【C++】string类完全解析与实战指南
0. 官方文档
string类的文档介绍:https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/?kw=string
c++文档参考网站(查文档常用):https://cplusplus.com
c++官方网站:https://en.cppreference.com/w/
1. string 类简介
string是表示字符串的字符串类
该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。
string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别名,typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator>
string;
不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。
注意:在使用string类时,必须包含#include头文件以及using namespace std;
2. string类的构造函数
函数名 功能string() (重点) // 构造空的string类对象,即空字符串string(const char* s) (重点) // 用C - string来构造string类对象string(size_t n, char c) // string类对象中包含n个字符cstring(const string & s) (重点) // 拷贝构造函数示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main() {string s1; // 1. 默认构造,构造一个空字符串 ""string s2("hello"); // 2. 用C风格字符串构造string s3("hello", 2); // 3. 用字符串"hello"的前2个字符"he"构造string s4(s2); // 4. 拷贝构造,s4是s2的副本string s5(s2, 1, 2); // 5. 从s2的下标1开始,截取2个字符,得到"el"string s6(s2, 1); // 6. 从s2的下标1开始,截取到末尾,得到"ello"string s7(10, 'a'); // 7. 构造一个包含10个字符'a'的字符串// 可以通过cout输出各个字符串s1 = s7; // 8. 使用赋值运算符重载cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}3. 遍历与迭代器
有多种方法可以遍历和修改string中的字符。
3.1 下标 [] 遍历
最常用和直观的方式,像操作数组一样操作string。
void test_string2() {string s1("hello");s1 += ' ';s1 += "world"; // s1 变为 "hello world"// 写操作:每个字符的ASCII值+1for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); ++i) {s1[i] += 1;}// 读操作for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); ++i) {cout << s1[i] << " ";}cout << endl;
}3.2 迭代器 (Iterator)
迭代器提供了另一种遍历容器的方式,行为类似指针。
// 写操作
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end()) {*it -= 1; // 将之前+1的操作还原++it;
}// 读操作
it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end()) {cout << *it << " ";++it;
}
cout << endl;3.3 范围for循环 (Range-based for loop)
C++11引入的语法糖,代码简洁,底层由编译器转换为迭代器实现。
for (auto ch : s1) {cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;3.4 其他迭代器
迭代器分为正向/反向、const/非const。const迭代器用于确保不修改数据。
int string2int(const string& str) {int val = 0;// const_iterator 用于只读遍历string::const_iterator it = str.begin();while (it != str.end()) {// *it = 'a'; // 错误!不能通过const_iterator修改值val = val * 10 + (*it - '0');++it;}return val;
}void test_string3() {string s1("hello world");// 反向迭代器,用于倒序遍历string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();while (rit != s1.rend()) {cout << *rit << " ";++rit;}cout << endl;string nums("12345");cout << string2int(nums) << endl; // 输出 12345
}迭代器分类
方向:正向、反向
属性:非const、const
排列组合共有4种迭代器,上面的代码只有三种,没有展示反向const迭代器。
反向const迭代器:
string::const_reverse_iterator rit = str.rbegin();4. string 容量操作
4.1 基本常用接口
string类提供了管理底层存储空间的函数。
void test_string4()
{string s1("hello world");string s2("hello");// size:字符串长度cout << s1.size() << endl; // 11cout << s2.size() << endl; // 5// length 也是获取字符串长度接口,但比较老了,现在一般使用 size 接口cout << s1.length() << endl; // 11cout << s2.length() << endl; // 5// 这个接口只会返回 9223372036854775807 ,当前编译环境下整形的最大值,在实际中没有什么意义cout << s1.max_size() << endl; // 9223372036854775807cout << s2.max_size() << endl; // 9223372036854775807// 获取 capacity// 实际上开出的空间是 capacity() 的返回值+1,多出来的一个字节的空间要装'\0'cout << s1.capacity() << endl; // 15(实际是16)cout << s2.capacity() << endl; // 15(实际是16)// string 类对象增长后会对原空间进行扩容s1 += "111111";cout << s1.size() << endl; // 17cout << s1.capacity() << endl; // 31// clear:清掉所有字符,但对象的 capacity 不会变,空间不会被释放s1.clear();cout << s1.size() << endl; // 0cout << s1.capacity() << endl; // 31
}我们可以编写代码查看 string 类对象在扩容时的 capacity 变化
void TestPushBack()
{string s;size_t sz = s.capacity();cout << "s grow:\n";for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i){s.push_back('c');if (sz != s.capacity()){sz = s.capacity();cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << endl;}}
}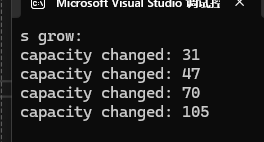
由上图打印结果可以看出,每次扩容基本上是之前容量的1.5倍大小。
4.2 reserve 扩容空间
reserve(n) 可以指定扩容至少容纳 n 个字符的内存,避免多次扩容,提高效率。
void TestPushBack() {string s;s.reserve(100); // 提前分配足够空间(可能比100稍大)size_t sz = s.capacity();cout << "capacity: " << sz << endl; // 111 (实际分配值)// ... 后续插入100个字符将不会再发生扩容 ...
}如下图打印结果所示,将capacity扩容至100之后就没有再发生过扩容:
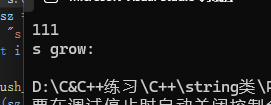
但实际中 reserve 不会指定多少就扩容到多少,而是会取整,string 需要考虑内存对齐。如上图所示,实际 capacity 扩容至 111(加上'\0'就是112)
4.3 resize 调整大小
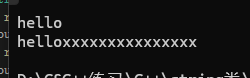
resize(n) 改变字符串的 size()。如果 n > size(),多出的部分会用空字符('\0')或指定字符填充;如果 n < size(),则截断字符串。
void test_string5() {string s("hello world");s.resize(5); // 截断,s变为"hello"cout << s << endl;s.resize(20, 'x'); // 扩容并填充'x',s变为"helloxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"cout << s << endl;
}
5. string 修改操作
string类支持多种添加和删除内容的方式。
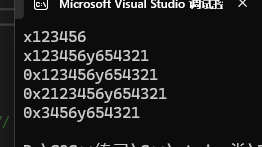
void test_string6() {string s;// 尾插字符s.push_back('x');// 尾插字符串s.append("123456");// 更常用的尾插方式:运算符重载 +=s += 'y';s += "654321";cout << s << endl; // x123456y654321// 任意位置插入s.insert(s.begin(), '0'); // 在开头插入字符'0's.insert(2, "2"); // 在下标2的位置插入字符串"2"cout << s << endl; // 02x123456y654321// 删除s.erase(2, 3); // 从下标2开始,删除3个字符cout << s << endl; // 023456y654321
}
注意:虽然 string 重载了 + 运算符,但 s1 = s2 + s3; 是传值返回,会产生临时对象的拷贝,效率较低。频繁拼接字符串应优先使用 +=。
6. string 字符串操作
6.1 c_str 获取C风格字符串
返回字符串的首地址,C语言的字符串,字符串末尾有一个 '\0'
// c_str
string s1 = "aRainRainRain";
const char* str = s1.c_str();
while (*str)
{cout << *str << " ";++str;
}
cout << endl;s1 += '\0'; // string可以包含'\0'
s1 += "world";
cout << s1 << endl; // 输出: aRainRainRain world (string对象完整内容)
cout << s1.c_str() << endl; // 输出: aRainRainRain (遇到内部的'\0'即终止)6.2 find / rfind / substr - 查找与子串
find(str, pos): 从pos开始向前查找子串str,返回其起始位置,找不到则返回string::npos。rfind(str, pos): 从pos开始向后查找,返回找到元素的下标。substr(pos, len): 从pos开始,截取长度为len的子串,返回这个子串(string 对象)。
void test_string8()
{string s1 = "string.cpp";string s2 = "string.c";string s3 = "string.txt";// find + npos:从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符再字符串中的位置,找不到返回npos// rfind:从字符串pos位置开始往前找字符c// substr:在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回size_t pos1 = s1.find('.'); // 找到返回下标,找不到返回nposif (pos1 != string::npos){cout << pos1 << endl;cout << s1.substr(pos1) << endl;}size_t pos2 = s2.find('.'); // 找到返回下标,找不到返回nposif (pos2 != string::npos){cout << pos2 << endl;cout << s2.substr(pos2) << endl;}size_t pos3 = s3.find('.'); // 找到返回下标,找不到返回nposif (pos3 != string::npos){cout << pos3 << endl;cout << s3.substr(pos3) << endl;}
}利用这些接口,我们可以轻松分离一个网址的协议、域名、资源名称:
void split_url(const string& url)
{// 分离协议 域名 资源名称// 例:https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/?kw=stringsize_t i1 = url.find(':');if (i1 != string::npos){// 取出协议cout << url.substr(0, i1) << endl;}size_t i2 = url.find('/', i1 + 3); // 从i1+3位置开始往后找if (i2 != string::npos){// 取出域名cout << url.substr(i1 + 3, i2 - (i1 + 3)) << endl;}// 取出资源名称// substr只给一个参数就是从pos位置往后截取到字符串结尾cout << url.substr(i2 + 1) << endl;
}
int main()
{string cpp_url("https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/?kw=string");split_url(cpp_url);return 0;
}6.3 string 字符串比较
可以直接使用比较运算符 (==, !=, <, <=, >, >=) 来比较两个string对象,或一个string对象和一个C风格字符串。比较规则是字典序。
(字典序:从第一个字符开始比较 ascii 值,相同则比较下一个,直到结束)
void test_string9()
{string s2("abcd");string s3("bbcd");cout << (s2 < s3) << endl; // Truecout << (s2 < "bbed") << endl; // Turecout << ("abcd" <= "ffcd") << endl; // True
}
