Python API接口实战指南:从入门到精通

🌟 Hello,我是蒋星熠Jaxonic!
🌈 在浩瀚无垠的技术宇宙中,我是一名执着的星际旅人,用代码绘制探索的轨迹。
🚀 每一个算法都是我点燃的推进器,每一行代码都是我航行的星图。
🔭 每一次性能优化都是我的天文望远镜,每一次架构设计都是我的引力弹弓。
🎻 在数字世界的协奏曲中,我既是作曲家也是首席乐手。让我们携手,在二进制星河中谱写属于极客的壮丽诗篇!
摘要
作为一名多年沉浸在API开发与集成领域的技术探索者,我深刻体会到API接口已成为现代软件开发的核心基石。在这个万物互联的时代,掌握API调用技术不再是锦上添花,而是开发者必备的基本技能。本文将带领大家深入Python API接口的奇妙世界,从基础概念到实战应用,全方位剖析如何利用Python高效调用各类API接口。我们将探讨RESTful API、GraphQL、WebSocket等不同类型接口的特点与应用场景,通过实际案例演示如何使用requests、aiohttp等库进行接口调用,并深入讨论认证机制、错误处理、性能优化等关键技术点。无论你是刚入门的新手,还是寻求提升的老手,这篇文章都将为你提供系统化的API接口调用知识体系,助你在这个API驱动的世界中游刃有余。让我们一起揭开API的神秘面纱,探索如何通过简单的Python代码连接无限可能!
一、API基础知识
1.1 什么是API
API(Application Programming Interface,应用程序编程接口)是软件组件之间定义的交互方式,允许不同的应用程序相互通信和共享数据。
# API调用的基本模式
import requests# 发送请求到API端点
response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/data')# 处理响应
if response.status_code == 200:data = response.json() # 解析JSON响应print(data)
else:print(f"请求失败: {response.status_code}")
1.2 API的类型
图1:API类型分类流程图 - 展示了主要API类型及其特点
1.3 API认证方式
不同的API使用不同的认证机制来确保安全访问:
# API密钥认证
import requestsapi_key = "your_api_key_here"
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}"}
response = requests.get("https://api.example.com/data", headers=headers)# OAuth 2.0认证
from requests_oauthlib import OAuth2Sessionclient_id = "your_client_id"
client_secret = "your_client_secret"
oauth = OAuth2Session(client_id)
# 获取授权URL和状态
authorization_url, state = oauth.authorization_url("https://example.com/oauth/authorize")
# 用户授权后获取token
token = oauth.fetch_token("https://example.com/oauth/token",authorization_response="callback_url_with_code",client_secret=client_secret)
# 使用token访问API
response = oauth.get("https://api.example.com/data")
二、Python API调用基础
2.1 常用HTTP库对比
| 库名称 | 特点 | 适用场景 | 异步支持 | 易用性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| requests | 简单直观,功能丰富 | 一般API调用 | 否 | ★★★★★ |
| aiohttp | 异步IO,高性能 | 高并发场景 | 是 | ★★★★☆ |
| httpx | 现代化,支持异步 | 需要HTTP/2的场景 | 是 | ★★★★☆ |
| urllib3 | 底层控制,线程安全 | 需要细粒度控制 | 否 | ★★★☆☆ |
| pycurl | 高性能,多协议支持 | 性能关键场景 | 否 | ★★☆☆☆ |
2.2 使用requests库调用RESTful API
import requests
import json# GET请求
def get_data(url, params=None, headers=None):"""发送GET请求获取数据参数:url (str): API端点URLparams (dict): 查询参数headers (dict): 请求头返回:dict: 响应数据"""response = requests.get(url, params=params, headers=headers)response.raise_for_status() # 如果请求失败则抛出异常return response.json()# POST请求
def create_resource(url, data, headers=None):"""发送POST请求创建资源参数:url (str): API端点URLdata (dict): 要发送的数据headers (dict): 请求头返回:dict: 响应数据"""if headers is None:headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}response = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(data), headers=headers)response.raise_for_status()return response.json()# 使用示例
try:# 获取用户列表users = get_data("https://api.example.com/users", params={"page": 1, "limit": 10},headers={"Authorization": "Bearer token123"})print(f"获取到 {len(users)} 个用户")# 创建新用户new_user = create_resource("https://api.example.com/users",{"name": "张三", "email": "zhangsan@example.com"},{"Authorization": "Bearer token123"})print(f"创建用户成功: {new_user['id']}")except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as e:print(f"HTTP错误: {e}")
except requests.exceptions.ConnectionError:print("连接错误: 请检查网络连接")
except requests.exceptions.Timeout:print("超时错误: 请求超时")
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:print(f"请求错误: {e}")
2.3 异步API调用
import asyncio
import aiohttp
import timeasync def fetch_data(session, url):"""异步获取单个URL的数据"""async with session.get(url) as response:return await response.json()async def fetch_all(urls):"""并发获取多个URL的数据"""async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:tasks = [fetch_data(session, url) for url in urls]# 并发执行所有任务results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)return results# 使用示例
async def main():# 需要获取数据的API端点列表urls = ["https://api.example.com/users/1","https://api.example.com/users/2","https://api.example.com/users/3","https://api.example.com/users/4","https://api.example.com/users/5"]start_time = time.time()results = await fetch_all(urls)end_time = time.time()print(f"异步获取 {len(results)} 个API结果,耗时: {end_time - start_time:.2f}秒")return results# 运行异步主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":results = asyncio.run(main())## 三、实战案例:常用API接口调用### 3.1 天气API调用```python
import requests
from datetime import datetimedef get_weather(city, api_key):"""获取指定城市的天气信息参数:city (str): 城市名称api_key (str): OpenWeatherMap API密钥返回:dict: 天气信息"""base_url = "https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather"params = {"q": city,"appid": api_key,"units": "metric", # 使用摄氏度"lang": "zh_cn" # 中文结果}response = requests.get(base_url, params=params)response.raise_for_status()weather_data = response.json()# 格式化天气信息formatted_data = {"城市": weather_data["name"],"天气": weather_data["weather"][0]["description"],"温度": f"{weather_data['main']['temp']}°C","体感温度": f"{weather_data['main']['feels_like']}°C","湿度": f"{weather_data['main']['humidity']}%","风速": f"{weather_data['wind']['speed']}m/s","更新时间": datetime.fromtimestamp(weather_data["dt"]).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")}return formatted_data# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":API_KEY = "your_openweathermap_api_key" # 替换为你的API密钥city = "北京"try:weather_info = get_weather(city, API_KEY)print(f"== {weather_info['城市']}天气信息 ==")for key, value in weather_info.items():if key != "城市":print(f"{key}: {value}")except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as e:print(f"获取天气信息失败: {e}")
3.2 翻译API调用
import requests
import uuid
import hashlib
import timedef translate_text(text, from_lang, to_lang, app_id, app_key):"""使用百度翻译API翻译文本参数:text (str): 要翻译的文本from_lang (str): 源语言代码,如'auto'自动检测,'zh'中文,'en'英文to_lang (str): 目标语言代码app_id (str): 百度翻译API的APP IDapp_key (str): 百度翻译API的密钥返回:str: 翻译后的文本"""endpoint = "https://fanyi-api.baidu.com/api/trans/vip/translate"# 生成随机数salt = str(uuid.uuid4())# 计算签名: appid+q+salt+密钥sign_str = app_id + text + salt + app_keysign = hashlib.md5(sign_str.encode()).hexdigest()# 组装请求参数params = {'q': text,'from': from_lang,'to': to_lang,'appid': app_id,'salt': salt,'sign': sign}# 发送请求response = requests.get(endpoint, params=params)result = response.json()# 检查是否有错误if 'error_code' in result:raise Exception(f"翻译错误 (代码: {result['error_code']}): {result.get('error_msg', '未知错误')}")# 提取翻译结果translated_text = result['trans_result'][0]['dst']return translated_text# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":APP_ID = "your_baidu_app_id" # 替换为你的百度翻译APP IDAPP_KEY = "your_baidu_app_key" # 替换为你的百度翻译密钥text_to_translate = "人工智能正在改变我们的世界"try:# 中文翻译为英文translated = translate_text(text_to_translate, 'zh', 'en', APP_ID, APP_KEY)print(f"原文: {text_to_translate}")print(f"译文: {translated}")# 防止API调用过于频繁time.sleep(1)# 再将结果翻译回中文back_translated = translate_text(translated, 'en', 'zh', APP_ID, APP_KEY)print(f"回译: {back_translated}")except Exception as e:print(f"翻译失败: {e}")
图3:翻译API调用时序图 - 展示了翻译API的完整调用流程
3.3 图像识别API调用
import requests
import base64
import jsondef recognize_image(image_path, api_key):"""使用百度AI图像识别API识别图片内容参数:image_path (str): 图片文件路径api_key (str): 百度AI平台的API密钥返回:dict: 识别结果"""# 获取访问令牌def get_access_token(api_key, secret_key):url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/oauth/2.0/token"params = {"grant_type": "client_credentials","client_id": api_key,"client_secret": secret_key}response = requests.post(url, params=params)return response.json().get("access_token")# 读取图片文件并进行base64编码with open(image_path, "rb") as f:image_data = base64.b64encode(f.read()).decode("utf-8")# 获取访问令牌access_token = get_access_token(api_key["api_key"], api_key["secret_key"])# 调用通用物体识别APIrecognize_url = f"https://aip.baidubce.com/rest/2.0/image-classify/v2/advanced_general?access_token={access_token}"headers = {"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"}data = {"image": image_data}response = requests.post(recognize_url, headers=headers, data=data)result = response.json()if "error_code" in result:raise Exception(f"识别错误 (代码: {result['error_code']}): {result.get('error_msg', '未知错误')}")return result# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":# 百度AI平台的API密钥信息API_INFO = {"api_key": "your_baidu_api_key","secret_key": "your_baidu_secret_key"}# 要识别的图片路径IMAGE_PATH = "example.jpg"try:result = recognize_image(IMAGE_PATH, API_INFO)print("图像识别结果:")for item in result["result"]:print(f"- {item['keyword']}: 置信度 {item['score']*100:.2f}%")except Exception as e:print(f"识别失败: {e}")## 四、API接口性能优化### 4.1 API调用性能指标```mermaid
%%{init: {'theme': 'neutral', 'themeVariables': { 'primaryColor': '#6495ED', 'primaryTextColor': '#fff', 'primaryBorderColor': '#4169E1', 'lineColor': '#6495ED', 'secondaryColor': '#B0C4DE', 'tertiaryColor': '#E6E6FA' }}}%%
pietitle API调用性能影响因素占比"网络延迟" : 35"服务器处理时间" : 25"数据序列化/反序列化" : 15"认证开销" : 10"客户端处理" : 10"其他因素" : 5
图2:API调用性能影响因素占比饼图 - 展示了影响API调用性能的主要因素及其占比
4.2 连接池与会话复用
import requests
from requests.adapters import HTTPAdapter
from urllib3.util.retry import Retrydef create_session():"""创建一个具有连接池和重试机制的会话对象返回:requests.Session: 配置好的会话对象"""session = requests.Session()# 配置重试策略retry_strategy = Retry(total=3, # 最多重试3次backoff_factor=0.5, # 重试间隔 = {backoff factor} * (2 ^ ({number of previous retries}))status_forcelist=[429, 500, 502, 503, 504], # 这些状态码会触发重试allowed_methods=["GET", "POST"] # 允许重试的HTTP方法)# 配置适配器,最大连接数为10adapter = HTTPAdapter(max_retries=retry_strategy, pool_connections=10, pool_maxsize=10)# 将适配器挂载到会话session.mount("http://", adapter)session.mount("https://", adapter)return session# 使用示例
def fetch_multiple_apis(urls):"""使用会话复用方式获取多个API数据参数:urls (list): API端点URL列表返回:list: 响应数据列表"""session = create_session()results = []for url in urls:try:response = session.get(url, timeout=(3.05, 27)) # (连接超时, 读取超时)response.raise_for_status()results.append(response.json())except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:print(f"请求 {url} 失败: {e}")results.append(None)return results# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":api_urls = ["https://api.example.com/data/1","https://api.example.com/data/2","https://api.example.com/data/3"]results = fetch_multiple_apis(api_urls)print(f"成功获取 {sum(1 for r in results if r is not None)} 个API结果,共 {len(api_urls)} 个")
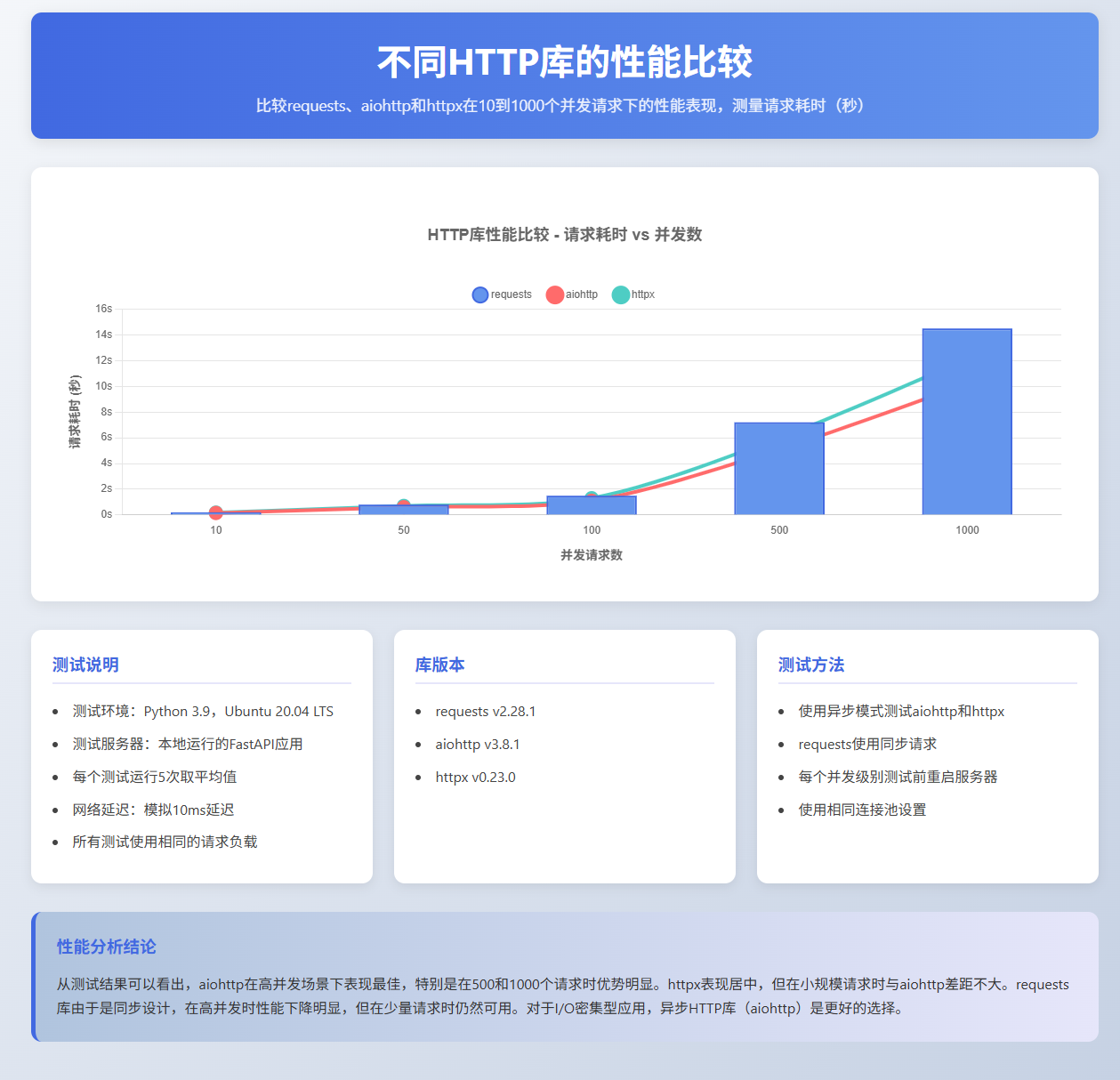
图4:不同HTTP库性能比较图 - 展示了不同HTTP库在不同请求数量下的性能表现
4.3 异步并发与限流
import asyncio
import aiohttp
import time
from aiohttp import ClientSession
from asyncio import Semaphoreclass RateLimiter:"""API调用限流器"""def __init__(self, calls_limit, time_period):"""初始化限流器参数:calls_limit (int): 时间段内允许的最大调用次数time_period (float): 时间段长度(秒)"""self.calls_limit = calls_limitself.time_period = time_periodself.calls_times = []async def acquire(self):"""获取调用许可,必要时等待"""now = time.time()# 清理过期的调用记录self.calls_times = [t for t in self.calls_times if now - t <= self.time_period]# 如果已达到限制,等待到最早的调用过期if len(self.calls_times) >= self.calls_limit:oldest_call = self.calls_times[0]wait_time = self.time_period - (now - oldest_call)if wait_time > 0:await asyncio.sleep(wait_time)# 记录本次调用时间self.calls_times.append(time.time())async def fetch_with_rate_limit(session, url, rate_limiter, semaphore):"""使用限流和并发控制获取API数据参数:session (ClientSession): aiohttp会话url (str): API端点URLrate_limiter (RateLimiter): 限流器semaphore (Semaphore): 并发控制信号量返回:dict: API响应数据"""# 获取限流许可await rate_limiter.acquire()# 获取并发许可async with semaphore:try:async with session.get(url) as response:if response.status == 200:return await response.json()else:print(f"请求失败: {url}, 状态码: {response.status}")return Noneexcept Exception as e:print(f"请求异常: {url}, 错误: {e}")return Noneasync def fetch_all_apis(urls, rate_limit=10, period=1.0, max_concurrency=5):"""批量获取API数据,带限流和并发控制参数:urls (list): API端点URL列表rate_limit (int): 每个时间段内的最大请求数period (float): 时间段长度(秒)max_concurrency (int): 最大并发请求数返回:list: API响应数据列表"""# 创建限流器和信号量rate_limiter = RateLimiter(rate_limit, period)semaphore = Semaphore(max_concurrency)async with ClientSession() as session:tasks = [fetch_with_rate_limit(session, url, rate_limiter, semaphore)for url in urls]return await asyncio.gather(*tasks)

图5:API调用策略选择矩阵 - 展示了不同API调用优化策略的实现复杂度与性能提升对比
五、API接口调用架构设计
5.1 API客户端封装
class APIClient:"""通用API客户端封装"""def __init__(self, base_url, auth_token=None, timeout=30):"""初始化API客户端参数:base_url (str): API基础URLauth_token (str): 认证令牌timeout (int): 请求超时时间(秒)"""self.base_url = base_url.rstrip('/')self.timeout = timeoutself.session = requests.Session()# 设置通用请求头self.session.headers.update({"Content-Type": "application/json","Accept": "application/json"})# 设置认证令牌if auth_token:self.session.headers.update({"Authorization": f"Bearer {auth_token}"})def _build_url(self, endpoint):"""构建完整的API URL"""endpoint = endpoint.lstrip('/')return f"{self.base_url}/{endpoint}"def _handle_response(self, response):"""处理API响应"""try:response.raise_for_status()return response.json()except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as e:# 尝试解析错误响应error_detail = {}try:error_detail = response.json()except:error_detail = {"message": response.text}raise APIError(status_code=response.status_code,message=f"HTTP错误: {e}",detail=error_detail)except ValueError:# 响应不是有效的JSONreturn {"raw_content": response.text}def get(self, endpoint, params=None):"""发送GET请求"""url = self._build_url(endpoint)response = self.session.get(url, params=params, timeout=self.timeout)return self._handle_response(response)def post(self, endpoint, data=None, json_data=None):"""发送POST请求"""url = self._build_url(endpoint)response = self.session.post(url, data=data, json=json_data, timeout=self.timeout)return self._handle_response(response)def put(self, endpoint, data=None, json_data=None):"""发送PUT请求"""url = self._build_url(endpoint)response = self.session.put(url, data=data, json=json_data, timeout=self.timeout)return self._handle_response(response)def delete(self, endpoint, params=None):"""发送DELETE请求"""url = self._build_url(endpoint)response = self.session.delete(url, params=params, timeout=self.timeout)return self._handle_response(response)class APIError(Exception):"""API错误异常"""def __init__(self, status_code, message, detail=None):self.status_code = status_codeself.message = messageself.detail = detailsuper().__init__(self.message)def __str__(self):if self.detail:return f"{self.message} - {self.detail}"return self.message# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":# 创建API客户端client = APIClient(base_url="https://api.example.com/v1",auth_token="your_auth_token_here")try:# 获取用户列表users = client.get("/users", params={"limit": 10})print(f"获取到 {len(users)} 个用户")# 创建新用户new_user = client.post("/users", json_data={"name": "张三","email": "zhangsan@example.com"})print(f"创建用户成功: ID={new_user['id']}")except APIError as e:print(f"API错误: {e}")
5.2 API接口适配器模式
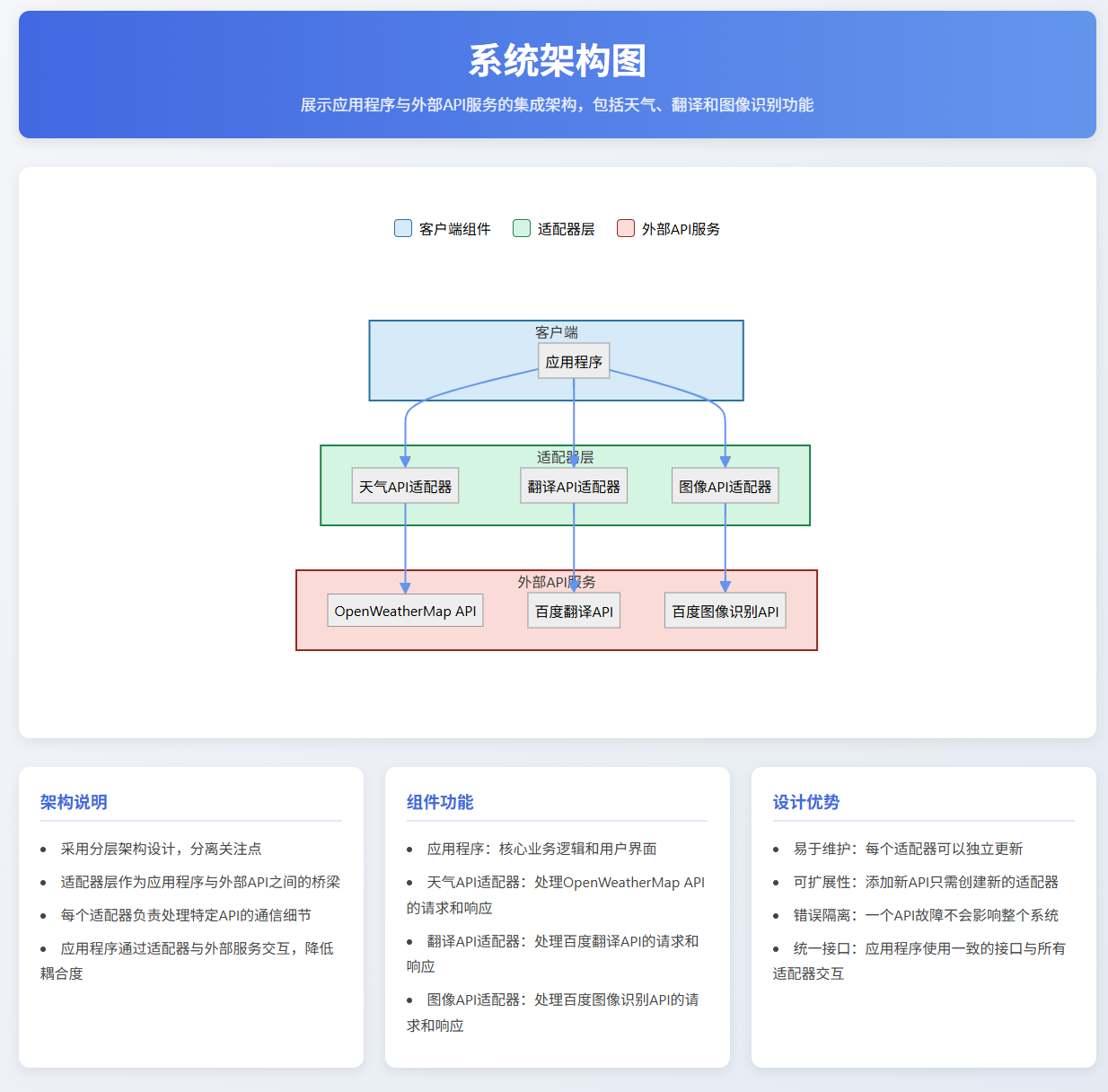
图6:API接口适配器架构图 - 展示了使用适配器模式统一不同API接口的架构设计
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
抽象接口
class TranslationService(ABC):
“”“翻译服务抽象接口”“”
@abstractmethod
def translate(self, text, source_lang, target_lang):"""翻译文本参数:text (str): 要翻译的文本source_lang (str): 源语言代码target_lang (str): 目标语言代码返回:str: 翻译后的文本"""pass
具体实现 - 百度翻译
class BaiduTranslation(TranslationService):
“”“百度翻译服务实现”“”
def __init__(self, app_id, app_key):self.app_id = app_idself.app_key = app_keydef translate(self, text, source_lang, target_lang):# 转换语言代码格式source = self._convert_lang_code(source_lang)target = self._convert_lang_code(target_lang)# 调用百度翻译APIimport uuidimport hashlibimport requestsendpoint = "https://fanyi-api.baidu.com/api/trans/vip/translate"salt = str(uuid.uuid4())sign_str = self.app_id + text + salt + self.app_keysign = hashlib.md5(sign_str.encode()).hexdigest()params = {'q': text,'from': source,'to': target,'appid': self.app_id,'salt': salt,'sign': sign}response = requests.get(endpoint, params=params)result = response.json()if 'error_code' in result:raise Exception(f"翻译错误: {result.get('error_msg', '未知错误')}")return result['trans_result'][0]['dst']def _convert_lang_code(self, lang_code):"""将标准语言代码转换为百度API使用的代码"""# 语言代码映射表mapping = {"en": "en","zh": "zh","ja": "jp","ko": "kor","fr": "fra","es": "spa","auto": "auto"}return mapping.get(lang_code.lower(), lang_code)
具体实现 - Google翻译
class GoogleTranslation(TranslationService):
“”“Google翻译服务实现”“”
def __init__(self, api_key):self.api_key = api_keydef translate(self, text, source_lang, target_lang):# 这里是Google翻译API的实现# 实际代码中需要使用Google Cloud Translation APIimport requestsurl = "https://translation.googleapis.com/language/translate/v2"params = {"q": text,"source": source_lang,"target": target_lang,"key": self.api_key}response = requests.post(url, params=params)result = response.json()if "error" in result:raise Exception(f"翻译错误: {result['error']['message']}")return result["data"]["translations"][0]["translatedText"]
使用示例
def translate_with_service(service, text, source=“auto”, target=“en”):
“”"
使用指定的翻译服务翻译文本
参数:service (TranslationService): 翻译服务实例text (str): 要翻译的文本source (str): 源语言代码target (str): 目标语言代码返回:str: 翻译后的文本
"""
try:result = service.translate(text, source, target)return result
except Exception as e:print(f"翻译失败: {e}")return None
客户端代码
if name == “main”:
# 创建百度翻译服务
baidu_service = BaiduTranslation(
app_id=“your_baidu_app_id”,
app_key=“your_baidu_app_key”
)
# 创建Google翻译服务
google_service = GoogleTranslation(api_key="your_google_api_key"
)# 要翻译的文本
text = "人工智能正在改变世界"# 使用百度翻译
baidu_result = translate_with_service(baidu_service, text, "zh", "en")
print(f"百度翻译结果: {baidu_result}")# 使用Google翻译
google_result = translate_with_service(google_service, text, "zh", "en")
print(f"Google翻译结果: {google_result}")
六、总结与最佳实践
“API不仅仅是技术接口,更是连接不同系统、不同团队、不同思想的桥梁。优秀的API调用代码应当像优秀的外交官一样,既能准确传达信息,又能优雅处理各种意外情况。” —— 软件架构师谚语
在这个万物互联的时代,API已经成为现代软件开发的核心基础设施。通过本文的学习,我们已经掌握了使用Python调用各种API接口的基本技能和高级技巧。以下是一些关键的最佳实践总结:
-
选择合适的HTTP库:根据项目需求选择合适的HTTP库,一般情况下requests是最佳选择,但高并发场景应考虑aiohttp等异步库。
-
错误处理与重试:永远不要假设API调用会成功,始终实现完善的错误处理和适当的重试机制。
-
性能优化:对于频繁调用的API,应使用连接池、会话复用等技术减少连接开销。
-
限流控制:尊重API提供方的限制,实现客户端限流以避免被封禁。
-
抽象与适配:使用适配器模式等设计模式,将具体API实现与业务逻辑分离。
-
安全性考虑:妥善保管API密钥,避免硬编码在代码中,使用环境变量或配置文件存储敏感信息。
-
文档与测试:为API调用代码编写清晰的文档和单元测试,确保其可维护性和稳定性。
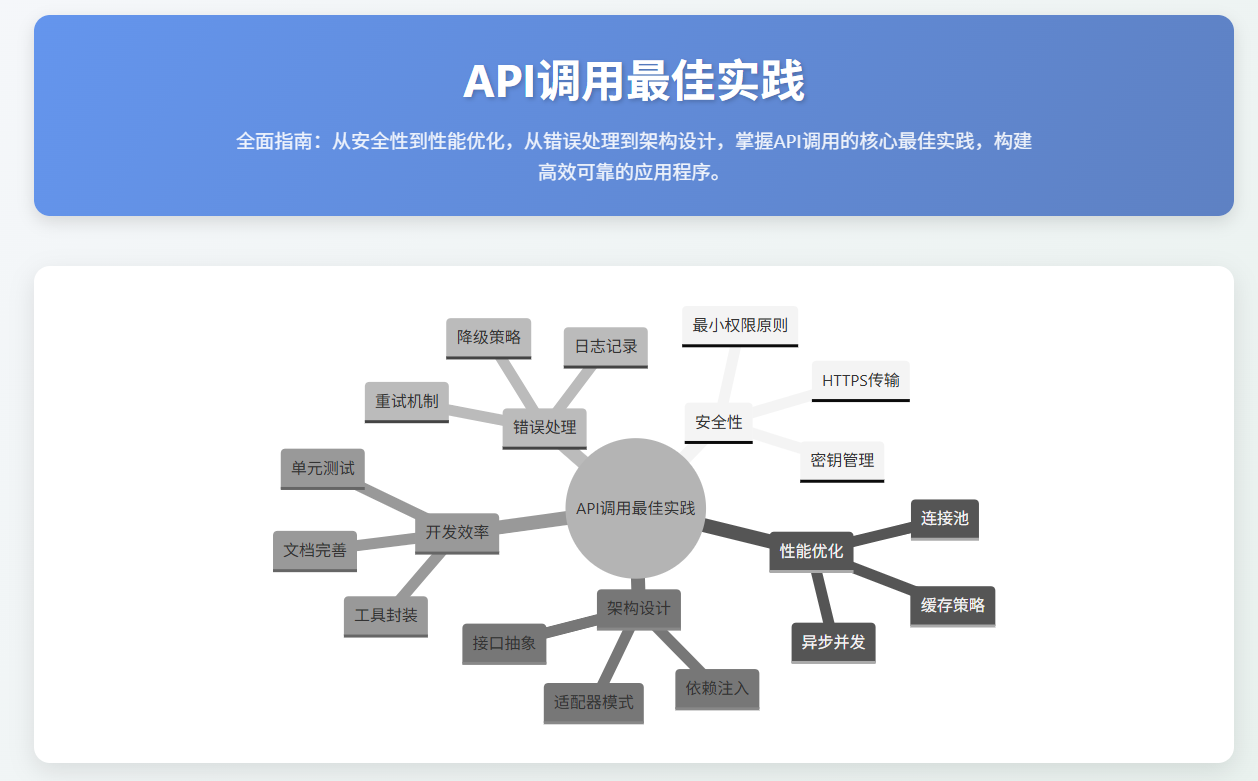

图7:API调用最佳实践思维导图 - 展示了API调用开发中的关键最佳实践
结语
从最初的简单HTTP请求,到如今的复杂分布式系统集成,API技术一直在不断演进。在这个过程中,Python凭借其简洁的语法和丰富的生态系统,成为了API调用的理想语言之一。
通过本文的学习,我们已经掌握了从基础到高级的Python API调用技术,包括RESTful API调用、异步并发、性能优化、架构设计等方面的知识。这些技能将帮助你在实际项目中更加高效地集成各种第三方服务,构建更加强大的应用程序。
记住,API调用不仅仅是技术问题,更是一种沟通艺术。优秀的API调用代码应当既能准确传达需求,又能优雅处理各种异常情况。希望本文能够帮助你在API的海洋中航行得更加顺利,构建出更加强大、可靠的应用程序。
在未来的开发中,随着微服务架构、云原生应用的普及,API调用技术将变得越来越重要。持续学习、实践和优化你的API调用代码,将使你在技术浪潮中保持竞争力。让我们一起,在这个API驱动的世界中,用代码连接无限可能!
■ 我是蒋星熠Jaxonic!如果这篇文章在你的技术成长路上留下了印记
■ 👁 【关注】与我一起探索技术的无限可能,见证每一次突破
■ 👍 【点赞】为优质技术内容点亮明灯,传递知识的力量
■ 🔖 【收藏】将精华内容珍藏,随时回顾技术要点
■ 💬 【评论】分享你的独特见解,让思维碰撞出智慧火花
■ 🗳 【投票】用你的选择为技术社区贡献一份力量
■ 技术路漫漫,让我们携手前行,在代码的世界里摘取属于程序员的那片星辰大海!
参考链接
- Python Requests官方文档
- aiohttp异步HTTP客户端/服务器文档
- RESTful API设计最佳实践
- 百度翻译API开发者文档
- OpenWeatherMap API文档
