spring cloud loadbalancer实现机房感知的负载均衡
1 概述
在同城多机房情景下,各个机房各自部署一套微服务集群,正常情况下微服务调用在本机房闭环。在如下某些灾难情景,可以尝试拉远调用以最大程度维持业务连续性,这些情景例如:
- A机房多个服务器宕机。
- 应用由于BUG发生OOM导致暂时性应用不可用、或者被kubelet重启,等应用重新正常运行需要5分钟以上。
为了实现拉远调用,进程的负载均衡逻辑需要感知机房位置,因此微服务注册到服务注册中心时需要夹带额外的元数据。
2 spring cloud loadbalancer
Spring Cloud LoadBalancer是Spring Cloud提供的一个用于微服务架构中的客户端负载均衡解决方案。它旨在取代Netflix Ribbon,提供了更现代化的API和更好的与Spring生态系统的集成。
2.1 主要特性
- 简化配置:
Spring Cloud LoadBalancer提供了简化的配置选项,并且可以通过应用程序属性文件轻松配置。 - 自动配置支持:
它能够自动与RestTemplate和Feign客户端集成,无需手动设置负载均衡逻辑。 - 反应式编程支持:
支持基于 WebFlux 的非阻塞 I/O 操作,对于构建高性能、响应式的微服务非常重要。 - 灵活的负载均衡策略:
内置多种负载均衡算法(如轮询、随机选择等),并且可以自定义实现以满足特定需求。 - 服务发现集成:
与Spring Cloud DiscoveryClient接口兼容,可以与Eureka、Consul等服务发现工具无缝协作。
2.2 自定义负载均衡的套路
2.2.1 步骤1
编写自定义负载均衡逻辑的类,内容如下:
package com.example.consumer.balancer;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectProvider;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.DefaultResponse;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.EmptyResponse;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.Request;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.Response;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.NoopServiceInstanceListSupplier;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.ReactorServiceInstanceLoadBalancer;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.SelectedInstanceCallback;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.ServiceInstanceListSupplier;public class MyNewLoadBalancer implements ReactorServiceInstanceLoadBalancer {private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(MyNewLoadBalancer.class);private final String serviceId;private ObjectProvider<ServiceInstanceListSupplier> serviceInstanceListSupplierProvider;private final String localDataCenter;/**
* * @param serviceInstanceListSupplierProvider a provider of
* * {@link ServiceInstanceListSupplier} that will be used to get available instances
* * @param serviceId id of the service for which to choose an instance
* */public MyNewLoadBalancer(ObjectProvider<ServiceInstanceListSupplier> serviceInstanceListSupplierProvider,String serviceId, String localDataCenter) {this.serviceId = serviceId;this.serviceInstanceListSupplierProvider = serviceInstanceListSupplierProvider;this.localDataCenter = localDataCenter;}@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")@Override// 核心方法,负载均衡的逻辑就是从choose()开始public Mono<Response<ServiceInstance>> choose(Request request) {ServiceInstanceListSupplier supplier = serviceInstanceListSupplierProvider.getIfAvailable(NoopServiceInstanceListSupplier::new);return supplier.get(request).next().map(serviceInstances -> processInstanceResponse(supplier, serviceInstances));}private Response<ServiceInstance> processInstanceResponse(ServiceInstanceListSupplier supplier,List<ServiceInstance> serviceInstances) {Response<ServiceInstance> serviceInstanceResponse = getInstanceResponse(serviceInstances);if (supplier instanceof SelectedInstanceCallback && serviceInstanceResponse.hasServer()) {((SelectedInstanceCallback) supplier).selectedServiceInstance(serviceInstanceResponse.getServer());}return serviceInstanceResponse;}private Response<ServiceInstance> getInstanceResponse(List<ServiceInstance> instances) {if (instances.isEmpty()) {if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {log.warn("No servers available for service: " + serviceId);}return new EmptyResponse();}// 同机房的服务实例List<ServiceInstance> sameDcInstances = instances.stream().filter(instance -> localDataCenter.equals(instance.getMetadata().get("DATA_CENTER"))).collect(Collectors.toList());// 其他机房的服务实例List<ServiceInstance> otherDcInstances = instances.stream().filter(instance -> !localDataCenter.equals(instance.getMetadata().get("DATA_CENTER"))).collect(Collectors.toList());// 两个服务实例列表,选择一个 List<ServiceInstance> selectedInstances = sameDcInstances.isEmpty() ?otherDcInstances : sameDcInstances;// 选好实例列表后,再使用随机方式挑选出一个int index = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(selectedInstances.size());ServiceInstance instance = selectedInstances.get(index);return new DefaultResponse(instance);}
}
2.2.2 步骤2
编写工厂类,不需要添加@Configuration:
package com.example.consumer.balancer;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.ReactorLoadBalancer;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.ServiceInstanceListSupplier;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.support.LoadBalancerClientFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;public class MyLoadBalancerConfig {@Beanpublic ReactorLoadBalancer<ServiceInstance> randomLoadBalancer(Environment environment, LoadBalancerClientFactory loadBalancerClientFactory){String name = environment.getProperty(LoadBalancerClientFactory.PROPERTY_NAME);// 本地机房的信息,从环境变量中获取即可String localDataCenter = environment.getProperty("spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.metadata.DATA_CENTER");return new MyNewLoadBalancer(loadBalancerClientFactory.getLazyProvider(name, ServiceInstanceListSupplier.class), name, localDataCenter);}
}
2.2.3 步骤3
在main类中使用@LoadBalancerClient或@LoadBalancerClients来指定刚刚创建工厂类:
package com.example.consumer;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.annotation.LoadBalancerClients;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.annotation.LoadBalancerClient;
import com.example.consumer.balancer.MyLoadBalancerConfig;@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableFeignClients
@LoadBalancerClient(name = "service-provider", configuration = MyLoadBalancerConfig.class)
// @LoadBalancerClients(defaultConfiguration = MyLoadBalancerConfig.class)
public class ConsumerApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApplication.class, args);}
}
2.2.4 完整代码
https://gitee.com/handsomeboylj/spring-cloud-nacos-demo
3 容灾方案
两边机房都正常时:

DC1机房的Provider应用临时不可用时,拉远调用另外机房的Provider应用:

4 测试
本次测试中,namespace dc1作为dc1机房,namespace dc2作为dc2机房,所有微服务实例都注册到同一个nacos服务中,所有微服务实例在网络层都是扁平的、可直接调用的(对应到现实里,就是是两个机房通过VPN或专线打通,容器网络使用underlay模式)。
git clone https://gitee.com/handsomeboylj/spring-cloud-nacos-demo.git
kubectl apply -f doc/k8s/dc-awareness/
部署成功后,如下:

dc1机房的一个消费者的IP是10.0.13.96,其工作端口是8082,接口是/consumer/call,调用可以看见结果,消费者和生产者都会响应自己所在的机房:

将dc1机房的生产者关闭后,再访问dc1机房的消费者的接口,可以看见响应是dc2,说明调用了机房2的生产者。
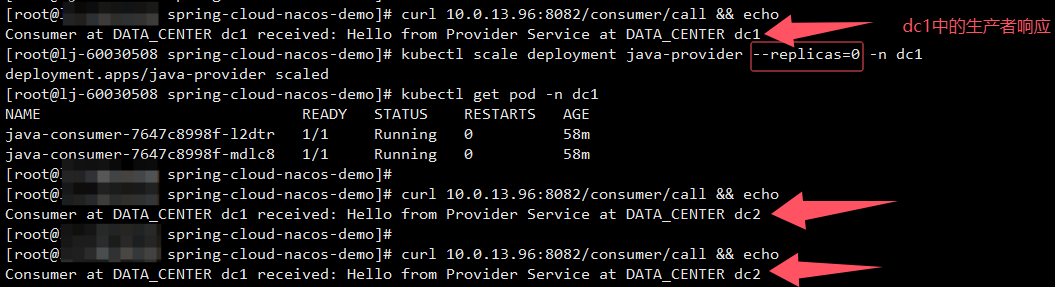
将dc1机房的生产者重新上线后,dc1的消费者从拉远调用转变成本机房调用。

5 小结
本文介绍拉远调用可临时维持业务系统的连续性,并且使用spring cloud loadbalancer来实现感知机房,优先本机房闭环调用,次之拉远调用。
