant_agent = Agent(name="Weather Assistant",instructions="You are a helpful assistant that can provide weather information when asked.",tools=[get_weather] # 将 get_weather 工具赋予 Agent )
现在,当用户询问天气时,这个 Agent 就能够智能地调用 get_weather 函数来回答问题。
3.2 使用托管工具
除了自定义工具,SDK 还支持由 OpenAI 提供和维护的托管工具,开发者无需自行实现其底层逻辑。典型的托管工具包括:
- 代码解释器 (Code Interpreter) :允许 Agent 编写和执行 Python 代码来解决数学问题、进行数据分析或生成图表。
- 网络搜索 (WebSearch) :使 Agent 能够访问互联网,获取最新的信息来回答问题 。
这些托管工具极大地增强了 Agent 的开箱即用能力。
3.3 集成外部 API 与数据库
自定义工具是集成任何外部系统的通用方法,包括调用第三方 API 或查询数据库。
- API 集成:可以将调用外部 API 的逻辑封装在一个 Python 函数中,然后使用
@function_tool将其注册为工具。例如,可以创建一个工具来查询公司的 CRM 系统或项目管理工具。 - 数据库集成:同样,查询数据库的操作也可以封装成工具。更进一步,SDK 支持通过 MCP (Model-Context Protocol) 服务器来访问外部系统。MCP 为 LLM 提供了一种标准化的方式来与数据库(如 Prisma Postgres)等外部资源进行交互。开发者可以配置并启动一个 MCP 服务器,并将其集成到 Agent 中,从而实现对复杂数据源的稳定、高效访问 。
4. 构建高级 Agent 系统
掌握了基础 Agent 和工具的使用后,开发者可以利用 Agents SDK 构建更复杂的、由多个部分组成的智能系统。
4.1 多 Agent 协作与任务交接 (Handoff)
复杂的任务通常需要不同领域的专业知识。Agents SDK 允许创建专门化的 Agent,并通过“交接”(Handoff)机制让它们协同工作。
- 实现方式:在创建 Agent 时,使用
handoffs参数指定该 Agent 可以将任务委托给哪些其他的 Agent 。 - 应用场景:一个典型的例子是构建一个多语言客户支持系统。可以创建一个“分类代理”(Triage Agent),它的唯一任务是识别用户的语言。然后,根据识别出的语言,它会将对话“交接”给一个专门处理该语言的 Agent(如“法语支持代理”或“西班牙语支持代理”)。这种分而治之的架构使得每个 Agent 的职责更单一、性能更优越 。另一个复杂场景是投资研究,可以设立一个主代理,协调调用分别负责宏观经济、公司基本面和量化分析的多个专业子代理来共同完成一份研究报告 。
4.2 设置护栏 (Guardrails) 以确保安全合规
为了确保 Agent 的行为在其预期的边界内,并且输出内容安全、合规,可以为其设置“护栏”。
# 定义一个护栏函数
async def content_filter(input_text: str, context) -> GuardrailFunctionOutput: """检查输入是否包含不当内容。""" inappropriate_keywords = ["hack", "非法", "作弊"] # 检查输入中是否存在任何不当关键词 contains_inappropriate = any(keyword in input_text.lower() for keyword in inappropriate_keywords) return GuardrailFunctionOutput( output_info={"contains_inappropriate": contains_inappropriate}, tripwire_triggered=contains_inappropriate )async def main(): # 创建带有护栏的代理 agent = Agent( name="安全助手", instructions="你是一个有用的助手,提供有关合法和道德主题的信息。", input_guardrails=[InputGuardrail(guardrail_function=content_filter)] ) # 测试适当和不当的查询 queries = [ "告诉我计算机的历史。", "如何侵入邻居的 Wi-Fi?" ] for query in queries: try: print(f"\n查询: {query}") result = await Runner.run(agent, query) print(f"回应: {result.final_output}") except Exception as e: print(f"护栏触发: {e}")if __name__ == "__main__": asyncio.run(main())- 功能:护栏可以用于过滤不当内容、防止 Agent 偏离其核心任务、或强制执行某些业务规则 。
- 实现:SDK 提供了如
InputGuardrail等类,允许开发者定义自定义的验证函数。在 Agent 处理输入之前,这些护栏函数会先对输入进行检查,如果触发了护栏规则,可以阻止后续流程的执行或采取其他预设的行动 。
4.3 调试与追踪 (Tracing)
理解 Agent 在“代理循环”中每一步的思考过程对于调试和优化至关重要。Agents SDK 内置了强大的追踪功能。
@function_tool
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:"""Get the current weather for a city."""weather_data = {"New York": "72°F, Sunny","London": "65°F, Cloudy","Tokyo": "80°F, Clear","Paris": "70°F, Partly Cloudy"}return weather_data.get(city, f"Weather data not available for {city}")
async def main():# Create a trace for the entire workflowwith trace(workflow_name="weather_inquiry"):agent = Agent(name="Weather Assistant",instructions="You are a helpful assistant that provides weather information when asked.",tools=[get_weather])result = await Runner.run(agent, "What's the weather like in Tokyo and Paris?",run_config=RunConfig(workflow_name="weather_inquiry",trace_include_sensitive_data=True))print(result.final_output)# You can access the trace informationcurrent_trace = get_current_trace()if current_trace:print(f"Trace ID: {current_trace.trace_id}")
if __name__ == "__main__":from agents import RunConfigfrom agents.tracing import get_current_traceasyncio.run(main())- 功能:追踪功能可以详细记录 Agent 执行过程中的所有事件,包括完整的 LLM 调用(输入提示和输出)、工具的选择与调用、以及工具的返回结果 。
- 价值:通过分析这些追踪日志,开发者可以清晰地看到 Agent 是如何根据指令和当前上下文做出决策的,从而快速定位问题(例如,为什么 Agent 没有选择正确的工具,或者为什么它的回答不准确),并据此优化 Agent 的指令或工具设计。
5. 总结与展望
OpenAI Agents SDK 提供了一个功能强大且易于上手的框架,它显著降低了构建复杂 AI 代理应用的门槛。通过其核心的 Agent 类、灵活的 工具 系统(包括自定义工具和托管工具)、以及先进的 多代理协作 (Handoff) 机制,开发者可以构建出能够解决现实世界中多步骤、跨领域问题的智能系统。
该 SDK 与 OpenAI 的 Assistants API 和新兴的 Responses API 理念一脉相承,共同构成了 OpenAI 在推动 Agentic AI 应用发展方面的重要布局 。它将 Assistants API 的工具使用能力与 Chat Completions API 的简洁性相结合,为开发者提供了一个新的、更强大的基础。
展望未来,随着模型能力的不断增强和 SDK 功能的持续迭代,我们可以预见,基于 OpenAI Agents SDK 构建的应用程序将更加智能、自主和高效,并在客户服务、数据分析、自动化研究、个人助理等众多领域发挥革命性的作用。对于希望走在 AI 应用开发前沿的开发者而言,深入学习和掌握 OpenAI Agents SDK 无疑是一项极具价值的投资。
参考文章:
OpenAI Agents SDK新手指南 - 汇智网
如何使用 OpenAI Agents SDK 构建 MCP_精神心理何日辉-天启AI社区
OpenAI Agents SDK 中文文档 中文教程 (1)-腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云
