0828 C++基础
Part 1.梳理思维导图
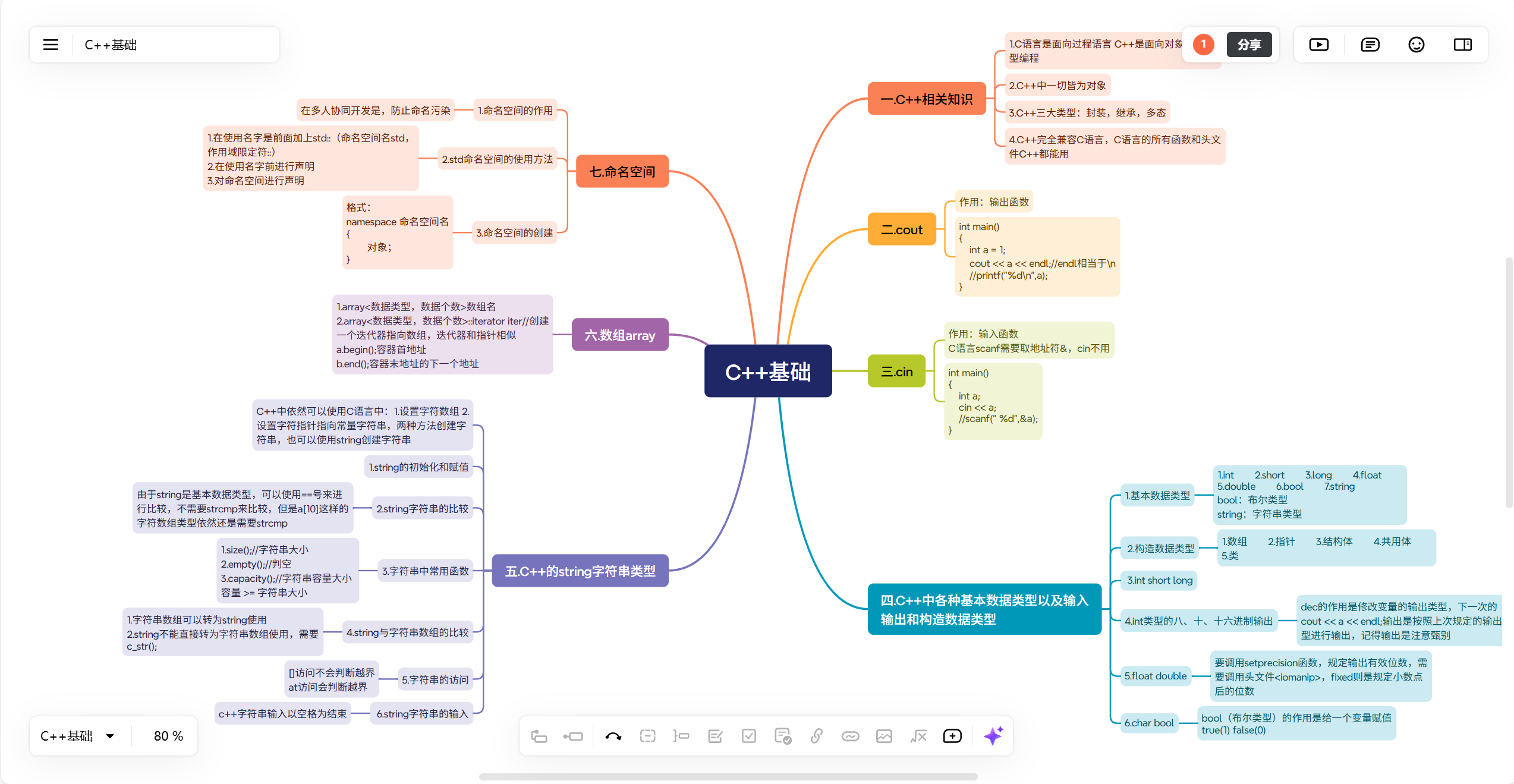
一.C++相关知识
1.C语言是面向过程语言 C++是面向对象语言 泛型编程
2.C++中一切皆为对象
3.C++三大类型:封装,继承,多态
4.C++完全兼容C语言,C语言的所有函数和头文件C++都能用
二.cout
作用:输出函数
int main()
{int a = 1;cout << a << endl;//endl相当于\n//printf("%d\n",a);
}三.cin
作用:输入函数
C语言scanf需要取地址符&,cin不用
int main()
{int a;cin << a;//scanf(" %d",&a);
}四.C++中各种基本数据类型以及输入输出和构造数据类型
1.基本数据类型
1.int 2.short 3.long 4.float 5.double 6.bool 7.string
bool:布尔类型
string:字符串类型
2.构造数据类型
1.数组 2.指针 3.结构体 4.共用体 5.类
3.int short long
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>using namespace std;int main()
{int a;short b;long c;cin >> a;//scanf(" %d",&a);cin >> b;//scanf(" %d",&b);cin >> c;//scanf(" %ld",&c);cout << a << endl;//printf("%d\n",a);cout << b << endl;//printf("%d\n",b);cout << b << endl;//printf("%d\n",c);
}4.int类型的八、十、十六进制输出
dec的作用是修改变量的输出类型,下一次的cout << a << endl;输出是按照上次规定的输出类型进行输出,记得输出是注意甄别
int main()
{int a = 10;cout << dec << a << endl;//十进制输出cout << oct << b << endl;//八进制输出cout << hex << b << endl;//十六进制输出
}5.float double
要调用setprecision函数,规定输出有效位数,需要调用头文件<iomanip>,fixed则是规定小数点后的位数
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>using namespace std;int main()
{double a = 1.23456; cout << a << setprecision(4) << endl;//四位有效数字 1.234cout << a << setprecision(4) << fixed << endl;//小数点后四位1.2345
}
6.char bool
bool(布尔类型)的作用是给一个变量赋值true(1) false(0)
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{char a = 'a';char b;cout << b << endl;cin >> b;bool c = true,d = false;cout << c << " " << d << endl;//1 0cout << boolalpha << c << endl;//truecout << c+c+d << endl;//1+1+0 = 2
}
五.C++的string字符串类型
C++中依然可以使用C语言中:1.设置字符数组 2.设置字符指针指向常量字符串,两种方法创建字符串,也可以使用string创建字符串
1.string的初始化和赋值
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{string a;a = "hello";//赋值string b = "world";//初始化cout << a << " " << b << endl;//hello worldstring c(a,3);//ldstring d(a,3,1);//lstring e(3,'a')://aaa
}
2.string字符串的比较
由于string是基本数据类型,可以使用==号来进行比较,不需要strcmp来比较,但是a[10]这样的字符数组类型依然还是需要strcmp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>using namespace std;int main()
{string a = "nihao";string b;cin >> b;if(a == b)cout << "二者相同" << endl;elsecout << "二者不同" << endl;
}
3.字符串中常用函数
1.size();//字符串大小
2.empty();//判空
3.capacity();//字符串容量大小
容量 >= 字符串大小
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{string a = "nihao";string b;if(!a.empty())//判断是否为空,空返回false,非空返回true{cout << a.size() << endl;//5cout << a.capacity() <<end1;//15}
}
4.string与字符串数组的比较
1.字符串数组可以转为string使用
2.string不能直接转为字符串数组使用,需要c_str();
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{string a = "nihao";string b;char c[32] = "niyeshi";b = c;cout >> b >> endl;//niyeshichar d[32];strcpy(d,a.c_str());cout >> d >> endl;//hello
}5.字符串的访问
[]访问不会判断越界
at访问会判断越界
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{string a = "nihao";cout << a[1] << endl;//icout << a[5] << endl;//' '输出一个空格cout << a.at(1) << endl;//icout << a.at(5) << endl;//字符串越界,会报错
}
6.string字符串的输入
c++字符串输入以空格为结束
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{string a;cin >> a;//abc aaacout << a << endl;//abcreturn 0;
}
六.数组array
1.array<数据类型,数据个数>数组名
2.array<数据类型,数据个数>::iterator iter//创建一个迭代器指向数组,迭代器和指针相似
a.begin();容器首地址
b.end();容器末地址的下一个地址
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main()
{array<int,5> a;array<int,5> iterator iter;for(iter = a.begin();iter != a.end(); iter++)//循环写入{cin >> *iter;}for(iter = a.begin();iter != a.end(); iter++)//循环输出{cout << *iter;}
}
七.命名空间
1.命名空间的作用
在多人协同开发是,防止命名污染
2.std命名空间的使用方法
1.在使用名字是前面加上std::(命名空间名std,作用域限定符::)
2.在使用名字前进行声明
3.对命名空间进行声明
#include <iostream>//using namespace std;//对命名空间进行声明//using std::cout,std::endl;//在使用名字前进行声明int main()
{std::cout << "hello" << std::endl;//使用名字是加上std::
}
3.命名空间的创建
格式:
namespace 命名空间名
{
对象;
}
#include <iostream>using namespace std;namespace test
{int a;
}int main()
{std::cin >> test::a;std::cout << test::a << std::endl;
}
Part 2.输入一个字符串判断大写字母、小写字母、数字、空格、其他字符个数
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <string.h>using namespace std;int main()
{string str;cout << "请输入一个字符串" << endl;getline(cin, str);//为了正常获取空格array<int,5> num = {0};array<int,5>::iterator iter;for(size_t i = 0; i < str.size();i++){iter = num.begin();if(str.at(i) >= 'A' && str.at(i) <= 'Z')*iter += 1;else if(str.at(i) >= 'a' && str.at(i) <= 'z')*(iter + 1) += 1;else if(str.at(i) >= '0' && str.at(i) <= '9')*(iter + 2) += 1;else if(str.at(i) == ' ')*(iter + 3) += 1;else*(iter + 4) += 1;}iter = num.begin();cout << "大写字母的个数: " << *iter << endl;cout << "小写字母的个数: " << *(iter + 1) << endl;cout << "数字的个数:" << *(iter+2) << endl;cout << "空格的个数: " << *(iter + 3) << endl;cout << "其他字符的个数: " << *(iter + 4) << endl;return 0;
}
