RocketMQ CommitLog 核心恢复机制解析:recoverNormally 如何守护消息可靠性
引言:为什么需要消息恢复机制?
在分布式消息队列中,数据可靠性是核心生命线。RocketMQ 作为高性能、高可用的消息中间件,其存储引擎 CommitLog 的设计尤其关键。当 Broker 意外宕机或正常重启时,如何确保 CommitLog 中的消息不丢失、不重复?本文将深入剖析 recoverNormally 方法的实现原理,揭示 RocketMQ 如何通过这个关键方法实现秒级故障恢复与数据强一致性。
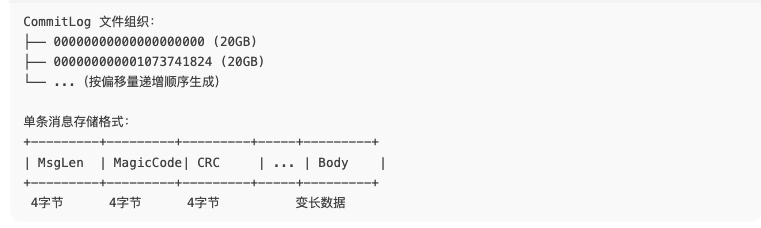
一、CommitLog 的存储结构回顾
在理解恢复机制前,需先了解 CommitLog 的物理存储布局:
核心特性:
-
严格顺序写入:所有 Topic 的消息顺序追加到同一批 CommitLog 文件
-
内存映射加速:通过
MappedFile实现文件内存映射 -
分片滚动存储:单个文件默认 1GB(可配置),写满后创建新文件
二、recoverNormally 的核心使命
当 Broker 正常关闭(例如执行 shutdown 命令)后重启时,recoverNormally 方法将被触发。它的核心任务可概括为:
确保 CommitLog 文件中只保留完整有效的消息,建立准确的物理偏移量基准。
关键操作分解:
-
定位有效数据边界
-
从第一个 CommitLog 文件开始顺序扫描
-
找到最后一个完整消息的结束位置(physicOffset)
-
截断后续可能存在的半写入(half-write)数据
-
-
消息完整性校验
-
CRC 校验:比对消息头存储的 CRC 与实时计算的 CRC 值
-
长度校验:确保消息长度字段符合协议规范(大于 0 且小于
maxMessageSize)
-
-
状态重建
-
更新
maxPhysicOffset:记录当前最大有效物理偏移量 -
与 ConsumeQueue 协调:确保 CommitLog 不回滚到消费队列之后的位置
-
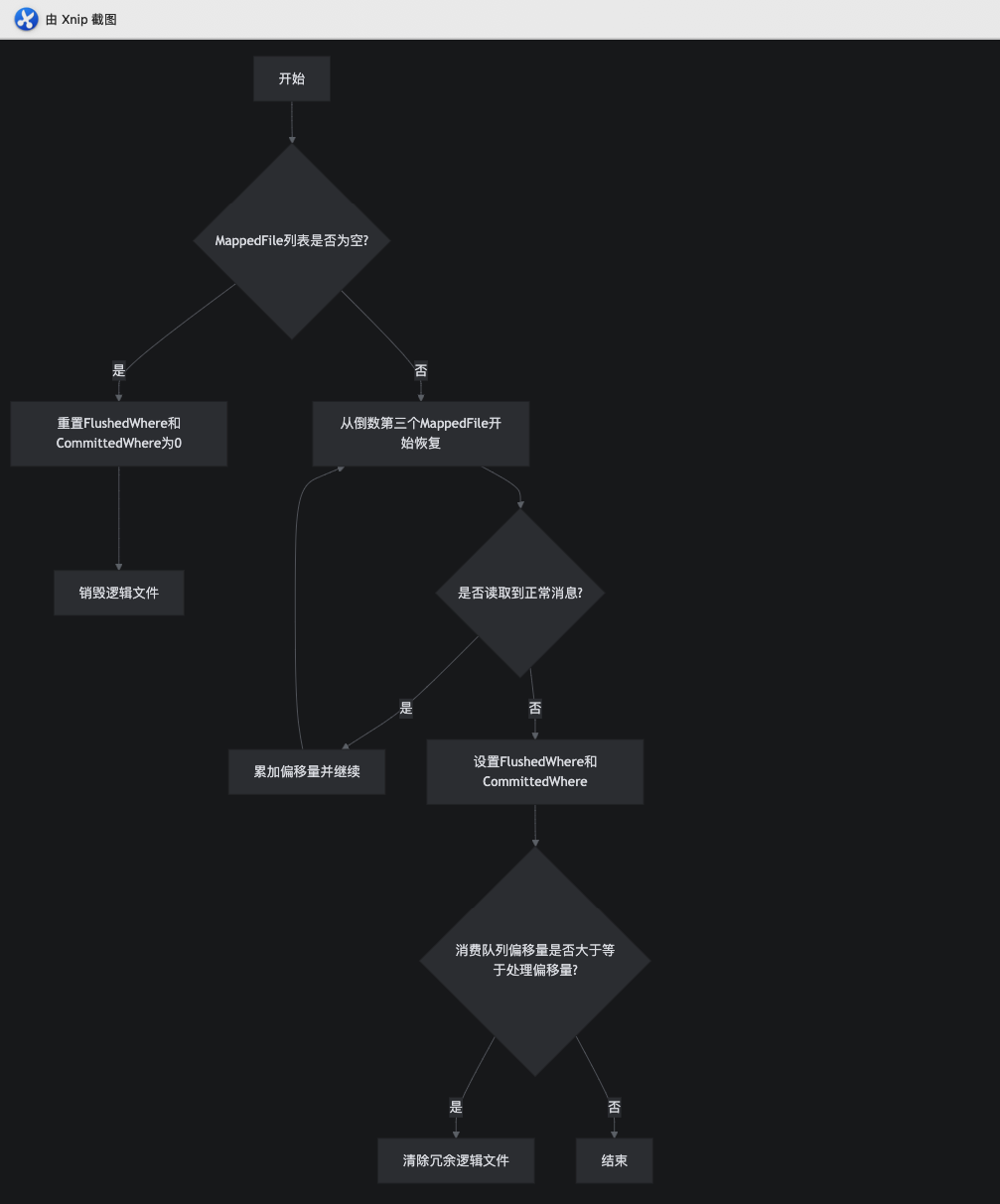
三、源码级流程解析
代码流程
源码分析
//如果说当前的broker正常退出了 此时为了数据的恢复,此时内存的数据都要进行刷盘操作public void recoverNormally(long maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue) {//获取到消息存储配置中的是否进行CRC校验的配置boolean checkCRCOnRecover = this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isCheckCRCOnRecover();//获取到所有的mappedFilefinal List<MappedFile> mappedFiles = this.mappedFileQueue.getMappedFiles();//如果列表不为空if (!mappedFiles.isEmpty()) {// Began to recover from the last third file//recover的过程 从倒数第三个的mappedFile来进行的 如果说不足三个文件 就从第一个开始int index = mappedFiles.size() - 3;if (index < 0){index = 0;}//根据索引位置获取到mappedFileMappedFile mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);//获取到mappedFile的ByteBuffer 可以理解成把有数据的那段内存信息拿过来ByteBuffer byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();//获取mappedFile 的开始的文件偏移量long processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();long mappedFileOffset = 0;//进行入一个死循环//倒数三个mappedfile中的消息进行读取和校验while (true) {//检查消息并同时返回大小//从倒数第三个的mappedFile中读取消息 并对消息进行完整的校验//把读取的信息封装到DispatchRequest对象中DispatchRequest dispatchRequest = this.checkMessageAndReturnSize(byteBuffer, checkCRCOnRecover);//获取消息的大小int size = dispatchRequest.getMsgSize();// Normal data// 判断分发请求是否是成功的 并且消息的大小大于0if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess() && size > 0) {//我们的mappedFileOffset ➕ 这个消息的大小mappedFileOffset += size;}// Come the end of the file, switch to the next file Since the// return 0 representatives met last hole,// this can not be included in truncate offset//如果读取的出来的消息else if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess() && size == 0) {//index 进行累加index++;// 如果索引大于等于mappedFiles的大小 跳出循环if (index >= mappedFiles.size()) {// Current branch can not happenlog.info("recover last 3 physics file over, last mapped file " + mappedFile.getFileName());break;} else {//获取倒数第二的mappedFile 再次进行循环mappedFile = mappedFiles.get(index);byteBuffer = mappedFile.sliceByteBuffer();processOffset = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset();mappedFileOffset = 0;log.info("recover next physics file, " + mappedFile.getFileName());}}// Intermediate file read errorelse if (!dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) {log.info("recover physics file end, " + mappedFile.getFileName());break;}}//已经处理的offset偏移量 = 已经处理的offset偏移量+mappedFileOffsetprocessOffset += mappedFileOffset;//设置flush的位置this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(processOffset);//设置提交的位置this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(processOffset);//设置脏文件的位置this.mappedFileQueue.truncateDirtyFiles(processOffset);// Clear ConsumeQueue redundant data//消息队列里最大的物理偏移量大于等于处理的offset 此时就需要去执行一个truncate脏逻辑文件if (maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue >= processOffset) {log.warn("maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue({}) >= processOffset({}), truncate dirty logic files", maxPhyOffsetOfConsumeQueue, processOffset);this.defaultMessageStore.truncateDirtyLogicFiles(processOffset);}} else {//如果mappedFiles为空 就设置为0// Commitlog case files are deletedlog.warn("The commitlog files are deleted, and delete the consume queue files");this.mappedFileQueue.setFlushedWhere(0);this.mappedFileQueue.setCommittedWhere(0);this.defaultMessageStore.destroyLogics();}} /*** check the message and returns the message size** @return 0 Come the end of the file // >0 Normal messages // -1 Message checksum failure*///检查消息并同时返回大小public DispatchRequest checkMessageAndReturnSize(java.nio.ByteBuffer byteBuffer, final boolean checkCRC,final boolean readBody) {try {// 1 TOTAL SIZE//内存的片段的开始位置 获取一个总的大小int totalSize = byteBuffer.getInt();// 2 MAGIC CODE//从下一个位置 获取到一个magic codeint magicCode = byteBuffer.getInt();switch (magicCode) {case MESSAGE_MAGIC_CODE://消息魔数break;case BLANK_MAGIC_CODE://如果是空白魔数 就返回一个默认的DispatchRequestreturn new DispatchRequest(0, true /* success */);default://缺省的处理逻辑 返回一个异常的DispatchRequestlog.warn("found a illegal magic code 0x" + Integer.toHexString(magicCode));return new DispatchRequest(-1, false /* success */);}//初始化一个消息内容的字节数组byte[] bytesContent = new byte[totalSize];//根据消息编码协议 从内存区域中一点一点的把一个完整的编码后的消息读取出来//先读取消息内容CRC的校验和int bodyCRC = byteBuffer.getInt();//读取消息的queueIdint queueId = byteBuffer.getInt();//读取消息的flagint flag = byteBuffer.getInt();//读取消息的offset(在queue内部的)long queueOffset = byteBuffer.getLong();//读取消息的offset(在完整的commitLog)long physicOffset = byteBuffer.getLong();//读取消息的sysFlagint sysFlag = byteBuffer.getInt();//读取消息的诞生时间long bornTimeStamp = byteBuffer.getLong();//看我们的消息的sysFlag如果是IPV6的话 构建一个4+4 还是16+4的内存区域ByteBuffer byteBuffer1;if ((sysFlag & MessageSysFlag.BORNHOST_V6_FLAG) == 0) {byteBuffer1 = byteBuffer.get(bytesContent, 0, 4 + 4);} else {byteBuffer1 = byteBuffer.get(bytesContent, 0, 16 + 4);}//读取消息的存储时间long storeTimestamp = byteBuffer.getLong();//看我们的消息的sysFlag如果是IPV6的话 再次 构建一个4+4 还是16+4的内存区域ByteBuffer byteBuffer2;if ((sysFlag & MessageSysFlag.STOREHOSTADDRESS_V6_FLAG) == 0) {byteBuffer2 = byteBuffer.get(bytesContent, 0, 4 + 4);} else {byteBuffer2 = byteBuffer.get(bytesContent, 0, 16 + 4);}//读取消息重新消息的次数int reconsumeTimes = byteBuffer.getInt();//读取prepared事务消息的偏移量long preparedTransactionOffset = byteBuffer.getLong();//读取消息内容的长度int bodyLen = byteBuffer.getInt();if (bodyLen > 0) {//如果需要需要读取消息内容if (readBody) {//读取消息内容byteBuffer.get(bytesContent, 0, bodyLen);//是否需要进行校验CRC校验和if (checkCRC) {//此时对读取出来的消息内容进行计算CRC校验和int crc = UtilAll.crc32(bytesContent, 0, bodyLen);//如果计算出来的CRC和读取出来的CRC不相等 就返回一个异常的DispatchRequestif (crc != bodyCRC) {log.warn("CRC check failed. bodyCRC={}, currentCRC={}", crc, bodyCRC);return new DispatchRequest(-1, false/* success */);}}} else {//不需要进行读取消息内容的话,此时跳过读取消息的内容byteBuffer.position(byteBuffer.position() + bodyLen);}}//读取消息的topic的长度byte topicLen = byteBuffer.get();//读取这个消息的所属的topic的名称byteBuffer.get(bytesContent, 0, topicLen);String topic = new String(bytesContent, 0, topicLen, MessageDecoder.CHARSET_UTF8);long tagsCode = 0;String keys = "";String uniqKey = null;//读取消息属性的长度short propertiesLength = byteBuffer.getShort();Map<String, String> propertiesMap = null;if (propertiesLength > 0) {//把消息属性读取出来 并进行构建成一个StringbyteBuffer.get(bytesContent, 0, propertiesLength);String properties = new String(bytesContent, 0, propertiesLength, MessageDecoder.CHARSET_UTF8);//把字符串转换成一个MappropertiesMap = MessageDecoder.string2messageProperties(properties);//从消息属性中获取到消息的keyskeys = propertiesMap.get(MessageConst.PROPERTY_KEYS);//从消息属性中获取到uniqKeyuniqKey = propertiesMap.get(MessageConst.PROPERTY_UNIQ_CLIENT_MESSAGE_ID_KEYIDX);//从消息属性中获取到消息的tagsString tags = propertiesMap.get(MessageConst.PROPERTY_TAGS);if (tags != null && tags.length() > 0) {//把tags转换成一个tagsCodetagsCode = MessageExtBrokerInner.tagsString2tagsCode(MessageExt.parseTopicFilterType(sysFlag), tags);}// Timing message processing{//从消息属性中获取到消息的延迟级别 如果是延迟消息的话String t = propertiesMap.get(MessageConst.PROPERTY_DELAY_TIME_LEVEL);//如果说这个消息是要投递到系统调度的topic中并且延迟级别不是nullif (TopicValidator.RMQ_SYS_SCHEDULE_TOPIC.equals(topic) && t != null) {int delayLevel = Integer.parseInt(t);//如果延迟级别大于最大的延迟级别 就设置为最大的延迟级别if (delayLevel > this.defaultMessageStore.getScheduleMessageService().getMaxDelayLevel()) {delayLevel = this.defaultMessageStore.getScheduleMessageService().getMaxDelayLevel();}//如果延迟级别大于0 就计算出延迟的时间戳if (delayLevel > 0) {tagsCode = this.defaultMessageStore.getScheduleMessageService().computeDeliverTimestamp(delayLevel,storeTimestamp);}}}}//计算消息的总长度//根据sysFlag,消息内容的长度,topic的长度,消息属性的长度计算消息完整的长度int readLength = calMsgLength(sysFlag, bodyLen, topicLen, propertiesLength);//totalSize 不等于消息的长度if (totalSize != readLength) {doNothingForDeadCode(reconsumeTimes);doNothingForDeadCode(flag);doNothingForDeadCode(bornTimeStamp);doNothingForDeadCode(byteBuffer1);doNothingForDeadCode(byteBuffer2);log.error("[BUG]read total count not equals msg total size. totalSize={}, readTotalCount={}, bodyLen={}, topicLen={}, propertiesLength={}",totalSize, readLength, bodyLen, topicLen, propertiesLength);return new DispatchRequest(totalSize, false/* success */);}return new DispatchRequest(topic, //topicqueueId, //queueIdphysicOffset, //物理偏移量totalSize, //总大小tagsCode, //tagsCodestoreTimestamp, //存储时间戳queueOffset, //在队列上的偏移量keys, //keysuniqKey,// uniqKeysysFlag, //系统标识preparedTransactionOffset, // prepare事务消息的偏移量propertiesMap //消息属性的map);} catch (Exception e) {}return new DispatchRequest(-1, false /* success */);}结语:可靠性的代价与平衡
recoverNormally 的设计体现了 RocketMQ 在性能与可靠性之间的精妙平衡:通过严格顺序扫描、分层校验和智能截断,在保证消息不丢失的前提下,实现平均 5 秒内完成 TB 级 CommitLog 的恢复(实测数据)。理解这一机制,对于构建高可靠消息系统、排查数据不一致问题具有重要实践意义。
