UnityDots学习(六)
五中介绍学习了Component的使用,此篇介绍System和Job常用Api
概述:
system是游戏在运行时Unity会自动运行,分成如下2个接口
-
SystemBase:
是 ECS 0.x 版本(旧版 ECS)的主要系统实现方式,基于 C# 类继承机制,使用传统的面向对象编程风格。它是 Unity 早期推广 ECS 时的核心组件,适合熟悉传统 Unity 编程的开发者快速上手。 -
ISystem:
是 ECS 1.x 版本(新版 ECS,也称为 "Burst Systems")引入的系统接口,基于 C# 接口和ref struct实现,专为高性能和内存效率优化。它利用了 C# 8.0 的接口默认方法和ref struct特性,是 Unity 未来主推的 ECS 系统实现方式。 -
适用场景
-
使用
SystemBase的情况:- 项目仍在使用旧版 ECS(0.x)或需要兼容旧代码。
- 对性能要求不极端,希望快速实现功能。
- 需要与传统 Unity 组件或 MonoBehaviour 交互。
-
使用
ISystem的情况:- 新项目或追求极致性能的场景(如 AAA 游戏、高并发模拟)。
- 需要充分利用 Burst 编译器和 DOTS 框架的新特性。
- 愿意学习更底层的 API 和函数式编程风格。
简单理解下,SystemBase中可以使用托管对象。但ISystem的性能更高。
示例:
SystemBase
public partial class EnemySystem: SystemBase
{private Transform player;protected override void OnUpdate(){if (player == null){player = GameObject.Find("Player").transform;return;}float3 p_Pos = player.transform.position;var entityMng = World.EntityManager;var entities = entityMng.GetAllEntities(Allocator.Temp);foreach (var entity in entities){if (entityMng.HasComponent<AgentComponent>(entity)){var ac = entityMng.GetComponentData<AgentComponent>(entity);if (ac.state == 0){//主角附近var lt =entityMng.GetComponentData<LocalTransform>(entity);lt.Position = p_Pos + new float3(UnityEngine.Random.Range(-25,25), -0.4f, UnityEngine.Random.Range(-25,25));entityMng.SetComponentData(entity, lt);ac.state = 1;entityMng.SetComponentData(entity, ac);}}}}
}ISystem:
[UpdateBefore(typeof(ActiveAnimationSystem))]
partial struct ChangeAnimationSystem : ISystem {[BurstCompile]public void OnCreate(ref SystemState state) {state.RequireForUpdate<AnimationDataHolder>();}[BurstCompile]public void OnUpdate(ref SystemState state) {AnimationDataHolder animationDataHolder = SystemAPI.GetSingleton<AnimationDataHolder>();ChangeAnimationJob changeAnimationJob = new ChangeAnimationJob {animationDataBlobArrayBlobAssetReference = animationDataHolder.animationDataBlobArrayBlobAssetReference,};changeAnimationJob.ScheduleParallel();}}Job 是可并行执行的自包含计算单元,通常处理一组独立的数据(如组件数组)。
Job可以在System内部创建并且分配到不同的线程进行调用从而实现CPU的高效利用。
Job在System下的示例:
[BurstCompile]
public partial struct UnitMoverJob : IJobEntity {public float deltaTime;public void Execute(ref LocalTransform localTransform, ref UnitMover unitMover, ref PhysicsVelocity physicsVelocity) {float3 moveDirection = unitMover.targetPosition - localTransform.Position;float reachedTargetDistanceSq = UnitMoverSystem.REACHED_TARGET_POSITION_DISTANCE_SQ;if (math.lengthsq(moveDirection) <= reachedTargetDistanceSq) {// Reached the target positionphysicsVelocity.Linear = float3.zero;physicsVelocity.Angular = float3.zero;unitMover.isMoving = false;return;}unitMover.isMoving = true;moveDirection = math.normalize(moveDirection);localTransform.Rotation =math.slerp(localTransform.Rotation,quaternion.LookRotation(moveDirection, math.up()),deltaTime * unitMover.rotationSpeed);physicsVelocity.Linear = moveDirection * unitMover.moveSpeed;physicsVelocity.Angular = float3.zero;}}在System里运行:
[BurstCompile]public void OnUpdate(ref SystemState state) {UnitMoverJob unitMoverJob = new UnitMoverJob {deltaTime = SystemAPI.Time.DeltaTime,};unitMoverJob.Run();//单线程unitMoverJob.ScheduleParallel();//多线程
}同时运行10000个单位,截图所示运行速度

那问题来了,什么情况下我们要使用IJob,什么情况下我们在System内部写逻辑即可。
1.直接在 System 内部写逻辑
-
实现方式:
在SystemBase.OnUpdate()或ISystem.OnUpdate()中直接编写代码,使用Entities.ForEach或循环遍历实体。 -
性能瓶颈:
-
通常在主线程执行,阻塞渲染和输入处理。
-
即使使用
ScheduleParallel(),也依赖于传统的Job接口,存在一定的调度开销。
-
-
使用 IJobEntity
-
实现方式:
定义独立的IJobEntity结构体,通过ScheduleParallel()并行执行,自动处理实体遍历。 -
性能优势:
-
并行效率更高:基于
Chunk级并行,减少缓存未命中。 -
内存访问优化:直接操作
ArchetypeChunk,数据局部性更好。 -
更低的调度开销:Unity 自动生成高效的调度代码。
-
Burst 兼容性更好:结构体形式更易被 Burst 编译为优化的本地代码。
-
2. 适用场景
优先使用 IJobEntity 的情况
-
处理大量实体(如粒子系统、寻路单元)。
-
计算密集型逻辑(如物理模拟、复杂 AI)。
-
需要充分利用多核 CPU,避免主线程阻塞。
-
追求极致性能,愿意编写更结构化的代码。
可直接在 System 内写逻辑的情况
-
少量实体(如 UI 相关实体)或简单初始化逻辑。
-
需要频繁与主线程数据交互(如读取输入或 Unity API)。
-
原型开发阶段,快速验证功能。
-
逻辑简单且无需并行(如单例组件处理)。
3. 性能优化建议
-
结合 Burst 编译:
为IJobEntity和System都添加[BurstCompile],但IJobEntity的结构体形式更易被 Burst 优化。 -
减少主线程同步:
避免在System中频繁调用JobHandle.Complete(),而IJobEntity的Run()方法仅用于简单场景。 -
数据布局优化:
IJobEntity默认基于Chunk处理,天然符合 ECS 的数据布局,减少缓存未命中。 -
避免托管代码:
IJobEntity内部应使用NativeContainer和Unity.Mathematics,避免托管对象(如List<T>)。
4. 总结
| 特性 | 直接在 System 内部写逻辑 | 使用 IJobEntity |
|---|---|---|
| 执行线程 | 主线程或工作线程 | 工作线程池(并行) |
| 性能上限 | 中等(依赖传统 Job) | 高(专为 ECS 优化) |
| 代码复杂度 | 低(直观) | 中(需定义独立结构体) |
| 适用场景 | 少量实体、简单逻辑 | 大量实体、计算密集型任务 |
结论:在 Unity ECS 中,IJobEntity是处理大量实体的首选方案,而直接在System内写逻辑适合快速迭代或简单场景。随着 Unity DOTS 框架的发展,IJobEntity的性能优势会愈发明显。
下面的常见API记录比较散,都是变学习变遇到的都记录下
1.禁用某个组件
entityManager.SetComponentEnabled
示例:需要注意被禁用的组件需要继承IEnableableComponent
public struct ExecuteMainThread : IComponentData,IEnableableComponent{}[BurstCompile]public void OnUpdate(ref SystemState state){EntityManager entityManager = World.DefaultGameObjectInjectionWorld.EntityManager;EntityQuery entityQuery = new EntityQueryBuilder(Allocator.Temp).WithAll<ExecuteMainThread>().Build(entityManager);NativeArray<Entity> entityArray = entityQuery.ToEntityArray(Allocator.Temp);//NativeArray<ExecuteMainThread> selectedArray = entityQuery.ToComponentDataArray<ExecuteMainThread>(Allocator.Temp);Debug.Log("ComponentCount:" + entityArray.Length);if (entityArray.Length > 0){for (int i = 0; i < entityArray.Length; i++){entityManager.SetComponentEnabled<ExecuteMainThread>(entityArray[i],false);}}}2.查询某entity带有附件条件Component
WithDisabled某个实体禁用了某个组件
![]()
WithPresent只要这个组件存在于某个实体就会被统计
![]()
代码示例:
public partial struct MyTestSystem: ISystem
{[BurstCompile]public void OnCreate(ref SystemState state){state.RequireForUpdate<ExecuteMainThread>();}[BurstCompile]public void OnUpdate(ref SystemState state){foreach (RefRW<A> a in SystemAPI.Query<RefRW<A>>().WithDisabled<B>()){Debug.Log("Has A DisableB:");}foreach (RefRW<A> a in SystemAPI.Query<RefRW<A>>().WithPresent<B>()){Debug.Log("Has A With Has B:");}}
}public struct A : IComponentData
{}public struct B : IComponentData, IEnableableComponent
{}3.获取某Component的Entity示例
使用WithEntityAccess
示例:
[BurstCompile]public void OnUpdate(ref SystemState state){foreach ((RefRW<A> a,Entity entity) in SystemAPI.Query<RefRW<A>>().WithDisabled<B>().WithEntityAccess()){Debug.Log("Has A DisableB:" + entity.Index);}}4.查询entity带有某组件二种方式
使用EntityQuery,一种是WithAll,另一种CreateEntityQuery
代码示例:
private void QueryFunction(){EntityManager entityManager = World.DefaultGameObjectInjectionWorld.EntityManager;EntityQuery entityQuery = new EntityQueryBuilder(Allocator.Temp).WithAll<A>().Build(entityManager);NativeArray<Entity> entityArray = entityQuery.ToEntityArray(Allocator.Temp);EntityQuery entityQuery2 =entityManager.CreateEntityQuery(typeof(A),typeof(B));}| 特性 | WithAll | CreateEntityQuery |
|---|---|---|
| API 类型 | 查询修饰符(链式调用) | 独立方法,返回 EntityQuery |
| 查询构建方式 | 声明式(链式调用) | 命令式(显式创建) |
| 性能优化 | 适合简单查询,自动优化 | 适合复杂查询,可手动缓存和复用 |
| 灵活性 | 只能在 Entities.ForEach 中使用 | 可独立使用,支持更多查询选项 |
| 查询条件 | 仅支持 WithAll、WithAny 等 | 支持 All、Any、None 组合 |
| 适用场景 | 快速编写一次性查询 | 复杂查询、需要频繁复用的查询 |
5.Dots下获取单例
使用SystemAPI.GetSingleton
代码示例:
PhysicsWorldSingleton physicsWorldSingleton = SystemAPI.GetSingleton<PhysicsWorldSingleton>();
CollisionWorld collisionWorld = physicsWorldSingleton.CollisionWorld;6.删除和添加实体
private void AddOrDesEntity(SystemState state){EntityManager entityManager = World.DefaultGameObjectInjectionWorld.EntityManager;EntityQuery entityQuery = new EntityQueryBuilder(Allocator.Temp).WithAll<A>().Build(entityManager);NativeArray<Entity> entityArray = entityQuery.ToEntityArray(Allocator.Temp);//获取CommandBufferEntityCommandBuffer entityCommandBuffer =SystemAPI.GetSingleton<EndSimulationEntityCommandBufferSystem.Singleton>().CreateCommandBuffer(state.WorldUnmanaged);//删除EntityentityCommandBuffer.DestroyEntity(entityArray[0]);//创建EntityEntity entity = entityCommandBuffer.CreateEntity();//添加组件entityManager.AddComponent<A>(entity);//删除组件entityManager.RemoveComponent<A>(entity);}7.验证实体的有效性
使用Exsit验证Entity使用HasComponent验证实体的组件

8.某System运行OnUpdate需要条件
用RequireForUpdate<XX>来判定
[BurstCompile]public void OnCreate(ref SystemState state){state.RequireForUpdate<ExecuteMainThread>();}伴有条件组件启用
WithOptions(EntityQueryOptions.XX | EntityQueryOptions.XX)
namespace Unity.Physics.Authoring
{/// <summary>/// Custom physics proxy baking system/// </summary>[UpdateInGroup(typeof(PostBakingSystemGroup))][WorldSystemFilter(WorldSystemFilterFlags.BakingSystem)]public partial class CustomPhysicsProxyBakingSystem : SystemBase{protected override void OnUpdate(){var transformFromEntity = GetComponentLookup<LocalTransform>();var physicsMassFromEntity = GetComponentLookup<PhysicsMass>();var physicsColliderFromEntity = GetComponentLookup<PhysicsCollider>();foreach (var (driver, entity) in SystemAPI.Query<RefRW<CustomPhysicsProxyDriver>>().WithEntityAccess().WithOptions(EntityQueryOptions.IncludePrefab | EntityQueryOptions.IncludeDisabledEntities)){transformFromEntity[entity] = transformFromEntity[driver.ValueRW.rootEntity];physicsMassFromEntity[entity] = PhysicsMass.CreateKinematic(physicsColliderFromEntity[driver.ValueRW.rootEntity].MassProperties);physicsColliderFromEntity[entity] = physicsColliderFromEntity[driver.ValueRW.rootEntity];}}}
}9.EntityStorageInfoLookUp
在 Unity DOTS(Data-Oriented Technology Stack)里,EntityStorageInfoLookup 是一个非常实用的查找类型,其主要功能是获取实体在内存中的存储信息。借助这些存储信息,开发者能够深入了解实体的内存布局,还可以基于实体所在的块或存储桶来实现高效的分组处理。
核心功能
- 获取实体块信息:可以查询某个实体所在的
ArchetypeChunk。 - 定位存储桶:能够确定实体处于哪个存储桶(Bucket)中。
- 内存布局分析:有助于分析实体在内存中的排列方式。
- 优化处理逻辑:可以基于实体的存储位置对处理逻辑进行分组优化.
举例,在Job里不允许使用系统API如图

平替后
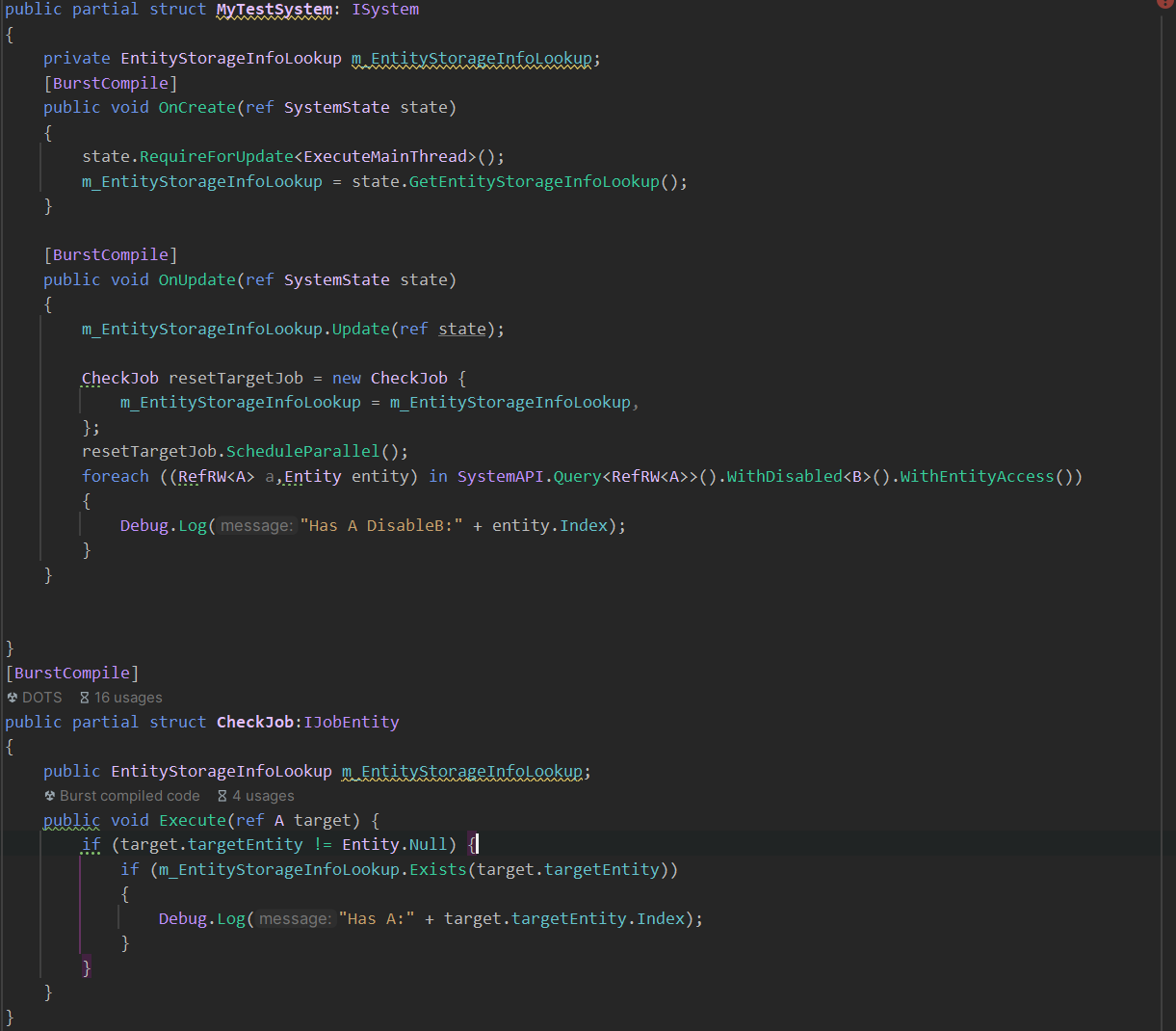
10.ComponentLookUp
在 Unity DOTS(Data-Oriented Technology Stack)中,ComponentLookup<T> 是一种高效的查找类型,用于在作业中快速访问和修改组件数据。与直接在查询中声明组件相比,它提供了更大的灵活性,允许你在运行时动态访问组件,甚至可以访问查询中未显式声明的组件。
使用方式跟字典差不多,Key为Entity Value为T对用的Component
示例:
public partial struct MyTestSystem: ISystem
{private ComponentLookup<B> m_AComponentLookup;[BurstCompile]public void OnCreate(ref SystemState state){//state.RequireForUpdate<ExecuteMainThread>();m_AComponentLookup = state.GetComponentLookup<B>(true);}[BurstCompile]public void OnUpdate(ref SystemState state){m_AComponentLookup.Update(ref state);CheckJob resetTargetJob = new CheckJob {m_EntityStorageInfoLookup = m_AComponentLookup,};resetTargetJob.ScheduleParallel();foreach ((RefRW<A> a,Entity entity) in SystemAPI.Query<RefRW<A>>().WithDisabled<B>().WithEntityAccess()){Debug.Log("Has A DisableB:" + entity.Index);}}}
[BurstCompile]
public partial struct CheckJob:IJobEntity
{public ComponentLookup<B> m_EntityStorageInfoLookup;public void Execute(ref A target) {//A的targetEntity需要有B组件if (m_EntityStorageInfoLookup.HasComponent(target.targetEntity)){B bb = m_EntityStorageInfoLookup[target.targetEntity];bb.bbValue = 100;}}
}public struct A : IComponentData
{public Entity targetEntity;
}public struct B : IComponentData, IEnableableComponent
{public int bbValue;
}11.Job内部组件访问限制问题
这么写Unity会报错,一个JOB不允许使用2个同样组件

多个Job可以安全访问同一个组件容器

12.骨骼动画
Unity的Dots系统原生不允许使用骨骼动画,可以使用平替的插件来弄也可以自己把一些Mesh烘焙到一个序列化文件中。运行时逐帧换Mesh来解决。类似下列这种

13.Dots版的GetComponent
使用SystemApi也可以加RW,RO这样的修饰符
![]()
14.Unity烘焙dynamic和none
dynamic是Unity会自动帮你添加好组件,比如localtrasnform,mesh等
none是只有一个空实体,可自行添加组件


