数据结构手撕--【栈和队列】
目录
1、栈
2、队列
1、栈
先进后出(都在栈顶进行操作)
使用数组结构比使用链式结构更优,因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价更小。并且采用动态长度的数组来表示。
定义结构体
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;//动态分配的指针数组,指向一个数组空间int top;//相当于数组下标int capacity;//动态数组容量,即可以容纳的STDataType元素的个数
}ST;初始化:
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}插入数据:
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);//先看有没有空间 再插入if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * (ps->capacity);//元素个数//tmp指向新开辟的空间 ps->a 是原来的空间位置 一个元素大小*元素个数 = 空间大小STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);//更新ps->capacity = newcapacity;ps->a = tmp;//新空间给a}ps->a[ps->top] = x; //top指向的是栈顶元素的下一个位置 所以先给值ps->top++;//再移动
}删除数据:直接对top--操作即可
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);//保证有数据可删除ps->top--;
}取栈顶元素:数组下标取
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);return ps->a[ps->top-1]; //-1指向栈顶元素位置
}判断是否为空:
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{if (ps->top == 0){return true;}else{return false;}
}打印函数:
void StackPrint(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);while (ps->top > 0){printf("%d", ps->a[ps->top - 1]);ps->top--;}printf("\n");
}使用while循环 top--
栈元素的个数:
因为top初始化的时候是0,所以直接返回top即可
eg:top=2,ps[0] ps[1] 刚好等于top的值
int Stack(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}销毁栈:
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}测试:
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{printf("%d", StackTop(&st));StackPop(&st);
}2、队列
只允许在一端进行插入,另一端进行删除。
队尾插入,对头删除。(先进先出)
采用链式结构优于数组结构,因为队列是头删,如果采用数组结构,删除了队头元素之后要对后面的元素全都向前挪动,这样效率太低了
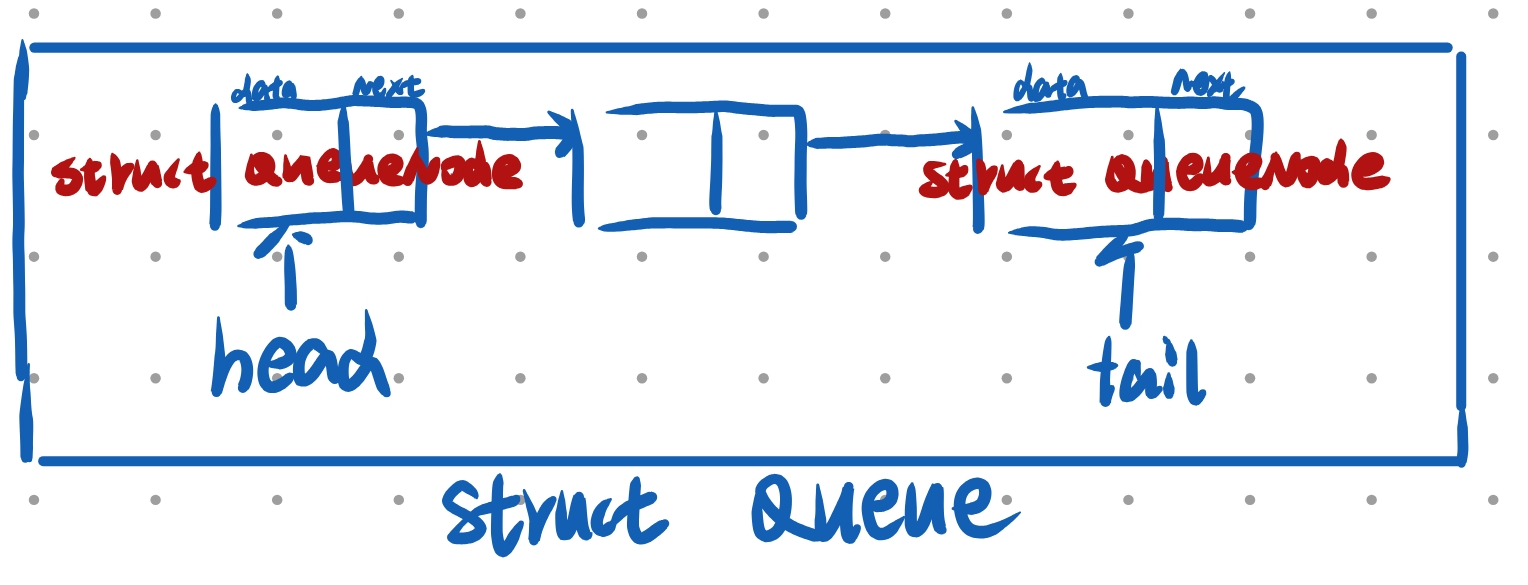
如图:

定义结构体:
typedef int QDataType;
//定义链式结构
typedef struct QueueNode
{//1、next //2、数据QueueNode* next;QDataType data;
}QN;
typedef struct Queue//定义一个结构体里面有两个指针
{QN* head; //链式结构类型的指针,指向对头QN* tail;//指向队尾
}Queue;结构示意图:
插入数据:链式结构只要插入数据,就要重新向内存申请空间
特殊情况:判断队列是否为空 为空时要将头尾指针都指向newnode
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);//1、链式结构只要插入数据,就要重新向内存申请空间QN* newnode = (QN*)malloc(sizeof(QN));newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;//2、判断队列是不是为空 为空头尾都指向newnode 不为空将newnode链入队尾if (pq->head == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else {pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}
}删除数据:头删
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->head);//1、指针指向头//2、通过头 找到头的下一个节点(新头)//3、free + 指针置空//4、换新头//5、边界情况:如果已经删除了最后一个元素QN* cur = pq->head;QN* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;pq->head = next;if (pq->head == NULL){pq->tail = NULL;}
}取队头和队尾数据
队头:
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->head);QN* cur = pq->head;return cur->data;
}队尾:
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->head);QN* cur = pq->tail;return cur->data;
}队列中元素的个数:使用指针指向队头,从头往后走,计数器++
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);int count = 0;QN* cur = pq->head;//先++操作 再向后移 因为开始cur就已经指向头节点了while (cur){count++;cur = cur->next;}return count;
}打印函数:
void QueuePrint(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QN* cur = pq->head;while (cur){printf("%d", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");
}测试:
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q)
{QDataType front = QueueFront(&q);printf("%d", front);QueuePop(&q);
}