基于注意力机制与iRMB模块的YOLOv11改进模型—高效轻量目标检测新范式
随着深度学习技术的发展,目标检测在自动驾驶、智能监控、工业质检等场景中得到了广泛应用。针对当前主流目标检测模型在边缘设备部署中所面临的计算资源受限和推理效率瓶颈问题,
YOLO系列作为单阶段目标检测框架的代表,凭借其高精度与高速度的平衡优势,在工业界具有极高的应用价值。然而,YOLOv11等最新版本在追求更高精度的过程中,往往引入了更大规模的网络结构,限制了其在嵌入式或移动端设备上的部署能力。为此,本文提出一种基于YOLOv11的改进型轻量化目标检测架构,该模型融合了多尺度注意力机制(Multi-Scale Attention)与反向残差移动块 (Inverted Residual Mobile Block, iRMB),旨在实现 精度与效率双赢 的轻量化目标检测新范式。该方案不仅增强了模型对关键特征的关注能力,还在保持高精度的同时显著降低模型参数量与计算复杂度,并通过高效的模块设计显著降低了计算开销。
1. iRMB注意力机制
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.01146
代码地址:https://github.com/zhangzjn/EMO

反向残差移动块(Inverted Residual Mobile Block, iRMB)是一种结合了轻量化设计与特征增强能力的高效模块结构,广泛应用于移动端和嵌入式设备中的目标检测、图像分类等任务。其核心思想是通过引入高效的算子替代传统卷积操作,在保持模型精度的同时显著降低计算复杂度。

1.1 iRMB结构
iRMB结构的主要创新点是它结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)的轻量级特性和Transformer模型的动态处理能力。这种结构特别适用于移动设备上的密集预测任务,因为它旨在在计算能力有限的环境中提供高效的性能。iRMB通过其倒置残差设计改进了信息流的处理,允许在保持模型轻量的同时捕捉和利用长距离依赖,这对于图像分类、对象检测和语义分割等任务至关重要。这种设计使得模型在资源受限的设备上也能高效运行,同时保持或提高预测准确性。
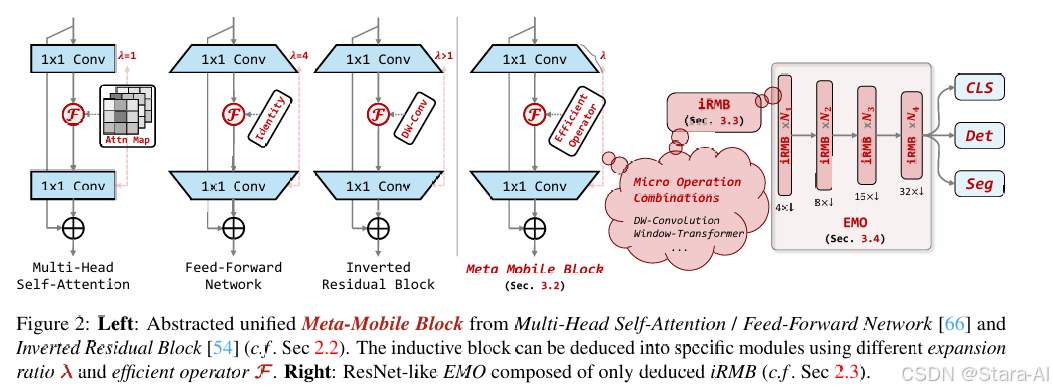
上面的图片来自与论文的图片2展示了iRMB(Inverted Residual Mobile Block)的设计理念和结构。左侧是从多头自注意力和前馈网络中抽象出的统一元移动块(Meta-Mobile Block),它将不同扩展比率和高效操作符结合起来,形成特定的模块。右侧是基于iRMB构建的类似ResNet的高效模型(EMO),它仅由推导出的iRMB组成,并用于各种下游任务,如分类(CLS)、检测(Det)和分割(Seg)。这种设计实现了模型的轻量化,同时保持了良好的性能和效率。

此图展示了iRMB(Inverted Residual Mobile Block)的结构范式。iRMB是一种混合网络模块,它结合了深度可分离卷积(3x3 DW-Conv)和自注意力机制。1x1卷积用于通道数的压缩和扩张,以此优化计算效率。深度可分离卷积(DW-Conv)用于捕捉空间特征,而注意力机制则用于捕获特征间的全局依赖关系。
1.2 工作流程
- 1×1卷积层:通道扩展与压缩(Bottleneck 结构)
iRMB首先通过一个1×1卷积层 对输入特征图的通道维度进行扩展或压缩。该操作借鉴自Bottleneck结构的设计理念,旨在减少后续操作的计算量,同时保留足够的语义信息。通常,通道会先被扩展(例如扩展比为6),以提升特征表达能力;随后再被压缩回原始维度。
- 高效算子(Efficient Operator)引入
在通道处理之后,iRMB引入了多种 高效算子 进行特征提取,包括但不限于:
- 深度可分离卷积(Depthwise Convolution, DWConv)
相较于标准卷积,DWConv 将空间滤波与通道映射解耦,大幅降低了参数量和计算量,特别适合资源受限场景。- 窗口注意力机制(Window-based Attention)
在部分改进版本中,iRMB可引入基于窗口的自注意力机制,实现局部区域内的长程依赖建模,从而增强模型对关键目标区域的关注能力。这些高效算子可根据具体任务需求灵活选择,使iRMB模块具备高度定制化特性。
- 1×1卷积层:通道恢复与整合
经过高效算子处理后,输出特征图再次通过一个1×1卷积层,将其通道数还原至与输入一致。此阶段不仅完成了通道维度的恢复,还实现了跨通道的信息融合,有助于进一步增强特征表达。
- 跳跃连接(Skip Connection)
最后,iRMB引入 跳跃连接(Residual/Skip Connection),将输入特征图与输出结果进行逐元素相加。这一机制源ResNet架构,能够有效缓解梯度消失问题,并保留低层细节信息,提升模型训练稳定性和最终性能。
2. iRMB 核心代码
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from functools import partial
from einops import rearrange
from timm.models.efficientnet_blocks import SqueezeExcite
from timm.models.layers import DropPath__all__ = ['iRMB', 'C2f_iRMB']inplace = Trueclass LayerNorm2d(nn.Module):def __init__(self, normalized_shape, eps=1e-6, elementwise_affine=True):super().__init__()self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(normalized_shape, eps, elementwise_affine)def forward(self, x):x = rearrange(x, 'b c h w -> b h w c').contiguous()x = self.norm(x)x = rearrange(x, 'b h w c -> b c h w').contiguous()return xdef get_norm(norm_layer='in_1d'):eps = 1e-6norm_dict = {'none': nn.Identity,'in_1d': partial(nn.InstanceNorm1d, eps=eps),'in_2d': partial(nn.InstanceNorm2d, eps=eps),'in_3d': partial(nn.InstanceNorm3d, eps=eps),'bn_1d': partial(nn.BatchNorm1d, eps=eps),'bn_2d': partial(nn.BatchNorm2d, eps=eps),# 'bn_2d': partial(nn.SyncBatchNorm, eps=eps),'bn_3d': partial(nn.BatchNorm3d, eps=eps),'gn': partial(nn.GroupNorm, eps=eps),'ln_1d': partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=eps),'ln_2d': partial(LayerNorm2d, eps=eps),}return norm_dict[norm_layer]def get_act(act_layer='relu'):act_dict = {'none': nn.Identity,'relu': nn.ReLU,'relu6': nn.ReLU6,'silu': nn.SiLU}return act_dict[act_layer]class ConvNormAct(nn.Module):def __init__(self, dim_in, dim_out, kernel_size, stride=1, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=False,skip=False, norm_layer='bn_2d', act_layer='relu', inplace=True, drop_path_rate=0.):super(ConvNormAct, self).__init__()self.has_skip = skip and dim_in == dim_outpadding = math.ceil((kernel_size - stride) / 2)self.conv = nn.Conv2d(dim_in, dim_out, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, groups, bias)self.norm = get_norm(norm_layer)(dim_out)self.act = get_act(act_layer)(inplace=inplace)self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path_rate) if drop_path_rate else nn.Identity()def forward(self, x):shortcut = xx = self.conv(x)x = self.norm(x)x = self.act(x)if self.has_skip:x = self.drop_path(x) + shortcutreturn xclass iRMB(nn.Module):def __init__(self, dim_in, norm_in=True, has_skip=True, exp_ratio=1.0, norm_layer='bn_2d',act_layer='relu', v_proj=True, dw_ks=3, stride=1, dilation=1, se_ratio=0.0, dim_head=8, window_size=7,attn_s=True, qkv_bias=False, attn_drop=0., drop=0., drop_path=0., v_group=False, attn_pre=False):super().__init__()dim_out = dim_inself.norm = get_norm(norm_layer)(dim_in) if norm_in else nn.Identity()dim_mid = int(dim_in * exp_ratio)self.has_skip = (dim_in == dim_out and stride == 1) and has_skipself.attn_s = attn_sif self.attn_s:assert dim_in % dim_head == 0, 'dim should be divisible by num_heads'self.dim_head = dim_headself.window_size = window_sizeself.num_head = dim_in // dim_headself.scale = self.dim_head ** -0.5self.attn_pre = attn_preself.qk = ConvNormAct(dim_in, int(dim_in * 2), kernel_size=1, bias=qkv_bias, norm_layer='none',act_layer='none')self.v = ConvNormAct(dim_in, dim_mid, kernel_size=1, groups=self.num_head if v_group else 1, bias=qkv_bias,norm_layer='none', act_layer=act_layer, inplace=inplace)self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)else:if v_proj:self.v = ConvNormAct(dim_in, dim_mid, kernel_size=1, bias=qkv_bias, norm_layer='none',act_layer=act_layer, inplace=inplace)else:self.v = nn.Identity()self.conv_local = ConvNormAct(dim_mid, dim_mid, kernel_size=dw_ks, stride=stride, dilation=dilation,groups=dim_mid, norm_layer='bn_2d', act_layer='silu', inplace=inplace)self.se = SqueezeExcite(dim_mid, rd_ratio=se_ratio,act_layer=get_act(act_layer)) if se_ratio > 0.0 else nn.Identity()self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(drop)self.proj = ConvNormAct(dim_mid, dim_out, kernel_size=1, norm_layer='none', act_layer='none', inplace=inplace)self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path else nn.Identity()def forward(self, x):shortcut = xx = self.norm(x)B, C, H, W = x.shapeif self.attn_s:# paddingif self.window_size <= 0:window_size_W, window_size_H = W, Helse:window_size_W, window_size_H = self.window_size, self.window_sizepad_l, pad_t = 0, 0pad_r = (window_size_W - W % window_size_W) % window_size_Wpad_b = (window_size_H - H % window_size_H) % window_size_Hx = F.pad(x, (pad_l, pad_r, pad_t, pad_b, 0, 0,))n1, n2 = (H + pad_b) // window_size_H, (W + pad_r) // window_size_Wx = rearrange(x, 'b c (h1 n1) (w1 n2) -> (b n1 n2) c h1 w1', n1=n1, n2=n2).contiguous()# attentionb, c, h, w = x.shapeqk = self.qk(x)qk = rearrange(qk, 'b (qk heads dim_head) h w -> qk b heads (h w) dim_head', qk=2, heads=self.num_head,dim_head=self.dim_head).contiguous()q, k = qk[0], qk[1]attn_spa = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scaleattn_spa = attn_spa.softmax(dim=-1)attn_spa = self.attn_drop(attn_spa)if self.attn_pre:x = rearrange(x, 'b (heads dim_head) h w -> b heads (h w) dim_head', heads=self.num_head).contiguous()x_spa = attn_spa @ xx_spa = rearrange(x_spa, 'b heads (h w) dim_head -> b (heads dim_head) h w', heads=self.num_head, h=h,w=w).contiguous()x_spa = self.v(x_spa)else:v = self.v(x)v = rearrange(v, 'b (heads dim_head) h w -> b heads (h w) dim_head', heads=self.num_head).contiguous()x_spa = attn_spa @ vx_spa = rearrange(x_spa, 'b heads (h w) dim_head -> b (heads dim_head) h w', heads=self.num_head, h=h,w=w).contiguous()# unpaddingx = rearrange(x_spa, '(b n1 n2) c h1 w1 -> b c (h1 n1) (w1 n2)', n1=n1, n2=n2).contiguous()if pad_r > 0 or pad_b > 0:x = x[:, :, :H, :W].contiguous()else:x = self.v(x)x = x + self.se(self.conv_local(x)) if self.has_skip else self.se(self.conv_local(x))x = self.proj_drop(x)x = self.proj(x)x = (shortcut + self.drop_path(x)) if self.has_skip else xreturn xdef autopad(k, p=None, d=1): # kernel, padding, dilation"""Pad to 'same' shape outputs."""if d > 1:k = d * (k - 1) + 1 if isinstance(k, int) else [d * (x - 1) + 1 for x in k] # actual kernel-sizeif p is None:p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-padreturn pclass Conv(nn.Module):"""Standard convolution with args(ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups, dilation, activation)."""default_act = nn.SiLU() # default activationdef __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, d=1, act=True):"""Initialize Conv layer with given arguments including activation."""super().__init__()self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p, d), groups=g, dilation=d, bias=False)self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)self.act = self.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()def forward(self, x):"""Apply convolution, batch normalization and activation to input tensor."""return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))def forward_fuse(self, x):"""Perform transposed convolution of 2D data."""return self.act(self.conv(x))class Bottleneck(nn.Module):"""Standard bottleneck."""def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5):"""Initializes a bottleneck module with given input/output channels, shortcut option, group, kernels, andexpansion."""super().__init__()c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channelsself.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k[0], 1)self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, k[1], 1, g=g)self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2self.iRMB = iRMB(c2)def forward(self, x):"""'forward()' applies the YOLO FPN to input data."""return x + self.iRMB(self.cv2(self.cv1(x))) if self.add else self.iRMB(self.cv2(self.cv1(x)))class C2f_iRMB(nn.Module):"""Faster Implementation of CSP Bottleneck with 2 convolutions."""def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5):"""Initialize CSP bottleneck layer with two convolutions with arguments ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups,expansion."""super().__init__()self.c = int(c2 * e) # hidden channelsself.cv1 = Conv(c1, 2 * self.c, 1, 1)self.cv2 = Conv((2 + n) * self.c, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)self.m = nn.ModuleList(Bottleneck(self.c, self.c, shortcut, g, k=((3, 3), (3, 3)), e=1.0) for _ in range(n))def forward(self, x):"""Forward pass through C2f layer."""y = list(self.cv1(x).chunk(2, 1))y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))def forward_split(self, x):"""Forward pass using split() instead of chunk()."""y = list(self.cv1(x).split((self.c, self.c), 1))y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))if __name__ == "__main__":# Generating Sample imageimage_size = (1, 64, 640, 640)image = torch.rand(*image_size)# Modelmodel = iRMB(64, 64)out = model(image)print(len(out))2.1 添加iRMB到YOLOv11
- 在
ultralytics/nn文件路径下新建一个文件包,随后新建一个iRMB.py文件

- 新建的
__init__.py文件中导入增加改进模块的代码包

- 在
task.py文件中注册

task.py文件中找到def parse_model(d, ch, verbose=True): # model_dict,input_channels(3)函数添加模块

eLif m in {GAM, CBAM, COOrdAtt, ECA, MLCA, ACmiX, HAT, ELA, CAA, iRMB}:c2 = ch[f]args = [c2, *args]
yolov11-iRMB.yaml
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLO11 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolo11n.yaml' will call yolo11.yaml with scale 'n'# [depth, width, max_channels]n: [0.50, 0.25, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 2624080 parameters, 2624064 gradients, 6.6 GFLOPss: [0.50, 0.50, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 9458752 parameters, 9458736 gradients, 21.7 GFLOPsm: [0.50, 1.00, 512] # summary: 409 layers, 20114688 parameters, 20114672 gradients, 68.5 GFLOPsl: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 25372160 parameters, 25372144 gradients, 87.6 GFLOPsx: [1.00, 1.50, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 56966176 parameters, 56966160 gradients, 196.0 GFLOPs# YOLO11n backbone
backbone:# [from, repeats, module, args]- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4- [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False, 0.25]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False, 0.25]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, True]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32- [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]]- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9- [-1, 1, iRMB, []]- [-1, 2, C2PSA, [1024]] # 10# YOLO11n head
head:- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 13- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3- [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False]] # 16 (P3/8-small)- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]- [[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 19 (P4/16-medium)- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]- [[-1, 11], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5- [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]] # 22 (P5/32-large)- [[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)

综上所述,iRMB是一种兼顾效率与性能的轻量化模块,凭借其高效的算子设计、灵活的结构配置以及强大的特征表达能力,在移动端目标检测等边缘计算任务中展现出巨大潜力。将其引入YOLOv11等主流检测框架中,不仅能显著降低模型复杂度,还能在一定程度上提升检测精度和鲁棒性。
