数据结构:栈和队列力扣算法题
基础知识:
数据结构:栈和队列(上)-CSDN博客
数据结构:栈和队列(下)-CSDN博客
1.用队列实现栈
225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
理解题意:

思路:
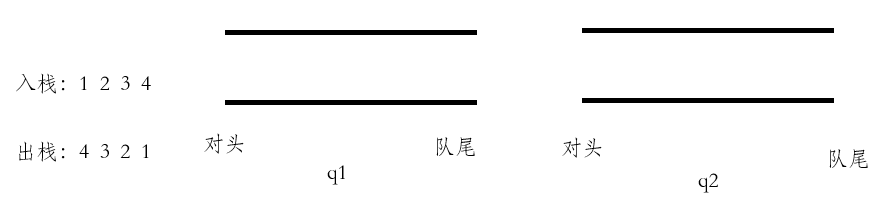
入栈:向不为空的队列中插入数据。
出栈:把不为空的队列中,前size-1个数据挪到另一个队列,再将最后一个数据出队列。
取栈顶:不能通过出栈来完成,需要找不为空的队列,返回队尾数据。
代码见下:
typedef int QDataType;
//定义结点结构
typedef struct QueueNode {QDataType data;struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;
//定义队列的结构
typedef struct Queue {QueueNode* phead;//队头QueueNode* ptail;//队尾int size;//队列中的有效个数
}Queue;
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QueueNode* cur = pq->phead;while (cur){QueueNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}//入队
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);//创建结点QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail!");exit(1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;pq->size++;//队列为空if (pq->phead == NULL){pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;}else {pq->ptail->next = newnode;pq->ptail = pq->ptail->next;}
}//队列判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->phead == NULL;
}//出队列,队头
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));pq->size--;//只有一个结点if (pq->phead == pq->ptail){free(pq->phead);pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;}else {QueueNode* next = pq->phead->next;free(pq->phead);pq->phead = next;}
}//取队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->phead->data;
}//取队尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->ptail->data;
}//队列有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);/*QueueNode* cur = pq->phead;int size = 0;while (cur){++size;cur = cur->next;}return size;*/return pq->size;
}
//以上为队列的结构和常用方法//定义两个队列
typedef struct {Queue q1;Queue q2;
} MyStack;//创建一个栈
MyStack* myStackCreate() {MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));QueueInit(&pst->q1);QueueInit(&pst->q2);return pst;
}void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {//向不为空的队列中插入数据if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);}else{QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);}
}int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {//栈不为空Queue* Emp = &obj->q1;Queue* noneEmp = &obj->q2;if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q2)){Emp = &obj->q2;noneEmp = &obj->q1;}//不为空队列的前size-1个数据挪到另一个队列while(QueueSize(noneEmp) > 1){// //取对头// int front = QueueFront(&noneEmp);// //入另一个队列// QueuePush(&Emp,front);//取对头,入另一个队列QueuePush(Emp,QueueFront(noneEmp));//出队列QueuePop(noneEmp);}//不为空队列数据出队int top = QueueFront(noneEmp);QueuePop(noneEmp);return top;
}
//取栈顶
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {//找不为空队列返回不为空队列的队尾if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){return QueueBack(&obj->q1);}else{return QueueBack(&obj->q2);}
}bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);free(obj);obj = NULL;
}/*** Your MyStack struct will be instantiated and called as such:* MyStack* obj = myStackCreate();* myStackPush(obj, x);* int param_2 = myStackPop(obj);* int param_3 = myStackTop(obj);* bool param_4 = myStackEmpty(obj);* myStackFree(obj);
*/2.用栈实现队列
232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
理解题意:

思路:
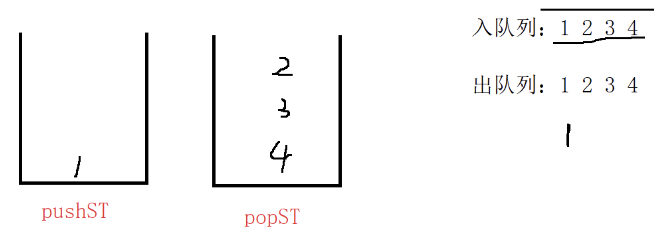
入队列:往pushST插入数据
出队列:popST不为空直接出,否则将pushST中的数据先倒过去再出数据。
取对头:逻辑和出队列相似,但是不出数据,popST不为空,直接取对头,否则将popST中的数据导入过去,再取对头。
//定义栈的结构
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack {STDataType* arr;int top;//指向当前栈顶元素的索引--正好为栈中有效的数据个数int capacity;//栈的空间大小
}ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps)
{ps->arr = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}//销毁
void STDesTroy(ST* ps)
{if (ps->arr)free(ps->arr);ps->arr = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}// ⼊栈
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);//判断空间是否足够if (ps->top == ps->capacity){//增容int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail!");exit(1);}ps->arr = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}//空间足够ps->arr[ps->top++] = x;
}//栈是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}//出栈
void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(!STEmpty(ps));ps->top--;
}//取栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(!STEmpty(ps));return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
}//获取栈中有效元素个数
int STSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}
//以上是栈结构的定义和常见方法typedef struct {ST pushST;ST popST;
} MyQueue;MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {MyQueue* pq = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));STInit(&pq->pushST);STInit(&pq->popST);return pq;
}void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {STPush(&obj->pushST,x);
}int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {//为空,先导入if(STEmpty(&obj->popST)){while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushST)){//取栈顶,入popST栈,出栈STPush(&obj->popST,STTop(&obj->pushST));STPop(&obj->pushST);}}//不为空直接出int top = STTop(&obj->popST);STPop(&obj->popST);return top;
}int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {//为空,先导入if(STEmpty(&obj->popST)){while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushST)){//取栈顶,入popST栈,出栈STPush(&obj->popST,STTop(&obj->pushST));STPop(&obj->pushST);}}//不为空直接出int top = STTop(&obj->popST);return top;
}bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {return STEmpty(&obj->popST) && STEmpty(&obj->pushST);
}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {STDesTroy(&obj->pushST);STDesTroy(&obj->popST);free(obj);obj =NULL;
}最终通过测试。
3.设计循环队列
622. 设计循环队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
循环队列的特点:
(1)对头删数据,队尾插入数据
(2)给定固定的空间,使用过程中不可以扩容
(3)环形队列满了,不能继续插入数据(即插入数据失败)
既可以由数组实现,也可以由循环链表实现。
理解题意:

思路:
初始化:链表需要申请四个结点并让其连接在一起,而数组只需要malloc四个字节大小的空间即可。
遍历:
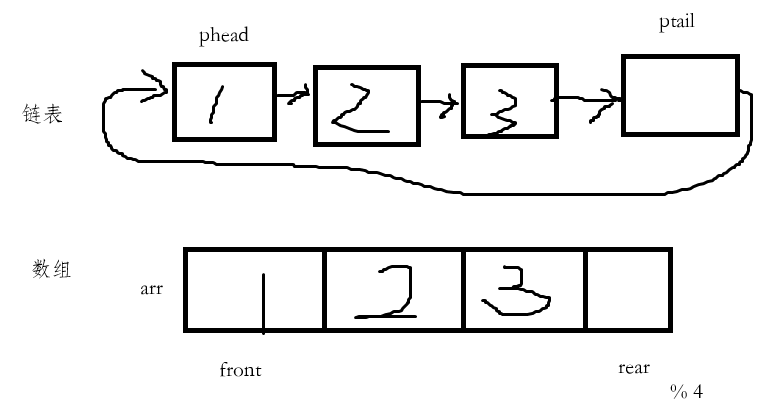
使用数组:
环形队列为空:front == rear ,环形队列满了:front == rear
如何区分环形队列是空还是满?且不额外增加计数器成员来保存对列中的有效数据个数。
我们需要额外增加一个空间,只要满足:(rear + 1) % (k + 1) == front,即可。
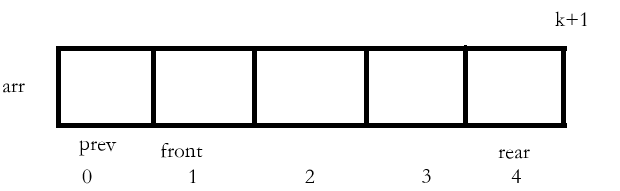
代码如下:
typedef struct {int* arr;int front;//对头int rear;//队尾int capacity;//循环队列的空间大小
} MyCircularQueue;MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {MyCircularQueue* pq = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));//申请k+1个空间pq->arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));pq->front = pq->rear = 0;pq->capacity = k;return pq;
}
// 检查循环队列是否为空
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {return obj->front == obj->rear;
}
//检查循环队列是否已满
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {return (obj->rear+1)%(obj->capacity+1) == obj->front;
}
//插入
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {//判满判空if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj)){return false;}obj->arr[obj->rear++] = value;obj->rear %= obj->capacity + 1;return true;
}
//删除
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return false;}//非空++obj->front;obj->front %= obj->capacity+1;return true;
}int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}return obj->arr[obj->front];
}int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}int prev = obj->rear -1;if(obj->rear == 0){prev = obj->capacity;}return obj->arr[prev];
}void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {if(obj->arr)free(obj->arr);free(obj);obj = NULL;
}
本章完。
