【万字精讲】 左枝清减·右枝丰盈:C++构筑的二叉搜索森林
目录
一、二叉搜索树
1.1 二叉搜索树概念
1.2二叉搜索树的理解
1.3 二叉搜索树操作
二叉搜索树的查找
二叉搜索树的插入
二叉搜索树的删除
二、二叉搜索树的实现
树节点的构造
BSTree类
树的构造
树的销毁
树的拷贝构造
树的插入
树的插入(递归)
树的删除
树的删除(递归)
三、 二叉搜索树的应用
KV模型:
BinarySearchTree.h:
总结
一、二叉搜索树
1.1 二叉搜索树概念
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以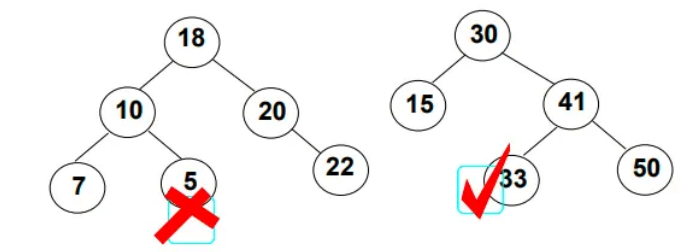 下性质的二叉树
下性质的二叉树
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
1.2二叉搜索树的理解
可以把搜索二叉树理解成一层一层的酒店房间,结点是数字可以看作是顾客的年龄,年龄比该节点大的住下一层的右边,比该节点小的住下一层的左边,依次往下住
把二叉搜索树想成“年龄分房的酒店 (酒店入住规则= 二叉搜索树规则)
- 前台(根节点): 第一个到达的顾客年龄
- 下一层左边房间 : 左子节点 - 只给更年轻的顾客
- 下一层右边房间 : 右子节点 - 只给更年长的顾客
- 再下一层 … : 递归下去 - 直到有空房就停下
举个例子:顾客陆续到达
顾客年龄依次到达:50 → 30 → 70 → 20 → 40 → 60 → 80
酒店楼层立刻变成这样(数字 = 顾客年龄):
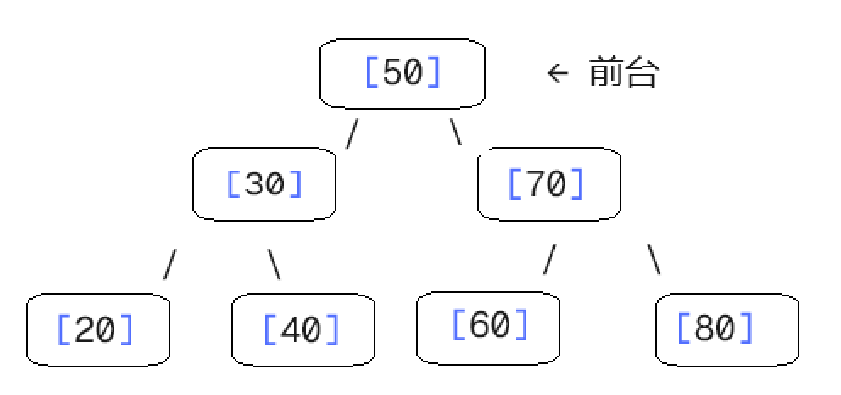
- 50 先到,住前台。
- 30 比 50 小,住左下
- 70 比 50 大,住右下
- 20 再比 30 小,继续往左下……
最终所有人都在唯一且正确的楼层
🔍 查房(find)
- 要找 60 岁的顾客:
- 前台 50:60 > 50 → 往右下。
- 到 70:60 < 70 → 往左下。
- 抓到 60,查房完成!
🧹 退房 (erase)
- 只带一个行李箱(只一个孩子):让孩子直接顶替房间。
- 带两个行李箱(两个孩子):找左下最年长的人(最大值)来顶替,再把那人自己的行李搬过来
⚠️ 极端情况
如果顾客总是年龄递增到达,酒店会变成一条长走廊(退化成链表),查房效率骤降。解决办法就是“平衡装修”——AVL 或红黑树,让楼层保持“矮胖”
AVL 或红黑树也能用这个酒店住房的思路来解释:
- 可以把 AVL 与红黑树也放进“酒店住房”的比喻里,只是它们在前台之外再雇了一个 “楼层管家”,专门在顾客入住或退房后 立即检查并调整房间布局,防止出现“长走廊”(小编在后文中会讲到)
总结:
二叉搜索树就是一座“按年龄自动分房”的智慧酒店,每次来人都严格遵循“更年轻的往左下一层,更年长的往右下一层”,查房永远知道往哪边走
1.3 二叉搜索树操作
二叉搜索树的查找
- 从根开始比较,查找,比根大则往右边走查找,比根小则往左边走查找
- 最多查找高度次,走到到空,还没找到,这个值不存在
把“查找”放进我们那间“年龄分房酒店”——场景

🏨 酒店前台:50 岁的大堂经理
你拿着一张写着 “找 60 岁客人” 的便签走进大堂。
- 50 经理扫了一眼便签:“60?比我年长,请往右边楼梯下一层。”
- 你下到右走廊,遇到 70 岁门房:70 低头一看:“60?比我年轻,请往左边楼梯再下一层”
- 你左转,迈入 60 岁客人的房门——灯光一亮,人就在眼前
🔍 如果便签写的是 45 岁
- 50 → “年轻,往左”
- 30 → “年长,往右”
- 40 → “年轻,往左”
- 左边空空如也——查无此人,你回到前台摇摇头
在 BST 酒店里,查找就像沿着楼梯口不断听到“比我小往左,比我大往右”的耳语,直到你推开正确的房门,或撞见一堵空墙
二叉搜索树的插入
插入的具体过程如下:
a. 树为空,则直接新增节点,赋值给root指针
b. 树不空,按二叉搜索树性质查找插入位置,插入新节点
把“插入”放进我们那间“年龄分房酒店”——场景:一座只有一条走廊、左右分叉的“年龄分房酒店”
顾客的年龄就是 key,酒店永远遵守两条铁律:
- 更年轻的只能住左边下一层
- 更年长的只能住右边下一层
🎬 第一幕:酒店开业(空树)
- 第一天,酒店空无一人
- 第一位顾客 50 先生到了
- 前台小姐一看:空房!直接把他请进 大堂 50 号房。
- 此时整棵树只有一个根节点:

🎬 第二幕:正常入住(非空树插入)
接着来了 30 、 70 、 20 、 40 、 60 、 80 ……每位新顾客的入住流程都是一套标准三步走:
- 领号——找“年龄参照人” 从前台(根_root)出发,一路比年龄(_key):
- 比我大 → 往右楼梯下
- 比我小 → 往左楼梯下
2. 找空房——直到撞见空指针 nullptr
- 走到楼梯尽头,发现“此处尚无房间”——这就是我要入住的空位。
3. 拿钥匙——原地造房间
- 把新顾客的年龄(_key)塞进新节点,挂在上一个人的左/右手边

伪代码 :
if (酒店空) {大堂 = new 房间(key);return;
}current = 大堂;
while (current 有房) {parent = current;if (key < current->年龄)current = 左边楼梯;elsecurrent = 右边楼梯;
}
// 此时 current 是空位置
newRoom = new 房间(key);
if (key < parent->年龄)parent->左房 = newRoom;
elseparent->右房 = newRoom;
二叉搜索树的删除
- 首先查找元素是否在二叉搜索树中,如果不存在,则返回, 否则要删除的结点可能分下面四种情况:
- a. 要删除的结点无孩子结点
- b. 要删除的结点只有左孩子结点
- c. 要删除的结点只有右孩子结点
- d. 要删除的结点有左、右孩子结点
- 看起来有待删除节点有4中情况,实际情况a可以与情况b或者c合并起来,因此真正的删除过程如下:
- 情况b:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除节点的左孩子结点--直接删除
- 情况c:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除结点的右孩子结点--直接删除
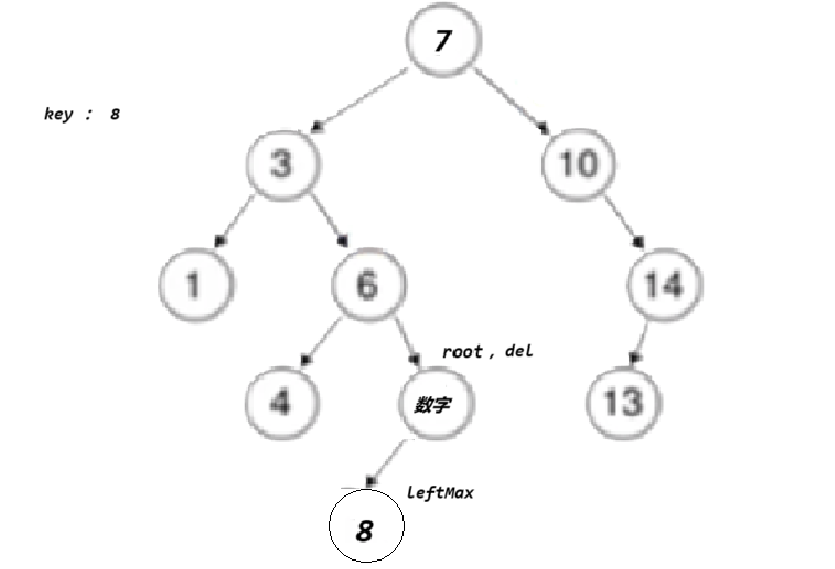
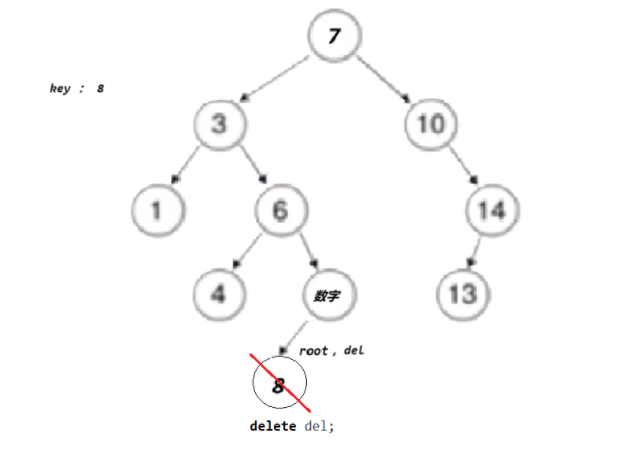
- 情况d:在它的右子树中寻找中序下的第一个结点(关键码最小),用它的值填补到被删除节点中,再来处理该结点的删除问题--替换法删除
二、二叉搜索树的实现
树节点的构造
template<class K>
class BSTreeNode// 结点
{
public:BSTreeNode(const K& key):right(nullptr),left(nullptr),_key(key){}BSTreeNode* right;BSTreeNode* left;K _key;
};BSTree类
ps : 好比作酒店,有各种入住的服务
树的构造
(ps : 树的根是Node* ,节点指针_root)
BSTree():_root(nullptr)
{
}树的销毁
(ps : 用后序遍历一个一个的销毁)
~BSTree()
{Destroy(root);
}树的拷贝构造
( ps : 用前序遍历递归)
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{_root = copy(t.root);
}
private:Node* copy(Node* root)//前序拷贝{if (root == nullptr){return nullptr;}Node* copyroot = new Node(root->key);copyroot->left = copy(root->left);copyroot->right = copy(root->right);return copyroot;}
树的插入
bool Insert(const K& key)
{if (_root == nullptr)//如果它是空的,则直接生成一个key值的结点,给_root{_root = new Node(key);return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur)//cur是key的节点,找到cur要放的位置,{if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->right;}else if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->left;}elsereturn false;}//只找到key要放的位置是不行的,你还要连接起它和它的parent结点cur = new Node(key);//new 类型 (值)if (parent->_key > key){parent->left = cur;}else{parent->right = cur;}return true;
}树的插入(递归)
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{_Insert(root, key);
}bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{if (root == nullptr){root = new Node(key);return true;}if (root->_key > key){_InsertR(root->left, key);}else if (root->_key < key){_InsertR(root->right, key);}else{return true;}
}树的删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->right;}else if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->left;}jelse//找到了,但我们不确定Key这个值在parent节点的左边还是右边{if (cur->left == nullptr)//左为空,则parnet要指向它的右边,只是不知道是parent的左指向它还是右指向它{if (cur == _root)//如果要删除的节点就是_root根节点 {_root = cur->right;} else {if (parent->right == cur)parent->right = cur->right;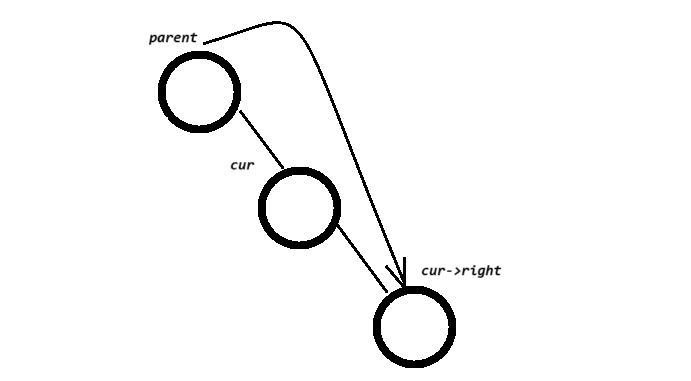
elseparnet->left = cur->right;}}
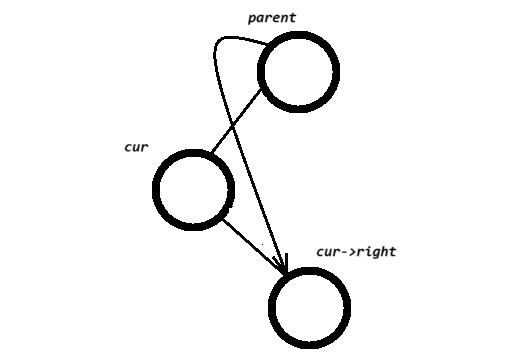
else if (cur->right == nullptr)//右为空,则parnet要指向它的左边,只是不知道是parent的左指向它还是右指向它{if (cur == _root)//如果要删除的节点就是_root根节点 {_root = cur->left;}else {if (parent->left == cur)parent->left = cur->left;
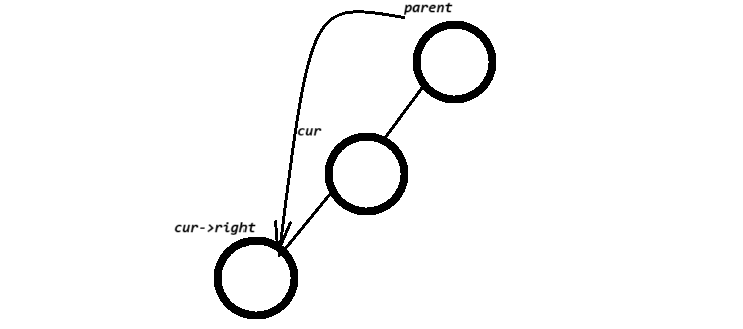
elseparnet->right = cur->left;
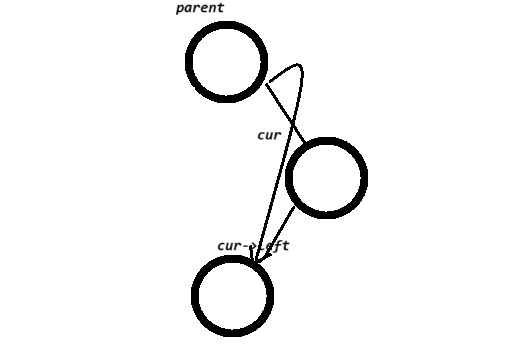
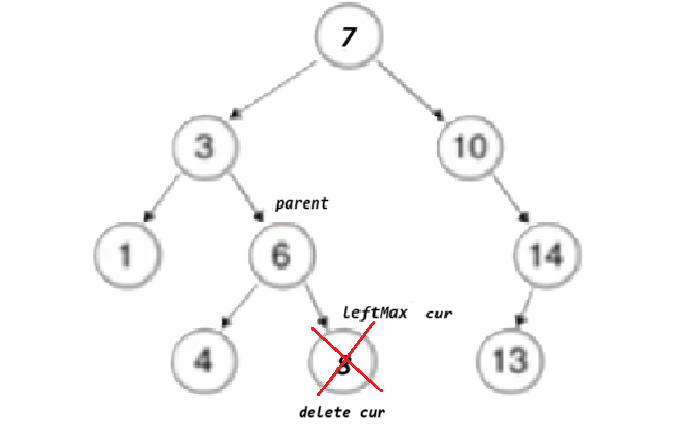
}}else//左,右都有节点// cur已经是要删除的位置了{ Node* leftMax = cur->left; //去cur的左边去找最大值Node* parent = cur;//parent是leftMax的parent节点
while (leftMax->right) // 找最右节点 // tmp 右为空,但左边可能有值{parent = leftMax;leftMax = leftMax->right;}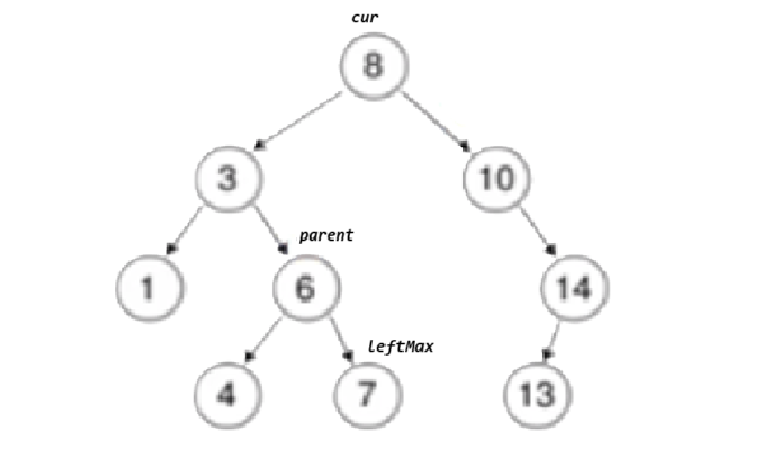
swap(cur->_key, leftMax->_key); 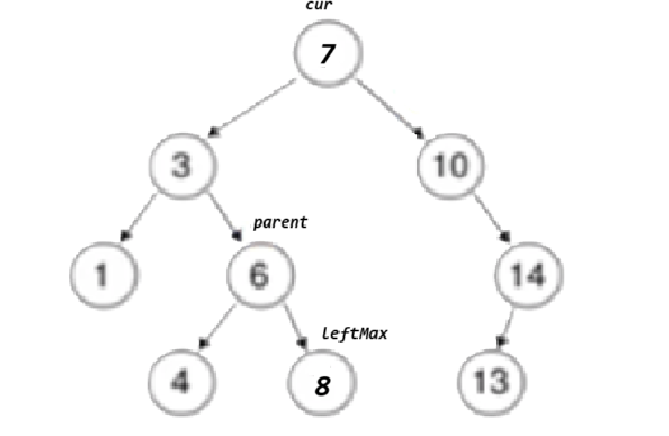
if (parent->left == leftMax)//确定leftMax是在parent的左边还是右边{parent->left = leftMax->left;}
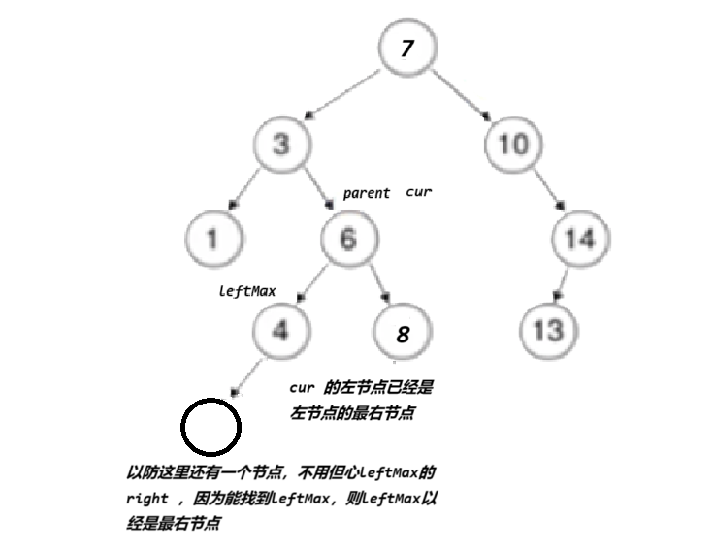
else{parent->right = leftMax->left;}
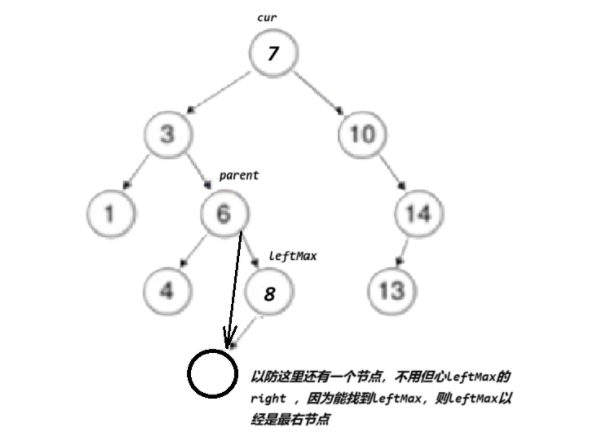
cur = lefMax}delete cur;return true;} }return false;
}
树的删除(递归)
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{_Erase(root, key);
}bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr)return false;if (root->_key < key){return _EraseR(root->_right, key);}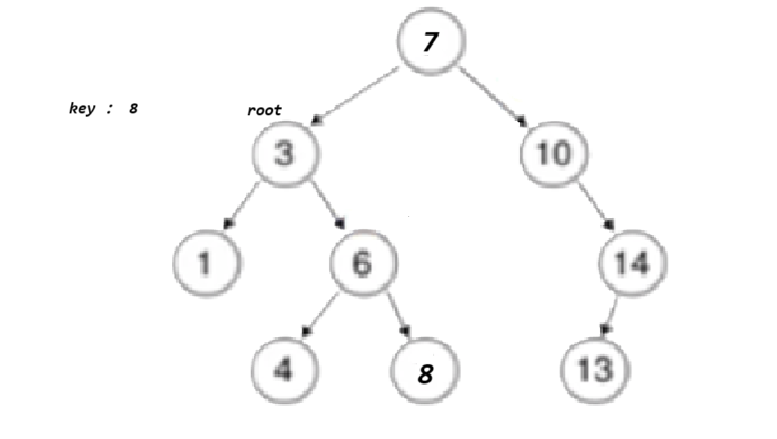
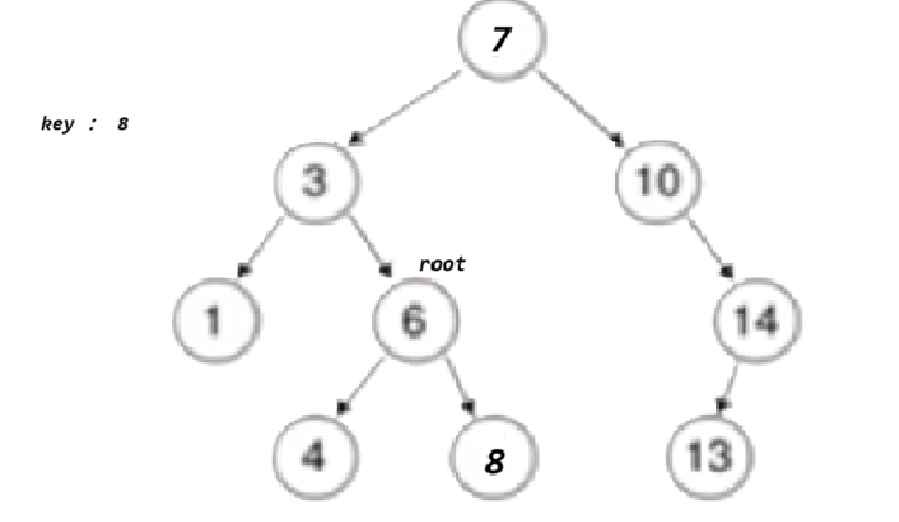
左为空:
else if (root->_key > key){return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}else{Node* del = root;// 1、左为空if (root->_left == nullptr){root = root->_right;}else if (root->_right == nullptr){root = root->_left;}else{Node* leftMax = root->_left;while (leftMax->_right){leftMax = leftMax->_right;}swap(root->_key, leftMax->_key);return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}delete del;return true;}}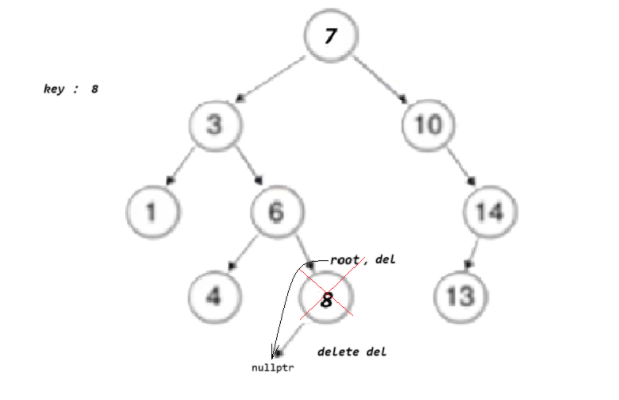
左右都不为空
// 3、左右都不为空if (root->_left == nullptr){root = root->_right;}else if (root->_right == nullptr){root = root->_left;}else{Node* leftMax = root->_left;while (leftMax->_right){leftMax = leftMax->_right;}swap(root->_key, leftMax->_key);return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}delete del;return true;}}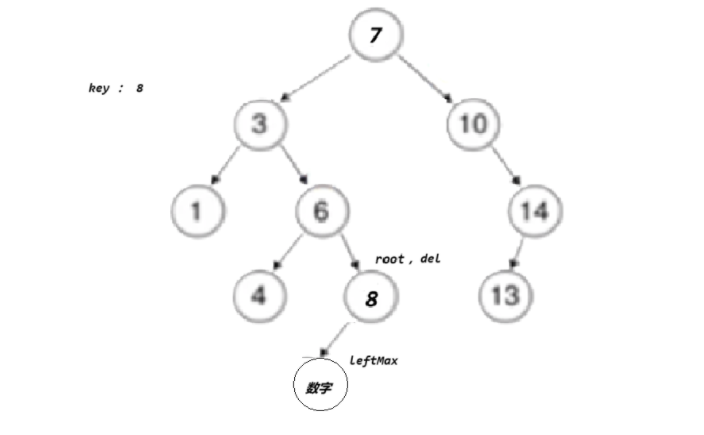

三、 二叉搜索树的应用
- K模型:K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值 ,比如:给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方式如下:以词库中所有单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构建一棵二叉搜索树在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误
- KV模型:每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即<Key, Value>的键值对,该种方式在现实生活中非常常见:比如英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英文单词与其对应的中文<word, chinese>就构成一种键值对;再比如统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,单词与其出现次数就是 <word, count>就构成一种键值对
KV模型:
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>using namespace std;template<class K,class V>
class BSTreeNode// 结点
{
public:BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value):right(nullptr), left(nullptr), _key(key),_value(value){}BSTreeNode* right;BSTreeNode* left;K _key;V _value;
};template<class K, class V>
class BSTree
{typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:BSTree():_root(nullptr){}BSTree(const BSTree<K, V>& t){_root = Copy(_root, t._root);}BSTree<K, V>& operator=(BSTree<K, V> t){swap(_root, t._root);return *this;}~BSTree(){Destory(_root);}bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(key, value);return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key>key){parent = cur;cur = cur->left;}else if (cur->_key<key){parent = cur;cur = cur->right;}elsereturn false;}cur = new Node(key, value);if (parent->_key > key){parent->left = cur;}else{parent->right = cur;}return true;}Node* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key){cur = cur->right;}else if (cur->_key > key){cur = cur->left;}elsereturn cur;}return nullptr;}bool Erase(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->right;}else if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->left;}else//找到了{if (cur->left == nullptr){if (cur == _root){cur = cur->right;}if (parent->left==cur)//确定cur是parent的哪边{parent->left = cur->right;}else{parent->right = cur->right;}}else if (cur->right == nullptr){if (cur == _root){cur = cur->right;}if (parent->left == cur)//确定cur是parent的哪边{parent->left = cur->left;}else{parent->right = cur->left;}}else{Node* leftMax = cur->left;Node* parent = cur;while (leftMax->right){parent = leftMax;leftMax = leftMax->right;}swap(leftMax->_key, cur->_value);swap(leftMax->_value, cur->_value);if (parent->left == leftMax)//确定leftMax是在parent的左边还是右边{parent->left = leftMax->left;}else{parent->right = leftMax->left;}cur = leftMax;}delete cur;return true;}}return false;}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_InOrder(root->left);cout << root->_key << " " << root->_value << endl;_InOrder(root->right);}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);}
private:Node* Copy(Node* root, const Node* copy){if (copy == nullptr){return nullptr;}root = new Node(copy->_key, copy->_value);root->left = Copy(root->left, copy->left);root->right = Copy(root->right, copy->right);return root;}void Destory(Node*& root){if (root == nullptr){return;}Destory(root->left);Destory(root->right);delete root;root = nullptr;}Node* _root = nullptr;
};void TestBSTree()
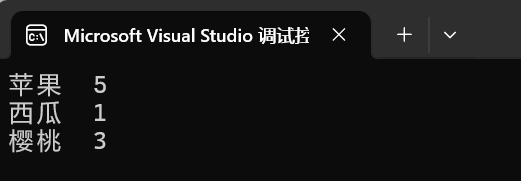
{BSTree<string, string> dict;dict.Insert("insert", "插入");dict.Insert("erase", "删除");dict.Insert("left", "左边");dict.Insert("string", "字符串");string str;while (cin >> str){auto ret = dict.Find(str);if (ret){cout << str << ":" << ret->_value << endl;}else{cout << "单词拼写错误" << endl;}}string strs[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "樱桃", "苹果", "樱桃", "苹果", "樱桃", "苹果" };// 统计水果出现的次BSTree<string, int> countTree;for (auto str : strs){auto ret = countTree.Find(str);if (ret == NULL){countTree.Insert(str, 1);}else{ret->_value++;}}countTree.InOrder();
}
运行结果:

BinarySearchTree.h:
#pragma once
template<class K>
class BSTreeNode// 结点
{
public:BSTreeNode(const K& key):right(nullptr),left(nullptr),_key(key){}BSTreeNode* right;BSTreeNode* left;K _key;
};template<class K>
class BSTree// 树📕
{typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:BSTree():_root(nullptr){}~BSTree(){Destroy(root);}BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t){_root = copy(t.root);}BSTree<K>& operator = (BSTree<K> t)//调用传值拷贝{swap(_root,t.root);return *this;}bool Insert(const K& key){if (_root == nullptr)//如果它是空的,则直接生成一个key值的结点,给_root{_root = new Node(key);return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur)//cur是key的节点,找到cur要放的位置,{if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->right;}else if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->left;}elsereturn false;}//只找到key要放的位置是不行的,你还要连接起它和它的parent结点cur = new Node(key);//new 类型 (值)if (parent->_key > key){parent->left = cur;}else{parent->right = cur;}return true;}bool InsertR(const K& key){_Insert(root, key);}bool Erase(const K& key){Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->right;}else if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->left;}else//找到了,但我们不确定Key这个值在parent节点的左边还是右边{if (cur->left == nullptr)//左为空,则parnet要指向它的右边,只是不知道是parent的左指向它还是右指向它{if (cur == _root)//如果要删除的节点就是_root根节点 {_root = cur->right;}else {if (parent->right == cur)parent->right = cur->right;elseparnet->left = cur->right;}}else if (cur->right == nullptr)//右为空,则parnet要指向它的左边,只是不知道是parent的左指向它还是右指向它{if (cur == _root)//如果要删除的节点就是_root根节点 {_root = cur->left;}else {if (parent->left == cur)parent->left = cur->left;elseparnet->right = cur->left;}}else//左,右都有节点// cur已经是要删除的位置了{ Node* leftMax = cur->left; //去cur的左边去找最大值Node* parent = cur;//parent是leftMax的parent节点while (leftMax->right) // 找最右节点 // tmp 右为空,但左边可能有值{parent = leftMax;leftMax = leftMax->right;}swap(cur->_key, leftMax->_key); if (parent->left == leftMax)//确定leftMax是在parent的左边还是右边{parent->left = leftMax->left;}else{parent->right = leftMax->left;}cur = lefMax}delete cur;return true;} }return false;}bool EraseR(const K& key){_Erase(root, key);}bool Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key){ cur = cur->right;}else if(cur->_key>key){cur = cur->left;}else{return true;}}return false;}bool FindR(const K& key){return _FindR(_root, key);}void Inorder(){_Inorder(_root);}private:Node* copy(Node* root)//前序拷贝{if (root == nullptr){return nullptr;}Node* copyroot = new Node(root->key);copyroot->left = copy(root->left);copyroot->right = copy(root->right);return copyroot;}void Destroy(Node* root)//走后序遍历{if (root == nullptr){return;}Destroy(root->left);Destroy(root->right);delete root;root = nullptr;}bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr){root = new Node(key);return true;}if (root->_key > key){_InsertR(root->left, key);}else if (root->_key < key){_InsertR(root->right, key);}else{return true;}}bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr){return false;}if (root->_key > key){reurn _EraseR(root->left, key);}else if (root->_key < key){return _EraseR(root->right, key);}else{//1.左为空if (root->left == nullptr) {root = root->right;}//2.右为空else if (root->right == nullptr){root = root->left;}//3.左,右都不为空else{Node* leftMax = root->left;while ( leftMax->right){leftMax = leftM->right;}swap(root->_key, leftMax->_key);//以经把要删的root->key给了root->left的最右节点return Erase(root->left, key);//所以只要从root->left开始删key值}delete root;return true;}}bool _FindR(Node* root,const K& key){if (root == nullptr)return false;if (root->_key < key){return _FindR(root->right, key);}else if (root->_key > key){return _FindR(root->left, key);}else{return true;}}void _Inorder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_Inorder(root->left);cout << root->_key << " ";_Inorder(root->right);}
private:Node* _root;
};void TestBSTree1()
{int a[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };BSTree<int> t;for (auto e : a){t.InsertR(e);}t.Inorder();
}
总结
用 C++ 的模板与指针,把“左小右大”的规则构造成一棵可生长的 BST:
插入像住房间,搜索似走迷宫,删除则三思
本文系统介绍了二叉搜索树(BST)的概念、实现和应用。主要内容包括:
1. BST的特性:左子树值小于根节点,右子树值大于根节点;
2. 核心操作:查找、插入和删除(包括直接删除和替换法删除);
3. 递归和非递归实现方式;
4. K模型和KV模型两种应用场景,如单词查询和统计;
5. 通过"年龄分房酒店"的生动比喻解释BST的工作原理
文中提供了完整的C++模板实现代码,包括节点结构、树类定义及各种操作方法
