【CF】Day61——Codeforces Round 939 (Div. 2) CD (思维构造 | 思维构造 + dfs枚举)
C. Nene's Magical Matrix
题目:
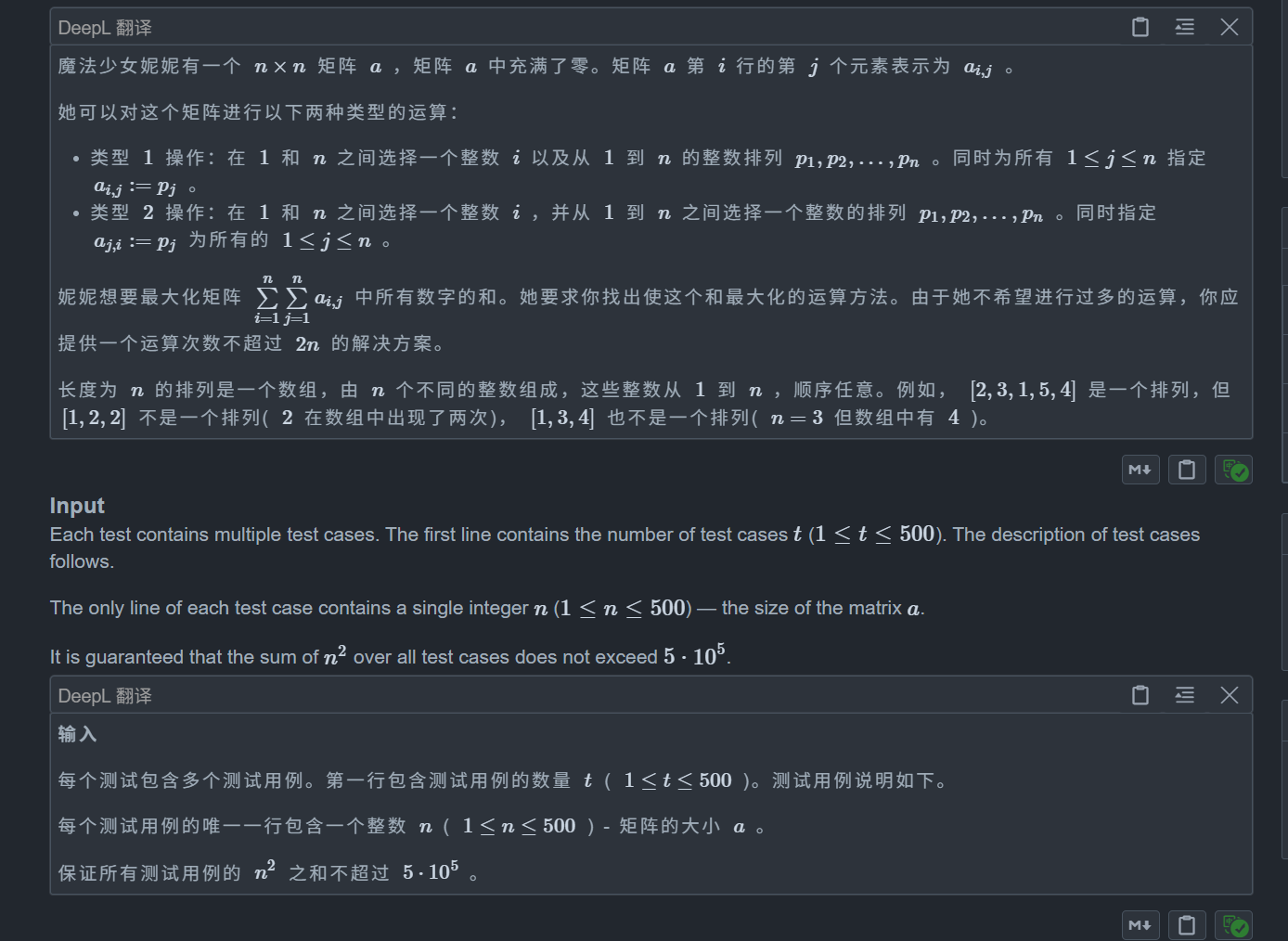
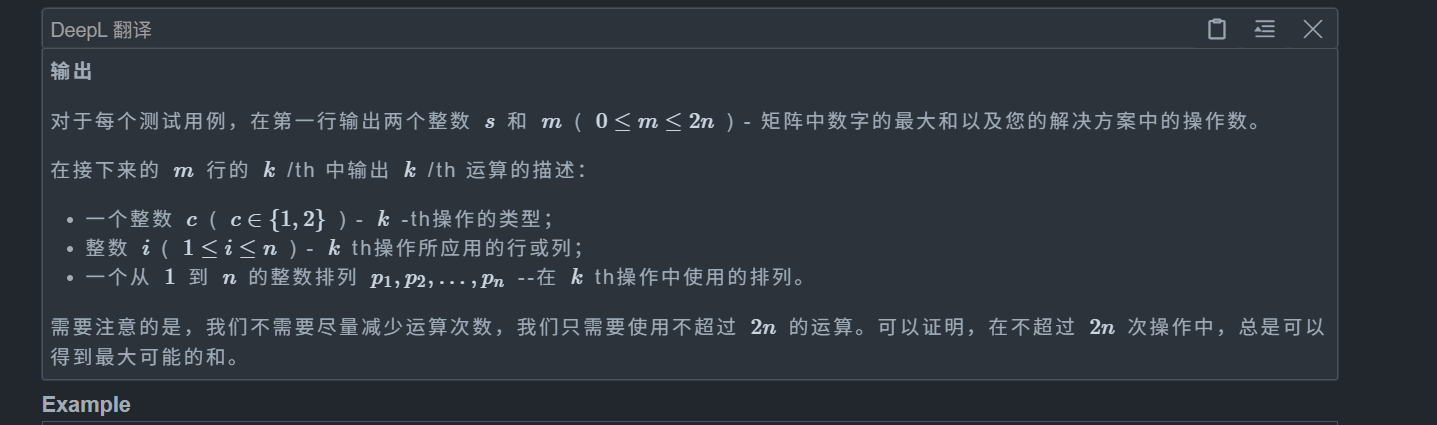
思路:
简单构造题
我们遇到这种指定操作的题,我们就尽量考虑最坏的情况,即用完给的次数
我们简单观察一下样例,我们可以参考样例看看能不能构造一个类似的例子
假设 n = 3,我们考虑能否构造出
1 2 3
2 2 3
3 3 3
答案是显然可以的,我们来看看如何构造,我们可以从后往前构造,即我们先填最后一列和最后一行,然后再填倒数第二列和倒数第二行,以此类推,最后刚好 2*n 次
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "Yes\n"
#define no cout << "No\n"void solve()
{int n;cin >> n;int sum = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){sum += i * (i * i - (i - 1) * (i - 1));}cout << sum << " " << 2 * n << endl;for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--){cout << 1 << " " << i << " ";for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)cout << j << " ";cout << endl;cout << 2 << " " << i << " ";for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)cout << j << " ";cout << endl;}
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);int t = 1;cin >> t;while (t--){solve();}return 0;
}D. Nene and the Mex Operator
题目:
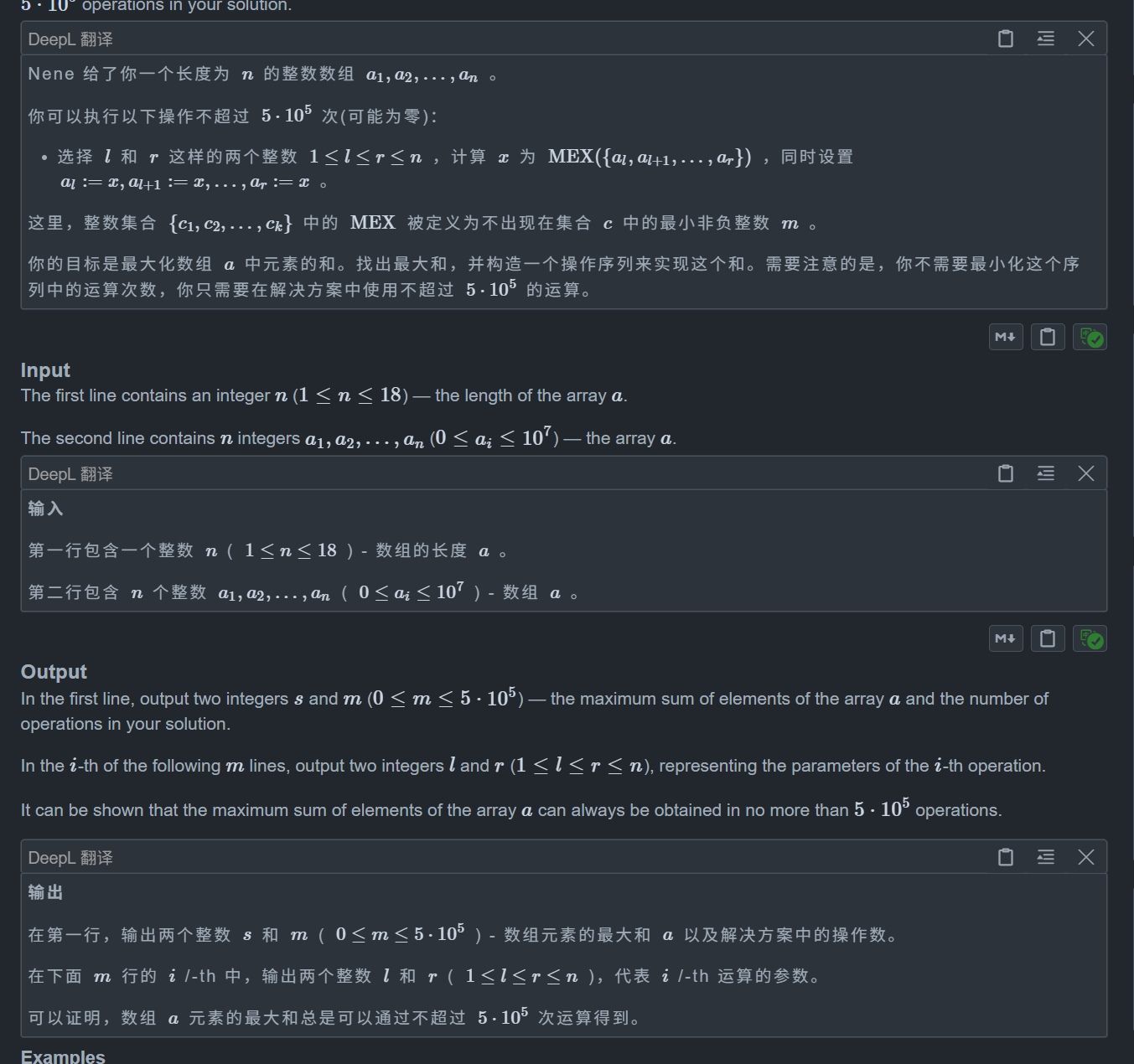
思路:
构造 + dfs枚举,非常好
我们观察可以发现到 n 非常小,我们完全可以使用暴力枚举来写
首先我们要知道对于任意的区间 l ~ r 我们最后一定能将区间内的数变成 r - l + 1,具体构造方法我们待会再说
然后我们可以枚举每一个位置选或者不选,对于不选的,那么其奉献就是 a[i] ,对于选的长段,其区间就是 len * len 其中 len 为区间长度
那么如何构造呢?我们发现只要我们能构造出 0 1 2 3 ... x 这样的,那么最后全选 l ~ r 即可构造出 x + 1 了,而如果要构造出 0 1 2 3 ... x ,那么就要先构造出 0 1 2 3 ... x - 1 ?,这样我们就能最后一次全选区间使得变成 x x x x ... x 了,然后再让前面的区间变成 0 1 2 3 ... x - 1 即可
所以我这里定义一个递归函数 operation,其作用是储存一个区间构造成 0 1 2 3 ... len 的操作步骤,那么按照上面说的,我们就要先operation(l, r - 1),然后再 改变 l ~ r,然后再 operation(l,r - 1),如果 l == r,那么说明是 0,那我们就跳过即可
但是如果我们直接这样写的话会有点小问题,因为每次操作我们会改变第一个数,如果其不是0,那我们就要操作,否则就不需要操作,而我们没考虑其情况,所以这里我是用一个数组代表第 l 位为 0 时要不要操作,如果要操作那我们就操作,否则不操作
为了方便操作,我们一开始将 l ~ r 之间的数全变成 0,同时记得特判 l == r,此时我们就不需要operation了,具体实现看代码,还是很有意思的一道题目
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "Yes\n"
#define no cout << "No\n"void solve()
{int n;cin >> n;vector<int> a(n+1,0);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){cin >> a[i];}int Length = 0;vector<pair<int, int>> op;vector<int> tempchose(n+1, 0), finalchose(n+1, 0);int finalsum = 0;auto sim_sum = [&]() ->int{int len = 0, sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++){if (!tempchose[i])sum += a[i]+ len * len,len = 0;elselen++;}return sum;};auto dfs = [&](auto self,int u) {if (u == n){int nowsum = sim_sum();if (finalsum < nowsum){finalsum = nowsum, finalchose = tempchose;}return;}tempchose[u] = 0;self(self, u + 1);tempchose[u] = 1;self(self, u + 1);};vector<int> checkl(n, 0);auto operation = [&](auto self,int l,int r) {if (l == r){if(checkl[l] == 1)op.push_back({ l,r }),checkl[l] = 0;return;}self(self,l, r - 1);op.push_back({ l,r });checkl[l] ^= 1;self(self, l, r - 1);};dfs(dfs, 0);for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++){if (finalchose[i]){Length++;}else{if (!Length) continue;int L = i - Length, R = i - 1;int haaszero = 0;for (int j = L; j <= R; j++)haaszero |= (a[j] == 0);for (int j = 0; j <= haaszero; j++)op.push_back({ L,R });if (L != R){operation(operation, L, R);}op.push_back({ L,R });Length = 0;}}cout << finalsum << " " << op.size() << endl;for (auto& x : op)cout << x.first + 1 << " " << x.second + 1 << endl;
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);int t = 1;//cin >> t;while (t--){solve();}return 0;
}