【CompletableFuture】基础Future (一)
【CompletableFuture】基础Future
- 1. Future理论知识
- 1.1 基本理解
- 1.2 常用方法
- 1.3 使用案例
- 1.4 注意事项
- 1.5 Future vs CompletableFuture
- 2. Future接口常用实现类FutureTask异步任务
- 2.1 类定义
- 2.2 核心属性
- 2.3 状态流转(state)
- 2.4 代码示例
- 2.5 FutureTask的优缺点
- 优点
- 缺点
- 2.6 书中介绍
- 附录
1. Future理论知识
/** ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.**//**** Written by Doug Lea with assistance from members of JCP JSR-166* Expert Group and released to the public domain, as explained at* http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/*/package java.util.concurrent;/*** A {@code Future} represents the result of an asynchronous* computation. Methods are provided to check if the computation is* complete, to wait for its completion, and to retrieve the result of* the computation. The result can only be retrieved using method* {@code get} when the computation has completed, blocking if* necessary until it is ready. Cancellation is performed by the* {@code cancel} method. Additional methods are provided to* determine if the task completed normally or was cancelled. Once a* computation has completed, the computation cannot be cancelled.* If you would like to use a {@code Future} for the sake* of cancellability but not provide a usable result, you can* declare types of the form {@code Future<?>} and* return {@code null} as a result of the underlying task.** <p>* <b>Sample Usage</b> (Note that the following classes are all* made-up.)* <pre> {@code* interface ArchiveSearcher { String search(String target); }* class App {* ExecutorService executor = ...* ArchiveSearcher searcher = ...* void showSearch(final String target)* throws InterruptedException {* Future<String> future* = executor.submit(new Callable<String>() {* public String call() {* return searcher.search(target);* }});* displayOtherThings(); // do other things while searching* try {* displayText(future.get()); // use future* } catch (ExecutionException ex) { cleanup(); return; }* }* }}</pre>** The {@link FutureTask} class is an implementation of {@code Future} that* implements {@code Runnable}, and so may be executed by an {@code Executor}.* For example, the above construction with {@code submit} could be replaced by:* <pre> {@code* FutureTask<String> future =* new FutureTask<String>(new Callable<String>() {* public String call() {* return searcher.search(target);* }});* executor.execute(future);}</pre>** <p>Memory consistency effects: Actions taken by the asynchronous computation* <a href="package-summary.html#MemoryVisibility"> <i>happen-before</i></a>* actions following the corresponding {@code Future.get()} in another thread.** @see FutureTask* @see Executor* @since 1.5* @author Doug Lea* @param <V> The result type returned by this Future's {@code get} method*/
public interface Future<V> {/*** Attempts to cancel execution of this task. This attempt will* fail if the task has already completed, has already been cancelled,* or could not be cancelled for some other reason. If successful,* and this task has not started when {@code cancel} is called,* this task should never run. If the task has already started,* then the {@code mayInterruptIfRunning} parameter determines* whether the thread executing this task should be interrupted in* an attempt to stop the task.** <p>After this method returns, subsequent calls to {@link #isDone} will* always return {@code true}. Subsequent calls to {@link #isCancelled}* will always return {@code true} if this method returned {@code true}.** @param mayInterruptIfRunning {@code true} if the thread executing this* task should be interrupted; otherwise, in-progress tasks are allowed* to complete* @return {@code false} if the task could not be cancelled,* typically because it has already completed normally;* {@code true} otherwise*/boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);/*** Returns {@code true} if this task was cancelled before it completed* normally.** @return {@code true} if this task was cancelled before it completed*/boolean isCancelled();/*** Returns {@code true} if this task completed.** Completion may be due to normal termination, an exception, or* cancellation -- in all of these cases, this method will return* {@code true}.** @return {@code true} if this task completed*/boolean isDone();/*** Waits if necessary for the computation to complete, and then* retrieves its result.** @return the computed result* @throws CancellationException if the computation was cancelled* @throws ExecutionException if the computation threw an* exception* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted* while waiting*/V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;/*** Waits if necessary for at most the given time for the computation* to complete, and then retrieves its result, if available.** @param timeout the maximum time to wait* @param unit the time unit of the timeout argument* @return the computed result* @throws CancellationException if the computation was cancelled* @throws ExecutionException if the computation threw an* exception* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted* while waiting* @throws TimeoutException if the wait timed out*/V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}翻译后结果
/** ORACLE 专有/机密。使用受许可条款约束。*//** 在 JCP JSR-166 专家组成员的协助下,由 Doug Lea 编写,* 并已发布到公共领域,如以下网址所述:* http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/*/package java.util.concurrent;/*** {@code Future} 表示一个异步计算的结果。* 提供了用于检查计算是否完成、等待其完成以及检索其结果的方法。* 只有在计算完成之后,才能使用 {@code get} 方法来获取结果;如有必要,该方法会阻塞直到计算完成。* 通过 {@code cancel} 方法可以取消计算。* 还提供了额外的方法来判断任务是否是正常完成或已被取消。* 一旦计算完成,就不能再取消该计算。* * 如果你希望使用 {@code Future} 实现可取消性但不需要返回结果,* 可以声明类型为 {@code Future<?>} 并让底层任务返回 {@code null} 作为结果。** <p>* <b>示例用法</b>(注意,以下类均为虚构):* <pre> {@code* interface ArchiveSearcher { String search(String target); }* class App {* ExecutorService executor = ...* ArchiveSearcher searcher = ...* void showSearch(final String target)* throws InterruptedException {* Future<String> future* = executor.submit(new Callable<String>() {* public String call() {* return searcher.search(target);* }});* displayOtherThings(); // 在搜索期间执行其他操作* try {* displayText(future.get()); // 使用 future 获取结果* } catch (ExecutionException ex) { cleanup(); return; }* }* }}</pre>** {@link FutureTask} 类是 {@code Future} 的一个实现类,它还实现了 {@code Runnable},* 因此可以由 {@code Executor} 执行。* 例如,上述使用 {@code submit} 的方式可以替换为如下形式:* <pre> {@code* FutureTask<String> future =* new FutureTask<String>(new Callable<String>() {* public String call() {* return searcher.search(target);* }});* executor.execute(future);}</pre>** <p>内存一致性效应:由异步计算所执行的操作,* 会 <a href="package-summary.html#MemoryVisibility"><i>先于(happen-before)</i></a>* 另一个线程中随后调用 {@code Future.get()} 方法之后的操作。** @see FutureTask* @see Executor* @since 1.5* @author Doug Lea* @param <V> 此 Future 的 {@code get} 方法返回的结果类型*/
public interface Future<V> {/*** 尝试取消此任务的执行。* 如果任务已经完成、已被取消,或因其他原因无法取消,则该尝试将失败。* 如果任务尚未启动并成功取消,那么该任务将永远不会被执行。* 如果任务已经启动,则参数 {@code mayInterruptIfRunning} 决定是否应中断执行此任务的线程,* 以尝试停止任务的执行。** <p>此方法返回后,对 {@link #isDone} 的调用将始终返回 {@code true}。* 如果此方法返回 {@code true},则对 {@link #isCancelled} 的调用也将返回 {@code true}。** @param mayInterruptIfRunning 如果应中断正在执行此任务的线程,则为 {@code true};* 否则,允许正在进行的任务继续完成。* @return 如果任务无法被取消(通常是因为它已经正常完成),则返回 {@code false};* 否则返回 {@code true}*/boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);/*** 如果此任务在正常完成之前已被取消,则返回 {@code true}。** @return 如果任务在完成之前被取消,则返回 {@code true}*/boolean isCancelled();/*** 如果此任务已完成,则返回 {@code true}。** 完成可能是由于正常结束、抛出异常或被取消——* 在所有这些情况下,此方法都将返回 {@code true}。** @return 如果此任务已完成,则返回 {@code true}*/boolean isDone();/*** 如有必要,等待计算完成,然后检索其结果。** @return 计算结果* @throws CancellationException 如果计算被取消* @throws ExecutionException 如果计算抛出异常* @throws InterruptedException 如果当前线程在等待期间被中断*/V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;/*** 如有必要,最多等待指定的时间以完成计算,然后(如果可用)检索其结果。** @param timeout 最长等待时间* @param unit 超时时间的时间单位* @return 计算结果* @throws CancellationException 如果计算被取消* @throws ExecutionException 如果计算抛出异常* @throws InterruptedException 如果当前线程在等待期间被中断* @throws TimeoutException 如果等待超时*/V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}上面代码是Java 并发包(java.util.concurrent)中的一个核心接口,由并发编程专家 Doug Lea 编写,并从 JDK 1.5 开始引入。它用于表示异步计算的结果。
即:一个任务可能还在执行,但你可以提前获取它的引用,并在之后查询、等待或取消它的执行。
1.1 基本理解
Future<T> 接口表示一个异步任务的结果,T 是结果的类型。它的主要用途是:
- 查询任务是否完成
- 获取任务结果
- 取消任务
1.2 常用方法
public interface Future<V> {// 取消任务boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning); // 判断任务是否被取消boolean isCancelled(); // 判断任务是否已完成boolean isDone(); // 获取任务结果(阻塞)V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; // 限时获取任务结果V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
1.3 使用案例
配合 ExecutorService 使用:
import java.util.concurrent.*;public class FutureExample {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();// 提交一个 Callable 任务,返回 FutureFuture<Integer> future = executor.submit(() -> {Thread.sleep(2000); // 模拟耗时操作return 42;});System.out.println("任务已提交,等待结果...");// 阻塞等待结果Integer result = future.get(); System.out.println("任务结果:" + result);executor.shutdown();}
}
1.4 注意事项
get()方法是阻塞的:如果任务没执行完,get()会一直阻塞等待。- 任务可以取消:通过
cancel(true)取消正在执行的任务(如果支持中断)。 - 配合 Callable 使用:与 Runnable 不同,Callable 可以有返回值。
- 推荐使用
CompletableFuture(Java 8 及以后):功能更强大,支持链式调用、异步处理等。
1.5 Future vs CompletableFuture

2. Future接口常用实现类FutureTask异步任务
/** ORACLE 专有/机密。使用需遵守许可证条款。*//** 由 Doug Lea 编写,并在 JCP JSR-166 专家组成员协助下完成。* 根据 http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ 中的说明,* 此代码发布到公有领域。*/package java.util.concurrent;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;/*** 一个可取消的异步计算任务。此类提供了 {@link Future} 的基础实现,* 包括启动和取消计算、查询是否完成,以及获取计算结果的方法。* 只有在计算完成后才能获取结果;如果尚未完成,调用 {@code get} 方法会阻塞。* 一旦计算完成,就不能重新开始或取消(除非使用 {@link #runAndReset} 方法重新执行)。** <p>{@code FutureTask} 可以用来包装一个 {@link Callable} 或 {@link Runnable} 对象。* 因为它实现了 {@code Runnable} 接口,所以可以提交到 {@link Executor} 中执行。** <p>除了作为一个独立的类使用外,此类还提供了一些受保护的功能,* 可供创建自定义任务类时使用。** @since 1.5* @author Doug Lea* @param <V> 此 FutureTask 的 {@code get} 方法返回的结果类型*/
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {/** 版本说明:与之前基于 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 的版本不同,* 当前设计通过使用 CAS 更新一个 “state” 字段来控制同步,* 避免了在取消竞争期间保留中断状态的问题。* 等待线程采用简单的 Treiber 栈结构。** 风格说明:与往常一样,我们绕过 AtomicXFieldUpdater 带来的开销,* 而直接使用 Unsafe 内在方法。*//*** 当前任务的运行状态,初始为 NEW。* 状态只会在 set、setException 和 cancel 方法中转换为终态。* 在完成过程中,状态可能暂时处于 COMPLETING 或 INTERRUPTING 状态。* 从中间状态转换为最终状态使用的是懒加载写入(比普通写入性能更好)。** 状态转换图:* NEW -> COMPLETING -> NORMAL* NEW -> COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONAL* NEW -> CANCELLED* NEW -> INTERRUPTING -> INTERRUPTED*/private volatile int state;private static final int NEW = 0;private static final int COMPLETING = 1;private static final int NORMAL = 2;private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3;private static final int CANCELLED = 4;private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5;private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6;/** 待执行的 Callable;执行完成后会置为 null */private Callable<V> callable;/** get() 返回的结果或抛出的异常 */private Object outcome; // 非 volatile,由 state 的读写保证可见性/** 正在执行任务的线程;在 run() 中通过 CAS 设置 */private volatile Thread runner;/** Treiber 栈结构,存储等待中的线程 */private volatile WaitNode waiters;/*** 根据任务状态返回结果或抛出异常。** @param s 完成状态码*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {Object x = outcome;if (s == NORMAL)return (V)x;if (s >= CANCELLED)throw new CancellationException();throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);}/*** 创建一个 FutureTask,在运行时会执行给定的 Callable。** @param callable 可调用任务* @throws NullPointerException 如果 callable 为 null*/public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {if (callable == null)throw new NullPointerException();this.callable = callable;this.state = NEW;}/*** 创建一个 FutureTask,在运行时会执行给定的 Runnable,并返回指定结果。** @param runnable 可运行任务* @param result 成功执行后返回的结果* @throws NullPointerException 如果 runnable 为 null*/public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);this.state = NEW;}public boolean isCancelled() {return state >= CANCELLED;}public boolean isDone() {return state != NEW;}public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {if (!(state == NEW &&UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW,mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED)))return false;try {if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {try {Thread t = runner;if (t != null)t.interrupt();} finally {UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED);}}} finally {finishCompletion();}return true;}public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {int s = state;if (s <= COMPLETING)s = awaitDone(false, 0L);return report(s);}public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {if (unit == null)throw new NullPointerException();int s = state;if (s <= COMPLETING &&(s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)throw new TimeoutException();return report(s);}/*** 当任务完成(包括取消)时调用。* 默认实现什么也不做。子类可以覆盖此方法来添加回调或记录。*/protected void done() { }/*** 设置成功结果(如果未设置或未取消)。** @param v 计算结果*/protected void set(V v) {if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {outcome = v;UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL);finishCompletion();}}/*** 设置异常结果(如果未设置或未取消)。** @param t 异常原因*/protected void setException(Throwable t) {if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {outcome = t;UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, EXCEPTIONAL);finishCompletion();}}public void run() {if (state != NEW ||!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,null, Thread.currentThread()))return;try {Callable<V> c = callable;if (c != null && state == NEW) {V result;boolean ran;try {result = c.call();ran = true;} catch (Throwable ex) {result = null;ran = false;setException(ex);}if (ran)set(result);}} finally {runner = null;int s = state;if (s >= INTERRUPTING)handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);}}/*** 执行任务但不设置结果,然后重置状态。* 如果任务执行过程中抛出异常或被取消则返回 false。*/protected boolean runAndReset() {if (state != NEW ||!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,null, Thread.currentThread()))return false;boolean ran = false;int s = state;try {Callable<V> c = callable;if (c != null && s == NEW) {try {c.call(); // 不设置结果ran = true;} catch (Throwable ex) {setException(ex);}}} finally {runner = null;s = state;if (s >= INTERRUPTING)handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);}return ran && s == NEW;}/*** 确保 cancel(true) 发出的中断只在 run/runAndReset 中传递。*/private void handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(int s) {if (s == INTERRUPTING)while (state == INTERRUPTING)Thread.yield();// Thread.interrupted(); // 清除中断状态(留空以允许用户处理)}/*** Treiber 栈中用于记录等待线程的节点。*/static final class WaitNode {volatile Thread thread;volatile WaitNode next;WaitNode() { thread = Thread.currentThread(); }}/*** 移除并唤醒所有等待线程,调用 done() 并清理 callable。*/private void finishCompletion() {for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {for (;;) {Thread t = q.thread;if (t != null) {q.thread = null;LockSupport.unpark(t);}WaitNode next = q.next;if (next == null)break;q.next = null;q = next;}break;}}done();callable = null;}/*** 等待任务完成,或因中断/超时而终止。*/private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)throws InterruptedException {final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;WaitNode q = null;boolean queued = false;for (;;) {if (Thread.interrupted()) {removeWaiter(q);throw new InterruptedException();}int s = state;if (s > COMPLETING) {if (q != null)q.thread = null;return s;}else if (s == COMPLETING)Thread.yield();else if (q == null)q = new WaitNode();else if (!queued)queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,q.next = waiters, q);else if (timed) {nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();if (nanos <= 0L) {removeWaiter(q);return state;}LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);}elseLockSupport.park(this);}}/*** 从等待链表中移除超时或中断的节点。*/private void removeWaiter(WaitNode node) {if (node != null) {node.thread = null;retry:for (;;) {for (WaitNode pred = null, q = waiters, s; q != null; q = s) {s = q.next;if (q.thread != null)pred = q;else if (pred != null) {pred.next = s;if (pred.thread == null)continue retry;}else if (!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,q, s))continue retry;}break;}}}// Unsafe 机制private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;private static final long stateOffset;private static final long runnerOffset;private static final long waitersOffset;static {try {UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();Class<?> k = FutureTask.class;stateOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("state"));runnerOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("runner"));waitersOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("waiters"));} catch (Exception e) {throw new Error(e);}}}FutureTask<V> 是 Java 并发包中的一个类,它同时实现了:
- Runnable:可被线程执行
Future<V>:可获取结果、支持取消
🔧 作用简述:
用于封装一个可以在未来执行并获取结果的任务,支持:
- 提交异步任务执行
- 等待任务完成并获取结果
- 支持任务取消、中断
- 支持异常处理

2.1 类定义
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {// 实现了 Runnable 和 Future 接口的组合接口
}public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {void run();
}
2.2 核心属性

2.3 状态流转(state)

2.4 代码示例

2.5 FutureTask的优缺点
优点
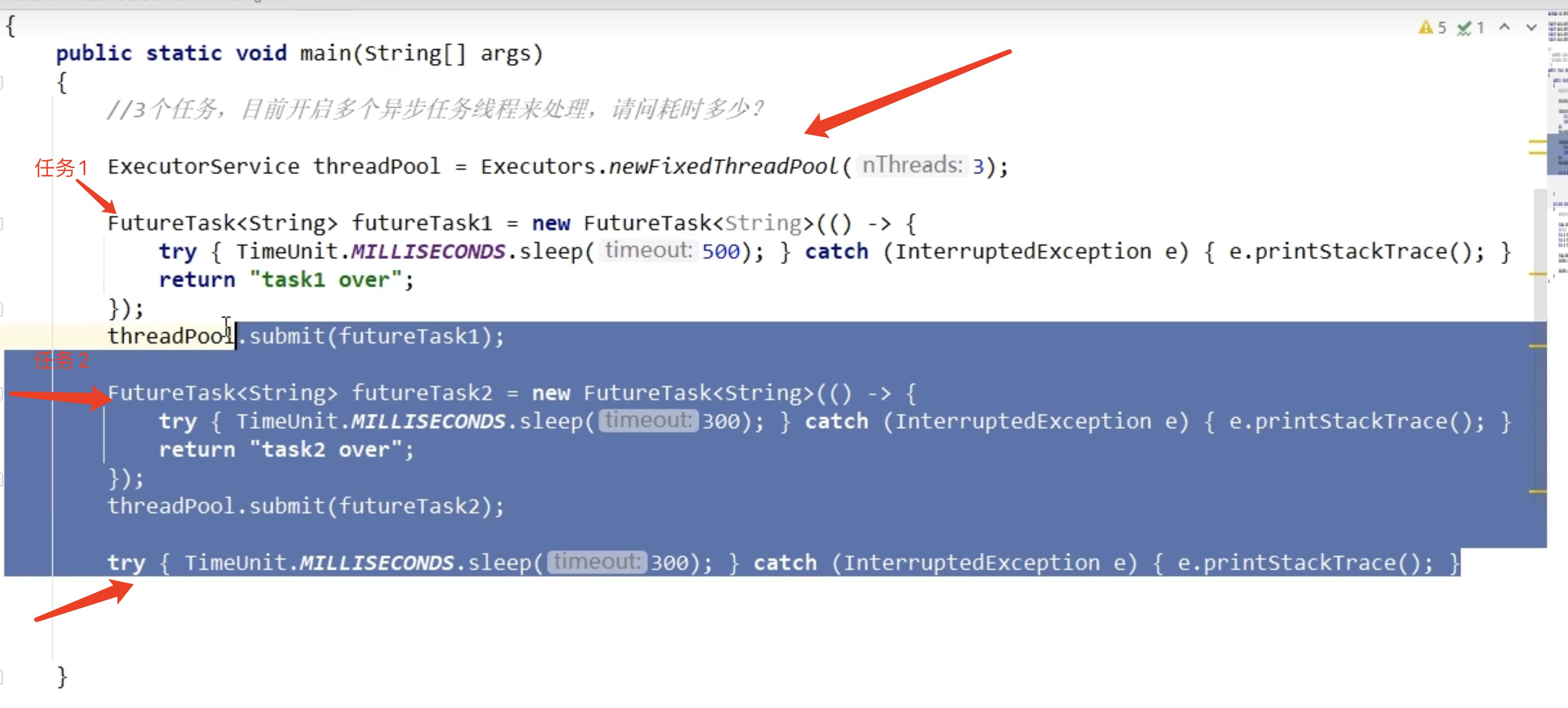
FutureTask结合线程池可以提高效率
缺点

Timeout

- get()方法是阻塞方法,一旦调用get方法求结果,如果没有计算完容易导致程序阻塞。
- Future获取的结果不是很好,只能通过阻塞或者轮训的方式获取到任务的结果。
2.6 书中介绍






附录
- 课程视频 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ar4y1x727?spm_id_from=333.788.player.switch&vd_source=240d9002f7c7e3da63cd9a975639409a&p=14
