Java基础day17-LinkedHashMap类,TreeMap类和集合工具类
目录
一、LinkedHashMap
1.LinkedHashMap类图
2.关键特点
3.代码演示
二、TreeMap
1.TreeMap基本使用
2.小结
三、Hashtable
1.关键特点
2.数据结构
四、集合工具类--Collections类
1.public static boolean disjoint(Collectionc1, Collectionc2)
判断两个集合中是否存在相同元素,如果存在,返回false,不存在,返回true;
2.public static void fill(Listlist, T obj):填充(覆盖)集合。
如果arrayList里面无内容,则填充不进去。为一个空数组。
3.public static int frequency(Collectionc, Object o):获取集合中,指定元素出现的频率(次数)。
4.public static T max(Collectioncoll):获取集合中的最大值。
5.public static T min(Collectioncoll):获取集合中的最小值。
6.public static void sort(Listlist):将集合中的所有元素排序。
7.public static void reverse(Listlist):将集合中的所有元素逆序。
8.public static void shuffle(Listlist):将集合中的所有元素随机乱序。
9.public static void swap(Listlist, int i, int j):交换集合中指定下标位置的两个元素。
10.public static int binarySearch(Listlist, T key):集合有序才能找。
一、LinkedHashMap
1.LinkedHashMap类图
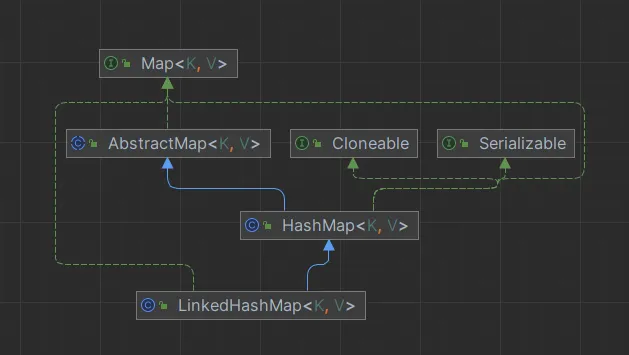
LinkedHashMap继承自HashMap,它的多种操作都是建立在HashMap操作的基础上的。同HashMap 不同的是,LinkedHashMap维护了一个双向链表,保证了插入的Entry中的顺序。这也是Linked的含义。 结构图如下:
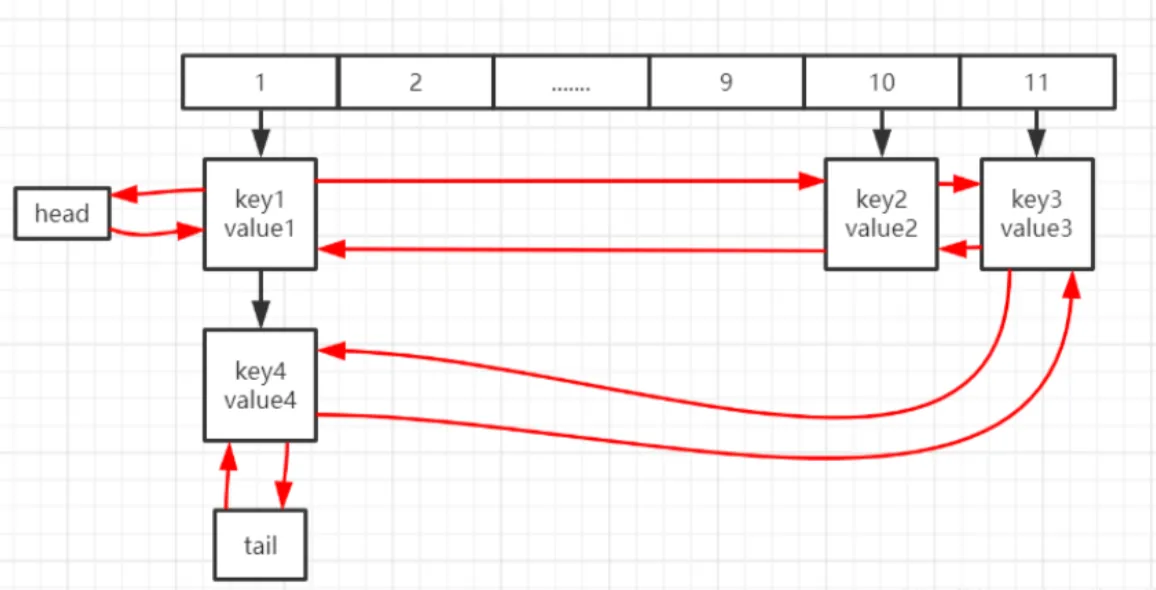
加入插入顺序为key1, key2, key3, key4, 那么就会维护一个红线所示的双向链表。为了实现双向链表,LinkedHashMap中提供了如下的Entry:
//LinkedHashMap中的node直接继承自HashMap中的Node。并且增加了双向的指针static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {//before表示上一个节点,after表示下一个节点//通过 before + after 属性,我们就可以形成一个以 Entry 为节点的链表。Entry<K,V> before, after;Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {super(hash, key, value, next);}}2.关键特点
1.LinkedHashMap是HashMap集合的子类
2.LinkedHashMap几乎和HashMap集合的用法一样。
3.只不过LinkedHashMap集合可以保证元素的插入顺序。(有序的)
4.LinkedHashMap集合是:有序不可重复。
5.LinkedHashMap集合的key也需要同时重写hashCode + equals。
6.LinkedHashMap集合底层的数据结构是:哈希表 + 双向链表。
3.代码演示
public class User {private String name;private int age;@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;User user = (User) o;if (age != user.age) return false;return name != null ? name.equals(user.name) : user.name == null;}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;result = 31 * result + age;return result;}public User(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "User{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}
public class Demo01 {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap<User,Integer> hashMap=new LinkedHashMap<>();hashMap.put(new User("l朗朗",30),6789);hashMap.put(new User("j吉娜",29),6767);hashMap.put(new User("s单依纯",25),9989);hashMap.put(new User("R朴彩英",28),9999);for (Map.Entry<User, Integer> entry:hashMap.entrySet()) {System.out.println(entry);}}
}
//运行结果
User{name='l朗朗', age=30}=6789
User{name='j吉娜', age=29}=6767
User{name='s单依纯', age=25}=9989
User{name='R朴彩英', age=28}=9999
二、TreeMap
1.TreeMap基本使用
HashMap是一种以空间换时间的映射表,它的实现原理决定了内部的Key是无序的,即遍历HashMap的Key时,其顺序是不可预测的(但每个Key都会遍历一次且仅遍历一次)。还有一种Map,它在内部会对Key进行排序,这种Map就是SortedMap。注意到SortedMap是接口,它的实现类是TreeMap。
┌───┐│Map│└───┘▲│┌────┴─────┐│ │
┌───────┐ ┌─────────┐
│HashMap│ │SortedMap│
└───────┘ └─────────┘▲│┌────┴────┐│ TreeMap │└─────────┘SortedMap保证遍历时以Key的顺序来进行排序。例如,放入的Key是"apple"、"pear"、"orange",遍历的顺序一定是"apple"、"orange"、"pear",因为String默认按字母排序:
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();map.put("orange", 1);map.put("apple", 2);map.put("pear", 3);for (String key : map.keySet()) {System.out.println(key);}// apple, orange, pear}
}使用TreeMap时,放入的Key必须实现Comparable接口。String、Integer这些类已经实现了Comparable接口,因此可以直接作为Key使用。作为Value的对象则没有任何要求。
如果作为Key的class没有实现Comparable接口,那么,必须在创建TreeMap时同时指定一个自定义比较器:
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<Person, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Person>() {public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) {return p1.name.compareTo(p2.name);}});map.put(new Person("Tom"), 1);map.put(new Person("Bob"), 2);map.put(new Person("Lily"), 3);for (Person key : map.keySet()) {System.out.println(key);}// {Person: Bob}, {Person: Lily}, {Person: Tom}System.out.println(map.get(new Person("Bob"))); // 2}
}class Person {public String name;Person(String name) {this.name = name;}public String toString() {return "{Person: " + name + "}";}
}注意到Comparator接口要求实现一个比较方法,它负责比较传入的两个元素a和b,如果a<b,则返回负数,通常是-1,如果a==b,则返回0,如果a>b,则返回正数,通常是1。TreeMap内部根据比较结果对Key进行排序。
从上述代码执行结果可知,打印的Key确实是按照Comparator定义的顺序排序的。如果要根据Key查找Value,我们可以传入一个new Person("Bob")作为Key,它会返回对应的Integer值2。
另外,注意到Person类并未覆写equals()和hashCode(),因为TreeMap不使用equals()和hashCode()。
再来看一个稍微复杂的例子:这次我们定义了Student类,并用分数score进行排序,高分在前:
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<Student, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student>() {public int compare(Student p1, Student p2) {return p1.score > p2.score ? -1 : 1;}});map.put(new Student("Tom", 77), 1);map.put(new Student("Bob", 66), 2);map.put(new Student("Lily", 99), 3);for (Student key : map.keySet()) {System.out.println(key);}System.out.println(map.get(new Student("Bob", 66))); // null?}
}class Student {public String name;public int score;Student(String name, int score) {this.name = name;this.score = score;}public String toString() {return String.format("{%s: score=%d}", name, score);}
}在for循环中,我们确实得到了正确的顺序。但是,且慢!根据相同的Key:new Student("Bob", 66)进行查找时,结果为null!
在这个例子中,TreeMap出现问题,原因其实出在这个Comparator上:
public int compare(Student p1, Student p2) {return p1.score > p2.score ? -1 : 1;
}在p1.score和p2.score不相等的时候,它的返回值是正确的,但是,在p1.score和p2.score相等的时候,它并没有返回0!这就是为什么TreeMap工作不正常的原因:TreeMap在比较两个Key是否相等时,依赖Key的compareTo()方法或者Comparator.compare()方法。在两个Key相等时,必须返回0。或者直接借助Integer.compare(int, int)也可以返回正确的比较结果。
public int compare(Student p1, Student p2) {if (p1.score == p2.score) {return 0;}return p1.score > p2.score ? -1 : 1;
}2.小结
(1)SortedMap在遍历时严格按照Key的顺序遍历,最常用的实现类是TreeMap;
(2)作为SortedMap的Key必须实现Comparable接口,或者传入Comparator;
(3)要严格按照compare()规范实现比较逻辑,否则,TreeMap将不能正常工作;
三、Hashtable
1.关键特点
无序、key唯一、key和value不允许为null,线程安全。
2.数据结构
哈希表=数组+单向链表。
四、集合工具类--Collections类
概述:
Collections是JDK提供的工具类,同样位于java.util包中。它提供了一系列静态方法,能更方便地操作各种集合。例如addAll()方法可以给一个Collection类型的集合添加若干元素。因为方法参数是Collection,所以我们可以传入List,Set等各种集合类型。
1.public static boolean disjoint(Collection<?> c1, Collection<?> c2)
判断两个集合中是否存在相同元素,如果存在,返回false,不存在,返回true;
List<String> list1= Arrays.asList("a阿里","b北京");
List<String> list2= Arrays.asList("a阿里","c北京");
boolean b1=Collections.disjoint(list1,list2);
System.out.println("是否完全不一样:"+b1);2.public static <T> void fill(List<? super T> list, T obj):填充(覆盖)集合。
如果arrayList里面无内容,则填充不进去。为一个空数组。
ArrayList<String> arrayList=new ArrayList<>(10);
arrayList.addAll(list1);
arrayList.addAll(list2);
Collections.fill(arrayList,"hello");
System.out.println(arrayList);3.public static int frequency(Collection<?> c, Object o):获取集合中,指定元素出现的频率(次数)。
int number=Collections.frequency(arrayList,"hello");
System.out.println("此元素出现的次数为:"+number);4.public static T max(Collection<? extends T> coll):获取集合中的最大值。
List<String> list= Arrays.asList("ab","ac","dc","cd","fr","yjh");
String max= Collections.max(list, new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String o1, String o2) {return o1.length()-o2.length();}
});
System.out.println("最大值为:"+max);5.public static T min(Collection<? extends T> coll):获取集合中的最小值。
String min=Collections.min(list);
System.out.println("最小值为:"+min);6.public static void sort(List<T> list):将集合中的所有元素排序。
Collections.sort(list);
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String o1, String o2) {return o1.length()-o2.length();}
});
System.out.println("排序后的集合为:"+list);7.public static void reverse(List<?> list):将集合中的所有元素逆序。
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println("反转后的集合为:"+list);8.public static void shuffle(List<?> list):将集合中的所有元素随机乱序。
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println("乱序后的集合为:"+list);9.public static void swap(List<?> list, int i, int j):交换集合中指定下标位置的两个元素。
List<String> list= Arrays.asList("ab","a","dc","cd","fr","yjh");
Collections.swap(list,0,1);
System.out.println("交换后的集合为:"+list);10.public static int binarySearch(List<?> list, T key):集合有序才能找。
int index=Collections.binarySearch(list,"ab");
System.out.println(index);